Ejercicios Planteados
Anuncio

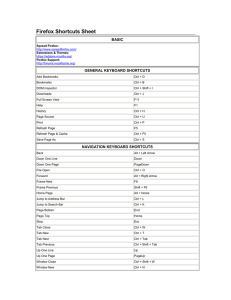
Programación Gráfica de Altas Prestaciones Ejercicio práctico 15/04/2015 Documents at your the corresponding account in hgpu.ugr.es You will find the following folder in your home folder: advection1d_code and the following files in this folder: advection1d.cu and Makefile. File advection1d.cu contains C+ CUDA C code of a linear advection solver. It includes the following: 1) The declaration of two kernels to perform the FD update (FD_kernel1 and FD_kernel2). 2) A GPU version of the solver (based on FD_kernel1). 3) A CPU version of the solver 4) Code to check the performance and accuracy. File Makefile is used to automatically compile and link the source code to generate the executable file (advection1d). Generating the executable file and executing the solver The Makefile will be activated by executing the make command in the terminal which generates a call to nvcc with the suitable choices and argumnents: > make nvcc -O3 -m64 -gencode arch=compute_35,code=sm_35 advection1d.cu -o advection1d Once we have built the executable file (advection1d), we can execute it by writing: ./advection1d ASSIGNMENTS FOR THE PARTICIPANTS These assignments involves to modify the file advection1d.cu. Therefore, it is recommendable to copy the filename with a different name to avoid the loss of information. So for example, we could copy the original file using another name with: > cp advectiontion1d.cu advectiontion1d_orig.cuand later perform modifications on advectiontion1d.cu. The work performed (1) Run the linear advection CUDA solver by varying the number of mesh points (the actual number of mesh points is n+1 where n is an integer variable) and the BLOCKSIZE (currently is 256 but you could test with 64, 128, 512, 1024,...). The goal is to study how these parameters affects the solver performance and to obtain conclusions. (2) In the linear advection CUDA solver, each thread just computes one value of the new vector state d_phi_new (see FD_kernel1 definition). Modify the definition of the kernel FD_kernel1 (global memory version of the FD Update) and the kernel launch in the file advection1d.cu, in order to impose that each CUDA thread computes two contiguous point values for the new state vector d_phi_new. (3) Modify the advectiontion1d.cu file to use the tiled version of the linear advection CUDA solver. The definition of the tiled kernel is included in the file ( kernel FD_kernel2). Study how is the solver performance affected by the new kernel and give your conclusions. The conclusions obtained from points (1) and (3) and the kernel Description obtained in (2) must be sent to jmmantas@ugr.es. Guía rápida de emacs Alterando el texto Ctrl k – kill, “mata” el texto. Esto implica que lo borra, pero lo mantiene guardado y puede ser recuperado con Ctrl Y. Ctrl y – “Yanks text”, pega el texto matado o cortado/copiado con w. Guardar y salir Ctrl x Ctrl s – Guardar un archivo Ctrl X Ctrl C – Salir de Emacs (pregunta si no has guardado) Ctrl S – Buscar strings incrementalmente (con Ctrl S sigo buscando hacia adelante, con Ctrl R busco hacia atrás y con enter termino la busqueda) Mover por páginas Ctrl v – (siguiente) Alt v – (anterior) Ctrl l – Limpiar la pantalla y volver a mostrar todo el texto, moviendo el texto alrededor del cursor al centro de la pantalla. Moverse entre el texto Ctrl n – Moverse a la siguiente línea Ctrl p – Moverse a la línea anterior Ctrl a – Moverse al comienzo de una línea Ctrl e – Moverse al final de una línea Alt a – Moverse al inicio de una oración Alt e – Moverse al final de una oración