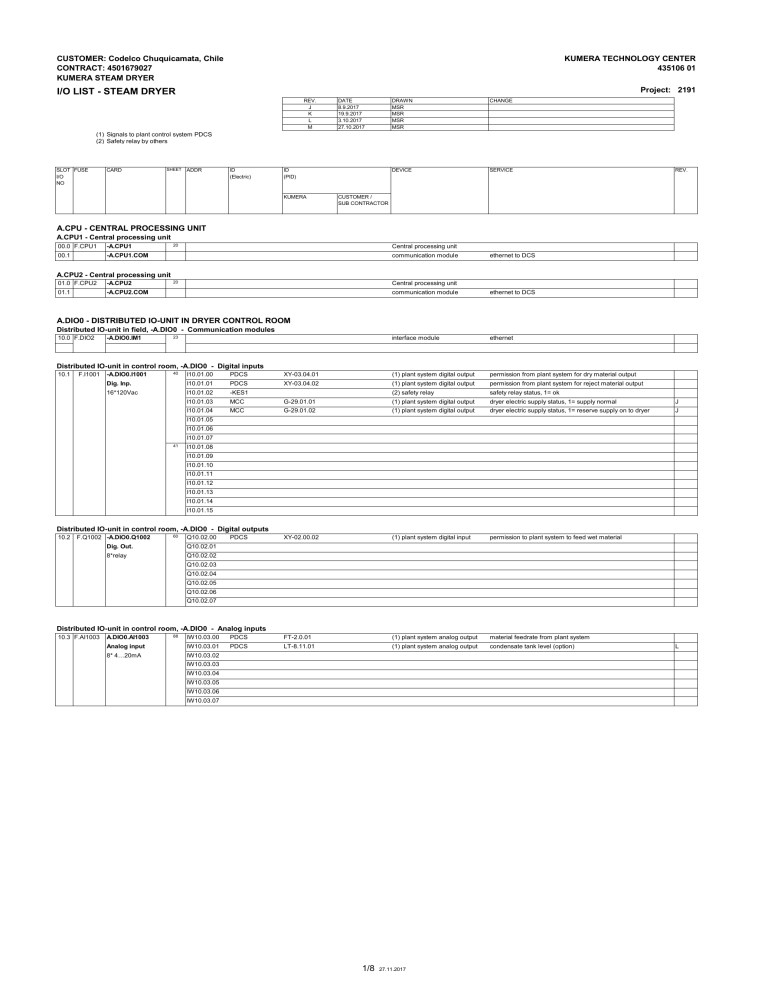
CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 KUMERA STEAM DRYER KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER 435106 01 Project: 2191 I/O LIST - STEAM DRYER REV. J K L M DATE 8.9.2017 19.9.2017 3.10.2017 27.10.2017 DRAWN MSR MSR MSR MSR CHANGE DEVICE SERVICE (1) Signals to plant control system PDCS (2) Safety relay by others SLOT FUSE I/O NO CARD SHEET ADDR ID (Electric) ID (PID) KUMERA REV. CUSTOMER / SUB CONTRACTOR A.CPU - CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT A.CPU1 - Central processing unit 00.0 F.CPU1 -A.CPU1 00.1 -A.CPU1.COM 20 Central processing unit communication module ethernet to DCS A.CPU2 - Central processing unit 01.0 F.CPU2 -A.CPU2 01.1 -A.CPU2.COM 20 Central processing unit communication module ethernet to DCS interface module ethernet A.DIO0 - DISTRIBUTED IO-UNIT IN DRYER CONTROL ROOM Distributed IO-unit in field, -A.DIO0 - Communication modules 10.0 F.DIO2 -A.DIO0.IM1 23 Distributed IO-unit in control room, -A.DIO0 - Digital inputs 10.1 F.I1001 -A.DIO0.I1001 40 I10.01.00 PDCS XY-03.04.01 (1) plant system digital output permission from plant system for dry material output Dig. Inp. I10.01.01 PDCS XY-03.04.02 (1) plant system digital output permission from plant system for reject material output 16*120Vac I10.01.02 -KES1 (2) safety relay safety relay status, 1= ok I10.01.03 MCC G-29.01.01 (1) plant system digital output dryer electric supply status, 1= supply normal J I10.01.04 MCC G-29.01.02 (1) plant system digital output dryer electric supply status, 1= reserve supply on to dryer J XY-02.00.02 (1) plant system digital input permission to plant system to feed wet material I10.01.05 I10.01.06 I10.01.07 41 I10.01.08 I10.01.09 I10.01.10 I10.01.11 I10.01.12 I10.01.13 I10.01.14 I10.01.15 Distributed IO-unit in control room, -A.DIO0 - Digital outputs 10.2 F.Q1002 -A.DIO0.Q1002 60 Q10.02.00 Dig. Out. Q10.02.01 8*relay Q10.02.02 PDCS Q10.02.03 Q10.02.04 Q10.02.05 Q10.02.06 Q10.02.07 Distributed IO-unit in control room, -A.DIO0 - Analog inputs 10.3 F.AI1003 A.DIO0.AI1003 88 IW10.03.00 PDCS FT-2.0.01 (1) plant system analog output material feedrate from plant system Analog input IW10.03.01 PDCS LT-8.11.01 (1) plant system analog output condensate tank level (option) 8* 4…20mA IW10.03.02 IW10.03.03 IW10.03.04 IW10.03.05 IW10.03.06 IW10.03.07 1/8 27.11.2017 L SLOT FUSE I/O NO CARD SHEET ADDR ID (Electric) ID (PID) DEVICE SERVICE interface module ethernet optical tranceiver ethernet, copper / fibre optics REV. A.DIO2 - DISTRIBUTED IO-UNIT NEAR STEAM DRYER Distributed IO-unit in field, -A.DIO2 - Communication modules 20.0 F.DIO2 -A.DIO2.IM1 20.1 -A.DIO2.OT 23 Eth ? Distributed IO-unit in field, -A.DIO2 - Digital inputs 20.8 F.I2008 -A.DIO2.I2008 42 F.I2009 S121C02 M-1.2.1 push button speed adjusting of main drive, 1 pulse = speed up 16*120Vdc I20.08.02 S121C03 M-1.2.1 push button speed adjusting of main drive, 1 pulse = speed down I20.08.03 S121C04 M-1.2.1 push button start drum forward, 1 pulse = start I20.08.04 S121C05 M-1.2.1 push button start drum reverse, 1 pulse = start reverse I20.08.05 S121C06 M-1.2.1 push button stop drum, 0 pulse = stop I20.08.06 S121C09 push button system reset, 1 = reset I20.08.07 B.LS08106 LS-8.1.6 level switch flash tank level, 0= high-high I20.08.08 B.LS020104 LS-2.1.4 level switch level of dry material hopper, 0=low I20.08.09 B.LS030106 LS-03.01.06 level switch level of concentrate in discharge end, 0=high-high I20.08.10 B.LS030112 LS-03.01.12 level switch level of concentrate in discharge end, 0=high-high I20.08.11 B.LS030110 LS-03.01.10 level switch level of reject hopper, 0=high-high I20.08.12 A1.3 A-1.3-XI fault alarm lubrication unit of girth gear, 0 = alarm I20.08.13 B.XS01205 XS-1.2.5 limit switch, brake 1 status of brake, 1=open I20.08.14 B.XS01215 XS-1.2.15 limit switch, brake 2 status of brake, 1=open I20.08.15 B.LS060101 LS-06.01.01 LSH-1100 level switch dust level in bag filter, highhigh, 0=above limit, hopper 1 I20.09.00 B.LS060102 LS-06.01.02 LSH-1200 level switch dust level in bag filter, highhigh, 0=above limit, hopper 2 Dig. Inp. I20.09.01 B.LS060103 LS-06.01.03 LSH-1300 level switch dust level in bag filter, highhigh, 0=above limit, hopper 3 16*120Vdc I20.09.02 B.LS060104 LS-06.01.04 LSH-1400 level switch dust level in bag filter, highhigh, 0=above limit, hopper 4 I20.09.03 A.060311XI1 A-06.03.11-XI1 KC-1104 cleaning control unit status, 1= last pulse active, chamber 1 F I20.09.04 A.060311XI2 A-06.03.11-XI2 KY-1104 cleaning control unit mode, 1=forced cleaning on, chamber 1 F I20.09.05 A.060311XI3 A-06.03.11-XI3 PSL-1104 cleaning control unit cleaning pressure detection, 1= ok in chamber 1 F I20.09.06 A.060312XI1 A-06.03.12-XI1 KC-1204 cleaning control unit status, 1= last pulse active, chamber 2 F I20.09.07 A.060312XI2 A-06.03.12-XI2 KY-1204 cleaning control unit mode, 1=forced cleaning on, chamber 2 F I20.09.08 A.060312XI3 A-06.03.12-XI3 PSL-1204 cleaning control unit cleaning pressure detection, 1= ok in chamber 2 F I20.09.09 A.060313XI1 A-06.03.13-XI1 KC-1304 cleaning control unit status, 1= last pulse active, chamber 3 F I20.09.10 A.060313XI2 A-06.03.13-XI2 KY-1304 cleaning control unit mode, 1=forced cleaning on, chamber 3 F I20.09.11 A.060313XI3 A-06.03.13-XI3 PSL-1304 cleaning control unit cleaning pressure detection, 1= ok in chamber 3 F I20.09.12 A.060314XI1 A-06.03.14-XI1 KC-1404 cleaning control unit status, 1= last pulse active, chamber 4 F I20.09.13 A.060314XI2 A-06.03.14-XI2 KY-1404 cleaning control unit mode, 1=forced cleaning on, chamber 4 F I20.09.14 A.060314XI3 A-06.03.14-XI3 PSL-1404 cleaning control unit cleaning pressure detection, 1= ok in chamber 4 F -A.DIO2.I2009 44 45 20.1 0 F.I2010 K I20.08.01 43 20.9 I20.08.00 Dig. Inp. I I20.09.15 H I20.10.00 H Dig. Inp. I20.10.01 H 16*120Vdc I20.10.02 -A.DIO2.I2010 46 47 H I20.10.03 B.SS060501 SS-06.05.01 SSL-1102 speed switch bag filter airlock feeder, pulses= rotation, chamber 1 I I20.10.04 B.SS060502 SS-06.05.02 SSL-1202 speed switch bag filter airlock feeder, pulses= rotation, chamber 2 I I20.10.05 B.SS060503 SS-06.05.03 SSL-1302 speed switch bag filter airlock feeder, pulses= rotation, chamber 3 I I20.10.06 B.SS060504 SS-06.05.04 SSL-1402 speed switch bag filter airlock feeder, pulses= rotation, chamber 4 I I20.10.07 B.XV060701XI1 XV-06.07.01-XI1 ZSO-1100 limit switch bag filter inlet valve position, 1=open, chamber 1 I20.10.08 B.XV060701XI2 XV-06.07.01-XI2 ZSC-1100 limit switch bag filter inlet valve position, 1=closed, chamber 1 I20.10.09 B.XV060702XI1 XV-06.07.02-XI1 ZSO-1200 limit switch bag filter inlet valve position, 1=open, chamber 2 I20.10.10 B.XV0607012I2 XV-06.07.02-XI2 ZSC-1200 limit switch bag filter inlet valve position, 1=closed, chamber 2 I20.10.11 B.XV060703XI1 XV-06.07.03-XI1 ZSO-1300 limit switch bag filter inlet valve position, 1=open, chamber 3 I20.10.12 B.XV060703XI2 XV-06.07.03-XI2 ZSC-1300 limit switch bag filter inlet valve position, 1=closed, chamber 3 I20.10.13 B.XV060704XI1 XV-06.07.04-XI1 ZSO-1400 limit switch bag filter inlet valve position, 1=open, chamber 4 I20.10.14 B.XV060704XI2 XV-06.07.04-XI2 ZSC-1400 limit switch bag filter inlet valve position, 1=closed, chamber 4 I20.10.15 20.1 1 F.I2011 -A.DIO2.I2011 48 I20.11.00 B.XV060711XI1 XV-06.07.11-XI1 ZSO-1108 limit switch bag filter outlet valve position, 1=open, chamber 1 Dig. Inp. I20.11.01 B.XV060711XI2 XV-06.07.11-XI2 ZSC-1108 limit switch bag filter outlet valve position, 1=closed, chamber 1 16*120Vdc I20.11.02 B.XV060712XI1 XV-06.07.12-XI1 ZSO-1208 limit switch bag filter outlet valve position, 1=open, chamber 2 I20.11.03 B.XV060712XI2 XV-06.07.12-XI2 ZSC-1208 limit switch bag filter outlet valve position, 1=closed, chamber 2 I20.11.04 B.XV060713XI1 XV-06.07.13-XI1 ZSO-1308 limit switch bag filter outlet valve position, 1=open, chamber 3 I20.11.05 B.XV060713XI2 XV-06.07.13-XI2 ZSC-1308 limit switch bag filter outlet valve position, 1=closed, chamber 3 I20.11.06 B.XV060714XI1 XV-06.07.14-XI1 ZSO-1408 limit switch bag filter outlet valve position, 1=open, chamber 4 I20.11.07 B.XV060714XI2 XV-06.07.14-XI2 ZSC-1408 limit switch bag filter outlet valve position, 1=closed, chamber 4 49 I20.11.08 I20.11.09 I20.11.10 I20.11.11 I20.11.12 I20.11.13 I20.11.14 I20.11.15 21.0 F.I2100 -A.DIO2.I2100 50 I21.0.00 B.XS01501/02 XS-1.5.01/.02 inductive sensor jump preventor status, support roller 1, 0= alarm Dig. Inp. I21.0.01 B.XS01503/04 XS-1.5.03/.04 inductive sensor jump preventor status, support roller 2, 0= alarm 16*120Vdc I21.0.02 B.XS01505/06 XS-1.5.05/.06 inductive sensor jump preventor status, support roller 3, 0= alarm I21.0.03 B.XS01507/08 XS-1.5.07/.08 inductive sensor jump preventor status, support roller 4, 0= alarm I21.0.04 B.SS030302 SS-03.03.02 speed switch reject airlock feeder, 1= rotation H I21.0.06 (condensate flow switches connection to customer system) M I21.0.07 (condensate flow switches connection to customer system) M I21.0.05 51 I21.0.08 I21.0.09 I21.0.10 I21.0.11 I21.0.12 I21.0.13 I21.0.14 I21.0.15 Distributed IO-unit in filed, -A.DIO2 - Digital outputs 2/8 27.11.2017 SLOT FUSE I/O NO CARD 21.1 F.Q2101 -A.DIO2.Q2101 21.2 SHEET 61 ADDR ID (Electric) ID (PID) DEVICE SERVICE Q21.01.00 A.060311XS1 A-06.03.11-XS1 KY-1104 cleaning control unit bag filter, forced cleaning, 1= command on, chamber 1 Dig. Outp. Q21.01.01 A.060312XS1 A-06.03.12-XS1 KY-1204 cleaning control unit bag filter, forced cleaning, 1= command on, chamber 2 8xrelay Q21.01.02 A.060313XS1 A-06.03.13-XS1 KY-1304 cleaning control unit bag filter, forced cleaning, 1= command on, chamber 3 Q21.01.03 A.060314XS1 A-06.03.14-XS1 KY-1404 cleaning control unit bag filter, forced cleaning, 1= command on, chamber 4 Q21.01.04 Y.XV060701 XV-06.07.01 FV-1100 shut-off valve bag filter inlet valve, 1=open command, chamber 1 Q21.01.05 Y.XV060702 XV-06.07.02 FV-1200 shut-off valve bag filter inlet valve, 1=open command, chamber 2 Q21.01.06 Y.XV060703 XV-06.07.03 FV-1300 shut-off valve bag filter inlet valve, 1=open command, chamber 3 Q21.01.07 Y.XV060704 XV-06.07.04 FV-1400 shut-off valve bag filter inlet valve, 1=open command, chamber 4 Q21.02.00 Y.XV060711 XV-06.07.11 FV-1108 shut-off valve bag filter outlet valve, 1=open command, chamber 1 Dig. Outp. Q21.02.01 Y.XV060712 XV-06.07.12 FV-1208 shut-off valve bag filter outlet valve, 1=open command, chamber 2 8xrelay Q21.02.02 Y.XV060713 XV-06.07.13 FV-1308 shut-off valve bag filter outlet valve, 1=open command, chamber 3 Q21.02.03 Y.XV060714 XV-06.07.14 FV-1408 shut-off valve bag filter outlet valve, 1=open command, chamber 4 Q21.02.05 Y.061001 Y-06.10.01 VBR-1102 vibrator filter hopper pneumatic vibrator, 1=virbation on, chamber 1 Q21.02.06 Y.061002 Y-06.10.02 VBR-1202 vibrator filter hopper pneumatic vibrator, 1=virbation on, chamber 2 Q21.02.07 Y.061003 Y-06.10.03 VBR-1302 vibrator filter hopper pneumatic vibrator, 1=virbation on, chamber 3 Q21.03.00 Y.061004 Y-06.10.04 VBR-1402 vibrator filter hopper pneumatic vibrator, 1=virbation on, chamber 4 -A.DIO2.Q2102 62 REV. Q21.02.04 21.3 F.Q2103 -A.DIO2.Q2103 63 Dig. Outp. Q21.03.01 8xrelay Q21.03.02 H121C01 A-1.2 signal light drive alarm, 1 = alarm Q21.03.03 A01220 A-1.2.20 alarm horn alarm horn, warning signal from equipment starting, 1= start Q21.03.04 A01220 A-1.2.20 alarm light alarm light, 1=start A1.3 A-1.3-XS lubrication unit lubrication unit start command, 1 = lubrication on Q21.03.05 Q21.03.06 Q21.03.07 21.4 -A.DIO2.Q2104 64 Q21.04.00 Dig. Outp. Q21.04.01 8xrelay Q21.04.02 Q21.04.03 Q21.04.04 Q21.04.05 Q21.04.06 Q21.04.07 Distributed IO-unit in field, -A.DIO2 - Analog inputs 20.2 F.AI2002 20.3 20.4 F.AI2004 20.5 20.6 F.AI2006 A.DIO2.AI2002 81 IW20.02.00 B.PT08101 PT-8.1.1 pressure sensor flash tank pressure IW20.02.01 B.LT08102 LT-8.1.2 pressure sensor flash tank level measurement Analog input IW20.02.02 B.PDIT060301 PDIT-6.3.1 filter cleaning unit pressure difference accross the filter 8* 4…20mA IW20.02.03 B.XT070501 XT-7.5.01 dust monitor off gas dust content after bag filter IW20.02.04 B.TE01203 TE-1.2.3 temperature sensor gearbox oil temperature, drive 1 IW20.02.05 B.TE01203 TE-1.2.13 temperature sensor gearbox oil temperature, drive 2 IW20.02.06 B.FT04101 FT-4.1.1 flow transmitter steam flow to dryer IW20.02.07 B.PT04101 PT-4.1.1 pressure sensor supply steam pressure, high pressure side IW20.03.00 B.TE04101 TE-4.1.1 temperature sensor steam temperature, high pressure side IW20.03.01 B.PT04201 PT-4.2.1 pressure sensor steam pressure to pressure, low pressure side Analog input IW20.03.02 B.TE04301 TE-4.3.1 temperature sensor steam temperature, low pressure side 8* 4…20mA IW20.03.03 B.TE07203 TE-7.2.3 temperature sensor temperature after bag filter IW20.03.04 B.TE03102 TE-3.1.2 temperature sensor output material temperature IW20.03.05 B.TE03103 TE-3.1.3 temperature sensor output material temperature IW20.03.06 B.PT03101 PT-3.1.1 pressure sensor pressure inside the discharge end chamber IW20.03.07 B.TE03104 TE-3.1.4 temperature sensor off gas temperature IW20.04.00 B.TE05101 TE-5.1.1 temperature sensor concdensate temperature before steam trap IW20.04.01 B.TE05201 TE-5.2.1 temperature sensor concdensate temperature after steam trap Analog input IW20.04.02 B.PT05102 PT-5.1.2 pressure sensor concdensate pressure before steam trap 8* 4…20mA IW20.04.03 B.PT05202 PT-5.2.2 pressure sensor concdensate pressure after steam trap IW20.04.04 B.FT07201 FT-7.2.1 flow sensor off gas flow measurement IW20.04.05 B.TE060730 TE-6.7.30 TE-1000 temperature sensor bag filter input IW20.04.06 B.TE060732 TE-6.7.32 TE-1004 temperature sensor bag filter output IW20.04.07 B.TE073012 M-7.3.01-TE2 TE-1716 temperature sensor offgas fan motor D-bearing temperature, fan 1 IW20.05.00 B.TE073013 M-7.3.01-TE3 TE-1718 temperature sensor offgas fan motor N-bearing temperature, fan 1 IW20.05.01 B.TE073112 M-7.3.11-TE2 TE-1816 temperature sensor offgas fan motor D-bearing temperature, fan 2 Analog input IW20.05.02 B.TE073113 M-7.3.11-TE3 TE-1818 temperature sensor offgas fan motor N-bearing temperature, fan 2 8* 4…20mA IW20.05.03 B.PV040201XI PV-4.2.1-XI control valve input steam valve position feedback IW20.05.04 B.TE070401 TE-7.4.01 TE-1700 temperature sensor offgas fan inboard bearing, fan 1 IW20.05.05 B.TE070402 TE-7.4.02 TE-1702 temperature sensor offgas fan outboard bearing, fan 1 IW20.05.06 B.TE070411 TE-7.4.11 TE-1800 temperature sensor offgas fan inboard bearing, fan 2 IW20.05.07 B.TE070412 TE-7.4.12 TE-1802 temperature sensor offgas fan outboard bearing, fan 2 IW20.06.00 B.XT070403 XT-7.4.03 VT-1700 vibration sensor offgas fan inboard bearing, fan 1 IW20.06.01 B.XT070404 XT-7.4.04 VT-1702 vibration sensor offgas fan outboard bearing, fan 1 Analog input IW20.06.02 B.XT070413 XT-7.4.13 VT-1800 vibration sensor offgas fan inboard bearing, fan 2 8* 4…20mA IW20.06.03 B.XT070414 XT-7.4.14 VT-1802 vibration sensor offgas fan outboard bearing, fan 2 IW20.06.04 B.QT070501 QT-5.3.01 conductivity sensor leak detection, condensate water conductivity I IW20.06.05 B.PV080501XI PV-8.5.1-XI control valve flash steam valve position feedback I IW20.07.00 B.TE060201 TE-6.2.01 TE1100 temperature sensor bag filter wall temperature, hopper 1 IW20.07.01 B.TE060202 TE-6.2.02 TE1200 temperature sensor bag filter wall temperature, hopper 2 Analog input IW20.07.02 B.TE060203 TE-6.2.03 TE1300 temperature sensor bag filter wall temperature, hopper 3 8* 4…20mA IW20.07.03 B.TE060204 TE-6.2.04 TE1400 temperature sensor bag filter wall temperature, hopper 4 IW20.07.04 B.TE060211 TE-6.2.11 TE1102 temperature sensor bag filter wall temperature, upper chamber 1 IW20.07.05 B.TE060212 TE-6.2.12 TE1202 temperature sensor bag filter wall temperature, upper chamber 2 IW20.07.06 B.TE060213 TE-6.2.13 TE1302 temperature sensor bag filter wall temperature, upper chamber 3 IW20.07.07 B.TE060214 TE-6.2.14 TE1402 temperature sensor bag filter wall temperature, upper chamber 4 IW20.07.00 B.TE010111 TE-1.1.11 temperature sensor Input gas temperature to drum K IW20.07.01 B.PDT010110 PDT-1.1.10 differential pressure sensor Pressure in the input end of the drum K A.DIO2.AI2003 A.DIO2.AI2004 A.DIO2.AI2005 A.DIO2.AI2006 82 83 84 85 PDIT-1002 IW20.06.06 IW20.06.07 20.7 A.DIO2.AI2007 21.6 F.AQ2105 A.DIO2.AI2106 86 87 Analog input IW20.07.02 8* 4…20mA IW20.07.03 IW20.07.04 IW20.07.05 IW20.07.06 IW20.07.07 Distributed IO-unit in field, -A.DIO2 - Analog outputs 3/8 27.11.2017 SLOT FUSE I/O NO CARD 21.5 F.AQ2105 A.DIO2.AQ2105 SHEET 88 ADDR ID (Electric) ID (PID) DEVICE SERVICE REV. PQW21.05.0 Y.PV421 PV-4.2.1 control valve actuator control of main steam control valve Analog output PQW21.05.1 Y.PV851 PV-8.5.1 control valve actuator control of flash tank presssure 4…20mA PQW21.05.2 Y.LV8101A LV-8.10.01A LV-8102A control valve actuator control of flash tank condensate level M PQW21.05.3 Y.LV8101B LV-8.10.01B LV-8102B control valve actuator control of flash tank condensate level M ID (elec.) ID (PID) DEVICE SERVICE REV. WIRELESS TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT (Modbus TCP) SLOT FUSE I/O NO X1 CARD SHEET ADDR Periphery devices Wireless receiver B.TE01101 TE-1.1.01 temperature sensor material temperature in drum, feed end, zone 1 B.TE01102 TE-1.1.02 temperature sensor material temperature in drum, middle part, zone 2 B.TE01103 TE-1.1.03 temperature sensor material temperature in drum, middle part, zone 3 B.TE01104 TE-1.1.04 temperature sensor material temperature in drum, discharge end, zone 4 G.M01201 M-1.2.01 frequency converter (PPO4) A.PRM - DEVICES WITH BUS INTERFACE Profibus DP Frequency converters DP 10 PQW500 frequency converter main drive frequency converter, master drive, command word PQW502 main drive frequency converter, master drive, reference PQW504 PZD3 PQW506 PZD4 PQW508 PZD5 PQW510 PZD6 PIW500 frequency converter main drive frequency converter, master drive, status word PIW502 main drive frequency converter, master drive, actual value PIW504 torque PIW506 current PIW508 motor winding temperature PIW510 PZD6 DP 11 G.M01211 M-1.2.11 PQW512 frequency converter (PPO4) frequency converter main drive frequency converter, follower drive, command word PQW514 main drive frequency converter, follower drive, reference PQW516 PZD3 PQW518 PZD4 PQW520 PZD5 PQW522 PZD6 PIW512 frequency converter main drive frequency converter, follower drive, status word PIW514 main drive frequency converter, follower drive, actual value PIW516 torque PIW518 current PIW520 motor winding temperature PIW522 PZD6 DP 12 G..M07301 M-7.3.01 PQW524 frequency converter (PPO4) frequency converter offgas fan 1, command word PQW526 offgas fan 1, reference PQW528 PZD3 PQW530 PZD4 PQW532 PZD5 PQW534 PZD6 PIW524 frequency converter offgas fan 1, status word 1 PIW526 offgas fan 1, actual value PIW528 torque PIW530 current PIW532 motor winding temperature PIW534 DP 13 PZD6 G..M07302 M-7.3.02 PQW536 frequency converter (PPO4) frequency converter offgas fan 2, command word PQW538 offgas fan 2, reference PQW540 PZD3 PQW542 PZD4 PQW544 PZD5 PQW546 PZD6 PIW536 frequency converter offgas fan 2, status word 1 PIW538 offgas fan 2, actual value PIW540 torque PIW542 current PIW544 motor winding temperature PIW546 DP 14 PQW548 PZD6 G.M081001 M-8.10.01 frequency converter frequency converter condensate pump 1, command word PQW550 condensate pump, reference PQW552 PZD3 PQW554 PZD4 PQW556 PZD5 PQW558 PIW548 PZD6 frequency converter condensate pump 1, status word PIW550 condensate pump 1, speed PIW552 torque PIW554 current PIW556 PZD5 4/8 27.11.2017 SLOT FUSE I/O NO CARD SHEET ADDR ID (Electric) ID (PID) DEVICE G.M081002 M-8.10.02 frequency converter PIW558 DP 15 SERVICE PZD6 PQW560 frequency converter condensate pump 2, command word PQW562 condensate pump 2, reference PQW564 PZD3 PQW566 PZD4 PQW568 PZD5 PQW570 PZD6 PIW560 frequency converter condensate pump 2, status word PIW562 condensate pump 2, speed PIW564 torque PIW566 current PIW568 PZD5 PIW570 DP 16 PZD6 G.M07105 M-7.1.05 PQW572 frequency converter frequency converter reject dust fan, command word PQW574 reject dust fan, reference PQW576 PZD3 PQW578 PZD4 PQW580 PZD5 PQW582 PZD6 PIW572 frequency converter reject dust fan, status word PIW574 reject dust fan, speed PIW576 torque PIW578 current PIW580 PZD5 PIW582 PZD6 Direct-on-line starters DP 20 A.M01202 M-1.2.02 PQW600 DOL starter main motor 1 fan DOL starter command word PQW602 analog output PQW604 logic output command register PIW600 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW602 average current PIW604 inputs status PIW606 outputs status PIW608 status DP 21 A.M01212 M-1.2.12 PQW620 DOL starter main motor 2 fan DOL starter command word PQW622 analog output PQW624 logic output command register PIW620 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW622 average current PIW624 inputs status PIW626 outputs status PIW628 status DP 22 A.M01205 M-1.2.05 PQW640 DOL starter main drive 1 brake DOL starter command word PQW642 analog output PQW644 logic output command register PIW640 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW642 average current PIW644 inputs status PIW646 outputs status PIW648 status DP 23 A.M01215 M-1.2.15 PQW660 DOL starter main drive 2 brake DOL starter command word PQW662 analog output PQW664 logic output command register PIW660 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW662 average current PIW664 inputs status PIW666 outputs status PIW668 status DP 24 A.M02101 M-2.1.01 PQW680 DOL starter input feeder vibra motor DOL starter command word PQW682 analog output PQW684 logic output command register PIW680 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW682 average current PIW684 inputs status PIW686 outputs status PIW688 status DP 25 A.M03301 M-3.3.01 PQW670 DOL starter reject screw feeder motor DOL starter command word PQW672 analog output PQW674 logic output command register PIW670 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW672 average current PIW674 inputs status PIW676 outputs status PIW678 status DP 26 PQW680 A.M03302 M-3.3.02 DOL starter reject air lock feeder motor DOL starter command word PQW682 analog output PQW684 PIW680 logic output command register DOL starter PIW682 main motor 1 fan, status word average current 5/8 27.11.2017 REV. SLOT FUSE I/O NO CARD SHEET ADDR ID (Electric) ID (PID) DEVICE SERVICE PIW684 inputs status PIW686 outputs status PIW688 status DP 27 A.M06501 M-6.5.01 PQW690 DOL starter airlock motor of bag filter chamber 1 DOL starter command word PQW692 analog output PQW694 logic output command register PIW690 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW692 average current PIW694 inputs status PIW696 outputs status PIW698 status DP 28 A.M06502 M-6.5.02 PQW700 DOL starter airlock motor of bag filter chamber 2 DOL starter command word PQW702 analog output PQW704 logic output command register PIW700 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW702 average current PIW704 inputs status PIW706 outputs status PIW708 status DP 29 A.M06503 M-6.5.03 PQW710 DOL starter airlock motor of bag filter chamber 3 DOL starter command word PQW712 analog output PQW714 logic output command register PIW710 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW712 average current PIW714 inputs status PIW716 outputs status PIW718 status DP 30 A.M06504 M-6.5.04 PQW720 DOL starter airlock motor of bag filter chamber 4 DOL starter command word PQW722 analog output PQW724 logic output command register PIW720 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW722 average current PIW724 inputs status PIW726 outputs status PIW728 status DP 31 A.M06601 M-6.6.01 PQW730 DOL starter screw feeder motor of bag filter chamber 1 and 2 DOL starter command word PQW732 analog output PQW734 logic output command register PIW730 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW732 average current PIW734 inputs status PIW736 outputs status PIW738 status DP 32 A.M06602 M-6.6.02 PQW740 DOL starter screw feeder motor of bag filter chamber 3 and 4 DOL starter command word PQW742 analog output PQW744 logic output command register PIW740 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW742 average current PIW744 inputs status PIW746 outputs status PIW748 status DP 33 A.M06603 M-6.6.03 PQW750 DOL starter screw feeder motor, material out from bag filters DOL starter command word PQW752 analog output PQW754 logic output command register