Unit 4: Recursos - Colegio Villa Fátima
Anuncio

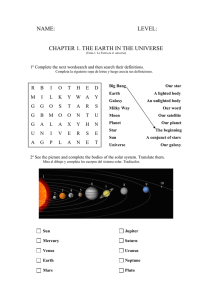
CONOCIMIENTO DEL MEDIO, TERCERO DE PRIMARIA RECURSOS Diccionario online: www.wordreference.com http://www.kidsastronomy.com/fun/make-a-solar-system.htm (juego para crear el sistema solar) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tNlhqPz5-Kw (canción de los planetas) http://www.macmillanelt.es/fileadmin/user_upload/Activities/Activities_ downloadables/Science_The_Solar_system_Worksheet.pdf Fichas escaneadas de refuerzo y ampliación TEMA 4: EL SISTEMA SOLAR Contenidos El universo y las galaxias. Los planetas que forman el Sistema Solar. Los movimientos de la Tierra: rotación y traslación. La Luna y las fases lunares. Los cuatro puntos cardinales. OBJETIVOS Identificar las características del universo Conocer los cuerpos que forman el Sistema Solar Reconocer los movimientos de la Tierra Identificar las fases lunares Utilizar la brújula y los mapas LÉXICO MÁS IMPORTANTE DE LA UNIDAD Solar system The planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune celestial body Galaxy is a group of stars, planets, gas and dust To orbit astronomers astronauts elliptical/spiral/irregular galaxy Milky Way Stars are self-luminous asteroids Asteroid belt The Earth rotates on its axis One rotation takes 24 hours Earth's rotation causes day and night Revolution: Earth orbits arount the Sun. The revolution takes approximately 365 days / a year Seasons: Winter, Spring, Summer, Autumn Northern Hemisphere Southern Hemisphere Satellites Phases of the Moon: New Moon, Full Moon, Waxing Moon, Waning Moon Compass: north, south, east, west Map Más abajo se encuentran las actividades, sus repuestas y la información del libro más importante que vamos trabajando en clase, junto con la página donde están y su traducción. UNIDAD 4: EL SISTEMA SOLAR Page 42 How many planets are there in the Solar System? Eight Can you name them? Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Does the Moon always look the same? No What does the moon orbit? The earth ¿Cuántos planetas tiene el Sistema Solar? Ocho ¿Puedes nombrarlos? Mercurio, Venus, Tierra, Marte, Júpiter, Saturno, Urano, Neptuno ¿Tiene la Luna siempre el mismo aspecto? No What instruments do we use to study the celestial bodies? Telescopes ¿Alrededor de qué cuerpo traza la Luna su órbita? De la Tierra What causes day and night? The Earth's rotation ¿Qué instrumentos usamos para estudiar los cuerpos celestes? Los telescopios ¿Qué causa el día y la noche? La rotación de la Tierra. Página 43 1 Listen and point Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Página 43 1 Escucha y señala Mercurio, Venus, Tierra, Marte, Júpiter, Saturno, Urano, Neptuno 2 Read the title of the song and the chorus. What is the song about? About the Solar System 2 Lee el título de la canción y el estribillo. ¿De qué trata la canción? Del Sistema Solar SONG Canción Vivimos en el Sistema Solar, que está en la Vía Láctea. Hay ocho planetas y todos tienen su nombre. EL primer planeta es Mercurio, que está muy cerca del Sol. We live in the Solar System. That's in the Milky Way. There are eight planets. And they all have a name. The first planet is Mercury And it's very near the Sun. Then comes Venus. Come on everyone! After the Earth, well, Mars comes next. Then it's Jupiter. Do you know the rest? Chorus Saturn is a big planet, you know it by its rings. Then comes Uranus with Neptune following. Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. Jupiter, Saturn and Uranus, too. Después viene Venus, venga todo el mundo! A continuación la Tierra, y Marte el siguiente. Después está Júpiter, ¿te sabes los demás? Estribillo Saturno es un planeta grande, lo reconocerás por sus anillos. Después viene Urano, y el siguiente Neptuno. Mercurio, Venus, Tierra y Marte. Júpiter, Saturno y Urano. Y finalmente, tenemos Neptuno. Estribillo And last of all we have Neptune! Chorus Page 45 How many galaxies are there in the universe? Billions The universe The universe is an enormous open space that contains the galaxies and all the celestial bodies. There are billions of galaxies in the universe. The universe is constantly expanding. Página 45 ¿Cuántas galaxias hay en el universo? Miles de millones El universo El universo es un enorme espacio abierto que contiene galaxias y los cuerpos celestiales. Hay miles de millones de galaxias en el universo. EL universo está en constante expansión. ¿Hay algo más grande que el universo? No Is there anything bigger than the universe? No Galaxies A galaxy is a group of stars, plantes, gas and dust that orbits a star. There are billions of stars in one galaxy. Scientists who study galaxies, stars and planets are called astronomers. What is an astronaut?a person who Galaxias Una galaxia es un grupo de estrellas, planetas, gas y polvo, que describe una órbita alrededor de una estrella. A los científicos que estudian las galaxias, las estrellas y los planetas se les llama astrónomos. travels in a space craft ¿Qué es un astronauta? Una persona que viaja en una nave espacial There are three different types of galaxies: an elliptical galaxy, a spiral galaxy, an irregular galaxy Hay tres tipos de galaxia diferentes: galaxia elíptica, galaxia espiral y galaxia irregular. The Milky Way La Vía Láctea Nuestra galaxia se llama la Vía Láctea. La Vía Láctea contiene millones de estrellas. La más importante para nosotros es el Sol. Podemos ver la Vía Láctea desde la Tierra. Mira hacia el cielo una noche clara. Verás muchas luces, como las de la foto. Se trata de la Vía Láctea. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way. The Milky way contains billions of stars. The most important star for us is the Sun. We can see the Milky Way from the Earth. Look up into the sky on a clear dark night. You will see a lot of lights across the sky, like th eones in the photo. That's the Milky Way. 4 Ordena estos términos de pequeño a grande: estrella, galaxia, universo 4 Order these terms from the smallest to the largest: star-galaxy-universe Página 46 The Solar System Our Solar Sytem consists of the Sun, eight planets, more than 130 planetary satellites, like the Moon, comets and asteroids. Stars Stars are self-luminous objects. Stars shine because they release energy produced by nuclear reactions at their core. Planets Planets are large objects that move around a star. There are eight planets in the Solar System. All the planets in the Solar System orbit the sun. 2 Look at the picture of the Solar System. Can you find the orbits of the planets? What shapes do they have? Elliptical Página 46: El Sistema Solar Nuestro Sistema Solar está formado por el Sol, ocho planetas, más de 130 satélites planetarios, como la Luna, cometas y asteroides. Estrellas Las estrellas son cuerpos con luz propia. Éstas brillan al liberar energía producida por las reacciones nucleares en sus núcleos. Planetas Son cuerpos grandes que se mueven alrededor de una estrella. Hay ocho planetas en el Sistema Solar. Todos los planetas describen una órbita alrededor del sol. 2 Observa la ilustración del Sistema Solar. ¿Puedes encontrar las órbitas de Asteroids los planetas? ¿Qué forma tienen? Elíptica Asteroids are large rocks. There are lots Asteroides of asteroids in the Asteroid Belt between Los asteroides son rocas muy grandes. the orbit of Mars and Jupiter. Hay muchos asteroides en el Cinturón de asteroides, situado entre la órbita de Marte y Júpiter. 3 Look at the Solar System. Can you identify the Asteroid Belt? Página 47 The Earth's rotation 1 Order the eight plantes in the Solar System. Begin with Mercury, the planet nearest the Sun. Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. The Earth's rotation The Earth rotates on its axis. This movement is the Earth's rotation. One rotation takes 24 hours. We call this a mean solar day. 2 How long does it take the Earth to complete one rotation? 