Gramática—resumen - Warren County Public Schools
Anuncio

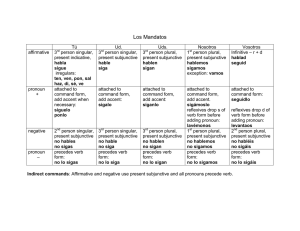
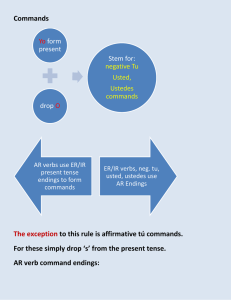
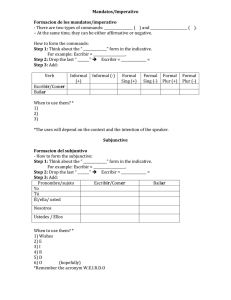
Page 1 of 12 Gramática—resumen GRAMÁTICA —RESUMEN Grammar Terms Adjective (pp. 7, 304, 413): a word that describes a noun Interrogative (p. 13): a word that asks a question Adverb (p. 212): a word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb Noun (p. 7): a word that names a person, an animal, a place, or a thing Command (pp. 188, 190, 208, 210, 338): a verb form used to tell someone to do something Number (p. 7): a term that categorizes a noun or pronoun as singular or plural Comparative (p. 304): a phrase that compares two different things Possessive (p. 112): an adjective or a pronoun that tells to whom the noun it describes belongs Conditional Tense (pp. 380, 454): a verb form that indicates that the action in a sentence could happen at a future time Preposition (pp. 336, 360, 378): a word that shows the relationship between its object and another word in the sentence Demonstrative (p. 84): an adjective or a pronoun that points out someone or something Direct Object (pp. 156, 158, 161, 186): a noun or pronoun that receives the action of the main verb in a sentence Future Tense (pp. 334, 356, 452): a verb form that indicates that the action in a sentence will happen in the future Present Perfect Tense (pp. 432, 435): a verb form that indicates that the action in a sentence has been done in the past Present Tense (pp. 17, 60, 408): a verb form that indicates that the action in a sentence is happening now Gender (p. 7): a term that categorizes a noun or pronoun as masculine or feminine Preterite Tense (pp. 38, 40, 42, 63, 86, 137, 430): a verb form that indicates that the action in a sentence happened at a particular time in the past Imperfect Tense (pp. 116, 137, 430): a verb form that indicates that an action in a sentence happened over an extended period of time or repeatedly in the past Progressive Tenses (pp. 135, 408): compound present and past tenses that indicate action going on at the time of the sentence Impersonal se (p. 411): the pronoun se used when the subject’s identity is not important Pronoun (pp. 156, 158, 161, 186, 190): a word that takes the place of a noun Indirect Object (pp. 158, 161, 186): a noun or pronoun that tells to whom/what or for whom/what the action in a sentence is done Reflexive Pronoun (p. 114): a pronoun that is used with reflexive verbs Infinitive (pp. 5, 286): the basic form of a verb, ending in -ar, -er, or -ir R24 RECURSOS Gramática—resumen Reflexive Verb (p. 114): a verb of which the subject receives the action Page 2 of 12 Subject (p. 10): the noun, pronoun, or noun phrase in a sentence that tells whom or what the sentence is about Verb (p. 9): a word that expresses action or a state of being Subjunctive Mood (pp. 232, 260, 263, 282, 284, 286, 306, 309): a form that indicates that a sentence expresses an opinion, a hope or wish, doubt, or emotion Superlative (p. 304): a phrase that describes which item has the most or least of a quality Nouns, Articles, and Pronouns Nouns Singular Nouns Plural Nouns Masculine Feminine Masculine Feminine amigo chico hombre suéter zapato amiga chica mujer blusa falda amigos chicos hombres suéteres zapatos amigas chicas mujeres blusas faldas To make a noun plural, add -s to a word ending in a vowel and -es to a word ending in a consonant. Articles Articles identify the class of a noun: masculine or feminine, singular or plural. Definite articles are the equivalent of the English word the. Indefinite articles are the equivalent of a, an, or some. Definite Articles Singular Plural Masculine Feminine el amigo los amigos la amiga las amigas Indefinite Articles Singular Plural Masculine Feminine un amigo unos amigos una amiga unas amigas RECURSOS Gramática—resumen R25 GRAMÁTICA–RESUMEN Nouns identify people, animals, places, or things. Spanish nouns are either masculine