PIW750 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW752 average current PIW754 inputs status PIW756 outputs status PIW758 status DP 34 A.M06901 M-6.9.01 MY1810 PQW760 DOL starter Penthouse vent fan 1 DOL starter command word PQW762 analog output PQW764 logic output command register PIW760 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW762 average current PIW764 inputs status PIW766 outputs status PIW768 status DP 35 PQW770 A.M06902 M-6.9.02 MY-1812 DOL starter Penthouse vent fan 2 DOL starter command word PQW772 analog output PQW774 PIW770 logic output command register DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW772 average current PIW774 inputs status PIW776 outputs status PIW778 status 6/8 27.11.2017 REV. SLOT FUSE I/O NO CARD SHEET ADDR ID (Electric) ID (PID) DEVICE SERVICE REV. DP 44 A.M07106 M-7.1.06 DOL starter Dust removal airlock feeder J DOL starter command word PQW770 PQW772 analog output PQW774 logic output command register PIW770 DOL starter main motor 1 fan, status word PIW772 average current PIW774 inputs status PIW776 outputs status PIW778 status DP 36 A.E060201 DOL starter bag filter heater, module 1 hopper DP 37 A.E060202 DOL starter bag filter heater, module 2 hopper DP 38 A.E060203 DOL starter bag filter heater, module 3 hopper DOL starter bag filter heater, module 4 hopper DP 39 A.E060204 DP 40 A.E060211 DOL starter bag filter heater, module 1 chamber DP 41 A.E060212 DOL starter bag filter heater, module 2 chamber DP 42 A.E060213 DOL starter bag filter heater, module 3 chamber DP 43 A.E060214 DOL starter bag filter heater, module 4 chamber DP 45 A.E01203 DOL starter gearbox heater E-1.2.03 7/8 27.11.2017 L SLOT FUSE I/O NO CARD SHEET ADDR ID (Electric) ID (PID) DEVICE SERVICE REV. DP 46 A.E01213 E-1.2.13 DOL starter gearbox heater L 8/8 27.11.2017 KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 1/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Rev. Date Written A 31.3.17 MSR B 6.7.17 MSR C 22.9.17 MSR D 11.10.17 MSR, HVM Approved CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION KUMERA STEAM DRYER 0 0.1 GENERAL Component and signal naming convention The tag numbers refer to P&I diagram 435110 /01, /02. NNN-xxxx NNN : customer's function code of signal or instrument xx : customer's identification code Some of the documents are common for Kumera’s different projects, and therefore in those documents the standard Kumera ID is used, which is as follows: NNN-y.x.z Where: NNN : is the function code of signal or instrument according to ISO 3511 standard y.x.z : number code taking into account part of the process and device, where the component is located. Basically as follows: y : plant unit or area x : device z : device related instrument, running number For example PT-4.2.1 means the pressure (P) transmitter (T) in the valve assembly in the pressure regulating unit (4.2) and it is in the first measurement loop (1). In the following text Kumera's standard ID is in brackets (). Please note, that in some documents a zero can precede numbers y, x or z. It is used for making automatic alphabetical order possible in the lists. Special identification KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 2/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION To identify signals more accurately in the logic and circuit diagrams and in instrument list a more specific identification is used. This is because in the same measurement loop there can be several inputs and outputs. The identification is made by extending the tag number with 2 or 3 characters as follows: NNN-y.x.z-ab Where: a: signal type (S=switch, I=indication,...), 1 or 2 characters b: running number, if needed (1, 2,…) When programmed to DCS (PLC) the different signals in same signal loop can be specified (in the variable names) with the extension. For example the control signal to the regulating valve PV-4.2.1 is PV-4.2.1-XS1 (XS = special switching function, 1 = running number). 0.2 Terminology Following abbreviations are used for defining signals. NV: Normal value SP: Set point LL: Low Low alarm L: Low alarm H: High alarm HH: High High alarm -: not applicable, not used PFC: potential free contact 24IO: 24Vdc IO signal 120IO 120Vac IO signal PS: Power supply Normal value (NV) is the expected process value. LL and HH alarms should in most cases cause stopping of equipment. In normal conditions process value shall stay between values L and H values. Set point SP is normal set point value of controller. Loop powered instrument gets its power from signal circuit (4...20 mA) and does not need separate power supply. 0.3 Operator interface The steam dryer line is controlled with PLC system. Generally operator controls the steam dryer system from operation station screen. It is called in this text Dryer operation station and its identification in electrical documents is –A.HMI. It consists of touch screen panel PC and it is installed in the cabinet (+CA0) door. A second control place, the supervisory control system (SV) of the plant, is connected via Ethernet Modbus TCP to PLC. From the plant system SV can be done most control and monitoring operations, which are available from HMI station. Many of basic configurations, especially the hardware related ones, are available only from the dryer HMI panel. Following short terms are used about control equipment: KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 3/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION PLC: The dryer control PLC running the main control code of the system. HMI: The operation station of the dryer installed near the dryer. It has complete user interface of the dryer PLC. SV: The plant DCS, which is a supervisory system. It has user interface only to part of the dryer PLC data and functions. The term DCS is used for referring generally to both HMI and SV. Local control panel (A-1.2) is situated on a maintenance platform near the dryer and has following control elements: - Start/reverse/stop buttons of dryer drum rotation - Speed adjusting buttons of rotation speed - Emergency stop button The remote IO unit (-A.DIO2) for field instrument connections is installed inside the local panel (A-1.2). Local panels of other motors are not in Kumera’s delivery. For manual steam controlling at dryer start there are mechanical steam pressure meters in the pressure regulating unit and in steam trap unit 0.4 Data logging All signals, which are measured by the PLC, are logged to the database of the dryer operation station HMI. These include, among other things, the steam, material and off gas temperatures, pressures, flows, dryer drive rotation speed and power demand and the concentrate feed rate. From software controllers the set points, actual values and controller output values are logged. The logging interval of measurement points in data file can be for example 1 minute. Every row in the data log file has a time stamp, which includes the date and time. Logged data can be exported from the HMI to standard files (such as .csv) for process data analysis purposes. The logged data can be read from the hard disk of HMI via an additional Ethernet port of HMI. For the safety reasons direct connection to the Ethernet network between PLC and HMI is not allowed from outside. Alarm list system displays all the LL, L, H and HH alarms of the analog measurements and alarms based on discrete input signals as well as alarms made in program code by combining several signals. All the alarms are saved to mass storage system of HMI, even though they are not particularly specified in following description. Alarms from the all motor starters (DOL and frequency converter) are displayed and saved, even though they are not explicitly specified in the text. 0.5 Scope of delivery In this text is described the equipment necessary for steam dryer operation. Note, that Kumera does not deliver all of these devices. The delivery scope is defined in Annex of the Contract. 0.6 0.6.1 Interfacing of dryer control system to plant systems Interface to plant control system Databus interface Databus to plant supervisory system (SV) KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 4/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION - Modbus TCP connection between dryer PLC and SV Optical/copper converter shall be used at longer distance. Their delivery is not, however, in Kumera's scope. - Direct connection from office network or internet to the dryer control system is not allowed. Traditional IO interface Following signals are coming from plant system to dryer PLC Material federate, 4…20 mA Dry material conveying system fault, PFC Signals from dryer PLC to plant system Material feeding allowed to dryer, PFC 0.6.2 1 1.1 Interface between dryer PLC and motor control center Profibus DP connection to individual motor starters in MCC DOL starters and frequency converters operate as slaves in bus For reducing the Profibus segment size, bus is divided to separate segments by a repeaters to be installed in MCC room. Repeaters by others. STEAM DRYER LOOPS Material temperature inside steam dryer TE-1101 ... 1104 (TE-1.1.01 … 1.1.04), TE-1101 ... 1104 (TT-1.1.01 … 1.1.04) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits TE-1.1.1 TE-1.1.2 TE-1.1.3 TE-1.1.4 Alarms: Interlocks: TE-1101 ... 1104 (TE-1.1.01 … 1.1.04), TE-1101 ... 1104 (TT-1.1.01 … 1.1.04) Temperature measurement of material inside drum. HMI and SV screen, unit °C 4…20 mA, Wireless HART, battery power 0…150°C °C NV 40, L 10, HH 130 °C NV 60, L 30, HH 130 °C NV 80, L 50, HH 130 °C NV 100, L 70, HH 130 L and HH alarms to alarm list - The rotating dryer drum has 4 temperature sensors. The sensors TE-1101 ... 1104 (TE1.1.1 … 1.1.4) are installed on the wall of the drum in one of the 5 pipe sections and axially in 4 points. Sensor TE-1101 (TE-1.1.1) is installed in the feed end to measure the input material temperature little after feeding point. Sensor TE-1104 (TE-1.1.2) is axially in next zone and after them is sensor TE-1103 (TE-1.1.3). In the last measuring zone there is sensor TE-1104 (TE-1.1.4). The temperatures can be observed from HMI/SV screen scaled as 0…150 °C. KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 5/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The temperature readings give necessary information to the operator during starting and stopping of the dryer for selecting appropriate operation actions. Measured temperatures are also used in the control of the steam as described in point " Operating modes / Temperature measurement inside drum ". Because the sensors are in the rotating part, the signals are transmitted wirelessly TE1101 ... 1104 (TT-1.1.1 … 1.1.4) from the dryer drum. The radio signals are received with receiver (TR-1.1), which is connected with Ethernet and Profibus DP communication to the PLC. 1.2 Main drive control, speed indication and control 5121-SVP-2001M1 (M-1.2.01), 5121-SVP2001M2 (M-1.2.11) Tag: Service: Control signal: Scaling: Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: Auto: Values, limits Local: Manual: Auto: Alarms: Interlocks: 5121-SVP-2001M1 (M-1.2.01), 5121-SVP-2001M2 (M-1.2.11), SI-1201 (M-1.2.01/.11-SI) SI-1211 (M-1.2.01/.11-XI) Dryer drum rotating drives Profibus DP Speed 0…100 %/ 0… 2 rpm Torque 0...200 %/ 0 ... 2060 Nm (2 x Tn) Profibus DP Starting and speed control from local panel. Frequency converter control is via PLC. Starting and speed control from HMI/SV screen From SV screen control of individual motors and brakes not possible Speed control from program based on material feed rate. Reverse rotation speed always limited to 0.3 rpm. Speed range 0.3 … 1.0 rpm Speed range 0.3 … 2.0 rpm Speed range 0.3 … 2.0 rpm Low speed monitoring, SI-1201/1211 (M-1.2.01/11-SI.LL), 0.1 rpm Frequency converter fault Stopping of drive at event: - Emergency shutdown - Emergency stop system activated - Dry material conveyor fault - Drive system internal fault, instant stop * motor fault * frequency converter fault * brake fault - Drive system internal fault, delayed stop * drive motor fan fault * girth gear lubrication fault - Steam flow stopped FIT-4101 (FT-4.1.01.LL), delayed stop KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 6/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The main rotating drive motors 5121-SVP-2001M1 (M-1.2.01) and 5121-SVP-2001M2 (M-1.2.11) of dryer drum are supplied with a frequency converters for enabling variable rotation speed of the drum. The drum is started and stopped using control elements at the HMI screen. The rotation speed can also be adjusted from the screen. Commands (on/off/reverse) and speed reference signal 0…2.0 rpm (drum speed) are signaled to the frequency converter via Profibus DP from the control PLC. The rotation speed is normally kept constant, when the material flow is constant. Guidelines for the rotation speed in different process situations will be defined on the basis of experience gathered during the start-up and commissioning. The rotation speed can also be controlled automatically based on material feed rate, when auto speed control mode is selected. Then speed follows the feed rate in steps. When feed rate has stayed in a preset time delay inside certain range, the speed reference is changed to the corresponding speed value. Idea is that speed stay normally always in constant value. The whole speed range is divided in 7 steps. The speed is changed slowly (in some minutes) from step to another using ramp function. Torques of the main motors NI-1201 (M-1.2.01-XI) and NI-1211 (M-1.2.11-XI) measured by the frequency converter are displayed at HMI screen scaled as 0...200% (100% = motor nominal 1030 Nm). Main motors rotation speeds SI-1201/1211 (M-1.2.01/11-SI) are measured and shown on the HMI screen as motor speed (0…2000 rpm) and as drum speed (0…2.0 rpm). 1.3 Main drive control with 2 motors The dryer drum is driven with 2 induction motors supplied by frequency converters. The load shall be shared equally to both motors. The sharing method depends is MasterFollower system of the ABB ACS880 series. The speed reference is transferred only to the master frequency converter via Profibus DP. It gives torque reference to the follower unit via master/follower link, which is a fiber optic cable. Follower gives back its status word. When there is failure in one frequency converter, both motors shall be stopped. 1.4 Dryer local panel controls (A-1.2) A local control panel is installed on the service platform near the steam dryer. The selection between local and remote mode is done from HMI screen. In local mode the drum can be started and stopped by switches and the drum rotation speed may be adjusted with buttons. Start and stop switches are connected to digital inputs of the PLC. PLC program processes the signals, after which the required control signals are transmitted to frequency converter, and starters of the brakes and fan motors via Profibus DP bus. (More detailed description of the different controls is in the in PLC program documentation.) 1.5 Temperature measurement of main motor winding TE-1201 (M-1.2.1-TE1), TE-1211 (M1.2.11-TE1) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits TE-1201 (M-1.2.1-TE2), TE-1211 (M-1.2.11-TE2) Motor winding high temperature HMI screen, unit °C PT100, resistance HH 150 °C KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 7/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Alarms: HH alarm to alarm list Interlocks: Activation causes alarm to HMI screen Motor winding temperature is measured with PT100 temperature sensors, which are connected to analog input card of the frequency converter. The winding temperature transferred via Profibus DP to dryer PLC and is displayed at HMI screen. 1.6 Gear box oil temperature TE-1203 (TE/TT-1.2.3), (TE/TT-1.2.13), (E-1.2.03), (E-1.2.13) Tag: drive 1 drive 2 Service: Control signal: Display: Signal type: Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: Auto: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: (TE/TT-1.2.3), (E-1.2.03A/B) (TE/TT-1.2.13), (E-1.2.13A/B), Gearbox oil heating and temperature measurement Profibus DP to starter HMI screen, °C 4…20 mA, loop powered Profibus DP, motor starter. Control according to oil temperature -10 ..120 °C °C, L -5, H 90 SP L and H alarms to alarm list - A temperature sensors measures the temperatures of the main gearboxes oil and gives it as 4...20mA signal to DCS. Temperatures are displayed in HMI screen scaled as -10 ... 120 ºC. Heater (E-1.2.03/13) is on, when temperature is below set point, typically 15°C. In gearbox there are needed 2 heating resistors because of the gearbox mechanics. The heaters of one gearbox are controlled with one common motor starter unit in MCC. 1.7 Main drive brakes 5121-SVP-2001M5 (M-1.2.5), 5121-SVP-2001M6 (M-1.2.15) Tag: thruster motor limit switch Service: Control signal: Scaling: Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: Auto: Values, limits 5121-SVP-2001M5 (M-1.2.5), 5121-SVP-2001M6 (M-1.2.15) ZS-1205 (M-1.2.5-ZS), ZS-1215 (M-1.2.15-ZS), Drum drive brake thrustors and position limit switches Profibus DP to starter From limit switch, PFC. Control from HMI screen Both brakes controlled with same command Control from drive control code - KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 8/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Alarms: Interlocks - Mismatching position feedback stop via drive control - Starter fault Emergency shutdown - Brake closes delayed via drive control Emergency stop activation - Brake closes short delay, hardwired The status of the main brakes 5121-SVP-2001M5/M6 (M-1.2.5/.15) are detected with a limit switch ZS-1205/1215 (M-1.2.5/15-ZS) attached to the brake. A closed contact provides a logic ‘1’ signal to DCS digital input in case the brake is open. The status limit switch signal is used for diagnosing the condition of brake. This feedback signal shall match the command (open/close) given to the brake. If the feedback differs from the command and this state lasts longer than the preset delay (preliminary 1 s), the motors are stopped. Emergency stop relay shall be equipped with delayed contacts (0...4 s), which interlock brake supply. Purpose is to not stop with brake from full speed. 1.8 Lubrication control (A-1.3) Tag: Service: Control signal: (A-1.3), (A-1.3-XS), XA-1230 (A-1.3-XI) Girth gear lubricator PFC, at closed contact is lubrication enabled Scaling: Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: Auto: Values, limits Alarms: PFC, lubricator fault, 0 = alarm Interlocks: From lubricator panel Starting control from DCS screen From drive control code: on, when drive running Fault including running out of grease Fault alarm at HMI screen Stopping of drive, when: - Lubricator fault lasted over set time period, 8 h Dryer has automatic lubricator for the girth gear (A-1.3). The lubrication sequence is on when the start command (A-1.3-XS) active. This means that DCS gives a closed contact to lubricator unit input. Opening the contact stops the lubrication sequence. DCS shall normally keep the command active when the dryer drive is running. Lubrication control unit gives an alarm XA-1230 (A-1.3-XI), when there is a malfunction in the system. Alarm signal is connected to DCS digital input. A normally closed contact opens in case there is a fault in the lubricator. In the lubricator there are timers and sensors for sequencing the lubricate pumping. If control unit detects a fault in the lubrication, for example due to component malfunction or extinction of lubricant, the pump stops and a fault signal activates in the lubricator unit. Also the alarm contact opens and initiates an alarm to PLC. Signal '0' means the alarm has initiated and it is displayed in the HMI screen. The alarm must be reset locally from the lubrication unit button to enable the lubrication unit to function again. KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 9/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION If the alarm is active longer than a predefined period, preliminary 8 h, the steam dryer rotation is automatically stopped. The error message can be read from the lubricator display. 1.9 Drive component fault situation If there is fault in some motor, in frequency converter or in brake, special measures has to be taken, if operation is wanted to be continued before the faulty component is repaired. Instructions for rotating the dryer drum with one drive unit are given in separate document. 1.10 Jump preventor ZSH-1501...1508 (XS-1.5.01,..., 08) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: ZSH-1501...1508 (XS-1.5.01,..., 08) Earth quake detection Inductive sensor, output 120IO L and H alarms to alarm list - At the each support rollers is installed a construction for keeping drum in place during earthquake. Jump preventor contains inductive proximity sensors for detecting its displacement. When the preventor position changes, alarm is activated and main drive is stopped. 2 STEAM DRYER FEED SYSTEM LOOPS 2.1 Feeding conveyor 5121-AVB-2001M (M-2.1.1) Tag: Service: Control signal: Scaling: Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: Auto: Values, limits Alarms: 5121-AVB-2001M (M-2.1.1) Input feed chute vibration motor Profibus DP to motor starter From motor starter via Profibus DP run, fault, mode (remote/ local) From local panel (by others), including local/remote switch Hardwired to motor starter Starting control from screen Starting control from line control code Motor starter alarm KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 10/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Interlocks: Stop when: - Emergency shutdown Start for short run when: - Chute level switch LSH-2104 (LS-2.1.4) activates The concentrate is fed to the steam dryer with chute feeder. The chute is vibrated by electric motor driven vibrator. Motor has constant speed and is running always intermittently when material feed is on to the steam dryer. The interval and the running time can be adjusted from DCS screen. Preliminary values are for interval 2 minutes and for running time 5 seconds. The vibration motor is also started for one 5 seconds cycle, when level switch LSH-2104 (LS-2.1.4) activates for longer than 1 second. Status of feeding (running/stop/fault) vibrator is detected from the motor starter and displayed in the HMI screen. 2.2 Level switch of input hopper LSH-2104 (LS-2.1.4) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: LSH-2104 (LS-2.1.4) Input feed chute too high level (HH) PFC Level HH alarm to alarm list Long activation shall stop upstream conveyors, time setting 5 s. - In upper part of input feeder is vibration type level switch for detecting clogging of the input feeder. It gives potential free contact signal "0", when material rises at the sensor level. Activation shall stop the upstream conveyors. It is not necessary to stop the upstream conveyors from the fault of vibration motor 5121AVB-2001M (M-2.1.1), if the level switch does not give alarm. 2.3 Material feed rate WT-2075 (FT-2.0.01) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: WT-2075 (FT-2.0.1) Incoming material feed rate HMI screen, unit t/h 4…20 mA 0…? 240 t/h t/h NV 230 L 20, HH 237 L and HH alarms (duration >5 s) to alarm list KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 11/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Material feed rate signal is sent from plant control system to dryer PLC analog input. Feed rate is displayed at the HMI screen, scaled from 0 to 240 tons/h. Feed rate signal is used for calculating minimum pressure in discharge chamber. 2.4 Permission for material input to dryer (XY-2.0.02) Tag: Service: Control signal: (XY-2.0.02) Signal to plant system SV for allowing input of wet material PFC from PLC output to SV system, 1= input allowed Scaling: Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: Auto: - Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: 3 3.1 From line control code Permission denied at: - Emergency stop activation - Emergency shutdown - Dryer under pressure too low PT-3101 (PT-3.1.1.HH) DISCHARGE SYSTEM LOOPS Steam Dryer Discharge End Pressure PT-3101 (PT-3.1.1) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: PT-3101 (PT-3.1.1) Pressure inside discharge chamber HMI, SV screen, unit kPa(g) 4…20 mA, HART, loop powered 0…-0.5 kPa(g) kPa(g) ) NV -0.1, L -0.4, H -0.01, HH -0.005 L and H and HH alarms to alarm list HH, too low under pressure to stop the feed - The negative pressure relative to the ambient pressure in the discharge end chamber of the steam dryer is measured with pressure transmitter PT-3101 (PT-3.1.01). It provides the pressure measurement to PLC as a 4…20 mA signal. The pressure is sensed from the discharge end chamber with impulse pipe, which goes approximately 50 mm inside the chamber. Pressure PT-3101 (PI-3.1.01) is displayed at the HMI and SV screen, scaled to 0...