tabla de derivadas derivadas de operaciones con funciones
Anuncio
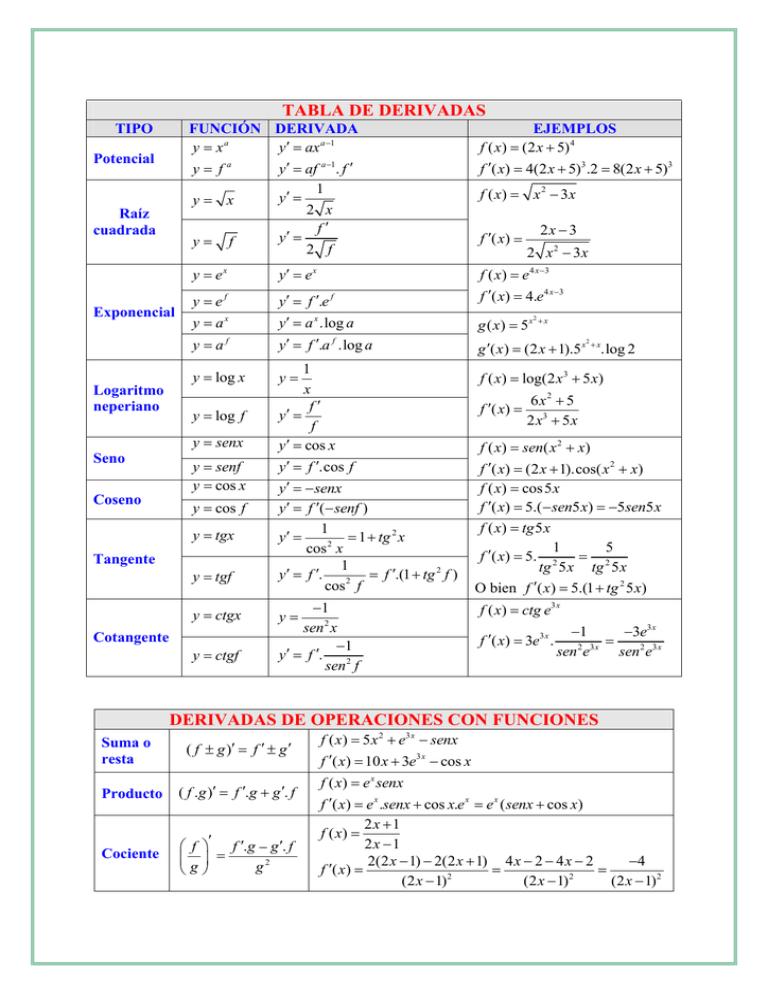
TABLA DE DERIVADAS TIPO FUNCIÓN DERIVADA y = xa y′ = ax a −1 y= fa y′ = af a −1. f ′ 1 y′ = y= x 2 x f′ y′ = y= f 2 f Potencial Raíz cuadrada Exponencial Logaritmo neperiano Seno Coseno EJEMPLOS f ( x) = (2 x + 5) 4 f ′( x) = 4(2 x + 5)3 .2 = 8(2 x + 5)3 f ( x) = x 2 − 3x f ′( x) = 2x − 3 2 x 2 − 3x y = ex y′ = e x y = ef y = ax y′ = f ′.e f y′ = a x .log a g ( x) = 5x y = af y′ = f ′.a f .log a g ′( x) = (2 x + 1).5 x + x.log 2 y = log x 1 x f′ y′ = f y′ = cos x y′ = f ′.cos f y′ = − senx y′ = f ′(− senf ) 1 y′ = = 1 + tg 2 x 2 cos x 1 y′ = f ′. = f ′.(1 + tg 2 f ) 2 cos f y = log f y = senx y = senf y = cos x y = cos f y = tgx Tangente y = tgf y = ctgx Cotangente y = ctgf y= −1 sen 2 x −1 y′ = f ′. sen 2 f y= f ( x ) = e 4 x −3 f ′( x) = 4.e 4 x −3 2 +x 2 f ( x) = log(2 x 3 + 5 x) f ′( x) = 6 x2 + 5 2 x3 + 5 x f ( x) = sen( x 2 + x) f ′( x) = (2 x + 1).cos( x 2 + x) f ( x) = cos 5 x f ′( x) = 5.(− sen5 x) = −5sen5 x f ( x) = tg 5 x 1 5 f ′( x) = 5. 2 = 2 tg 5 x tg 5 x O bien f ′( x) = 5.(1 + tg 2 5 x) f ( x) = ctg e3 x f ′( x) = 3e3 x . −1 −3e3 x = sen 2 e3 x sen 2 e3 x DERIVADAS DE OPERACIONES CON FUNCIONES Suma o resta ( f ± g )′ = f ′ ± g ′ Producto ( f .g )′ = f ′.g + g ′. f Cociente f ′ f ′.g − g ′. f = g2 g f ( x) = 5 x 2 + e3 x − senx f ′( x) = 10 x + 3e3 x − cos x f ( x) = e x senx f ′( x) = e x .senx + cos x.e x = e x ( senx + cos x) 2x +1 f ( x) = 2x −1 2(2 x − 1) − 2(2 x + 1) 4 x − 2 − 4 x − 2 −4 = = f ′( x) = 2 2 (2 x − 1) (2 x − 1) (2 x − 1) 2