or feminine. They are also either singular (identifying one thing) or plural (identifying more than one thing). Masculine nouns usually end in -o and feminine nouns usually end in -a. Page 3 of 12 Nouns, Articles, and Pronouns cont. Pronouns A pronoun takes the place of a noun. The choice of pronoun is determined by how it is used in the sentence. Direct Object Pronouns me te lo, la nos os los, las yo tú usted él, ella Indirect Object Pronouns me te le Pronouns Used After \Prepositions Subject Pronouns nos os les nosotros(as) vosotros(as) ustedes ellos(as) Reflexive Pronouns me te se nos os se de mí de ti de usted de él, de ella de nosotros(as) de vosotros(as) de ustedes de ellos(as) Demonstrative Pronouns éste(a), esto ése(a), eso aquél(la), aquello éstos(as) ésos(as) aquéllos(as) GRAMÁTICA–RESUMEN Adjectives Adjectives describe nouns. In Spanish, adjectives must match the number and gender of the nouns they describe. When an adjective describes a group containing both genders, the masculine form is used. To make an adjective plural, apply the same rules that are used for making a noun plural. Most adjectives are placed after the noun. R26 Adjectives Singular Plural RECURSOS Gramática—resumen Masculine Feminine el chico guapo el chico paciente el chico fenomenal el chico trabajador los chicos guapos los chicos pacientes los chicos fenomenales los chicos trabajadores la chica guapa la chica paciente la chica fenomenal la chica trabajadora las chicas guapas las chicas pacientes las chicas fenomenales las chicas trabajadoras Page 4 of 12 Adjectives cont. Sometimes adjectives are placed before the noun and shortened. Grande is shortened before any singular noun. Several others are shortened before a masculine singular noun. Possessive adjectives identify to whom something belongs. They agree in gender and number with the noun possessed, not with the person who possesses it. Shortened Forms alguno bueno malo ninguno algún chico buen chico mal chico ningún chico primero tercero primer chico tercer chico grande gran chico(a) Possessive Adjectives Masculine Singular Plural mi amigo tu amigo su amigo mis amigos tus amigos sus amigos Feminine nuestro amigo vuestro amigo su amigo nuestros amigos vuestros amigos sus amigos Demonstrative adjectives point out which noun is being referred to. Their English equivalents are this, that, these, and those. mi amiga tu amiga su amiga mis amigas tus amigas sus amigas Demonstrative Adjectives Plural Masculine Feminine este amigo ese amigo aquel amigo estos amigos esos amigos aquellos amigos esta amiga esa amiga aquella amiga estas amigas esas amigas aquellas amigas Interrogatives Interrogatives ¿Adónde? ¿Cómo? ¿Cuál(es)? ¿Cuándo? ¿Cuánto(a)? ¿Cuántos(as)? ¿Dónde? ¿Por qué? ¿Qué? ¿Quién(es)? RECURSOS Gramática—resumen R27 GRAMÁTICA–RESUMEN Singular Interrogative words are used to ask questions. nuestra amiga vuestra amiga su amiga nuestras amigas vuestras amigas sus amigas Page 5 of 12 Comparatives and Superlatives Comparatives Comparatives are used when comparing two different things. Comparatives más () más interesante que… Me gusta correr más que nadar. menos () menos interesante que… Me gusta nadar menos que correr. There are a few irregular comparatives. When talking about people, use mayor and menor. When talking about quality, use mejor and peor. Age Quality mayor menor mejor peor tan(to) () tan interesante como… Me gusta leer tanto como escribir. When talking about numbers, de is used instead of que. más de cien… menos de cien… GRAMÁTICA–RESUMEN Superlatives Superlatives are used to distinguish one item from a group. They describe which item has the most or least of a quality. The ending -ísimo(a) can be added to an adjective to form a superlative. Superlatives Singular Plural Singular Plural Masculine Feminine el chico más alto el chico menos alto los chicos más altos los chicos menos altos la chica más alta la chica menos alta las chicas más altas las chicas menos altas mole buenísimo