-0.5 kPa(g). The normal operation point is approximate -0.1 kPa(g). An alarm is initiated above value 0.01 kPa(g) or below -0.4 kPa(g). KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 12/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION To prevent dust coming out from drum, feed is stopped, if under pressure less than LL. The pressure signal is used as one basis in controlling the offgas gas fan. 3.2 Control concept for air flow through the dryer TIC-3104 (TIC-3.1.04), (XY-3.1.01) The off gas consists of the evaporated water from the material and of the air coming from the feed end into the dryer. In addition there can be nitrogen, which is used to reduce the ignition risk of the concentrate dust. To keep the process in good state, the water content in the exhaust gas should be in certain limits. Therefore basically the air flow and thus the exhaust gas flow should be in relation to the concentrate feed rate. Exhaust gas flow is determined by adjusting the offgas fan M-1700/1800 (M-7.3.01/02) speed. 3.2.1 Exhaust gas flow control principle Off gas flow is controlled according to under pressure inside the discharge chamber PT3101 (PT-3.1.01). The set point for the pressure is calculated form the input material flow p sp = Ka * Qmat + Kb where : p sp vacuum pressure set point [kPa] (absolute value in relation to atmosphere) Ka capacity factor [kPa*h/ton] Kb pressure factor [kPa] Qmat material flow [ton/h]. This signal can be made for example from the material input feeder capacity set point (0...100 %), scaled by a calculation element (XY3.1.01). The pressure factor shall be big enough to maintain always negative pressure inside discharge chamber. The factors Ka and Kb shall be adjustable by operator, so that input material moisture variations can be compensated manually. Settings Ka = 0.0006 kPa*h/ton and Kb = 0.04 kPa can be used as preliminary values. Using the above-mentioned values for instance for a material flow of 80 ton/h, a pressure set point (p sp) can be calculated as follows: p sp = 80 ton/h * 0.0006 kPa*h/ton + 0.04 kPa = 0.088 kPa When under pressure decreases, fan speed is increased and vice versa. The off gas temperature is controlled with software controller TIC-3104 (TIC-3.1.04). It also affects to the off gas fan speed. Normally temperature controller TIC-3104 (TIC-3.1.04) shall not interfere the under pressure controller (PIC-3.1.01). Only if the temperature TE-3104 (TE-3.1.04) exceeds limit, the low limit of pressure controller shall be increased. If this low limit goes now over the normal output value of the pressure controller (PIC3.1.01), which is based on the material flow, output is increased. Then fan speed is increased and so the off gas temperature will decrease. Operator shall give set point for the temperature controller TIC-3104 (TIC-3.1.04), which is functioning as the high limit for xs-the off gas temperature. Note, that in normal process conditions this set point is not reached. The airflow is measured with flow sensor FE-7201 (FE-7.2.01). KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 13/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION 3.2.2 Maintaining negative pressure in the system There should be a minimum limit for fan speed, because the under pressure in dryer shall be guaranteed all the time. Also alarm is activated if pressure goes below limit L-limit of PI-3101 (PT-3.1.01.L). The minimum limit of the useful speed range of the fan depends on the feed rate and can be changed automatically. The minimum value of the negative pressure is determined according to linear formula: pmin = Ka * Qmat + Kb where : pmin vacuum pressure set point [kPa] (absolute value of vacuum in relation to atmosphere) Ka capacity factor [kPa*h/ton] Kb pressure factor [kPa] Qmat material flow [ton/h]. This signal can be made for example from the material input feeder capacity set point (0...100 %), scaled by a calculation element (XY-3.1.01). The factors Ka and Kb shall be adjustable by operator, so that input material moisture variations can be compensated manually. Settings Ka = 0.001 kPa*h/ton and Kb = 0.01 kPa can be used as preliminary values. Using the above-mentioned values for instance for a material flow of 35 ton/h, a pressure set point (psp) can be calculated as follows: pmin = 35 ton/h * 0.001 kPa*h/ton + 0.01 kPa = 0.045 kPa Controller TIC-3104 (TIC-3.1.04) controls the fan speed. In case the discharge end pressure (PT-3.1.1) goes under the limit pmin, fan speed is not decreased anymore. Pmin is set to minimum value of the controller TIC-3104 (TIC-3.1.04). The airflow is measured with flow sensor FE-7201 (FE-7.2.01). 3.3 Dried material temperature TE-3102 (TE-3.1.02), TE-3103 (TE-3.1.03), TIC-3102 (TIC-3.1.02) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: TE/TT-3102 (TE/TT-3.1.02), TE/TT-3102 (TE/TT-3.1.03) Dry material temperature measurement HMI, SV screen, unit °C 4…20 mA, HART, loop powered 0…150 °C °C NV 115, L 95, H 125, HH 135 L and H alarms to alarm list Activation of HH shall cause emergency shutdown - KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 14/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Temperature sensors are installed in the discharge end hopper for measuring the material temperature at the point where the material drops from the dryer drum to the discharge end hopper. The sensor signals are displayed at the DCS, tagged TT-3102 (TT-3.1.02) and TT-3103 (TT-3.1.03), and scaled to 0…150°C. The normal operating point is 115 °C. An alarm is initiated at the DCS when the temperature exceeds 125 °C or falls below 95 °C. These are preliminary values, which shall be confirmed during commissioning. The output material temperature is used in auto mode to control the input steam pressure with controller TIC-3102 (TIC-3.1.02). For details, see chapter “Automatic mode, material temperature feedback, TIC-3102 (TIC-3.1.02)”. 3.4 Steam Dryer offgas temperature TE-3104 (TE-3.1.04) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: TE/TT-3104 (TE/TT-3.1.04) Dry material temperature measurement HMI, SV screen, unit °C 4…20 mA, HART, loop powered 0…200 °C °C NV 125, LL 90, L 100, H 135, HH 140 L and H alarms to alarm list Activation of HH shall cause emergency shutdown Activation of LL shall cause stopping of material feeding - Temperature sensor TE-3104 (TE-3.1.04) is installed in the exhaust gas duct for measuring the air temperature. The signal is displayed in the HMI screen TI-3104 (TI3.1.04) scaled to 0…200 °C. The normal operating point is 125 °C as preliminary value. Alarm is initiated when the temperature exceeds 135 °C (H) or falls below 100 °C (L). Feed shutdown limit can be set as the temperature 90 °C (LL) and steam shutdown limit set as 140°C (HH). The used (HH) value depends on the chosen filter material. The sensor (TE-3.1.04) is in a dusty gas stream, which is very abrasive. The sensor element is equipped with a thick metallic protection tube. Ignitation preventing When temperature of the concentrate goes higher, the risk of the ignition of the dust rises. Therefore emergency shutdown is activated, if temperature TE-3104 (TE-3.1.04) rises too high (over HH limit). In emergency shutdown, steam supply is closed. 3.5 Dried material level switches LSH-3106 (LS-3.1.06), LSH-3110 (LS-3.1.10), LSH-3112 (LS3.1.12) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits LSH-3106 (LS-3.1.06), HH level in discharge hopper LSH-3112 (LS-3.1.12), HH level in discharge hopper LSH-3110 (LS-3.1.10), HH limit in reject hopper Level detections in discharge chamber HMI, SV screen animation PFC - KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 15/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Alarms: Interlocks: HH alarms to stop drum and material feeding - In the dryer discharge end hopper and reject hopper there are a vibration type level switches. Level switches LSH-3106 (LS-3.1.06.HH) and LSH-3112 (LS-3.1.12.HH) are installed in the material hopper for initiating a HighHigh alarms at the PLC. The sensor LSH-3110 (LS-3.1.10.HH) is in reject hopper respectively initiates HighHigh alarm. The sensors are equipped with cover which is installed approximately 100 mm above the sensing element for avoiding false alarms from falling material. Each sensor has an output relay with one changeover contact. The relay is connected to PLC digital input, so that when level is under the switch, the signal is a logical ‘1’ (contact closed). When material level rises to the switch level, the signal is a logical ‘0’, (contact open). The HighHigh level switch is used to interlock the drum and material feed to the dryer. If the sensor is activated for a certain time (nominal 3 s), the drum and upstream material feed is stopped. The operator can start the drum or material feed manually only after the material level in the discharge end has lowered to an acceptable level, meaning alarms HighHigh deactivated. 3.6 Airlock feeder (M-3.3.02), (SS-3.3.02) Tag: Service: Control signal: Scaling: Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: Auto: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: (M-3.3.02) (SS-3.3.02) Airlock in reject outlet Profibus DP to starter Start Profibus DP, Run, fault, remote control from starter From local panel (by others), including local/remote switch Hardwired to motor starter From screen From line control code Speed detector signal does not match to command Stop at: - Signal from plant system “stop reject” (XY-3.4.02). - Emergency stop activation - Emergency shutdown - Screw conveyor (M-3.3.01) stop Reject airlock feeder will be stopped, if plant system cannot take material (XY-3.4.02). Condition of the feeder is monitored with speed detector. If the signal of the sensor ("1"= rotates) does not match to the given command in specified time (1 s), motor is stopped and an alarm is activated. 3.7 Screw conveyor 5121-TRS-3001M (M-3.3.01) Tag: 5121-TRS-3001M (M-3.3.01) KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 16/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Service: Control signal: Scaling: Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: Auto: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: crew conveyor for reject Profibus DP to starter Start Profibus DP Run, fault, remote control from starter From local panel (by others), including local/remote switch Hardwired to motor starter From screen From line control code Stop at: - Signal from plant system “stop reject” (XY-3.4.02). - Emergency stop activation - Emergency shutdown Reject screw feeder will be stopped, if plant system cannot take material (XY-3.4.02). Screw feeder is delivered by others. 3.8 Output material sample (XV-3.1.07) At the bottom of the discharge end hoppers there are sample hole for taking manually samples for dryness measurements. 3.9 Gate valves (V-3.2.1), (V-3.2.11), (V-3.2.21) Below hoppers there are manually operated gate valves (V3.2.1), (V3.2.11) and (V3.2.21) for shutting off the dry material to pneumatic conveyor system. They are not in Kumera's scope and not connected to PLC. 4 4.1 STEAM PRESSURE REGULATING SYSTEM LOOPS Steam Dryer Incoming Steam Flow Indication FIT-4101 (FIT-4.1.01) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: FIT-4101 (FIT-4.1.01) Steam flow measurement HMI, SV screen, unit t/h As auxiliary information at screen also raw signal m3/h 4…20 mA, HART, loop powered According to temperature and pressure Sensor gives volume flow m3/h After compensation 0… 50 t/h t/h NV 44.7, L 1, HH 48 L and HH alarms to alarm list KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 17/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Interlocks: - The incoming steam flow to the dryer is measured using Vortex type flow sensor FIT4101 (FIT-4.1.1). Sensor gives measuring result as volume flow. The whole steam flow measurement system consists of the flow sensor FIT-4101 (FIT4.1.1) and flow conditioner (V-4.1.05), which is in upstream pipe. This arrangement reduces the needed straight lengths for the accurate measurement. The sensor and flow conditioner are assembled in flow measurement unit (4.1), which is delivered as one separate part. This unit can be mounted to suitable place. Piping between steam flow unit and pressure regulation unit (4.) is not in Kumera's scope. The signals from the sensors TE-4101 (TE-4.1.01) and PT-4101 (PT-4.1.01) are used to calculate steam density in the actual process condition from temperature and pressure. For the operator steam mass flow is calculated using density and it displayed on HMI and SV screen scaled as 0... 50.00 t/h. Below is the formula for the steam mass flow calculation: F 2 = F1 * ρ 2 Where: F1 : < Formula 0 > Flow signal from the flow transmitter [m3/h]. It is directly proportional to volume flow. T2 : Actual steam temperature [K] TE-4101 (TE-4.1.01). p2 : Actual steam pressure ps [Pa(a)] (signal PI-4101 (PI-4.1.01) + 101.325 kPa ) ρ2 : Actual steam density [kg/m3] of the sensor. It is calculated using <Formula 2 >. Specific volume of steam in condition (T, p) can be calculated with following formula (Mollier's formula): 3.1 2 6 13,5 v = (461.11*T/p - 1.45 / ((T/100) ) - 0.603096 *p /(10 *(T/100) < Formula 1 > It is valid for saturated and superheated steam with reasonable accuracy. In the formula temperature T shall be expressed in [K] and pressure p in [Pa]. Steam density is: ρ = 1 / v [kg/m ] 3 < Formula 2 > Calculating of the mass flow value can be done as follows: 1. First to get specific volume is assigned in < Formula 1 > : T2 T [K], p2 p [Pa (abs)] )) [m3/kg] KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 18/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION 2. Then ρ2 is calculated using < Formula 2 >. 3. The mass flow is then calculated with < Formula 0 >. Alternative If available, the steam measurement can also be corrected using the standard flow measurement correction software module of the DCS system. 4.2 Incoming Steam to pressure regulating unit Pressure indication PT-4101 (PT-4.1.01) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: PT-4101 (PT-4.1.01) Supply steam pressure measurement HMI screen, unit kPa(g) 4…20 mA, HART, loop powered 0…2500 kPa(g) kPa(g) NV 2200, L 50, H 2250, HH 2280 L and H alarms to alarm list HH to activate emergency shutdown - Pressure of the steam supply before the pressure regulating unit is measured and displayed at HMI screen PI-4101 (PI-4.1.01). The nominal supply pressure is 2200 kPa(g). The pressure is displayed in DCS screen scaled 0…2500 kPa(g). Alarm is given from high and low pressures. Exceeding of HH limit shall activate emergency shutdown of the dryer system. Incoming pressure to the pressure regulating unit shall be constant, the pressure shall not normally vary more than 200 kPa. 4.3 Incoming steam to pressure regulating unit temperature (TE-4.1.01) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: (TE-4.1.01) Supply steam temperature measurement HMI screen, °C 4…20 mA, HART, loop powered 0…250 °C °C NV 220, HH 240 HH alarm to alarm list - The steam temperature is measured upstream side of the pressure regulating unit with PT100 type temperature sensor TE-4101 (TE-4.1.01), equipped with transmitter 4…20mA. Temperature is displayed at the DCS screen scaled 0…250 ºC. 4.4 Steam Dryer Incoming Steam Pressure PIC-4201 (PIC-4.2.1), PT-4201 (PT-4.2.1) Tag: PT-4201 (PT-4.2.1) PIC-4201 (PIC-4.2.1) KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 19/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: Dryer steam pressure measurement and control HMI, SV screen, unit kPa(g) 4…20 mA, HART, loop powered 0…2500 kPa(g) kPa(g) NV 2000, LL 50, L variable, H var., HH 2100 L and H alarms to alarm list HH to activate emergency shutdown - The inlet pressure to steam dryer PT-4201 (PT-4.2.01) is measured by a pressure transmitter, and signaled in kPa(g). The pressure signal initiates at the PLC: - Pressure indication PI-4201 (PI-4.2.01), scaled 0 to 2500 kPa(g) at the screen. - Pressure alarm function PT-4201 (PT-4.2.01.L) and PT-4201 (PT-4.2.1.H) - Emergency shut down at HH value PT-4201 (PT-4.2.01.HH) Pressure alarm function PT-4201 (PT-4.2.01.L) to warn the operator of too low steam pressure at the steam input for the dryer. The L and H pressure alarms of PT-4201 (PT-4.2.01.L) and PT-4201 (PT-4.2.01.H) are to warn the operator about abnormal values. The limits for their activation are calculated automatically from the current set point of the controller PIC-4201 (PIC-4.2.01). L limit is Set point – tolerance and H limit is Set point + tolerance. Preliminary the tolerance (allowed deviation from set point) is 50 kPa. The expected operating point for output side is at 300 …2000 kPa(g). 4.4.1 Steam control valve PV-4201 (PV-4.2.01) Tag: PV-4201 (PV-4.2.01) Service: Steam pressure control valve Control signal: 4…20 mA, HART, power Fail to close. Scaling: 4…20mA /0…100%. Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: From HMI screen 0…100% Auto: From pressure controller PIC-4.2.01 Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: Closing at: - Emergency shutdown - Emergency stop activation - Flash tank HH-level LIC-8102 (LIC-8.1.02.HH) is exceeded - Flash tank HH-pressure PT-8101 (PT-8.1.01.HH) is exceeded KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 20/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The output material dryness is correlated to its temperature. The primary control for material dryness is performed by adjusting the steam pressure and thus the temperature of the heating elements inside the dryer. The control valve PV-4201 (PV-4.2.01) controls the steam pressure to the dryer. The pressure, which is measured with transmitter PT-4201 (PT-4.2.01), is used as regulating variable and controlled with a PID type software controller PIC-4201 (PIC-4.2.01). Flash tank HH-level and HH-pressure interlocks are automatically reset, when process value returns below the limit. The maximum opening of control valve PV-4201 (PV-4.2.01) is limited with stop screws in the actuator to limit the needed discharge capacity of safety valve PSV-4.2.01. 4.4.2 Operating Modes The steam dryer operating modes are described below. In the operation instructions of the steam dryer control system is described, how the modes are changed. Manual mode Manual mode is available from the HMI panel, which is located dryer control room. In manual mode, the operator controls the steam temperature manually by adjusting the steam pressure set point (MAN SP), 0…2000 kPa(g) of the controller function PIC-4201 (PIC-4.2.01). The pressure controller controls the opening (0…100 %) of the control (PV4.2.01) so that the desired pressure PI-4201 (PI-4.2.01) is achieved. At the screen the operator can observe the pressure, temperature and flow, which change as the opening of the valve changes. The primary regulated variable is the material dryness, which the operator monitors via material temperature TE-3102 (TE-3.1.02) / TE-3103 (TE-3.1.03) and output air temperature TE-3104 (TE-3.1.4) measurements. The changes in the material temperature shall be studied after a delay, approximately 5…30 minutes, so that the whole effect of the control action is visible. Automatic mode, material temperature feedback TIC-3102 (TIC-3.1.02) In automatic mode the input steam pressure is controlled using a temperature feedback from the measured material temperature TE-3102 (TE-3.1.02) / TE-3103 (TE-3.1.03). Other possibility is to use the off-gas air temperature (TE-3.1.04) as feedback signal. A software based PID controller TIC-3102 (TIC-3.1.02) takes the material temperature TE-3102 (TE-3.1.2) as the actual value. The other sensor TE-3103 (TE-3.1.03) is on standby and can be taken into use (by software switch from screen) in case there is a problem with the primary sensor. The controller TIC-3102 (TIC-3.1.02) output controls the set point (AUTO SP) of the steam input pressure controller PIC-4201 (PIC-4.2.01). For establishing a correlation between material temperature and dryness, the logged data of the drying operation shall be studied. Based on this data the temperature set point can be selected for getting the desired dryness. Temperature measurement inside drum Variation of the moisture content of the feed material has delayed effect on the output material temperature. The controller response can be made faster by introducing also material temperature inside the drum, TI-1101...1104 (TI-1.1.01,... ,0.4) into the control loop. The axial temperature profile of the material inside the dryer from feed end to discharge end is measured as follows: KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 21/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Tzone1 = temperature in zone 1, TI-1101 (TI-1.1.01) Tzone2 = temperature in zone 2, TI-1102 (TI-1.1.02) Tzone3 = temperature in zone 3, TI-1103 (TI-1.1.03) Tzone4 = temperature in zone 4, TI-1104 (TI-1.1.04) The effect of the temperatures can be taken into control in following way. For each zone is given reference temperature value, which corresponds the "ideal" drying of the material. The difference of actual temperature of the zone Tzonei from its reference value TSPí is made to contribute to a term, which is added to the steam pressure reference for the pressure controller PIC-4201 (PIC-4.2.01). This is a feed forward control addition (XY-1.1.01) to the temperature control loop TIC-3102 (TIC-3.1.02), which should reduce the disturbances caused by variations input material moisture. The material flow is also taken in account to get faster response to the temperature control. Average of the signal WT-2075 (FT-2.0.01) is calculated from certain time. It is used as one factor for the correction to the pressure controller. Qave = average of material flow WT-2075 (FT-2.0.01) [t/h] Qmat = (Qave - Qmin) / 100, where Qmin = 0 t/h (preliminary) Average is calculated from last 10 minutes (preliminary). The correction for the pressure reference can be calculated as follows: pSPcorr = k * ( k1 * (TSP1 - Tzone1) + k2 * (TSP2 - Tzone2) + k3 * (TSP3 - Tzone3) + k4 * (TSP4 - Tzone4) + k5 * Qmat ) This correction is added to the pressure reference, which is coming from the output of controller TIC-3102 (TIC-3.1.02). When process is running in steady state and each actual value is near its set point, the correction needed for the pressure is near zero. The reference temperature TSPí and the coefficient ki are adjustable parameters for each zone. The temperature reference of the zone can be established on the logged data from the drying process. The coefficients k1, k2, k3 and k4 give the weight of each zone to the control. Their sum shall be one. The coefficient for the material flow k5 coefficient can in range 0 ... 20, preliminary value k5 = 2. The whole effect of the material temperature in drum and material flow to the steam pressure set point PIC-4201 (PIC-4.2.01) is determined by setting the amplifying factor k Alternatively the feed forward signal can be programmed to controller module of the used software, if this feature is there available. The value of correction pSPcorr shall be limited to -1000 ... +1000 kPa. In addition there shall be locking, that the set point of PIC-4201 (PIC-4.2.1) is always over 300 kPa(g). 