24 hours 3 Observa el Sistema Solar. ¿Puedes identificar el Cinturón de Asteroides? Página 47 La rotación de la Tierra 1 Ordena los ocho planetas del Sistema Solar. Empieza con Mercurio, el planeta más cercano al Sol. Mercurio, Venus, Tierra, Marte, Júpiter, Saturno, Urano, Neptuno. La rotación de la Tierra La Tierra rota sobre su propio eje. Este movimiento se llama rotación. Una rotación dura 24 horas. Lo llamamos un día solar medio. 2 ¿Cuánto tarda la Tierra en completar una rotación? 24 horas Día y noche La rotación de la Tierra produce el día y The rotation of the Earth causes day and la noche. La Tierra completa una rotación night. The Earth completes one rotation sobre su eje cada 24 horas. Cuando on its axis every 24 hours. When we are nuestra parte de la Tierra se encuentra facing the Sun our side of the Earth is de cara al Sol, entonces está iluminada y illuminated and we experience daytime. por eso es de día. Cuando en cambio, When we are facing away from the Sun, it estamos de espaldas al sol, dicha parte de is dark and we experience night-time. la Tierra está oscura y por tanto es de noche. Day and night 4 Complete the sentences. Use the words 4 Completa las frases. Usa las palabras from the box ( planets, rotation, stars, del recuadro (planetas, rotación, the Sun) a. Planets are large objects that orbit the Sun. b. When the Earth rotates on its axis this is called the Earth's rotation. cThe Sun is the most important star in our Solar System. d. Stars are self-luminous objects. estrellas, Sol) Los planetas son objetos grandes que describen su órbita alrededor del Sol. Cuando la Tierra rota sobre su propio eje, este movimiento se llama la rotación de la Tierra. El Sol es la estrella más importante de nuestro Sistema Solar. Las estrellas son cuerpos con luz propia. Página 48 The Earth's revolution 1 What causes day and night? The Earth's rotation. Revolution The Earth orbits around the Sun. This movement is called revolution. The Earth's revolution takes approximately 365 days. The Earth's orbit around the Sun is elliptical. 2 How long does it take the Earth to complete one cycle around the Sun? Can you think of another term for this period? Approximately 365 days/ year 3 Does every year have 365 days? No, leap years have 366 days. The Seasons The seasons are the result of the incline of the Earth's axis. This incline means that different parts of Earth receive Página 48 La traslación de la Tierra 1 ¿Qué causa el día y la noche? La rotación de la Tierra. Traslación La Tierra tiene su órbita alrededor del Sol. Este movimiento se llama traslación. La traslación de la Tierra es de aproximadamente 365 días., La órbita de la Tierra alrededor del Sol es elíptica. 2 ¿Cuánto tarda la Tierra en completar un ciclo alrededor del Sol? ¿ Hay otro término para este periodo? Aproximadamente 365 días/ Año 3 ¿Tienen todos los años 365 días? No, los años bisiestos tienen 366 días. Las estaciones Las estaciones son el resultado de la inclinación de la Tierra sobre su eje. Esta inclinación significa que diferentes partes de la Tierra reciben diferentes cantidades de luz y de calor. different amount of sunlight and heat. When it is summer in the Southern Hemisphere it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere because the Southern Hemisphere is looking at the Sun. The Earth orbits the Sun constantly, so after some time the Northern Hemisphere looks at the Sun and enjoys the summer. Cuando es verano en el hemisferio sur, es inverno en el hemisferio norte porque el hemisferio sur está mirando hacia el Sol. La Tierra está en constante movimiento alrededor del Sol, así que después de un tiempo, el hemisferio Norte se encuentra mirando hacia el Sol, por lo que disfruta del verano. At the same time it is winter in the Southern Hemisphere. Entonces, es inverno en el hemisferio sur. Página 49 Página 49 La Luna 1 ¿Qué causa las estaciones? La traslación de la Tierra The Moon 1 What causes the seasons? The Earth's revolution Satellites The Moon is the only natural satellite that orbits the Earth. A satellite is an object that revolves around another object. 