frijoles buenísimos pasta buenísima enchiladas buenísimas Affirmative and Negative Words Affirmative words are used to talk about something or someone, or to say that an event also or always happens. Negative words are used to refer to no one or nothing, or to say that events do not happen. Remember, to make a sentence negative, you must have no or another negative word before the verb. R28 RECURSOS Gramática—resumen Affirmative Negative algo alguien algún (alguna) alguno(a) siempre también nada nadie ningún (ninguna) ninguno(a) nunca tampoco Page 6 of 12 Adverbs Adjective → Adverb Adverbs modify a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. Many adverbs in Spanish are made by changing an existing adjective. reciente frecuente fácil normal especial feliz cuidadoso(a) rápido(a) lento(a) tranquilo(a) → → → → → → → → → → recientemente frecuentemente fácilmente normalmente especialmente felizmente cuidadosamente rápidamente lentamente tranquilamente Verbs: Regular Verbs Simple Tenses Present Subjunctive Imperfect Preterite Future Conditional Present Commands hablo hablas Infinitive hablar habla Present Participle hablando hablamos Past Participle hablado habláis hablan hablaba hablabas hablaba hablábamos hablabais hablaban hablé hablaste habló hablamos hablasteis hablaron hablaré hablarás hablará hablaremos hablaréis hablarán hablaría hablarías hablaría hablaríamos hablaríais hablarían hable hables hable hablemos habléis hablen habla no hables hable hablemos hablen como comes Infinitive comer come Present Participle comiendo comemos Past Participle comido coméis comen comía comías comía comíamos comíais comían comí comiste comió comimos comisteis comieron comeré comerás comerá comeremos comeréis comerán comería comerías comería comeríamos comeríais comerían coma comas coma comamos comáis coman come no comas coma comamos coman vivía vivías vivía vivíamos vivíais vivían viví viviste vivió vivimos vivisteis vivieron viviré vivirás vivirá viviremos viviréis vivirán viviría vivirías viviría viviríamos viviríais vivirían viva vivas viva vivamos viváis vivan vive no vivas viva vivamos vivan Infinitive vivir Present Participle viviendo Past Participle vivido vivo vives vive vivimos vivís viven Note: The following regular verbs have irregular past participles: abrir→abierto, descubrir→descubierto, escribir→escrito, romper→roto RECURSOS Gramática—resumen R29 GRAMÁTICA–RESUMEN Indicative Page 7 of 12 Verbs: Regular Verbs cont. Compound Tenses Present Perfect he has ha hemos habéis han Present Progressive hablado comido vivido estoy estás está estamos estáis están hablando comiendo viviendo Past Progressive estaba estabas estaba estábamos estabais estaban Stem–Changing Verbs GRAMÁTICA–RESUMEN Infinitive in -ar Present Indicative Present Subjunctive cerrar e→ie cierro cierras cierra cerramos cerráis cierran cierre cierres cierre cerremos cerréis cierren probar o→ue pruebo pruebas prueba probamos probáis prueban pruebe pruebes pruebe probemos probéis prueben jugar u→ue juego juegas juega jugamos jugáis juegan juegue juegues juegue juguemos juguéis jueguen like cerrar: comenzar, despertarse, empezar, merendar, nevar, pensar, recomendar, sentarse like probar: acostarse, almorzar, contar, costar, encontrar(se), mostrar, recordar, volar R30 RECURSOS Gramática—resumen hablando comiendo viviendo Page 8 of 12 Stem–Changing Verbs cont. Infinitive in -er Present Indicative Present Subjunctive perder e →ie pierdo pierdes pierde perdemos perdéis pierden pierda pierdas pierda perdamos perdáis pierdan poder o →ue puedo puedes puede podemos podéis pueden pueda puedas pueda podamos podáis puedan like perder: atender, entender, querer like poder: devolver (past participle: devuelto), doler, llover, mover, resolver (past participle: resuelto), volver (past participle: vuelto) Infinitive in -ir present participle: pidiendo dormir o→ue, u present participle: durmiendo sentir e→ie, i present participle: sintiendo Subjunctive Present Preterite Present