4.4.3 Protection of steam pipes For reducing risk of damages in possible leaks in the steam pipes some measures shall be made in the control system. Most vulnerable are the flexible pipes between pressure regulating unit and steam dryer. The hot steam leaks are risk for work safety. Pressure drop A leak can be detected from sudden drop of pressure at the output side of the control valve PV-4201 (PV-4.2.01). In the DCS program there should be monitoring for the rate KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 22/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION of change of the pressure (ZY-4.2.01). If the derivative (change speed) of the pressure exceeds a pre-defined value, it is considered as possible leak and a shut-down of the control valve PV-4201 (PV-4.2.01) is performed. Also steam supply to the dryer system should be shut down. Abnormal pressure The actual steam pressure PT-4201 (PT-4.2.01) shall be monitored and if it the pressure is outside of the allowed pressure window around the set point PIC-4201 (PIC-4.2.01.L ... PIC-4.2.01.H) for certain period, shut-down shall be performed. The window limits can be preliminary 100 kPa down and up from the current pressure set point. The delay before shut-down can be some seconds. Excess flow As third method should be used the HH-limit of the steam flow FI-4101 (FI-4.1.01). If the flow is over the extreme high limit, steam shall be shut-down. 4.4.4 Protection of pressurized pipes at low temperatures To avoid damages during start-up, steam pressure should be kept under 1000 kPa(g), when temperature of the heating elements is below 20°C. An interlocking shall be made in the DCS program as follows. When the off-gas temperature (TE-3.1.04) is below 20°C, maximum set point of steam pressure (PIC-4.2.1) shall be limited to 1000 kPa(g). Also an alarm shall be activated, when temperature (TE-3.1.04) is below 20°C and pressure (PT-4.2.01) is over 1000 kPa(g). This is for reminding the operator of not allowed process state, when he is adjusting pressure using the manual valve (CV-4.2.01). 4.4.5 Limiting temperatures temperature, when drum stopped Because of the self-ignition possibility of the material, the temperature of the steam piping shall be limited, when process is not on. The maximum pressure set point is forced under 300 kpa(g), when drum is not rotating. Then pipe temperature stays under 150°C. 4.5 Steam Dryer Incoming Steam Pressure Relief Valve PSV-4201 (PSV-4.2.01) A pressure relief valve PSV-4201 (PSV-4.2.01) is installed at the low-pressure side of the pressure regulation unit for over pressure protection of the steam dryer devices. Its activation value is 2300 kPa(g). The pressure at the supply point to the steam dryer system shall be kept in all times under 2500 kPa(g). 4.6 Manual control valve for incoming steam (CV-4.2.01) A manually operated control valve (CV-4.2.1) is installed as by-pass for the main control valve (PV-4.2.01). It is used when starting up cold steam dryer. The valve has only a local function and cannot be operated from the DCS screen. The starting up value and desired maximum feed rate to be used during main control valve failure shall be taken into account when selecting the capacity for the valve. The capacity is preliminarily estimated as 4000 kg/h. Note: There shall be a shut-off valve for the supply steam before the pressure regulating unit to ensure work safety in maintenance of the components. This valve is not in Kumera's scope. 4.7 Steam Dryer Incoming Steam Pressure Indication (PI-4.2.02) A mechanical pressure meter PI-4202 (PI-4.2.02) is installed at the pressure regulating unit for displaying the steam pressure at dryer side of the control valve. It can be used at KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 23/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION starting up of the dryer, when steam is carefully supplied to the cold dryer using the manual valve (CV-4.2.01). This indication is only local. 4.8 Steam Dryer Incoming Steam Temperature Indication TE-4301 (TE-4.3.01) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: TE-4301 (TE-4.3.1) Dryer steam temperature measurement HMI(, SV) screen, unit °C 4…20 mA, HART, loop powered 0…250 °C °C NV 144...215, HH 240 HH alarms to alarm list - The steam temperature is measured at the input of the dryer with PT100 type temperature sensor TE-4301 (TE-4.3.01). The temperature is displayed at the DCS screen, tagged TI-4301 (TI-4.3.01) scaled as 0…250 °C. 4.9 Shut-off valve for pipe connection (V-4.3.02) In the low pressure side there is pipe inlet, which is equipped with shut-off valve (V-4.3.2) and blind flange. During the starting-up phase of the steam dryer this inlet can be used to lubricate the rotary joint with water, when steam is not available. The flange can be opened only with tools, which minimize the risk of unintentional steam outbreak. 5 STEAM TRAP UNIT LOOPS 5.1 Steam trap unit (XV-5.1.01), (XV-5.1.02), (XV-5.1.03), PT-5102 (PT-5.1.02), PT-5202 (PT5.2.02), Tag: PT-5102 (PT-5.1.02), PT-5202 (PT-5.2.02), PI-5104 (PI-5.1.04) mechanical, PI-5205 (PI-5.2.05) mechanical Service: Pressure in steam trap unit Display: HMI screen, unit kPa(g) Signal type: 4…20 mA, loop powered Compensation: Scaling: 0…2500 kPa(g) Values, limits kPa(g) ) PT-5102 (PT-5.1.02) NV 500…2000, L 50, HH 2100 PT-5202 (PT-5.2.02) NV 300, L 50, HH 500 Alarms: Interlocks: L and HH alarms to alarm list - KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 24/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION A steam trap unit is installed near to the steam dryer for removing the condensate water from the dryer’s condensate pipe. The steam trap unit consists of three steam traps (XV5.1.01), (XV-5.1.02) and (XV-5.1.03), which are installed in different pipe branches. All steam traps are expansion chamber type. No-return valves V-5.2.01, V-5.2.02 and V-5.2.03 are installed for preventing backwards flow. Before and after the steam traps there are pressure transmitters PT-5102 (PT-5.1.02) and PT-5202 (PT5.2.02) for monitoring the condition of the steam traps. Mechanical pressure meters PI-5104 (PI-5.1.04) and PI-5205(PI-5.2.05) are installed for indicating the pressures before and after the steam traps. They can be used for monitoring the function and condition of the steam traps. The meters are not connected to DCS. 5.2 Steam trap unit temperatures TE-5101 (TE-5.1.01), TE-5201 (TE-5.2.01) Tag: TE/TT-5101 (TE/TT-5.1.01), TE/TT-5201 (TE/TT-5.2.01) Service: Temperature measurement in steam trap unit Display: HMI screen, unit °C Signal type: 4…20 mA, HART, loop powered Compensation: Scaling: 0…250 °C Values, limits °C TE-5101 (TE-5.1.1) NV 150…215, L 100, HH 220 TE-5201 (TE-5.2.1) NV 130…150, L 90, HH 160 Alarms: L and HH alarms to alarm list Interlocks: - Before and after the steam traps there are temperature sensors TE-5101 (TE-5.1.1) and TE-5201 (TE-5.2.1) for monitoring the condition of the steam traps. 5.3 Condensate handling system The condensate from dryer is collected into a flash tank 5123-EST-2001. Flash tank pressure and level is controlled according to following descriptions. From flash tank, the condensate is lead to a condensate tank. Steam and condensate is cooled before transferring to a condensate tank 5123-EST-2002. The transferring of condensate water via the control valve from tank 5123-EST-2001 to tank 5123-EST-2002 is based on pressure difference between the tanks. It shall be noted that in special situations the pressure of tank flash 5123-EST-2001 can be low. For example, when dryer is stopped for short period and kept warm, the pressure is low, but after all water is coming from the dryer to the flash tank. Measures shall be taken to ensure water removing from the tank to prevent overfilling of it. 5.3.1 Flash tank Level control LV-8102A (LV-8.10.01A), LV-8102B (LV-8.10.01B), PT-8101 (PT8.1.01), LT-8102 (LT-8.1.02), LIC-8102 (LIC-8.1.02), XY-8102 (XY-8.1.02) Tag: LV-8102A (LV-8.10.01A) LV-8102B (LV-8.10.01B) PT-8101 (PT-8.1.01) KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 25/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION LT-8102 (LT-8.1.02) Pressure and level in flash tank HMI screen, unit kPa(g) 4…20 mA, HART, loop powered PT-8101 (PT-8.1.01), 0…600 kPa(g) LT-8102 (LT-8.1.02), 0...3 m, level from pressure difference LV-8102A/B (FV-8.10.01A/B), 0...100%, 4...20mA Values, limits Pressure, kPa(g) PT-8101 (PT-8.1.1) NV 300, LL 30, L var., H var., HH 480 LT-8102 (LT-8.1.2) NV 300, LL 30, HH 480 Level, m LIC-8102 (LIC-8.1.2) NV 1.5, LL 0.2, L var., H var., HH 2.8 Alarms: LL, L and H alarms to alarm list PT-8101 (PT-8.1.01.HH) to interlock steam control valve (PV-4.2.01) LIC-8102 (LIC-8.1.02.HH) to interlock steam control valve (PV-4.2.01) Interlocks: Level of the flash tank is controlled by letting out condensate via control valve LV-8102A or B (LV-8.10.01A or B). Condensate from the flash tank is going to the condensate tank 5123-EST-2002 via condensate cooler 5123-ENF-3002. The valve LV-8102B (LV-8.10.01B) works as stand-by unit for the LV-8102A (LV8.10.01A). It can be taken in operation with software switch at DCS screen. The water level in the tank is measured with a pressure transmitter located above the water level PT-8101 (PT-8.1.01) and one transmitter LT-8102 (LT-8.1.02) in the bottom part of the tank. These provide pressure as 0…600 kPa(g), signaled via 4…20mA to DCS. By calculating the difference between the pressures (XY-8.1.2), the water level is determined. Normal value is approximately 1.5 m water above the lower sensor. It means hydrostatic differential pressure 15 kPa. This is changed to level height (meters) in calculating program module (XY-8.1.02). This value is displayed in unit meters at DCS display (0.00 … 3.00 m). The water level in the flash tank is controlled with software based PID-type controller LIC8102 (LIC-8.1.02). When level exceeds the set point, the flow valve LV-8102A or B (LV8.10.01A or B) is opened so that water flow out of the tank increases. When the level falls below the set point value, the valve opening is decreased. Alarm is activated for the operator, when pressure in the tank PT-8101 (PT-8.1.01) exceeds H-value. If the pressure exceeds the HH-value (480 kPa(g)), steam supply to dryer shall be closed, reference to steam control valve PV-4201 (PV-4.2.01) is set to minimum. The activation limits of the L and H values of the surface level are calculated automatically from the set point of LIC-8102 (LIC-8.1.02). L limit is set point - tolerance. H limit is set point + tolerance. The preliminary value for tolerance is 0.5 m. When the water level LIC-8102 (LIC-8.1.02) in the tank exceeds the HH-value, steam control valve (PV-4.2.1) is shut off. Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: The activation limits of the L and H values of the tank pressure are calculated automatically from the set point of PIC-8101 (PIC-8.1.01). L limit is set point - tolerance. H limit is set point + tolerance. KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 26/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The preliminary value for tolerance is 30 kPa. 5.3.2 Pressure control of flash tank PV-8501 (PV-8.5.01), PIC-8101 (PIC-8.1.01), Tag: PV-8501 (PV-8.5.1) ZT-8501 (PV-8.5.1-XI) position feedback PIC-8101 (PIC-8.1.1) Service: Flash tank pressure control Control signal: 4…20 mA, HART, loop powered 4…20mA / 0…100%, fail to open. Scaling: 0…100 % Feedback signal 4...20mA Operation modes: Valve position control Local: Manual: From HMI screen 0…100% Auto: From pressure controller PIC-8101 (PIC-8.1.01) Values, limits Maximum set point 350 kPa(g) Alarms: see PT-8.1.01 Interlocks: Valve open at: - Emergency shutdown Pressure set point maximum 350 kPa(g) Pressure of the flash tank 5123-EST-2001 is controlled by letting out steam via control valve PV-8501 (PV-8.5.01). Steam from the flash tank is going to the condensate tank via steam cooler. Valve has pneumatic actuator, which is opened by springs if control signal or instrument air fails. In fault situation (for example earth quake) valve opens and pressure is released from the tank via normal route. Pressure controller PIC-8101 (PIC-8.1.01) measures tank pressure with the pressure transmitter PT-8101 (PT-8.1.01) and opens and closes valve accordingly. Normal set point is 300 kPa(g). Nominal steam flow is 7 t/h. The nominal pressure across the control valve is 50 kPa(g). The set point of the tank pressure controller shall be kept under value 350 kPa(g) to keep the condensate water temperature under the allowed limit of the condensate pump (150°C). 5.3.3 Starting and stopping of flash tank operation When the steam supply to dryer is started, the level / pressure controller LIC-812 / PIC8101 (LIC-8.1.2 / PIC-8.1.01) shall be active and level / pressure is controlled by letting out steam /condensate trough control valve FV81001 / PV-8501 (FV-8.10.01 / PV-8.5.01). Both valves shall be in automatic mode to enable the operation automatically. 5.3.4 Pressure safety valve for flash tank PSV-8103 (PSV-8.1.03) In the flash tank a mechanical safety valves are installed for overpressure protection. Operation point of valve PSV-8103 (PSV-8.1.03) is 600 kPa(g). Safety valves are not connected to dryer PLC. KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 27/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION 5.3.5 Flash tank over level switch LSH-8106 (LS-8.1.06) Tag: LSH-8106 (LS-8.1.6) Service: Flash tank overfill detection Display: animation in DCS screen Signal type: PFC, sensor power 24Vdc Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: HH alarms to alarm list Activation shall activate emergency shutdown Interlocks: In the upper part of the tank there is a level switch, which operates as back-up safety device in case the water level in tank goes too high. When the level switch activates (=signal 0) more than 2 s, the steam supply to the dryer shall be stopped by closing the control valve PV-4201 (PV-4.2.01) and emergency shutdown of the system is started. 5.3.6 Condensate pumping from condensate tank (5123-EST-2002), (M-8.3.01), (M-8.3.02), FS8311 (FS-8.3.11), FS-8321 (FS-8.3.21), PI-8330 (PI-8.3.30) Tag: (M-8.3.01), (M-8.3.02) FS-8311 (FS-8.3.11), FS-8321 (FS-8.3.21), PI-8330 (PI-8.3.30) Service: Condensate pumping from condensate tank Control signal: To be defined by customer Scaling: To be defined by customer Feedback signal Frequency converters, Profibus DP. Flow detection sensors (FS-8.3.11/21), PFC. Operation modes: Local: To be defined by customer Frequency converter control is via PLC. Manual: Starting and speed control from screen Auto: Starting and speed control from program based on tank surface. Values, limits min speed ?1200 rpm Alarms: Frequency converter faults No flow at active pump Interlocks: Stop at: - Emergency shutdown - Tank level LL limit LT-8102 (LT8.1.2.LL) - Flow alarm at duty pump FS-8311 (FS-8.3.11), FS-8321 (FS-8.3.21) Note! KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 28/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The control of the pumps M-8.3.01 and M-8.3.02 is not made in the dryer control system. Pumps shall be controlled by customer's control system. Pumping unit including the pumps M8.3.01/.02 tranfers the condensate water from tank 5123-EST-2002 to tank 5126-EST2003. The water level in the condensate tank is controlled with software based PID-type controller LIC-8111 (LIC-8.11.01). When level exceeds the set point, the condensate pump (M-8.3.01) speed is increased so that water flow out of the tank increases. When the level falls below the set point value, the pump speed is decreased. If the required pump speed decreases below the minimum available speed of the pump (preliminary 1200 rpm), the pump is stopped. It is re-started when condensate level is above the set point of controller LIC-81101 (LIC-8.11.01). One of the pumps (M-8.3.01) and (M-8.3.02) is a duty pump and the other is a standby pump. The shut-off valves of the pumps are normally open and the non-return valves prevent backwards flow in stopped pump. If duty pump fails, alarm is activated in HMI screen and the stand-by pump is started automatically. Failure is detected from too high water level LIC-81101 (LIC-8.11.01.H) and frequency converter faults. DCS allocates duty pump status to this now operating pump. A function shall be programmed so that the duty pump status is changed between the pumps so that both pumps are used alike. This can be based on running hours or by simply starting pumps in turns. In this way the possible failures in pumps can be detected sooner. In the inlet lines of the condensate pumps are installed flow switches for detecting low flow FS-8311/8321 (FS-8.3.11/21). The switch of the duty pump is monitored always, when pump is running. If then no flow is detected in preset time, alarm is activated. Reason for low flow can be a closed valve in line or in fault situation empty condensate tank or faulty sensor. A pressure gauge PI-8330 (PI-8.3.30) is installed for monitoring the pressure in the output pipe. To ensure safe operation of the pumps, they must be located well beneath of the level of the condensate tank (see NPSH of pump). The draining shut-off valves of the pumps can be used to empty the tank. During production stoppage, the condensate pump is stopped. The pump motor is started automatically, when level in the tank exceeds a starting level, which can be the same as the set point of the level. Then the pump motor speed will follow the output of the level controller LIC-81101 (LIC-8.11.01). When dryer is stopped, condensate flow will go down. The condensate pump can be stopped manually to keep the water level in the tank. If the level goes under LL value of LT-81101 (LT-8.11.01), pump shall be stopped automatically, preliminary 0.2 m. 5.4 Condensate conductivity measurement (QT-5.3.01) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: QT-5301 (QT-5.3.01) Monitoring of conductivity of condensate HMI, SV screen, unit % 4…20mA, PS 120Vac 0...1000 μS/cm KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 29/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: Conductivity, μS/cm NV < 10, H 20, HH 100 H and HH alarms to alarm list - For detecting leaks in the steam piping of the steam dryer a conductivity sensor (QT5.3.01) is installed in steam trap unit. Water from the input side of the unit is lead via cooler to the conductivity sensor element. Maximum allowed temperature for the element is 120°C. The water flow to the element is adjusted with the manual control valve V5.3.02 so that temperature measured by mechanical temperature (TI-5.3.03) meter is below 80°C in all operation points. The expected water flow is 6 kg/h. If conductivity of the condensate water increases above the H or HH limit, alarm is given to operator. 6 6.1 BAG FILTER LOOPS Shut-off valves of bag filter FV-1100...1400 (XV-6.7.01...6.7.04), FV-1108...1408 (XV6.7.11...6.7.14) Tag: valves limit switches Service: Control signal: Scaling: Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: Auto: FV-1100 (XV-6.7.01), FV-1200 (XV-6.7.02), FV-1300 (XV-6.7.03), FV-1400 (XV-6.7.04), FV-1108 (XV-6.7.11), FV-1208 (XV-6.7.12), FV-1308 (XV-6.7.13), FV-1408 (XV-6.7.14), ZSO/ZSC-1100 (XV-6.7.01-XI1/XI2), ZSO/ZSC-1200 (XV-6.7.02-XI1/XI2), ZSO/ZSC-1300 (XV-6.7.03-XI1/XI2), ZSO/ZSC-1400 (XV-6.7.04-XI1/XI2) ZSO/ZSC-1108 (XV-6.7.11-XI1/XI2), ZSO/ZSC-1208 (XV-6.7.12-XI1/XI2), ZSO/ZSC-1308 (XV-6.7.13-XI1/XI2), ZSO/ZSC-1408 (XV-6.7.14-XI1/XI2) Bag filter shutoff valves PFC, 24Vdc Valve opens, when activated. Open (-XI1) and close (-XI2) position limit switches From HMI screen open and close From HMI screen open and close KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 30/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: Error, when feedback does not match to command Closing at: - Emergency shutdown In the input sides of the bag filter there are pneumatically controlled shut-off valves FV1100 (XV-6.7.01), FV-1200 (XV-6.7.02), FV-1300 (XV-6.7.03) and FV-1400 (XV-6.7.04). At output side FV-1108 (XV-6.7.11), FV-1208 (XV-6.7.12), FV-1308 (XV-6.7.13), FV-1408 (XV-6.7.14),They can be controlled from HMI screen manually. Actuators of the valves are controlled with pneumatic magnet valves coil voltage 24 Vdc. Digital outputs PLC remote IO unit control the pneumatic valves. In the actuators there are limit switches for open positions ZSO (-XI1) of valves, for example ZSO-1100 (XV-6.7.01-XI1). For closed positions are the limit switches ZSC (XI2), for example ZSC-1408 (XV-6.7.14-X2). The potential free contacted are connected to digital inputs of the PLC. 6.2 Trace heating of bag filter (A-6.2) Tag: Heaters, hoppers HTR-1100 (E-6.2.01), HTR-1200 (E-6.2.02), HTR-1300 (E-6.2.03), HTR-1400 (E-6.2.04) walls HTR-1102 (E-6.2.11), HTR-1202 (E-6.2.12), HTR-1302 (E-6.2.13), HTR-1402 (E-6.2.14) Sensors TE-1100 (TE/TT-6.2.01), TE-1200 (TE/TT -6.2.02), TE-1300 (TE/TT -6.2.03), TE-1400 (TE/TT -6.2.04) TE-1102 (TE/TT -6.2.11), TE-1202 (TE/TT -6.2.12), TE-1302 (TE/TT -6.2.13), TE-1402 (TE/TT -6.2.14) Service: Bag filter trace heating Signal type: J-type thermocouple, 4...20 mA Display HMI screen, °C Control signal: Profibus DP to starter Scaling: 0...200°C Operation modes: Local: Manual: Heating enabling from HMI screen Auto: Heating enabling from HMI screen Values, limits °C NV 110, LL 90, L 100, H 130, HH 140 Alarms: Heater alarm to alarm list Interlocks: Heating stopping at: - Emergency shutdown For bag filter walls there is an electrical trace heating system. It includes the heating elements and temperature sensors on the walls. Heating is divided to 8 groups, 4 hoppers and 4 upper parts of the of the bag filter chambers. Heating element are supplied from starters in the electrical room. They are control via Profibus DP similarly as the motor starters. PLC program switch off heating, when wall temperature set point is reached. If temperature falls below "set value" - "hysteresis", heater is switched on again. Hysteresis value is preliminary 3°C. For example, if set point is 105°C, power is switched off at it and switched on again at 102°C. KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 31/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION There are two set points, one for the hoppers and and one for the walls. The hysteresis is common for all 8 heating groups. When wall temperature is over the L limit, the drying process is allowed to start. For overheating protection in case for example sensor failure a time based power limitation is made. Power to heating element is switch off for certain time, even if temperature control requires heating. The forced off-time period is preliminary 2 minutes in a ten minute period. 6.3 Bag cleaning system of bag filter (A-6.3) Tag: Devices KY-1104 (A-6.3.11), KY-1204 (A-6.3.12), KY-1304 (A-6.3.13), KY-1404 (A-6.3.14) Feedback signals PDT-1002 (PDT-6.3.01) KY-1104 (A-6.3.11-XI1), KC-1104 (A-6.3.11-XI2), PSL-1104 (A-6.3.11-XI3), KY-1204 (A-6.3.12-XI1), KC-1104 (A-6.3.12-XI2), PSL-1204 (A-6.3.12-XI3), KY-1304 (A-6.3.13-XI1), KC-1304 (A-6.3.13-XI2), PSL-1304 (A-6.3.13-XI3), KY-1404 (A-6.3.14-XI1), KC-1404 (A-6.3.14-XI2), PSL-1404 (A-6.3.14-XI3), Control signals KY-1104 (A-6.3.11-XS1), KY-1204 (A-6.3.12-XS1), KY-1304 (A-6.3.13-XS1), KY-1404 (A-6.3.14-XS1), Service: Cleaning of bag filter bags Signal type: PDT-1002 (PDT-6.3.01) 4…20 mA, own power Feedback PFC Control PFC Scaling: 4…20mA/ 0…4 kPa Operation modes: Local: Additional cleaning with local switch Manual: Auto: From HMI screen additional cleaning Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: PDT-1002 (PDT-6.3.01) kPa HH 3 HH alarm to alarm list Cleaning disabling at: - Emergency shutdown Bag filter bags are cleaned by pressure air pulses. System is controlled automatically by its own control unit. The cleaning is done periodically and also based on the pressure difference across the bags. Refer to bag filter supplier manual. Each of the 4 chambers has ITS own cleaning control unit. KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 32/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The pressure difference across the filters PDT-1002 (PDT-6.3.01) is displayed at HMI screen. 