2 What type of celestial body is the Moon? A satellite Phases of the Moon New Moon The dark side of the Moon faces the Earth, the Sun doesn't illuminate the Moon, so we do not see the Moon in this phase. Full Moon Satélites La luna es el único satélite natural cuya órbita es alrededor de la Tierra. Un satélite es un cuerpo que se mueve alrededor de otro objeto. 2 ¿Qué tipo de cuerpo celeste es la Luna? Un satélite. Fases de la Luna Luna nueva La parte oscura de la Luna está enfocada hacia la Tierra, el Sol no la ilumina, por lo que no vemos a la Luna en esta fase. The Moon's illuminated side is facing the Luna llena Earth. The Moon is completely illuminated by direct sunlight. La parte iluminada de la Luna está de cara a la Tierra. La Luna está completamente Waxing Moon iluminada por la luz directa del Sol. The fraction of the Moon that is illuminated is growing. Luna creciente Waning Moon The fraction of the Moon that is illuminated is reducing. La fracción de la Luna que está iluminada va en aumento. Luna menguante La fracción de la Luna que está iluminada va en disminución. 3 Look at the phases of the Moon again and listen. Which phase or phases of the Moon are being described? Full Moon, New Moon, Waxing Moon or Waning Moon. 3 Observa las fases de la Luna y escucha. ¿Qué fase o fases de la Luna se 4 Correct the sentences. describen? Luna llena, luna nueva, luna A When there is a New Moon the part of creciente, luna menguante. the Moon that faces the Earth is illuminated. (Full) 4 Corrige las frases: B The Sun-->Earth orbits around the Earth--> Sun Cuando hay luna nueva la parte de la Luna que mira hacia la Tierra está iluminada C The Moon is an artificial satellite of (llena) the Earth (natural) EL Sol-->Tierra tiene su órbita alrededor de la Tierra-->Sol La Luna es un satélite artificial -->natural de la >Tierra Página 50 The four compass points Página 50 Los cuatro puntos cardinales 1 What are the four phases of the Moon? 1 ¿Cuáles son las cuatro fases de la luna? New Moon, Waxing Moon, Full Moon, Waning Moon. Una brújula A compass Los cuatro puntos cardinales son: Norte, The four compass points are: north, east, Este, Sur, Oeste. Usamos los puntos south and west. We use the compass points to navigate and to read maps. cardinales para navegar e interpretar mapas. Maps Mapas Los mapas son representaciones de la Tierra. Son también dibujos de lugares. Cada tipo de mapa nos indica un tipo de información diferente. Maps are representations of the Earth. They are also pictures ofplaces. Different maps show different information. 2 ¿Qué información podemos extraer de 2 What information can we find in these estos mapas? Mapa del metro- mapa de maps? Metro map- information about the las paradas Underground stations. Mapa de España- ríos, lagos y montañas Map of Spain- rivers, lakes and mountains de España Mapa de Europa- los países y sus in Spain. fronteras. Map of Europe- countries and their borders. 4 ¿Dónde se encuentra el lugar donde vivies? En el este de España 4 Where is the place you live located? In Información de los mapas the east Information on maps Hay tres elementos que pueden ayudarnos There are three elements that help us to a interpretar los mapas. read maps. La leyenda: nos muestra lo que The key shows what the different representan los símbolos del mapa. symbols represent. The scale shows the relationship between La escala: nos muestra la relación entre el the size of something on the map and its tamaño de algo en el mapa y su tamaño real size. real. The North arrow shows the direction of north. 5 Find these things on the map above: park, scale, school, North arrow, key La flecha Norte: nos muestra la dirección del Norte. 5 Encuentra en el mapa: un parque, la escala, escuela, flecha Norte, la leyenda