6.4 Dust conveying system of bag filter M-1102...1402 (M-6.5.01...6.5.04), SSL-1102...1402 (SS-6.5.01...6.5.04), LSH-1100...1400 (LS-6.1.01...6.1.04), Tag: airlock feeders speed switches level switches Service: Control signal: Scaling: Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: Auto: Values, limits Alarms: M-1102 (M-6.5.01), M-1202 (M-6.5.02), M-1302 (M-6.5.03), M-1402 (M-6.5.04), SSL-1102 (SS-6.5.01), SSL-1202 (SS-6.5.02) SSL-1302 (SS-6.5.03), SSL-1402 (SS-6.5.04) LSH-1100 (LS-6.1.01), LSH-1200 (LS-6.1.02), LSH-1300 (LS-6.1.03), LSH-1400 (LS-6.1.04), Dust removing from bag filter chambers Profibus DP to starter Profibus DP from motor starters PFC from level switches From local panel (by others), including local/remote switch Hardwired to motor starter From HMI screen From line control code Dust level alarm in HMI screen Motor starter alarms Interlocks: - Airlock feeders stop, when corresponding screw (M-6.6.01 or .02) or the common screw (M-6.6.03) stops. - Emergency shutdown Dust from the bag filter chambers is conveyed trough airlock feeders M-1102...1402 (M6.5.01/02/03/04) and screw conveyors (M-6.6.01/02) to screw conveyor (M-6.6.03), which takes the dust to dry material output of the discharge chamber of the steam dryer. If bag filter level switches activate, alarm is given to operator at HMI screen, who shall manually clear the situation. 6.5 Vibrators of bag filter VBR-1100...1400 (Y-6.10.01...6.10.04) Tag: Service: Control signal: Scaling: Feedback signal Operation modes: VBR-1100 (Y-6.10.01), VBR-1200 (Y-6.10.02), VBR-1300 (Y-6.10.03), VBR-1400 (Y-6.10.04) Vibrating of bag filter hoppers PLC output - KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 33/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Local: Manual: Auto: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: Additional vibration cycle from HMI screen Periodic cycles from line control code Stop at emergency shutdown In the lower parts of the bag filter chambers are installed pneumatically operated vibrators to prevent sticking of concentrate dust to back filter walls. They are started periodically. Preliminary: 5 seconds run with 2 minutes interval. 6.6 Dust conveying system of bag filter (M-6.6.01/02/03) Tag: Service: Control signal: Scaling: Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: Auto: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: (M-6.6.01), (M-6.6.02), (M-6.6.03) Dust conveying Profibus DP to starter Profibus DP from starter From local panel (by others), including local/remote switch Hardwired to motor starter From HMI screen From line control code Starter fault Stop at emergency shutdown Dust conveying from filter to discharge end. Delivery by others. 6.7 Ventilation fans MY-1810 (M-6.9.01), MY-1812 (M-6.9.02) Description to be added. 7 EXHAUST GAS SYSTEM LOOPS 7.1 7.1.1 Exhaust gas flow (FE-7.2.1) Flow measurement Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: (FE-7.2.01), flow sensor (TE-7.2.03), temperatue sensor Offgas flow measurement HMI, SV screen, flow unit Nm3/h Additional display in unit m3/h can be activated separately Ultrasonic sensor 4…20 mA, PS 120 (220)Vac KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 34/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: According to temperature 0…90000 Nm3/h Nm3/h NV 70265, LL 5000, HH 85000 LL and HH alarms to alarm list Low flow value LL shall interlock nitrogen supply to dryer - The off gas flow through the system is measured from the duct after the filter. It is displayed in the DCS screen scaled as 0…90000 Nm3/h. The sensor gives the actual flow F1 [m3/h]. The flow value shall be compensated for displaying the flow in standard state (0 °C, 101.325 kPa(g)) as normal cubic meters [Nm3/h],. F2 = F1 * ( p2 + 101.325 ) / ( p1 + 101.325 ) * ( T1 + 273.15 ) / ( T2 + 273.15 ) T1 : p1 : F2 : T2 : p2 : Standard gas temperature, 0 °C. Standard gas pressure [kPa(g)], 101.325 kPa(g) Flow [Nm3/h], in standard state. Actual air temperature at sensor [°C ] (TT-7.2.03). Actual gas pressure [kPa(g)], near atmosphere pressure 72 kPa(g). If not measured, constant value can be inputted to formula. Correction software module of DCS can be used for compensation, if it is available. 7.1.2 7.2 Flow sensor mounting In addition adequate straight lengths are needed before and after the sensor. The needed straight lengths are less, when smaller duct diameter is used. Steam Dryer exhaust gas temperature TE-7203 (TE-7.2.03) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: TE/TT-7203 (TE/TT-7.2.03) Offgas after bag filter temperature measurement HMI, SV screen, unit °C 4…20 mA, HART, loop powered 0…200 °C °C NV 125, LL 90, L 100, H 135, HH 140 L and H alarms to alarm list Activation of HH shall cause emergency shutdown - Temperature sensor TE-7203 (TE-7.2.03) is installed in the exhaust gas duct for measuring the air temperature. The signal is displayed in the HMI screen scaled to 0…200 °C. The normal operating point is 125 °C as preliminary value. Alarm is initiated when the temperature exceeds H limit (135 °C). Steam shutdown limit set as 140°C (HH). KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 35/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION 7.3 Offgas fan M-1700 (M-7.3.01), M-1800 (M-7.3.02) Tag: Motor M-1700 (M-7.3.01), M-1800 (M-7.3.02) Winding temperature TE-1700ABC (M-07.03.01-TE1) TE-1800ABC (M-07.03.02-TE1 Motor bearing temperature TE-1716 (M-07.03.01-TE2), D-end TE-1718 (M-07.03.01-TE3), N-end TE-1816 (M-07.03.02-TE2) TE-1818 (M-07.03.02-TE3) Fan bearing temperature TE-1700 (TE-07.04.01), inboard TE-1702 (TE-07.04.02), outboard TE-1800 (TE-07.04.11) TE-1802 (TE-07.04.12) Fan bearing vibration VT-1700 (XT-07.04.03), inboard VT-1702 (XT-07.04.04), outboard VT-1800 (XT-07.04.13) VT-1802 (XT-07.04.14) Service: Offgas fan Control signal: Profibus DP Scaling: 0…100 % Feedback signal Profibus DP Operation modes: Local: To be defined by customer Manual: Starting and speed control from HMI screen Auto: Starting from line control, speed from controller (TIC-3.1.4) Values, limits Temperatures, °C Motor winding H 140, HH 155 Motor bearing H 80, HH 100 Fan bearing H 70, HH 90 Vibration, mm/s H 1.0, HH 4.0 Alarms: Starter fault Interlocks: Stop at: - Emergency shutdown There are two parallel off gas fans after the bag filter, which blow the gas from dryer to common stack. Off gas fans are supplied with frequency converters. Fans are started simultaneously and have same speed reference. Speed is controlled with (PIC-3.1.01) in auto mode, see chapter "Exhaust gas flow control principle". The motor winding temperature sensors are connected directly to frequency converters. They shall be parametrized to trip motor, when temperature rises over insulation class KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 36/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION limit (F class 155°C). Winding temperature is transferred via bus to PLC and displayed in HMI screen. 7.4 Dust removal fan from reject (M-7.1.05) Tag: Service: Control signal: Scaling: Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: Auto: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: (M-7.1.05) Dust removal from the reject chute to offgas line Profibus DP 0…100 % Profibus DP To be defined by customer Starting and speed control from HMI, SV screen Starting from line control, Speed follows the main fan NV 500...1000 m3/h pressure rise approximately 2 kPa Starter fault Stop at: - Emergency shutdown The dust from the reject chute is removed with fan M-7.1.05, which is supplied with frequency converter. Before the fan there is a cyclone, which removes excess dust, which is lead out via airlock feeder M-7.1.06. In auto mode starting and speed reference shall follow the control of the offgas fan. In plant starting up phase the speed scale is defined so, that the suction is adequate in all process situations. 7.5 Airlock feeder of dust removal cyclone (M-7.1.06) Tag: Service: Control signal: Scaling: Feedback signal Operation modes: Local: Manual: Auto: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: (M-7.1.06) Material removing from the cyclone of dust removal system Profibus DP Profibus DP To be defined by customer Starting and speed control from HMI, SV screen Starting from line control NV 1000 kg/h Starter fault Stop at: - Emergency shutdown The material from the cyclone of the reject dust removal system is moved with airlock feeder M-7.1.06. Motor has constant speed and started to both directions with DOL-R starter. KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 37/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION Airlock feeder is running always, when fan M-7.1.06 is running. 7.6 Dust monitoring sensor XT-7501 (XT-7.5.01) Tag: Service: Display: Signal type: Compensation: Scaling: Values, limits Alarms: Interlocks: XT-7501 (XT-7.5.1) Monitoring of dust content after bag filter HMI, SV screen, unit % 4…20mA, PS 24Vdc Inductive electrification principle Shall be set, when process is running HH alarms to alarm list The dust content of offgas after bag filter is measured using dust monitor sensor XT-7501 (XT-7.5.1). When output signal of the sensor exceeds the set limit, alarm is given to operator. The setting of the alarm limit is done first finding out the normal dust flow in the pipe during the process. The alarm limit can be set for example to be 2...4 times bigger than the normal value. If possible, the sensor should be calibrated with dust measuring system to the get relation between the sensor output and real dust content [g/Nm3]. 8 STEAM DRYER ROTATION CONTROL AND INTERLOCKING 8.1 8.1.1 Dryer Drum Drive Equipment numbers: 5121-SVP-2001M1 (M-1.2.01), 5121-SVP-2001M2 (M-1.2.11), Main motor 5121-SVP-2001M3 (M-1.2.02), 5121-SVP-2001M4 (M-1.2.12), Main motor fan 5121-SVP-2001M5 (M-1.2.05), 5121-SVP-2001M6 (M-1.2.15), Brake thruster motor Local control panel (A-1.2) 8.1.2 Drive electric motors Drum rotation motor is driven with frequency converters for adjusting the rotation speed of the dryer. The motors 5121-SVP-2001M1 (M-1.2.01) and 5121-SVP-2001M2 (M1.2.11) are equipped with a separate cooling fans 5121-SVP-2001M3 (M-1.2.02), 5121SVP-2001M4 (M-1.2.12) to secure a sufficient cooling at low speeds. Because of high frequency stray currents, which are present in frequency converter operation, the drive motor shall be equipped with insulated N-end bearing. This is to prevent possible bearing problems. 8.1.3 Drum drive control description Dryer drive consists of several pieces of equipment, which can be controlled in local manual mode via PLC. Local panel (A-1.2) controls are connected to PLC, which takes care of the proper sequencing of the motor and the brake. KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 38/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The local control panel (A-1.2) for the dryer operation is installed near the dryer drum. It includes start, reverse and stop buttons, buttons for adjusting speed reference and an emergency stop push button. The software mode selector switch at the HMI/SV screens determines the control place. When selector is in ‘local’, control is from the local panel buttons and when selector is in position ’remote’, control is from HMI. The rotation speeds and their limitations in different situations are described in chapter “Main drive control, speed indication and control (M-1.2.01), (M-1.2.11)”. Main drive torque limitation Acceleration ramp time for steam dryer can be set to value 30 s. This leads to moderate torque for drive mechanics in start. In emergency stop dryer drum shall be stopped quickly. This is done by stopping motor without ramp and closing mechanical brake with short delay. To limit the peak torque in emergency stop, torque setting of brake shall not be bigger than 1000 Nm (total 2000 Nm). For further decrease the stress to drive mechanics, the mechanical brake is closed after delay. Then drum decelerates first by the load before mechanical brake stop the rotation. This function can be made by using safety relay, which is equipped with delayed contacts for the brake. Proper delay is 1...2 seconds. 8.1.4 Automatic line control mode Rotation start sequence Start signal is initiated, which causes the following: - Checking, that the motor is not rotating. Waiting for brake close signal, before continuing start sequence. - Start signal for alarm device (A-1.2.20) (sound and light) for warning about movement, relay output in remote IO unit +DIO2. The beacon device is not in Kumera's scope. - Brakes are opened by starting thruster motors 5121-SVP-2001M5/M6 (M-1.2.5/15) after adjustable delay 0...1 s - Motors 5121-SVP-2001M1/M11 (M-1.2.1/11) are started after adjustable delay 0...1 s. When start signal is in frequency converter input, it starts using ramp adjusted in frequency converter. The running speed will be the one adjusted from DCS screen. - Fan motor 5121-SVP-2001M3/M4 (M-1.2.2/12) is started. Rotation stop sequence Start signals is reset, subsequently: - Motor 5121-SVP-2001M1/M11 (M-1.2.01/11) powers are switched off. Motor stop due to friction and drum unbalance. - Fan motor 5121-SVP-2001M3/M4 (M-1.2.02/12) is stopped - Brake 5121-SVP-2001M5/M6 (M-1.2.05/15) is closed after a delay (45 s) so that drum has time to rotate back to a balanced position due to unbalanced material at the drum wall. When delay is running, starting of motor is prevented. KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 39/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The adjustable delays in starting enable the adjusting of the proper starting sequence at site, so that the mechanical and electrical delays of brake and motor drive can be compensated. The fan motor is set to run always when the main motor is running. 8.1.5 Manual control mode Rotation start sequence Manual starting of the dryer drum rotation is identical to the starting from the HMI. The only difference is that the initial command comes from the local panel instead of the HMI screen. The speed is controlled by using the push buttons (increase/decrease) in the local panel. When for example the speed-up button is pressed, the speed reference is stepped up as long as the button is pressed. Sequential steps are for example 3 times a second when button is pressed. The basic step increment can be 1% of the whole range 0…1 rpm. Rotation stop sequence Stopping the dryer drum manually differs from the auto mode stop of the drum rotation. The manual mode stopping is designed for maintenance work purpose and it stops the drive and holds the drum with the brake immediately, when stop button is pressed. Dryer drum rotation is stopped in manual mode as follows: Start signals is reset, which causes the following: 8.2 - Motor 5121-SVP-2001M1/M11 (M-1.2.01/11) powers are switched off, frequency converter stops without ramp. - Brakes 5121-SVP-2001M5/M6 (M-1.2.05/15) are closed without delay, when the main motor is switched off. This way the drum can be positioned accurately for maintenance work. - There shall be a delay (2 s) after brake close signal before re-starting of motor. - Fan 5121-SVP-2001M3/M4 (M-1.2.2/12) motor is stopped Interlocks for dryer drive Dryer drum rotating is internally interlocked to: - Emergency stop relay position - Safety switch position - Lubricator status signal - Steam pressure indication - Downstream equipment running status - Level switches in discharge chamber A fault alarm from the lubricator is indicated to the operator on the HMI screen. A stop of is activated when alarm has been on a certain time, preliminary value 4 hours. An alarm shall be given to operator, in case the drum motor is running for a certain time (default 15 min / 0.1 MPa) without steam pressure PT-4201 (PT-4.2.1) in dryer feed line. This is because the rotary joint of steam needs water lubrication and cannot stand rotation without steam. The drum rotation is interlocked externally to the downstream equipment. If pneumatic conveyor is stopped, the drum will be locked. More detailed control description is expressed in PLC program. The emergency stop system is hard-wired. The e-stop buttons and safety relays shall be selected and the connections shall be made so that the installation fulfills the local safety standards. Status of the safety relay is connected to PLC input. KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 40/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION 8.3 Work safety aspects Generally, most dangerous moving parts of the dryer are protected with separate shields, and the shields can be opened only with tools. However, there are some points that pose a potential danger if not taken into consideration if personnel are allowed to work at dryer area during running of the equipment. The wireless temperature sensors are sticking out from the drum surface level, and when drum is rotating can hit persons moving or things left in the vicinity of the dryer. The steam- and condensate system arrangement at the discharge end of the drum is very dangerous during running of the dryer, if not properly and adequately shielded from approaching of personnel. It shall be protected with mechanical shield or a cabin structure as shown in main assembly drawing xto prevent people to enter the dangerous area when the dryer is rotating. Note, that the shield is not included in Kumera’s delivery but must be built locally by Client. The shield structure shall be made so that entering the area accidentally is not possible. If access doors are used, those must be interlocked to the control system to stop the drum when accessed. This can be based for example on limit switches installed at shields or doors, which can be opened manually without using tools. Otherwise the access openings must be such that those cannot be opened manually without using tools. 9 NITROGEN SYSTEM LOOPS Not used. 10 OPERATION OF STEAM DRYER . 10.1 Starting sequence of steam dryer Dryer starting is a part of the drying line control. Here is explained only the part that is in Kumera delivery. General preparing work needed before the starting of the dryer is explained in the document xxxx "Test-run and start-up instructions". The operator shall do the start-up preparation manually. The operator can activate the line start command after the preliminary conditions are ready. 10.1.1 Preliminary work (manually by operator): See doc. xxxx “Operation Instructions” - Start of offgas system - Start of the steam supply to dryer and condensate water system - Start of the dryer rotation 10.1.2 The line start command from HMI (dryer is rotating and heating with steam is on) - Start of dry material equipment downstream after discharge chamber (automatic) - Start of airlock feeder (M-3.3.02) (automatic) KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 41/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION - Start of concentrate feeding chute conveyor vibrator 5121-AVB-2001M (M-2.1.01) (automatic) - Start of the equipment upstream before the conveyor (automatic) 10.2 Stopping sequence of steam dryer 10.2.1 Normal line stop Stop command from HMI by the operator: - Stopping of concentrate feed by stopping the feed to the line (automatic) - Stopping up stream equipment including feed conveyor 5121-AVB-2001M (M2.1.01) with delay to enable emptying the line. (delayed, automatic) - Adjusting the steam pressure to lower level (waiting mode) automatically - Stopping of rotary feeders (M-3.3.02) (delayed for emptying the line, automatic) - Stopping of downstream equipment (delayed, automatic) - Stopping of the steam dryer rotation (delayed, automatic) - Stopping the steam supply (delayed, automatic) - Stopping of nitrogen supply (delayed, automatic) - Stopping of off gas fan (delayed, automatic) 10.2.2 Emergency stop When emergency stop button of steam dryer is pressed: - Steam dryer rotation and air lock feeder are stopped - The upstream conveyor equipment are stopped - Steam supply to dryer is shut off, and the control valve PV-4201 (PV-4.2.01) is adjusted to a minimum position. 11 TRACE HEATING Trace heating is highly recommended for preventing sticking of material to the inner surfaces of dryer line equipment. The purpose of trace heating is to keep the surface always in high enough temperature, so that condensation of water will not happen. The walls of discharge chamber (E-3.1.08), dry material conveyors and the offgas duct (E-7.1.01) shall be trace heated. The control of heating should be based on measured temperature of the walls. The detailed control of heaters is not in the scope of this description. 12 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM 12.1 Control power The control power (120V 50Hz 1 phase) for the PLC, IO-units and operation unit is supplied and backed up with central UPS of the plant. The IO voltage of PLC is 120 Vac. 12.2 Reserve power Following loads of the steam dryer process can be supplied from the reserve power, see single line diagram 434114 /01: KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 42/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION - Main motors 5121-SVP-2001M1 (M-01.2.01), 5121-SVP-2001M2 (M-01.2.11) and their fan motors 5121-SVP-2001M3 (M-01.1.02), 5121-SVP-2001M4 (M-01.1.12), - Brakes 5121-SVP-2001M5 (M01.2.05), 5121-SVP-2001M6 (M-01.2.15) - Off gas fan M-1700 (M-07.3.01) The reserve power can be used during power failure to rotate the dryer drum to reduce the risk of agglomeration of concentrate to the inner parts of the dryer. 12.2.1 Procedure at power failure situation When power failure at plant stops the dryer line, basically there is some time before there is increased risk for sticking of material to the interior of dryer. All the needed operations can be done manually and the rotation is recommended to be started in 10 minutes. Here is assumed that the power to the control system is available (UPS). The supply to the backed-up equipment shall be switched to be taken from the reserve power. The electric power system design is by others and the details are not discussed here. 12.2.2 Control system functions for power failure handling Interface to plant system concerning the electrical supply status is via 2 digital inputs to the dryer PLC. "Electrical system status" signal (G-29.1.01) is "1", when electrical supply system is working in normal connection. Signal goes down, when there is power failure. Signal "reserve power" (G-29.1.02) is "1", when the reserve power is connected to feed the backed-up loads of the dryer system. When the reserve power signal is on, there will come automatically some changes in the dryer PLC function. After operator has also selected "Power failure mode", the PLC takes off the interlock from the dry material conveyors thus enabling the starting of the dryer drum rotation. Also the speed limits of the rotating drive and off gas fan are forced down, so that only low speeds are available. During mains power failure the dryer line devices shall be changed to manual mode, so that they can be controlled individually from the HMI/SV screens. The whole drive system consisting of the two motors, their fans and brakes are controlled as one unit both in remote and local mode. 12.2.3 Dryer running during power failure During the power failure the dryer rotating drive shall be run at minimum speed (0.3 rpm). Also the the fan (M-07.3.01) speed shall be adjusted to low value. Steam should be supplied to dryer, if it is available and the control power is healthy enabling the 4...20 mA signal to valve PV-4201 (PV-4.2.01). Also the instrument air shall be available for the control valve. If the valve PV-4201 (PV-4.2.01) cannot be used, steam can be supplied to the dryer using the manual by-pass valve (CV-4.2.01). Steam pressure PT-4201 (PT-4.2.01) can be adjusted and monitored from the screen and should be controlled to a low value. Rotation shall be continued approximately 4...6 hours when there is steam available and the material is drying. After that the dryer can be stopped. Then it can be started for short periods in some hour interval. If the steam is not available the rotation shall be continued longer. The material dryness can be monitored using the material sample hole (XV-3.1.07), when there is enough material still falling out from the drum. The material temperature sensors in drum give also clue about the dryness. KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 43/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION 12.2.4 Things to be considered Even though new material is not introduced into the dryer, dry material will come out to the discharge chamber. Therefore there shall be enough space where the dry material is lead into, so that the discharge chamber will not be full. It shall be noted that the seals of steam rotary joint of the dryer need lubrication. Normally the steam works as lubricant. If the steam is not available during the power failure, the rotation shall be stopped. The rotary joint can also be lubricated with water, which can be entered via the valve V4.3.02. One should be careful when using this option and shall remember to close the valve and reinstall the blind flange, before again supplying the steam into the system. 12.3 Motor control 12.3.1 Communication Communication between dryer PLC and the motor starters and the frequency converters in the motor control center (MCC) is made with Profibus DP network. The direct on line starters (DOL) have Schneider Tesys (model ??) starter device. 12.3.2 Data to dryer PLC From each motor starter following data is transferred: - motor current - voltage - power - motor power factor - temperature (thermal status calculated by the starter device) From motor with frequency converter torque is available and it is transferred to PLC. From motors, where there are installed analog temperature sensors in the winding, the actual winding temperature is transferred. 12.3.3 Data displaying on operator screens On the process window for the operator is displayed: - motor torque, % of nominal torque - motor power, % of nominal power (if torque is not displayed) - motor temperature, °C (motors with sensors in winding) On the maintenance window is displayed: - motor torque, Nm and % - motor power, kW and % - motor current, A and % - voltage, V - motor power factor, cosfii - thermal status, % - motor winding (and bearing) temperature, °C (motors with sensors in winding or bearings) This same data is also displayed in starting dialog windows of individual motors. It is then available easily by clicking motor symbol also for normal operators, when needed. KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 44/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION 13 MISCELLANEOUS 13.1 Emergency shutdown The steam dryer system is shut down automatically in following situations Mains power failure Flash tank is full detected by level switch (LS-8.1.06) Operator activates emergency stop from HMI or SV screen Mains power failure stops normally most of conveyors depending on the electric supply connections. When the mains power detection relay indicates power failure the whole line is stopped. This includes also shutting down the steam supply to dryer by closing the control valve (PV-4.2.01) In emergency shutdown following actions are made: Steam supply to dryer is stopped by closing the control valve PV-4201 (PV-4.2.01) Stopping of material feed to system (not in Kumera's scope) Stopping dryer drum using normal procedure, electric supply to drive motors 5121SVP-2001M1/M2 (M-1.2.01/11) is cut off from frequency converters (coasting stop). Brakes 5121-SVP-2001M5/M6 (M-1.2.05/15) are closed after delay to enable drum to fall back to balanced position. Motor fan 5121-SVP-2001M5/M6 (M-1.2.02/12) are stopped. Vibration feeder 5121-AVB-2001M (M-2.1.01) is stopped. Off gas fan M-1700/1800 (M-7.3.01/02) are stopped The valves FV-1100...1408 (XV-6.7.01....14) off gas ducts before and after bag filter are closed Dust conveyors M-1102/1202/1302/1402 (M-6.5.01/02/03/04), (M-6.6.01/02/03) are stopped Airlock feeder (M-3.3.02) and screw 5121-TRS-3001M (M-3.3.01) are stopped 13.2 Ignition risk in exhaust gas line High temperature of the concentrate and its dust in off gas increases risk of the ignition of material. Therefore the temperatures of offgas gas and dried concentrate are monitored and, emergency shutdown is activated, if gas temperature or dried concentrate temperature rise too high (HH limit). This kind of situation can happen for example, when material feed is stopped while high temperature steam is still supplied. In emergency shutdown steam supply is closed and material feed and the whole conveying line is stopped. During normal operation the oxygen level in dryer is low, because in offgas there is water vapour. In special situations, such as shut-downs, when no new material is supplied into the drum, water vapour content decreases and oxygen level goes near the normal air value. This increases risk of ignition of copper concentrate, because temperature can also go up at the same time. As rule for design of off gas line including selection of bag filter and conveyors, no dried concentrate should be accumulated anywhere in the line. The accumulated concentrate is a possible source of fire. KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER doc. 435111 01 45/ 46 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION 0 GENERAL .........................................................................................................................................................................1 Component and signal naming convention ...................................................................................................................1 Terminology .................................................................................................................................................................2 Operator interface ........................................................................................................................................................2 Data logging .................................................................................................................................................................3 Scope of delivery..........................................................................................................................................................3 Interfacing of dryer control system to plant systems .....................................................................................................3 0.6.1 Interface to plant control system ........................................................................................................................3 0.6.2 Interface between dryer PLC and motor control center ......................................................................................4 STEAM DRYER LOOPS ...................................................................................................................................................4 1.1 Material temperature inside steam dryer TE-1101 ... 1104 (TE-1.1.01 … 1.1.04), TE-1101 ... 1104 (TT-1.1.01 … 1.1.04) ....................................................................................................................................................................................4 1.2 Main drive control, speed indication and control 5121-SVP-2001M1 (M-1.2.01), 5121-SVP-2001M2 (M-1.2.11) ..........5 1.3 Main drive control with 2 motors ...................................................................................................................................6 1.4 Dryer local panel controls (A-1.2) .................................................................................................................................6 1.5 Temperature measurement of main motor winding TE-1201 (M-1.2.1-TE1), TE-1211 (M-1.2.11-TE1) .........................6 1.6 Gear box oil temperature TE-1203 (TE/TT-1.2.3), (TE/TT-1.2.13), (E-1.2.03), (E-1.2.13) ............................................7 1.7 Main drive brakes 5121-SVP-2001M5 (M-1.2.5), 5121-SVP-2001M6 (M-1.2.15) ..........................................................7 1.8 Lubrication control (A-1.3) ............................................................................................................................................8 1.9 Drive component fault situation ....................................................................................................................................9 1.10 Jump preventor ZSH-1501...1508 (XS-1.5.01,..., 08) ..............................................................................................9 STEAM DRYER FEED SYSTEM LOOPS..........................................................................................................................9 2.1 Feeding conveyor 5121-AVB-2001M (M-2.1.1) ............................................................................................................9 2.2 Level switch of input hopper LSH-2104 (LS-2.1.4)......................................................................................................10 2.3 Material feed rate WT-2075 (FT-2.0.01) .....................................................................................................................10 2.4 Permission for material input to dryer (XY-2.0.02) ......................................................................................................11 DISCHARGE SYSTEM LOOPS ......................................................................................................................................11 3.1 Steam Dryer Discharge End Pressure PT-3101 (PT-3.1.1).........................................................................................11 3.2 Control concept for air flow through the dryer TIC-3104 (TIC-3.1.04), (XY-3.1.01)......................................................12 3.2.1 Exhaust gas flow control principle ....................................................................................................................12 3.2.2 Maintaining negative pressure in the system ...................................................................................................13 3.3 Dried material temperature TE-3102 (TE-3.1.02), TE-3103 (TE-3.1.03), TIC-3102 (TIC-3.1.02) .................................13 3.4 Steam Dryer offgas temperature TE-3104 (TE-3.1.04) ...............................................................................................14 3.5 Dried material level switches LSH-3106 (LS-3.1.06), LSH-3110 (LS-3.1.10), LSH-3112 (LS-3.1.12) ..........................14 3.6 Airlock feeder (M-3.3.02), (SS-3.3.02) ........................................................................................................................15 3.7 Screw conveyor 5121-TRS-3001M (M-3.3.01) ...........................................................................................................15 3.8 Output material sample (XV-3.1.07) ...........................................................................................................................16 3.9 Gate valves (V-3.2.1), (V-3.2.11), (V-3.2.21) ..............................................................................................................16 STEAM PRESSURE REGULATING SYSTEM LOOPS ...................................................................................................16 4.1 Steam Dryer Incoming Steam Flow Indication FIT-4101 (FIT-4.1.01) .........................................................................16 4.2 Incoming Steam to pressure regulating unit Pressure indication PT-4101 (PT-4.1.01)................................................ 18 4.3 Incoming steam to pressure regulating unit temperature (TE-4.1.01)..........................................................................18 4.4 Steam Dryer Incoming Steam Pressure PIC-4201 (PIC-4.2.1), PT-4201 (PT-4.2.1) ...................................................18 4.4.1 Steam control valve PV-4201 (PV-4.2.01)........................................................................................................19 4.4.2 Operating Modes .............................................................................................................................................20 4.4.3 Protection of steam pipes ................................................................................................................................21 4.4.4 Protection of pressurized pipes at low temperatures ........................................................................................22 4.4.5 Limiting temperatures temperature, when drum stopped .................................................................................22 4.5 Steam Dryer Incoming Steam Pressure Relief Valve PSV-4201 (PSV-4.2.01) ...........................................................22 4.6 Manual control valve for incoming steam (CV-4.2.01) ................................................................................................22 4.7 Steam Dryer Incoming Steam Pressure Indication (PI-4.2.02) ....................................................................................22 4.8 Steam Dryer Incoming Steam Temperature Indication TE-4301 (TE-4.3.01) ..............................................................23 4.9 Shut-off valve for pipe connection (V-4.3.02) ..............................................................................................................23 STEAM TRAP UNIT LOOPS ...........................................................................................................................................23 5.1 Steam trap unit (XV-5.1.01), (XV-5.1.02), (XV-5.1.03), PT-5102 (PT-5.1.02), PT-5202 (PT-5.2.02), ...........................23 5.2 Steam trap unit temperatures TE-5101 (TE-5.1.01), TE-5201 (TE-5.2.01) .................................................................. 24 5.3 Condensate handling system .....................................................................................................................................24 5.3.1 Flash tank Level control LV-8102A (LV-8.10.01A), LV-8102B (LV-8.10.01B), PT-8101 (PT-8.1.01), LT-8102 (LT-8.1.02), LIC-8102 (LIC-8.1.02), XY-8102 (XY-8.1.02) ................................................................................................24 5.3.2 Pressure control of flash tank PV-8501 (PV-8.5.01), PIC-8101 (PIC-8.1.01), ................................................... 26 5.3.3 Starting and stopping of flash tank operation ...................................................................................................26 5.3.4 Pressure safety valve for flash tank PSV-8103 (PSV-8.1.03) ...........................................................................26 5.3.5 Flash tank over level switch LSH-8106 (LS-8.1.06)..........................................................................................27 5.3.6 Condensate pumping from condensate tank (5123-EST-2002), (M-8.3.01), (M-8.3.02), FS-8311 (FS-8.3.11), FS-8321 (FS-8.3.21), PI-8330 (PI-8.3.30) ........................................................................................................................27 5.4 Condensate conductivity measurement (QT-5.3.01)...................................................................................................28 BAG FILTER LOOPS ......................................................................................................................................................29 6.1 Shut-off valves of bag filter FV-1100...1400 (XV-6.7.01...6.7.04), FV-1108...1408 (XV-6.7.11...6.7.14) ......................29 6.2 Trace heating of bag filter (A-6.2) ...............................................................................................................................30 6.3 Bag cleaning system of bag filter (A-6.3) ....................................................................................................................31 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 1 2 3 4 5 6 6.4 Dust conveying system of bag filter M-1102...1402 (M-6.5.01...6.5.04), SSL-1102...1402 (SS-6.5.01...6.5.04), LSH1100...1400 (LS-6.1.01...6.1.04), ..........................................................................................................................................32 6.5 Vibrators of bag filter VBR-1100...1400 (Y-6.10.01...6.10.04) .....................................................................................32 6.6 Dust conveying system of bag filter (M-6.6.01/02/03) .................................................................................................33 6.7 Ventilation fans MY-1810 (M-6.9.01), MY-1812 (M-6.9.02) .........................................................................................33 7 EXHAUST GAS SYSTEM LOOPS ..................................................................................................................................33 7.1 Exhaust gas flow (FE-7.2.1) .......................................................................................................................................33 7.1.1 Flow measurement ..........................................................................................................................................33 7.1.2 Flow sensor mounting......................................................................................................................................34 7.2 Steam Dryer exhaust gas temperature TE-7203 (TE-7.2.03) ......................................................................................34 7.3 Offgas fan M-1700 (M-7.3.01), M-1800 (M-7.3.02) .....................................................................................................35 7.4 Dust removal fan from reject (M-7.1.05) .....................................................................................................................36 7.5 Airlock feeder of dust removal cyclone (M-7.1.06) ......................................................................................................36 7.6 Dust monitoring sensor XT-7501 (XT-7.5.01) .............................................................................................................37 8 STEAM DRYER ROTATION CONTROL AND INTERLOCKING .....................................................................................37 8.1 Dryer Drum Drive .......................................................................................................................................................37 8.1.1 Equipment numbers:........................................................................................................................................37 8.1.2 Drive electric motors ........................................................................................................................................37 8.1.3 Drum drive control description .........................................................................................................................37 8.1.4 Automatic line control mode.............................................................................................................................38 8.1.5 Manual control mode .......................................................................................................................................39 8.2 Interlocks for dryer drive .............................................................................................................................................39 8.3 Work safety aspects ...................................................................................................................................................40 9 NITROGEN SYSTEM LOOPS .........................................................................................................................................40 10 OPERATION OF STEAM DRYER ...................................................................................................................................40 10.1 Starting sequence of steam dryer .........................................................................................................................40 10.1.1 Preliminary work (manually by operator): .........................................................................................................40 10.1.2 The line start command from HMI (dryer is rotating and heating with steam is on) ...........................................40 10.2 Stopping sequence of steam dryer ........................................................................................................................41 10.2.1 Normal line stop...............................................................................................................................................41 10.2.2 Emergency stop...............................................................................................................................................41 11 TRACE HEATING ...........................................................................................................................................................41 12 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM...................................................................................................................................................41 12.1 Control power .......................................................................................................................................................41 12.2 Reserve power......................................................................................................................................................41 12.2.1 Procedure at power failure situation .................................................................................................................42 12.2.2 Control system functions for power failure handling .........................................................................................42 12.2.3 Dryer running during power failure ...................................................................................................................42 12.2.4 Things to be considered ..................................................................................................................................43 12.3 Motor control .........................................................................................................................................................43 12.3.1 Communication................................................................................................................................................43 12.3.2 Data to dryer PLC ............................................................................................................................................43 12.3.3 Data displaying on operator screens ................................................................................................................43 13 MISCELLANEOUS ..........................................................................................................................................................44 13.1 Emergency shutdown ...........................................................................................................................................44 13.2 Ignition risk in exhaust gas line .............................................................................................................................44 KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile Project 2191 Doc. 435113 01 CONTRACT: 4501679027 KUMERA STEAM DRYER Electric consumer list Rev. G H I J Equipment Kumera Customer / (Subcontracto r) Change Voltage Reserve Service power Pn / kW Sn / kVA 177,0 V RP 3*460V 50Hz RP M -01.2.01 Frequency converter Electric motor 160,00 M -01.2.02 Electric motor 0,75 1,1 1500 3*460V 50Hz M -01.2.05 Electric motor 0,32 0,53 G -01.2.11 177,0 M -01.2.11 Frequency converter Electric motor 160,00 M -01.2.12 Electric motor 0,75 1,1 1500 3*460V 50Hz M -01.2.15 Electric motor 0,32 0,53 3000 3*460V 50Hz A -01.3. Lubricator 0,2 1*220V 50Hz M -01.4.01 Electric motor E -01.2.03 A E -01.2.03 B E -01.2.13 A E -01.2.13 B M -02.1.01 M -03.3.02 Heater Heater Heater Heater Electric motor Electric motor 0,27 2,20 type 2) sep K 2) dri On, when main drive running K 1,1 FT Electric motor, integrated in the brake thrustor Frequency converter installed in cabinet NEMA 12 (IP54), Always when dryer line is on NEMA mounting, foot, encl.IP55, PT100, separate cooling fan, insulated N-end bearing Always when dryer line is on Integrated in main motor, IP55, ? A 0,53 - Always when dryer line is on Integrated in main motor, IP55, ? A K 0,2 Always when dryer line is on K In heating pipe maintenance O Accoding to oil temperature Accoding to oil temperature Accoding to oil temperature Accoding to oil temperature Intermittent (approx 5%) Always when dryer line is on K K sep E K bfi C K bfi C K bfi C K bfi C K bfi C K bfi C K bfi C K bfi C K bfi 1,2 CT According to wall temperatures According to wall temperatures According to wall temperatures According to wall temperatures According to wall temperatures According to wall temperatures According to wall temperatures According to wall temperatures Always on, when dryer line running Always when dryer line is on K bfi 0,71 1,2 CT Always when dryer line is on K bfi 0,71 1,2 CT Always when dryer line is on K bfi RP Fan motor of main motor DOL - 0,75 1,1 FT 3000 3*460V 50Hz RP Main drive brake, drive 1 DOL - 0,32 0,53 - 3*460V 50Hz RP Frequency converter for main drive 1 Main drive motor CB - VSD ND 113 CT RP Fan motor of main motor DOL - 0,75 RP Main drive brake, drive 1 DOL - 0,32 CB 3*460V 50Hz Lubrication of girth gear and pinion Hoist for pipe elements 0,5 0,5 0,5 0,5 0,4 3,2 1*220V 50Hz 1*220V 50Hz 1*220V 50Hz 1*220V 50Hz 3000 3*460V 50Hz 1500 3*460V 50Hz Gearbox oil heater Gearbox oil heater Gearbox oil heater Gearbox oil heater Input chute vibration motor Airlock feeder for reject DOL DOL DOL DOL DOL DOL-R Bag filter trace heater, hopper 1 Bag filter trace heater, hopper 2 Bag filter trace heater, hopper 3 Bag filter trace heater, hopper 4 Bag filter trace heater, straight walls 1 Bag filter trace heater, straight walls 2 Bag filter trace heater, straight walls 3 Bag filter trace heater, straight walls 4 Bag filter cleaning system Ctr (DOL) Ctr (DOL) Ctr (DOL) Ctr (DOL) Ctr (DOL) Ctr (DOL) Ctr (DOL) Ctr (DOL) Ctr? CB? DOLR ND 0,71 DOLR ND DOLR ND E -06.2.02 (HTR1200) Heater 4,5 3*460V 50Hz E -06.2.03 (HTR1300) Heater 4,5 3*460V 50Hz E -06.2.04 (HTR1400) Heater 4,5 3*460V 50Hz E -06.2.11 (HTR1102) Heater 10,5 3*460V 50Hz E -06.2.12 (HTR1202) Heater 10,5 3*460V 50Hz E -06.2.13 (HTR1302) Heater 10,5 3*460V 50Hz E -06.2.14 (HTR1402) Heater 10,5 3*460V 50Hz Cleaning system 1,0 1*220V 50Hz M -06.5.01 (MY-1102) Electric motor 0,75 1,2 ?1500 3*460V 50Hz Airlock feeder of bag filter chamber 1 M -06.5.02 (MY-1202) Electric motor 0,75 1,2 ?1500 3*460V 50Hz M -06.5.03 (MY-1302) Electric motor 0,75 1,2 ?1500 3*460V 50Hz Airlock feeder of bag filter chamber 2 Airlock feeder of bag filter chamber 3 Manufacturer Remarks Deli very Rev Torque Operation time type CT 3*460V 50Hz 27.11.2017 K Electr. kVA 113 4,5 Scope: K = Kumera, O = others Frequency converter installed in cabinet NEMA 12 (IP54), Always when dryer line is on NEMA mounting, foot, encl.IP55, PT100, separate cooling fan, insulated N-end bearing Always when dryer line is on Integrated in main motor, IP55, ? A Mech. kW ND Heater Location: F = field, C = control room/system, L = local panel, D = DCS Load type: CT: constant torque, FT: fan, NLS: no-load start, LS: loaded start Esimated load VSD (HTR1100) S = signal only, I = device/instrument Ctr: Contactor, Sw: Control switch, CB: circuit breaker or fuses Model - 1500 3*460V 50Hz Fix : fixed compartment VSD: Variable speed drive, frequency converter Specification CB 1500 3*460V 50Hz Starter design: WiDr : withdrawable compartment DOL-2W : direct on line, 2 speed/2 winding Duty Load data class Frequency converter for main drive 1 Main drive motor E -06.2.01 A -06.3. Starter / electr. supply ND /HD rpm Starter type: DOL: direct on line starter, DOLR: direct on line, reversible ND: normal duty, HD: heavy duty M-6.9.01/0.2 to 1x115V50Hz Nominal Nominal power, power mech. electrical (automatic column) G -01.2.01 Motor speed ns Installed power Date 18.8.2017 22.9.2017 9.10.2017 14.11.2017 Scope K/O Comp. ID Drawn MSR MSR MSR MSR 126 126 CB 0,27 1,8 0,5 0,5 0,5 0,5 0,36 2,6 1 K dri Galvi dri K 2) sep K 2) dri K K K K dri Galvi dri sep delivery by others, power to be confirmed 4) 4) 4) 4) dri I I dri I I K 1/2 Equipment Kumera Customer / (Subcontracto r) Motor speed ns Installed power Voltage Reserve Service power Nominal Nominal power, power mech. electrical (automatic column) Sn / kVA 0,75 1,2 ?1500 3*460V 50Hz 0,3 0,3 6,1 1800 1*120V 50Hz 1800 1*120V 50Hz 3000 3*460V 50Hz 0,7 1500 3*460V 50Hz 166,0 3*460V 50Hz (MY-1402) Electric motor A -06.8. M -06.9.01 M -06.9.02 M -07.1.05 (MY-1810) Electric motor (MY-1812) Electric motor Electric motor 0,19 0,19 5,50 M -07.1.06 Electric motor 0,37 G -07.3.01 (MY1700) Frequency converter Electric motor (MY1000) Frequency converter Electric motor rpm V G -07.3.02 M -07.3.02 G -08.3.01 166,0 150,0 Frequency converter Electric motor Space heater M -08.3.01 M -08.3.01 E G -08.3.02 1500 3*460V 50Hz 1500 3*460V 50Hz 20,5 3*460V 50Hz 0,05 3000 3*460V 50Hz 1*220V 50Hz 20,5 3*460V 50Hz 0,05 3000 3*460V 50Hz 1*220V 50Hz 18,5 M -08.3.02 M -08.3.02 E Frequency converter Electric motor Space heater A -30.1.01 Control unit 1,0 A -30.1.02 Remote IO unit 0.5 A -30.2.01 Control unit 1,0 Installed motor power (mech.) Installed power (electr.) 18,5 671 3*460V 50Hz 1*120V 50Hz, UPS 1*120V 50Hz, UPS 1*120V 50Hz, UPS kW 811,4 kVA type RP Airlock feeder of bag filter chamber 4 Bagfilter control unit Penthouse vent fan Penthouse vent fan Fan for reject dust removal Control unit 150,0 Duty Load data class ND /HD Pn / kW M -06.5.04 M -07.3.01 Starter / electr. supply RP DOLR Model Manufacturer Remarks Electr. kVA Airlock feeder of the dust DOL-R removal cyclone Frequency converter of of gas CB fan Offgas fan motor VSD Always when dryer line is on K 0,71 1,2 CT 0,186 0,186 4 0,33 0,33 4,4 FT bfi Always when dryer line is on K bfi bfi bfi sep 0,37 0,71 CT Always when dryer line is on K sep I O sep F bfi F Frequency converter of of gas CB fan Offgas fan motor VSD sep F bfi F Frequency converter of condensate pump 1 Condensate pump 1 Electric motor space heater CB Frequency converter of condensate pump 2 Condensate pump 2 Electric motor space heater CB Dryer PLC, +CA0 CB VSD Ctr VSD Ctr K 130,6 FT Always when dryer line is on NEMA mounting, foot, encl. IP55, PT100, insulated N-end bearing 130,6 FT Always when dryer line is on NEMA mounting, foot, encl. IP55, PT100, insulated N-end bearing 11,6 FT 0,05 One pump as duty pump Always on, when pump not running 12,9 - 11,6 2) K 2) O 12,9 - K O 145 - brushless DC motor brushless DC motor K 145 - Rev Torque Operation time type K DOL DOL VSD Deli very Esimated load Mech. kW ND Specification Scope K/O Comp. ID FT 2) K chs chs O - K 2) chs chs 1 K sep Remote IO unit cabinet +A01.2 CB 0,5 K sep Dryer operation station, +A.HMI 0,5 K sep CB 522,2 kW 589,9 kVA J - K 0,05 One pump as duty pump Always on, when pump not running K J Mechanical power, estimated Electric power, estimated Delivery code sep = separately / integrated in : Notes: 1) 2) 3) 27.11.2017 prs = pressure reducing station, sts = steam trap station, dri = dryer drive unit, sco = screw conveyor, alf =air lock feeder mcc = motor control center, bfi = bag filter, cru = crusher, chs = condensate handling system Powers in table expressed in kW, motor rating may be in HP. More details in field component list In list basically only data of equipment in Kumera's delivery 2/2 KUMERA TECHNOLOGY CENTER Project 2191 435123 01 CUSTOMER: Codelco Chuquicamata, Chile CONTRACT: 4501679027 KUMERA STEAM DRYER INSTRUMENT AND SIGNAL LIST Rev. Date I 11.9.2017 J K Change Drawn MSR 27.9.2017 1 = Steam Dryer 7 = Exhaust Gas System DCS= Plant DCS, PLC= PLC of dryer, FC= frequency conv. 2 = Feed System 8= FC=spring to close, FO=spring to open, FL=fail to latch PDCS= plant DCS, i = signals defined in other row of device 3 = Discarge System 9 = Nitrogen system In component ID: i = input, o = output of DCS MS= motor starter unit, OD= other device 4 = Pressure Regulating Station Type: SW = signal only, HW = device/instrument, - = mechnics 24IO = digital inputs/outputs 24Vdc, 24IOR = digital remote inputs/outputs 24Vdc 5 = Steam Trap Station Scope: K = Kumera, O = others, - = only signal /part of component 120IO, 230IO = digital inputs/outputs 120Vac, 230Vac Location: F = field, L = local panel, D = DCS program/screen, C = DCS wiring panel, M = MCC PFC = potential free contact, PFC-R = potential free contact in remote IO unit IOBus = connection via system data bus (Profibus DP) HVM Notes: Data of each signal loop is written normally on sensor's row only. Device data is on the row of its main motor (generally). Environment: Altitude 2800 m, pressure 72 kPa(a), temperature -5 ... 30ºC Kumera Customer Tag / Instrument /signal /device Service Tag (Subcontractor tag) Signal Connection: General: SP = setpoint, normal or nominal value, LL,L,H,HH = alarms MSR 10.10.02017 Dryer areas (1. number of tag) Abbreviations: Measuring/ operation range Instrument data Process material Signal (automatic column) TE-01.01.01 TE-1101 Temperature sensor Material in drum, feed end TI-01.01.01 TT-01.01.01 TE-01.01.02 TI-1101 TT-1101 TE-1102 Temperature indication Temperature transmitter Temperature sensor Material temperature in drum Wireless transmitter Material in drum, middle part TI-01.01.02 TT-01.01.02 TE-01.01.03 TI-1102 TT-1102 TE-1103 Temperature indication Temperature transmitter Temperature sensor Material temperature in drum Wireless transmitter Material in drum, middle part TI-01.01.03 TT-01.01.03 TE-01.01.04 TI-1103 TT-1103 TE-1104 Temperature indication Temperature transmitter Temperature sensor Material temperature in drum Wireless transmitter Material temperature in drum, discharge end TI-01.01.04 TT-01.01.04 PDT-01.01.10 TI-1104 TT-1104 PDT-1110 Temperature indication Temperature transmitter Pressure differential sensor Material temperature in drum Wireless transmitter Pressure in the input end of the drum Manifold Manifold for differential pressure sensor, 3-valve V-01.01.10 TE-01.01.11 TE-1111 Temperature sensor Input gas temperature to drum TT-01.01.11 TR-01.01. TT-1111 TR-1100 Temperature transmitter Temperature receiver Input gas temperature to drum Wireless receiver G-01.02.01 M-01.02.01 M-01.02.01-SC 5121-SVP-2001M1 SC-1201 Frequency converter Electric motor Frequency converter M-01.02.01-SI M-01.02.01-TE1 M-01.02.01-XI SI-1201 TE-1201 NI-1201 Speed alarm and indication Temperature sensor Torque display M-01.02.02 E-01.02.03 TE-01.02.03 5121-SVP-2001M3 TE-1203 Electric motor Space heater Temperature sensor Main drive frequency converter, drive 1 Main drive motor 1 Rotation speed reference to frequency converter. Dryer drum rotating speed, DCS display Main motor winding, PT100, motor 1 Main motor load torque signal from frequency converter 1 Main motor fan, motor 1. Gearbox space heater, drive 1 Gear oil temperature, drive 1. TI-01.02.03 TT-01.02.03 M-01.02.05 TI-1203 TT-1203 5121-SVP-2001M5 Temperature indication Temperature transmitter Brake thruster M-01.02.05-ZS G-01.02.11 M-01.02.11 M-01.02.11-SI M-01.02.11-TE1 M-01.02.11-XI ZS-1205 Limit switch Frequency converter Electric motor Speed alarm and indication Temperature sensor Torque display M-01.02.12 E-01.02.13 TE-01.02.13 5121-SVP-2001M4 TE-1213 Electric motor Space heater Temperature sensor TI-01.02.13 TT-01.02.13 M-01.02.15 TI-1213 TT-1213 5121-SVP-2001M6 Temperature indication Temperature transmitter Brake thruster M-01.02.15-ZS A-01.02.20 A-01.03.-XI A-01.03.-XS A-01.03. ZS-1215 XL-1220 XA-1230 Limit switch Alarm device Fault alarm Lubrication unit Lubricator M-01.04.01 XS-01.05.01 XS-01.05.02 XS-01.05.03 XS-01.05.04 XS-01.05.05 XS-01.05.06 XS-01.05.07 5121-TCL-3003M ZSH-1501 ZSH-1502 ZSH-1503 ZSH-1504 ZSH-1505 ZSH-1506 ZSH-1507 5121-SVP-2001M2 SI-1211 TE-1211 NI-1211 Electric motor Proximity sensor Proximity sensor Proximity sensor Proximity sensor Proximity sensor Proximity sensor Proximity sensor 0% 100 % unit SP 0 150 °C 40 0 0 150 150 °C °C LL L H 60 HH Sensor type 130 PT100, 4wire 130 80 130 PT100, 4wire PT100, 4wire 150 °C 100 130 PT100, 4wire 0 1 150 kPa(g) -0.1 -0.3 °C 0 0 0 1500 2 2 Nm rpm rpm 0 0 0 2 200 200 rpm °C % -0.01 PT100, 4wire K Wireless HART, 2.4GHz i PLC HW F K i SW D - i i HW F K Wireless HART, 2.4GHz i PLC HW F K SW D - HW F K HW F K i SW D - i HW F K 4...20mA HART DCS loop HW F K - - - HW F K 4...20mA HART DCS loop HW F K A A Wireless HART, 2.4GHz i A PT100 flange, DN25 PN40 thread (impulse pipe) thread (impulse pipe) 27 /18 27 /18 225 225 225 ATEX II 3 D ATEX II 3 D ATEX II 3 D wireless, separate wireless, separate wireless, separate Cu-conc., abrasive Cu-conc., abrasive Cu-conc., abrasive -0.1 -0.1 Air (wet), dust, -0.1 NPT 1/2" air -0.1 ambient air 0 headmounted - -0.1 NPT 1/4-18 ATEX II 3 D - - 25 -5, +130 - - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 40 25 -5, +130 - - 1 F K HW F K PLC FC PLC 1 HW M K HW F K 1 SW D - 1 1 1 SW D - HW F K i PLC FC PLC SW D - IOBus MS 1 HW F K 4…20mA PLC HW F K i PLC PLC MS SW D - HW F K HW F K HW F K HW M K HW F K 1 1 1 SW D - HW F K SW D - 1 HW F K HW F K SW D - HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F O? SW D - SW D - HW F K HW F O HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K IObus PT100 24Vdc 120 °C 10 90 0 ? Nm on 0 0 0 0 0 off 1500 2 2 200 200 Nm rpm rpm °C % IOBus mech. PFC i PLC PLC FC PLC FC PLC IOBus MS IObus i 0.05 i 2.05 PT100 1025 Nm loop 1 1 1 1 Signals from SD and PD transmitters sensor integrated in gearbox 1 -10 120 °C 10 90 4…20mA PLC i IOBus PLC PLC MS ? off off on off Nm on on off on mech. PFC PLC ?3 on on on on on on on 1 1 1 1 PFC PFC i off off off off off off off loop - ton inductive inductive inductive inductive inductive inductive inductive 120IO 120IO 120IO 120IO 120IO 120IO 120IO 1/6 PLC PLC PLC 120Vac MS PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC loop loop loop loop loop loop loop 27.11.2017 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Rev I 1 -10 i Main drive brake, electro-hydraulic thruster, drive 2 Status of brake, 1=open, drive 2 Alarm beacon for dryer movement Lubrication unit alarm Start command, 1= lubrication on Lubrication of girth gear and pinion. Includes control unit. Hoist motor, element handling Jump preventor status, support roller 1 Jump preventor status, support roller 1 Jump preventor status, support roller 2 Jump preventor status, support roller 2 Jump preventor status, support roller 3 Jump preventor status, support roller 3 Jump preventor status, support roller 4 battery flange, DN25 PN40 27 /18 - HW i PLC i Main drive brake, electro-hydraulic thruster, drive 1 Status of brake, 1=open, drive 1 Main drive frequency converter, drive 2 Main motor, drive 2 Dryer drum rotating speed, DCS display Main motor winding, P100, motor 2 Main motor load torque signal from frequency converter 2 Main motor fan, motor 2. Gearbox space heater, drive 2 Gear oil temperature, drive 2 battery flange, DN25 PN40 °C -0.1 1 i Ethernet/ Profibus DP i 1025 Nm PLC PLC PLC battery ATEX II 3 D kPa(g) K F 310 kPa(g) F D mm 27 /18 max max DN PN/ (min) instrum /materia CL ent l °C °C HW HW mm Approvals, material, ATEX, IP Remark Cont roller SW L nom. Dig in Dig out An in An out IO bus Barrier i flange, DN25 PN40 D max (min) Loc. Scope i battery Type nom. Type i i 2.05 Cu-conc., abrasive T PLC i 0.05 wireless, separate p Wireless HART, 2.4GHz i -0.005 50 Material Instrument/ signal Information A A Connec- Power tion to supply Transmitte r, Actuator I/O for DCS (or PLC) Type i -1 Connection Process pipe Class i 0 6 = Bag Flter Barrier: marked if needed for hazardous environment sensor integrated in gearbox Kumera Tag Customer Tag / (Subcontractor tag) Instrument /signal /device Service Measuring/ operation range Instrument data Process material Signal (automatic column) XS-01.05.08 FT-02.00.01 XY-02.00.02 ZSH-1508 WT-2075 M-02.01.01 LS-02.01.04 PI-03.01.01 PIC-03.01.01 PT-03.01.01 5121-AVB-2001M LSH-2104 PI-3101 100 % off 0 on on 260 off on off unit SP LL L H HH Sensor type Class Type 120IO Electric motor Level switch Pressure indication Pressure controller Pressure transmitter V-03.01.01 Gauge valve Pressure sensor shut-off valve - - XY-03.01.01 Calculation element Concentrate feed rate signal effect to exhaust gas flow Temperature of the dryed material, hopper - - 4...20mA, HART PLC i PLC PLC 0 0 TI-03.01.02 TIC-03.01.02 TI-3102 TIC-3102 Temperature indication Temperature controller TT-03.01.02 TE-03.01.03 TT-3102 TE-3103 Temperature transmitter Temperature element Temperature of the dryed material Dryed material temperature control loop, setpoint to steam pressure Temperature of the dryed material Temperature of the dryed material, hopper TI-03.01.03 TT-03.01.03 TE-03.01.04 TI-3103 TT-3103 TE-3104 Temperature indication Temperature transmitter Temperature sensor Temperature of the dryed material Temperature of the dryed material Exhaust gas temperature TI-03.01.04 TIC-03.01.04 TI-3104 TIC-3104 Temperature indication Temperature controller TT-03.01.04 LS-03.01.06 TT-3104 LSH-3106 Temperature transmitter Level switch Exhaust gas temperature Temperature (exhaust gas flow) control of the discharge end, high/low -alarm Exhaust gas temperature Level of concentrate in discharge end, highhigh XV-03.01.07 E-03.01.08 LS-03.01.10 LSH-3110 Sample extraction hole Trace heating Level switch Output material sample Discharge chamber heating Level of concentrate in reject hopper, highhigh on off LS-03.01.12 LSH-3112 Level switch Level of concentrate in discharge end, highhigh on off Gate valve Gate valve Gate valve Electric motor Electric motor Speed monitor Gate valve Signal FI-04.01.01 FIT-04.01.01 FI-4101 FIT-4101 Flow display Flow sensor PI-04.01.01 PI-4101 Pressure indication PT-04.01.01 PT-4101 TE-04.01.01 TE-4101 XY-03.04.02 Signal TE-04.01.01-TW 0 100 -0.5 Temperature element 5121-TRS-3001M 230 20 4…20mA 250 PFC IOBus PFC i TE-3102 Manual shut-off for dry material Manual shut-off for dry material Manual shut-off for dry material Screw feeder for reject Airlock feeder for reject Speed detection of reject airlock feeder Manual shut-off for reject Signal from plant system to allow dry material output from dryer Signal from plant system to allow reject output from dryer Input steam flow Input steam flow t/h kg/h TE-03.01.02 V-03.02.01 V-03.02.11 V-03.02.21 M-03.03.01 M-03.03.02 SS-03.03.02 V-03.03.02 XY-03.04.01 inductive Connec- Power tion to supply Jump preventor status, support roller 4 Input material feed rate to steam dryer Signal to plant system for giving permission to wet material feed Input feeder vibration motor Material level high high alarm in input hopper Pressure inside the discharge end Discharge chamber pressure controller Pressure inside the discharge end chamber PT-3101 Proximity sensor Plant system Signal 0% Connection 150 % kPa °C 0 100 % 0 150 °C i -0.1 -0.4 115 95 -0.01 125 4...20mA HART -0.005 135 PT100, 4wire A i i 115 95 125 135 PT100, 4wire A 4...20mA, HART i i 0 200 °C 125 100 135 140 PT100, 4wire A 4...20mA, HART i 0 100 on off i PFC vibration MS PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC D L mm mm - PLC PLC vibration PFC PLC vibration PFC PLC - off on 120IO off on PFC MS MS PLC PLC off on PFC PLC IOBus IOBus loop - loop loop loop loop thread (impulse pipe) impulse pipe, thread flange, DN25 PN40 flange, DN25 PN40 thread G1/2" G1/2" 27 /18 27 /18 12 120Vac flange DN50 A flange DN50 A 300 thread 24 Input steam temperature (high pressure side) - - Temperature sensor Input steam temperature (high pressure side) 0 250 °C 220 Thermowell 50 2250 2280 240 PT100, 4wire A °C 1 1 -0.1 105 130 40 ATEX II 3 D ATEX II 3 D ATEX II 3 D headmounted headmounted headmounted Cu-concentr. Cu-concentr. Air (wet), dust -0.1 -0.1 0 0 -0.1 Cu-concentr. ATEX II 3 D -0.1 110 130 loop flange i HW F K HW D O SW D - HW F K HW F K SW D - SW D - HW F K 1 - - - F K - - SW D - - - HW F K - - SW D - SW D - - - HW F K HW F K - - SW D - HW F K HW F K SW D - SW D - HW F K HW F K HW F K manual, not DCS HW F O 1) F K 1 1 1 1 - - - 1 ATEX II 3 D -0.1 110 130 - - 1 HW ATEX II 3 D Cu-concentr. -0.1 110 130 - - 1 HW F K - - HW F O HW F O HW F O HW F O HW F K E HW F K G Steam 316L AISI 316 headmounted 2200 2500 220 226 Steam 2200 2500 220 226 Steam 2200 2500 220 226 226 80 - - HW F O 1 SW D - - - 1 SW D - SW D K HW F K SW D - 8" 300 1 8" 300 1 HW F K 8" 300 1 HW F K HW F K ASME TI-04.01.01 TI-4101 Temperature indication Supply steam temperature (high pressure side) i PLC SW D - TT-04.01.01 V-04.01.01 TT-4101 Temperature transmitter Gauge valve mA -transmitter Pressure sensor shut-off valve i PLC - HW F K F K V-04.01.05 V-04.01.11 V-04.01.12 V-04.01.13 V-04.01.14 CV-04.02.01 ???PV-4201 Flow conditioner Shut-off valve Steam trap Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Control valve PIC-04.02.01 PIC-4201 Pressure indicating controller Steam flow measurement flow stabilizing Shut-off for input pipe steam trap Steam trap for input pipe Shut-off for input pipe steam trap Water draining from impulse pipe Manual control valve for steam adjusting steam input in start-up Pressure control of dryer steam PSV-04.02.01 PSV-4201 Pressure safety valve Dryer steam pressure PT-04.02.01 PT-4201 Pressure transmitter Dryer steam pressure PV-04.02.01 PV-4201 Control valve Pressure regulating valve for adjusting steam input to dryer PV-04.02.01-XI V-04.02.01 ZT-4201 Control valve Gauge valve Control valve position feedback Pressure sensor shut-off valve Calculation element Detecting of sudden pressure drop, derivative of pressure PT-4.2.1 ZY-04.02.01 - - impulse pipe, thread - 4000 kg/h - - 0 100 % - - 2300 kPa(g) - - 0 2500 kPa(g) 4…20mA HART PLC 0 50000 kg/h 4…20mA HART PLC 4…20mA - PLC - - - 41734 kg/h 2000 19100… 44700 50 2100 2/6 27.11.2017 steam 2500 226 Steam, 2500 2500 2500 2500 2500 2500 226 226 226 226 226 226 flange flange flange flange 0 G1/2" flange - flange 1/2" 2-1/2" manual 2200 220 120 8" 300 - 8" 1" 1" 1" 8" 2 1/2" 300 300 300 300 300 300 HW F K - F K - F K - F K - F K HW F K SW D - HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K - F K SW D - 1 1 flange 4" /6" loop impulse pipe, thread G1/2" loop flange 8" - G1/2" impulse pipe, thread I - - Rev Cu-concentr. 316L 200 /65 Loc. Scope - 1 8" Type Remark Cont roller 1 - M30 weld-in 2200 kPa(g) Dig in Dig out An in An out IO bus Barrier 1 1 loop kPa(g) 300 120Vac PLC 2500 580 300 4…20mA HART 0 225 DN50 A G1/2" Pressure of supply steam (high pressure side) 225 120Vac impulse pipe, thread Pressure transmitter kPa(g) max max DN PN/ (min) instrum /materia CL ent l °C °C air flange loop kPa(g) nom. 1 PLC 2500 vortex Air (wet), dust, ATEX II 3 D G1/2" 4…20mA HART 0 47000 max (min) 1 PLC Pressure of supply steam (high pressure side) 500 nom. - i 44672 (3878) T CU-conc. 120Vac PLC 50000 kg/h (5000) (m3/h) p Instrument/ signal Information 1 4...20mA HART 0 Approvals, material, ATEX, IP Material I/O for DCS (or PLC) PLC PLC i % PLC PLC PLC Type Transmitte r, Actuator Process pipe 316L pneumatic, ASME FC Section VIII, div.1 ed. 2013 Steam 2000 2500 215 226 Steam 2000 2500 215 226 Steam, 2000 2500 212 steam 2500 4"/6" 300 10" 300 240 8" 300 215 8" 300 80 120 1 1 1 scaling 4...20mA/ 0...5000 m3/h, local display not to DCS D Kumera Tag Customer Tag / (Subcontractor tag) Instrument /signal /device Service Measuring/ operation range Instrument data Process material Signal (automatic column) 0% 100 % unit 0 2500 kPa(g) SP LL L H HH Sensor type Class Type Connection Connec- Power tion to supply Type D L mm - - Separating for steam control valve, before Separating for steam control valve, after Pressure meter shut-off valve - - Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Temperature sensor Water draining from impulse pipe Water draining from impulse pipe Input steam temperature (low pressure side) - Temperature indication Temperature transmitter Shut-off valve Temperature sensor Dryer input steam temperature mA -transmitter Shut-off valve for connection to pipe Condensate temperature before steam trap Thermowell Temperature indication Temperature transmitter Shut-off valve Steam trap Condensate temperature before steam trap Concdensate temperature before steam trap Concdensate temperature before steam trap Condensate line shut-off valve Condensate handling from steam dryer, expansion chamber type Pressure indication Pressure transmitter Pressure of condensate before steam traps Pressure of condensate before steam trap V-05.01.02 XV-05.01.02 Shut-off valve Steam trap V-05.01.03 XV-05.01.03 PI-04.02.02 Pressure meter Dryer steam pressure, mechanical V-04.02.02 V-04.02.03 V-04.02.04 Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Gauge valve V-04.02.10 V-04.02.11 TE-04.03.01 TE-04.03.01-TW TI -04.03.01 TT-04.03.01 V-04.03.02 TE-05.01.01 TE-05.01.01-TW TI-05.01.01 TT-05.01.01 V-05.01.01 XV-05.01.01 PI-4202 TE-4301 - - 0 250 °C 240 PT100, 4wire A - TI-4301 TT-4301 TE-5101 TI-5101 TT-5101 i i - 0 250 °C 0 21000 kg/h (0.5MPa ) 0 2500 Condensate line shut-off valve Condensate handling from steam dryer, expansion chamber type 0 21000 kg/h (0.5MPa ) Shut-off valve Steam trap Condensate line shut-off valve Condensate handling from steam dryer, expansion chamber type 0 21000 kg/h (0.5MPa ) Pressure meter Condensate line pressure before steam traps 0 2500 V-05.01.04 V-05.01.05 V-05.01.06 V-05.01.07 V-05.01.08 V-05.01.09 Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Gauge valve V-05.01.10 PI-05.01.02 PT-05.01.02 215 4…20mA HART PI-5102 PT-5102 210 100 220 PT100, 4wire A 4…20mA HART - i i i i - - - 2000 10 4…20mA 2100 PLC PLC PLC - i kPa(g) PLC flange impulse pipe, thread flange flange loop weld-in loop flange impulse pipe, thread Condensate line shut-off valve, discharge Condensate line shut-off valve, discharge Condensate line shut-off valve, discharge Condensate line shut-off valve, by-pass Condensate line shut-off valve, discharge Pressure meter shut-off valve - Gauge valve Condensate pressure sensor shut-off Temperature sensor Condensate temperature after steam trap PI-5202 PT-5202 Thermowell Temperature indication Temperature transmitter One direction valve Pressure indication Pressure transmitter Condensate temperature after steam trap Concdensate temperature after steam trap Concdensate temperature after steam trap Condensate line one direction valve Pressure of condensate after steam traps Pressure of condensate after steam trap PI-5205 One direction valve One direction valve Shut-off valve Pressure meter Condensate line one direction valve Condensate line one direction valve Condensate line shut-off valve Condensate line pressure after steam traps V-05.02.05 V-05.02.06 V-05.02.07 V-05.02.08 V-05.02.09 V-05.02.10 Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Gauge valve Condensate line shut-off valve Condensate line shut-off valve Condensate line shut-off valve, discharge Condensate line shut-off valve, discharge Condensate line shut-off valve, discharge Pressure meter shut-off valve - - - V-05.02.11 Gauge valve Condensate pressure sensor shut-off - Conductivity sensor Conductivity transmitter Control valve Conductivity of condensate water Conductivity of condensate water Manual adjusting water flow to conductivity sensor Conductivity measuement shut-off valve Temperature of water to conductivity sensor, mechanical Level of dust in bag filter hopper, highhigh, chamber 1 Level of dust in bag filter hopper, highhigh, chamber 2 Level of dust in bag filter hopper, highhigh, chamber 3 Level of dust in bag filter hopper, highhigh, chamber 4 Wall heating, hopper 1 Bag filter temperature, hopper 1 Bag filter temperature, hopper 1 Wall heating, hopper 2 4...20 mA TE-05.02.01-TW TI-05.02.01 TT-05.02.01 V-05.02.01 PI-05.02.02 PT-05.02.02 V-05.02.02 V-05.02.03 V-05.02.04 PI-05.02.05 QE-05.03.01 QIT-05.03.01 V-05.03.02 TI-5201 QE-5301 QIT-5301 V-05.03.04 TI-05.03.03 Shut-off valve Temperature meter LS-06.01.01 LSH-1100 Level switch LS-06.01.02 LSH-1200 Level switch LS-06.01.03 LSH-1300 Level switch LS-06.01.04 LSH-1400 Level switch E-06.02.01 TE-06.02.01 TT-06.02.01 E-06.02.02 HTR-1100 TE-1100 TT-1100 HTR-1200 Trace heater Temperature sensor Temperature transmitter Trace heater 160 PT100, 4wire A 2500 kPa(g) 300 10 F K - F K - F K 2500 2500 2400 226 226 10" 10" 10" 300 300 300 - F K - F K HW F K HW F K SW D - HW F K - F K HW F K HW F K SW D - HW F K - F K HW F K SW D - HW F K ASME 24 200 /65 AISI 316 headmounted steam, condensate 2000 2500 2300 212 226 226 1 212 215 226 226 226 2" 2" 300 300 - F K 212 HW F K 2500 2" steam, condensate flange DN50 steam, condensate 316L 2000 215 2500 2" 2" 300 300 70 4" 300 1 impulse pipe, thread G1/2" steam, condensate 212 226 4" 300 HW F K flange 2500 2500 2500 2500 2500 2500 226 226 226 226 226 215 300 300 300 300 300 300 F K - F K - F K - F K - F K 120 1" 1" 1" 2" 1" 4" - - - - F K - - 2500 215 120 4" 300 - F K 4…20mA HART PLC 8" 300 HW F K - - HW F K i i SW D - i i HW F K - PLC - F K SW D - HW F K 2500 flange flange flange flange loop impulse pipe, thread G1/2" steam, condensate impulse pipe, thread G1/2" steam, condensate weld-in 24 200 /65 i AISI 316 headmounted condensate 300 700 144 flange impulse pipe, thread 2500 G1/2" 316L condensate 300 flange - 700 144 2500 2500 2500 flange flange impulse pipe, thread 226 170 flange flange flange flange flange 3" 3" 3" 8" 300 300 300 300 - F K - F K - F K HW F K 300 300 300 300 300 300 - F K - F K - F K - F K - F K - F K not to DCS 120 8" 300 - F K 1/2" 300 HW F K I HW F K J G1/2" condensate 2500 226 PLC i thread G1" condensate 2500 226 condensate 2500 226 1/2" 300 HW F K condensate 2500 226 1/2" 300 HW F K 1 HW F K D 130 1 HW F K D 110 130 1 HW F K D 110 130 1 HW F K D °C on off capacitive PFC PLC 120Vac thread 1-1/4" ? ATEX II 3 D Cu-concentr. -0.1 110 130 on off capacitive PFC PLC 120Vac thread 1-1/4" ? ATEX II 3 D Cu-concentr. -0.1 110 on off capacitive PFC PLC 120Vac thread 1-1/4" ? ATEX II 3 D Cu-concentr. -0.1 on off capacitive PFC PLC 120Vac thread 1-1/4" ? ATEX II 3 D Cu-concentr. -0.1 on 0 off 200 IOBus J-type 4...20mA MS PLC on off 27.11.2017 1 120 200 3/6 300 not to DCS 3" 3" 1" 1" 1" 8" impulse pipe, thread i 8" not to DCS 226 226 226 226 226 226 - 60 300 Rev 2500 2500 2500 2500 2500 2500 G1/2" MS 70 condensate G½" condensate i 3" 226 226 226 impulse pipe, thread IOBus 1 ASME - loop 150 0 140 300 300 226 226 m3/h 90 1" 4" ASME 0.006 110 1 - i °C 120 K - 200 - K - 20 300 300 300 F - uS/cm 8" 10" 8" F - 1000 226 226 215 HW - 0 2500 2500 2500 - - kPa(g) K 300 300 - 2500 F 2" 2" - 0 HW 226 226 4…20mA 2100 300 212 - 0 10" 215 steam, condensate - 90 2000 226 2500 Remark Cont roller 2" - 144 AISI 316 Steam Loc. Scope flange - °C 200 /65 headmounted Dig in Dig out An in An out IO bus Barrier Type steam, condensate - 250 condensate °C max max DN PN/ (min) instrum /materia CL ent l °C °C DN50 loop - 0 kPa(g) flange flange TE-5201 kPa(g) nom. - - TE-05.02.01 max (min) condensate Instrument/ signal Information T nom. 2000 I/O for DCS (or PLC) 2" - kPa(g) p steam i - PI-5104 Steam 8" 8" G1/2" 1/2" 1/2" 24 Material flange weld-in flange - mm G1/2" i - PI-05.01.04 - PLC PLC impulse pipe, G½" flange Approvals, material, ATEX, IP Transmitte r, Actuator Process pipe 1 1 1 Kumera Tag Customer Tag / (Subcontractor tag) Instrument /signal /device Service Measuring/ operation range Instrument data Process material Signal (automatic column) TE-06.02.02 TT-06.02.02 E-06.02.03 TE-06.02.03 TT-06.02.03 E-06.02.04 TE-06.02.04 TT-06.02.04 E-06.02.11 TE-06.02.11 TT-06.02.11 E-06.02.12 TE-06.02.12 TT-06.02.12 E-06.02.13 TE-06.02.13 TT-06.02.13 E-06.02.14 TE-06.02.14 TT-06.02.14 PDIT-06.03.01 TE-1200 TT-1200 HTR-1300 TE-1300 TT-1300 HTR-1400 TE-1400 TT-1400 HTR-1102 TE-1102 TT-1102 HTR-1202 TE-1202 TT-1202 HTR-3102 TE-1302 TT-1302 HTR-1402 TE-1402 TT-1402 PDIT-1002 Temperature sensor Temperature transmitter Trace heater Temperature sensor Temperature transmitter Trace heater Temperature sensor Temperature transmitter Trace heater Temperature sensor Temperature transmitter Trace heater Temperature sensor Temperature transmitter Trace heater Temperature sensor Temperature transmitter Trace heater Temperature sensor Temperature transmitter Differential pressure sensor Bag filter temperature, hopper 2 Bag filter temperature, hopper 2 Wall heating, hopper 3 Bag filter temperature, hopper 3 Bag filter temperature, hopper 3 Wall heating, hopper 4 Bag filter temperature, hopper 4 Bag filter temperature, hopper 4 Wall heating, upper part, chamber 1 Bag filter temperature, upper chamber 1 Bag filter temperature, upper chamber 1 Wall heating, upper part, chamber 2 Bag filter temperature, upper chamber 2 Bag filter temperature, upper chamber 2 Wall heating, upper part, chamber 3 Bag filter temperature, upper chamber 3 Bag filter temperature, upper chamber 3 Wall heating, upper part, chamber 4 Bag filter temperature, upper chamber 4 Bag filter temperature, upper chamber 4 Pressure difference accross the bag filter A-06.03.11-XS1 KY-1104 Cleaning unit A-06.03.11-XI1 A-06.03.11-XI2 A-06.03.11-XI3 A-06.03.12-XS1 KC-1104 KY-1104 PSL-1104 KY-1204 A-06.03.12-XI1 A-06.03.12-XI2 A-06.03.12-XI3 A-06.03.13-XS1 0% 100 % unit SP LL 0 200 °C 110 90 on 0 off 200 on 0 off 200 0 0 0 200 200 200 °C °C °C °C °C 110 110 110 110 110 110 90 90 90 90 90 90 L H HH 140 140 140 140 140 140 140 Sensor type J-type J-type J-type J-type J-type J-type J-type Class Type Connection Connec- Power tion to supply 4...20mA PLC i i IOBus MS PLC 4...20mA i i IOBus MS PLC 4...20mA i i IOBus MS PLC 4...20mA i i IOBus 4...20mA MS PLC i i IOBus MS PLC 4...20mA i i IOBus MS PLC 4...20mA Type D L mm mm Approvals, material, ATEX, IP Transmitte r, Actuator Material Process pipe p I/O for DCS (or PLC) T nom. max (min) nom. kPa(g) kPa(g) °C max max DN PN/ (min) instrum /materia CL ent l °C °C Dig in Dig out An in An out IO bus Barrier on Cleaning unit Cleaning unit Pressure switch Cleaning unit Status, 1= last pulse active, Chamber 1 Mode, 1=forced cleaning on, Chamber 1 Cleaning unit air, low pressure, chamber 1 Remote control, 1= cleaning forces, Chamber 2 off off off off on on on on 1 1 1 KC-1204 KY-1204 PSL-1204 KY-1304 Cleaning unit Cleaning unit Pressure switch Cleaning unit Status, 1= last pulse active, Chamber 2 Mode, 1=forced cleaning on, Chamber 2 Cleaning unit air, low pressure, chamber 2 Remote control, 1= cleaning forced, Chamber 3 off off off off on on on on 1 1 1 A-06.03.13-XI1 A-06.03.13-XI2 A-06.03.13-XI3 A-06.03.14-XS1 KC-1304 KY-1304 PSL-1304 KY-1404 Cleaning unit Cleaning unit Pressure switch Cleaning unit Status, 1= last pulse active, Chamber 3 Mode, 1=forced control on, Chamber 3 Cleaning unit air, low pressure, chamber 3 Remote control, 1= cleaning forced, Chamber 4 off off off off on on on on 1 1 1 A-06.03.14-XI1 A-06.03.14-XI2 A-06.03.14-XI3 M-06.05.01 SS-06.05.01 KC-1404 KY-1404 PSL-1404 M-1102 SSL-1102 Cleaning unit Cleaning unit Pressure switch Electric motor Proximity switch off off off on on on 1 1 1 M-06.05.02 SS-06.05.02 M-1202 SSL-1202 Electric motor Proximity switch M-06.05.03 SS-06.05.03 M-1302 SSL-1302 Electric motor Proximity switch M-06.05.04 SS-06.05.04 M-1402 SSL-1402 Electric motor Proximity switch V-06.05.11 V-06.05.12 V-06.05.13 V-06.05.14 M-06.06.01 M-06.06.02 M-06.06.03 XV-06.07.01 FV-1100 Slide gate Slide gate Slide gate Slide gate Electric motor Electric motor Electric motor Shut-off valve Status, 1= last pulse active, Chamber 4 Mode, 1=forced cleaning on, Chamber 4 Cleaning unit air, low pressure, chamber 4 Airlock feeder of bag filter chamber 1 Airlock feeder of bag filter speed detection, chamber 1 Airlock feeder of bag filter chamber 2 Airlock feeder of bag filter speed detection, chamber 2 Airlock feeder of bag filter chamber 3 Airlock feeder of bag filter speed detection, chamber 3 Airlock feeder of bag filter chamber 4 Airlock feeder of bag filter speed detection, chamber 4 Shut-off above airlock feeder, manual Shut-off above airlock feeder, manual Shut-off above airlock feeder, manual Shut-off above airlock feeder, manual Screw feeder of bag dfilter chamber 1 and 2 Screw feeder of bag dfilter chamber 3 and 4 Bag filter dust screw conveyor common Offgas duct shut-off before bag filter, chamber 1 XV-06.07.01-XI1 XV-06.07.01-XI2 XV-06.07.02 ZSO-1100 ZSC-1100 FV-1200 Limit switch Limit switch Shut-off valve Offgas shutoff valve open status Offgas shutoff valve close status Offgas duct shut-off before bag filter, chamber 2 off off XV-06.07.02-XI1 XV-06.07.02-XI2 XV-06.07.03 ZSO-1200 ZSC-1200 FV-1300 Limit switch Limit switch Shut-off valve Offgas shutoff valve open status Offgas shutoff valve close status Offgas duct shut-off before bag filter, chamber 3 off off XV-06.07.03-XI1 XV-06.07.03-XI2 XV-06.07.04 ZSO-1300 ZSC-1300 FV-1400 Limit switch Limit switch Shut-off valve Offgas shutoff valve open status Offgas shutoff valve close status Offgas duct shut-off before bag filter, chamber 4 off off XV-06.07.04-XI1 XV-06.07.04-XI2 XV-06.07.11 ZSO-1400 ZSC-1400 FV-1108 Limit switch Limit switch Shut-off valve Offgas shutoff valve open status Offgas shutoff valve close status Offgas duct shut-off after bag filter, chamber 1 off off XV-06.07.11-XI1 XV-06.07.11-XI2 XV-06.07.12 ZSO-1108 ZSC-1108 FV-1208 Limit switch Limit switch Shut-off valve Offgas shutoff valve open status Offgas shutoff valve close status Offgas duct shut-off after bag filter, chamber 2 off off XV-06.07.12-XI1 XV-06.07.12-XI2 XV-06.07.13 ZSO-1208 ZSC-1208 FV-1308 Limit switch Limit switch Shut-off valve Offgas shutoff valve open status Offgas shutoff valve close status Offgas duct shut-off after bag filter, chamber 3 off off off on off on off on 1 1 1 1 120IO IOBus 120IO IOBus 120IO IOBus IOBus IOBus K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K 1 1 IOBus F 1 off 120IO HW 1 1 Remote control, 1= cleaning forced, Chamber 1 on K 1 1 kPa off F 1 1 4 IOBus HW 1 1 0 i Cont roller 1 °C PLC Loc. Scope 1 200 i Type 1 integrated in cleaning unit A-6.3 MS PLC thread M18 1 MS PLC HW F K thread M18 1 HW F K MS PLC thread M18 1 HW F K MS PLC thread M18 1 HW F K HW F K removed HW F K removed HW F K HW F K HW F O HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K 1 MS MS MS 1 1 1 1 on on 1 1 1 on on 1 1 1 on on 1 1 1 on on 1 1 1 on on 1 1 1 on on 1 1 1 4/6 Remark 1 0 4…20mA Instrument/ signal Information 27.11.2017 Rev Kumera Tag Customer Tag / (Subcontractor tag) Instrument /signal /device Service Measuring/ operation range Instrument data Process material Signal (automatic column) 0% 100 % on on XV-06.07.13-XI1 XV-06.07.13-XI2 XV-06.07.14 ZSO-1308 ZSC-1308 FV-1408 Limit switch Limit switch Shut-off valve Offgas shutoff valve open status Offgas shutoff valve close status Offgas duct shut-off after bag filter, chamber 4 off off XV-06.07.14-XI1 XV-06.07.14-XI2 TE-06.07.30 ZSO-1408 ZSC-1408 TE-1000 Limit switch Limit switch Temperature sensor Offgas shutoff valve open status Offgas shutoff valve close status Offgas in bag filter inlet off off TE-06.07.32 TE-1004 Temperature sensor Offgas in bag filter outlet M-06.09.01 M-06.09.02 Y-06.10.01 Y-06.10.02 Y-06.10.03 Y-06.10.04 E-07.01.01 G-07.01.05 M-07.01.05 M-07.01.06 MY-1810 MY-1812 VBR-1100 VBR-1200 VBR-1300 VBR-1400 Electric motor Electric motor Vibrator Vibrator Vibrator Vibrator Trace heating (option) Frequency converter Electric motor Electric motor Penthouse vent fan Penthouse vent fan Filter hopper pneumatic vibrator, chamber 1 Filter hopper pneumatic vibrator, chamber 2 Filter hopper pneumatic vibrator, chamber 3 Filter hopper pneumatic vibrator, chamber 4 Offgas line heating Fan for reject dust Fan for reject dust Airlock feeder of dust removal cyclone FE-07.02.01 FE-7201 Flow sensor Flow of the off gas to stack FI-07.02.01 FI-7201 Flow indicatIon FIT-07.02.01 TE-07.02.03 FIT-7201 TE-7203 Flow transmitter Temperature sensor Flow of the output gas from bag filter, DCS display Flow of the exhaust gas after bag filter Offgas temperature after bag filter TT-07.02.03 G-07.03.01 M-07.03.01-SC M-07.03.01 M-07.03.01-TE1 M-07.03.01-TE2 M-07.03.01-TE3 M-07.03.01-XI TT-7203 Temperature transmitter Frequency converter Speed control Electric motor Temperature sensor Temperature sensor Temperature sensor Torque display Offgas temperature after bag filter Exhaust gas fan frequency converter, fan 1 Speed control from DCS Exhaust gas fan motor 1 Offgas fan motor winding, PT100 Offgas fan motor bearing D-end, PT100 Offgas fan motor bearing N-end, PT100 Offgas fan motor load torque M-07.03.01-SI G-07.03.02 M-07.03.02-SC M-07.03.02-XI SI-1700 SC-1800 JI-1800 Speed indication Frequency converter Speed control Torque display M-07.03.02-SI M-07.03.02 M-07.03.02-TE1 M-07.03.02-TE2 M-07.03.02-TE3 TE-07.04.01 TE-07.04.02 XT-07.04.03 XT-07.04.04 TE-07.04.11 TE-07.04.12 XT-07.04.13 XT-07.04.14 XT-07.05.01 PIC-08.01.01 PT-08.01.01 SI-1800 M-1800 TE-1800ABC TE-1816 TE-1818 TE-1700 TE-1702 VT-1700 VT-1702 TE-1800 TE-1802 VT-1800 VT-1802 XT-7501 PIC-8101 PT-8101 LIC-08.01.02 LT-08.01.02 SC-1700 M-1700 TE-1700ABC TE-1716 TE-1718 JI-1700 unit SP LL L H HH Sensor type Class Type Type D L mm mm Approvals, material, ATEX, IP Material p nom. max (min) nom. kPa(g) kPa(g) °C max max DN PN/ (min) instrum /materia CL ent l °C °C Dig in Dig out An in An out IO bus Barrier 1 1 1 1 4...20mA, HART 4...20mA, HART IOBus off off off off 0 0 1000 1000 0 90000 Nm3/h 0 200 °C 0 1500 rpm 70265 10000 115 80000 100 135 150 ultrasonic PT100, 4wire A Exhaust gas fan speed, DCS screen Exhaust gas fan frequency converter, fan 2 Speed control from DCS Offgas fan motor load torque 0 0 0 0 1500 1500 1500 200 rpm rpm rpm % Speed indication Electric motor Temperature sensor Temperature sensor Temperature sensor Temperature sensor Temperature sensor Vibration sensor Vibration sensor Temperature sensor Temperature sensor Vibration sensor Vibration sensor Dust detector Pressure controller Pressure sensor Exhaust gas fan speed, DCS screen Exhaust gas fan motor 2 Offgas fan motor winding, PT100 Offgas fan motor bearing D-end, PT100 Offgas fan motor bearing N-end, PT100 Offgas fan bearing, inboard fan 1 Offgas fan bearing, outboard fan 1 Offgas fan bearing, inboard fan 1 Offgas fan bearing, outboard fan 1 Offgas fan bearing, inboard fan 2 Offgas fan bearing, outboard fan 2 Offgas fan bearing, inboard fan 2 Offgas fan bearing, outboard fan 2 Leak detecting after bag filter Pressure of the steam in flash tank Pressure in condensate tank 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1500 1500 200 200 200 200 200 rpm rpm °C °C °C °C °C LIC-8102 LT-8102 Level controller Pressure sensor Controlling of water level Condensate level in flash tank XY-08.01.02 PSV-08.01.03 XY-8102 PSV-8103 Calculation element Pressure safety valve LS-08.01.06 V-08.01.07 V-08.01.08 G-08.03.01 LSH-8106 140 80 80 70 70 °C °C 70 70 F K HW M K HW F K SW D - HW F K HW F K HW F K HW M O SW D - HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K D - welded +2 -1/ +4 110 110 150 150 125 150 1 ?1000 1 1 1 K/O F K thread G1/2" 9 580 AISI 316 headmounted Air (wet) +0.1 -0.1 / +0.1 1 1 1 1 1 i PLC i i i SW D - i i SW D - i FC FC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K HW F K SW D - HW F K SW D - HW F K SW D - HW F K HW F K - F K - F K HW M O HW F K HW F K SW D - SW D - HW M O HW F K HW F K SW D - SW D - - F K HW F K - F K 4...20mA 4...20mA 4...20mA 4...20mA 600 kPa(g) 30 480 4…20mA HART Calculation of water level in tank Safety valve of flash tank 0 3 550 0.2 2,8 kPa(g) Level switch Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Frequency converter High level of condensate tank Shut-off valve for pressure transmitter Shut-off valve for pressure transmitter Pumping of water from condensate tank, pump 1 on M-08.03.01 Electric motor Pumping of water from condensate tank, pump 1 M-08.03.01-E M-08.03.01-XS M-08.03.01-SC M-08.03.01-SI G-08.03.02 Space heater Frequency converter Frequency converter Frequency converter Frequency converter Pump motor space heating Commands for ondensate pump 1, start/stop Speed reference to pump 1 Condensate pump torque, pump 1 Pumping of water from condensate tank, pump 2 M-08.03.02 Electric motor Pumping of water from condensate tank, pump 2 M-08.03.02-E M-08.03.02-XS M-08.03.02-SC M-08.03.02-SI V-08.03.10 FS-08.03.11 V-08.03.12 V-08.03.13 Space heater Frequency converter Frequency converter Frequency converter Shut-off valve Flow switch Shut-off valve One direction valve Pump motor space heating Commands for ondensate pump 2, start/stop Speed reference to pump 2 Condensate pump torque, pump 2 Condensate pump line shut-off valve Detection of dry running of pump 1 Condensate pump line shut-off valve, drain Condensate pump line non-return valve PFC 120Vac weld-in 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 air (wet) 500 1-1/2" 316L condensate /steam, max 300 500 144 160 150 - 150 1 PLC flange 1-1/2" 316L condensate /steam, max 300 500 144 160 150 - 150 1 - flange 8" / 10" condensate /steam 300 500 144 170 8"/10" 150 flange 1-1/2" 1-1/2" 1-1/2" condensate 300 500 500 500 144 170 160 160 150 150 150 IObus i FC - 1 flange PLC PLC - 1100 HW dusty air concentrate dust Air, 40% H2O, nom.point - 0 rpm K M 4…20mA HART 3000 M D 480 1000 O HW 1 HW 30 m3/h / head 60m F SW kPa(g) 50 K HW 1 1 4...20mA vibration F i 600 off K HW i 0 1,5 41700 kg/h F 1 4...20mA m K HW SW PT100 triboelectric F 1 1 1 1 i 4...20mA % K HW - i PT100 90 90 F PT100 4...20mA 200 200 K HW PLC i FC FC PLC PLC 4...20mA 0 0 K M IObus IObus 155 100 100 90 90 M HW 1 1 PLC IObus Tn= 1200 Nm K 4…20mA HART PT100 Tn= 1200 Nm K F HW i loop IObus 155 100 100 F HW K i i 140 80 80 HW F i i rpm °C °C °C % K HW - i Nm3/h kg/h F 1 i IObus K HW PLC i - K F K 120Vac 120Vac F HW F PLC 120Vac HW 120Vac flange flange 300 AISI 316 condensate condensate - 1 1 flange 3" / 2" condensate 300 500 144 170 3" 150 MCC - 2980 1 H 50 1000 3000 m3/h / head 60m rpm 1100 IObus PLC i FC 1 flange 3" / 2" condensate 300 500 144 170 3" 150 MCC - 2980 1 H 120IO - 5/6 PLC 27.11.2017 flange 120Vac thread condensate G1/2" condensate flange condensate flange condensate 300 500 600 500 1000 144 160 170 160 160 6" 6" 1" 3" 150 150 150 150 1 Remark Rev Cont roller HW 4...20mA 120Vac Loc. Scope 1 IOBus 120Vac on on on on Type PLC MS MS PLC PLC PLC PLC PLC FC MS IOBus Instrument/ signal Information T on on 1500 200 200 200 200 FS-8311 Connec- Power tion to supply Transmitte r, Actuator I/O for DCS (or PLC) 1 0 0 0 0 0 SC-8301 SI-8301 Connection Process pipe H 1) H Duct: Din=?1000, s=?8, ins.thi. 100, mat ?ASTM A36, vertical D Kumera Tag Customer Tag / (Subcontractor tag) Instrument /signal /device Service Measuring/ operation range Instrument data Process material Signal (automatic column) V-08.03.14 V-08.03.20 FS-08.03.21 V-08.03.22 V-08.03.23 V-08.03.24 PI-08.03.30 0% FS-8321 Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Flow switch Shut-off valve One direction valve Condensate pump line shut-off valve Mechanical pressure meter V-08.03.30 Gauge valve V-08.03.31 V-08.03.32 One direction valve Shut-off valve V-08.03.34 V-08.03.35 E-08.03.40 E-08.03.41 PV-08.05.01 Shut-off valve Shut-off valve Heater Heater Control valve PV-8501 unit SP LL L H HH Sensor type Class Type - Condensate pump line shut-off valve Condensate pump line shut-off valve Detection of dry running of pump 2 Condensate pump line shut-off valve, drain Condensate pump line non-return valve Shut-off valve Pressure meter PI-8330 100 % 120IO - Connection Connec- Power tion to supply PLC - - - Shut-off valve for pressure meter - Condensate line non-return valve Condensate pump line shut-off valve, condensate out condensate draining from pump unit condensate draining from pump unit Trace heating of pump pipe branch 1 Trace heating of pump pipe branch 1 Output steam flow from flash tank. - 0 1.0 MPa(g) - 0 7000 kg/h 6600 4...20mA, HART 120Vac Type D L mm mm Approvals, material, ATEX, IP Transmitte r, Actuator Material flange condensate flange condensate thread condensate G1/2" flange condensate flange condensate flange condensate Process pipe p Instrument/ signal Information T nom. max (min) nom. kPa(g) kPa(g) °C 300 I/O for DCS (or PLC) 1000 500 600 500 1000 1000 500 144 max max DN PN/ (min) instrum /materia CL ent l °C °C Dig in Dig out An in An out IO bus Barrier Type Loc. Scope - F K HW F K - F K Remark Rev Cont roller 160 160 170 160 160 3" 6" 6" 1" 3" 150 150 150 150 150 160 170 3" 3" 150 150 HW F K 3" 150 - F K 1 impulse pipe, thread G1/2" condensate - impulse pipe, thread G1/2" condensate 500 170 - ? condensate 160 160 3" 3" 150 150 F K condensate 1000 1000 - ? - F K - ? condensate 160 160 1" 1" 150 150 F K condensate 500 500 - ? HW F K HW F O HW F O 1 HW F K 1 HW F O K 1 HW F O K SW D O PLC flange 6" pneumatic, ASME FO Section VIII, steam, 300 300 600 144 144 170 120 8" 150 div.1 ed. 2013 PV-08.05.01-XI LV-08.10.01-A ZT-8501 LV-8102A Control valve Control valve Valve position feedback Controlling of condensate flow from flash tank LV-08.10.01-B LV-8102B Control valve LIC-08.11.01 Level controller Controlling of condensate flow from flash tank, stand-by Level control of condensate tank LT-08.11.01 G-29.01.01 Level measurement Electric supply Condensate level in condensate tank Plant electrical supply to dryer, status, 1= normal G-29.01.02 Electric supply Plant electrical supply to dryer, reserve power active 1 0 100 % 0 100 % -.. 57 Notes: 1) If trace heating will be installed, connection to DCS shall be defined separately 6/6 27.11.2017 20 49 5 49 4 level controller in customer's system