pido pides pide pedimos pedís piden pedí pediste pidió pedimos pedisteis pidieron pida pidas pida pidamos pidáis pidan duermo duermes duerme dormimos dormís duermen dormí dormiste durmió dormimos dormisteis durmieron duerma duermas duerma durmamos durmáis duerman siento sientes siente sentimos sentís sienten sentí sentiste sintió sentimos sentisteis sintieron sienta sientas sienta sintamos sintáis sientan GRAMÁTICA–RESUMEN pedir e→i, i Indicative like pedir: competir, conseguir (consigo), despedirse, repetir, seguir (sigo), servir, vestirse like dormir: morir (past participle: muerto) like sentir: divertirse, preferir, requerir, sugerir RECURSOS Gramática—resumen R31 Page 9 of 12 Spell–Changing Verbs buscar cruzar Preterite: busqué, buscaste, buscó, buscamos, buscasteis, buscaron Present Subjunctive: busque, busques, busque, busquemos, busquéis, busquen Preterite: crucé, cruzaste, cruzó, cruzamos, cruzasteis, cruzaron Present Subjunctive: cruce, cruces, cruce, crucemos, crucéis, crucen like buscar: explicar, identificar, marcar, practicar, pescar, sacar, secar(se), tocar like cruzar: almorzar (o →ue), comenzar (e →ie), empezar (e →ie) conducir Present Indicative: conduzco, conduces, conduce, conducimos, conducís, conducen Preterite: conduje, condujiste, condujo, condujimos, condujisteis, condujeron Present Subjunctive: conduzca, conduzcas, conduzca, conduzcamos, conduzcáis, conduzcan GRAMÁTICA–RESUMEN like conducir: producir, reducir, traducir conocer Present Indicative: conozco, conoces, conoce, conocemos, conocéis, conocen Present Subjunctive: conozca, conozcas, conozca, conozcamos, conozcáis, conozcan like conocer: crecer, nacer, ofrecer, pertenecer construir Present Indicative: construyo, construyes, construye, construimos, construís, construyen Preterite: construí, construiste, construyó, construimos, construisteis, construyeron Present Subjunctive: construya, construyas, construya, construyamos, construyáis, construyan Present Participle: construyendo creer Preterite: creí, creíste, creyó, creímos, creísteis, creyeron Present Participle: creyendo Past Participle: creído like creer: leer R32 RECURSOS Gramática—resumen escoger Present Indicative: escojo, escoges, escoge, escogemos, escogéis, escogen Present Subjunctive: escoja, escojas, escoja, escojamos, escojáis, escojan like escoger: proteger esquiar Present Indicative: esquío, esquías, esquía, esquiamos, esquiáis, esquían Present Subjunctive: esquíe, esquíes, esquíe, esquiemos, esquiéis, esquíen llegar Preterite: llegué, llegaste, llegó, llegamos, llegasteis, llegaron Present Subjunctive: llegue, llegues, llegue, lleguemos, lleguéis, lleguen like llegar: apagar, jugar (u → ue), pagar reunir Present Indicative: reúno, reúnes, reúne, reunimos, reunís, reúnen Present Subjunctive: reúna, reúnas, reúna, reunamos, reunáis, reúnan Page 10 of 12 Irregular Verbs andar Preterite: anduve, anduviste, anduvo, anduvimos, anduvisteis, anduvieron caer Present Indicative: caigo, caes, cae, caemos, caéis, caen Preterite: caí, caíste, cayó, caímos, caísteis, cayeron Present Subjunctive: caiga, caigas, caiga, caigamos, caigáis, caigan Present Participle: cayendo Past Participle: caído dar Present Indicative: doy, das, da, damos, dais, dan Preterite: di, diste, dio, dimos, disteis, dieron Present Subjunctive: dé, des, dé, demos, deis, den Present Indicative: digo, dices, dice, decimos, decís, dicen Preterite: dije, dijiste, dijo, dijimos, dijisteis, dijeron Future: diré, dirás, etc. Conditional: diría, dirías, etc. Present Subjunctive: diga, digas, diga, digamos, digáis, digan Commands: di (tú), no digas (neg. tú), diga (Ud.), digamos (nosotros), digan (Uds.) Present Participle: diciendo Past Participle: dicho Present Indicative: he, has, ha, hemos, habéis, han Preterite: hube, hubiste, hubo, hubimos, hubisteis, hubieron Future: habré, habrás, etc. Conditional: habría, habrías, etc. Present Subjunctive: haya, hayas, haya, hayamos, hayáis, hayan hacer Present Indicative: hago, haces, hace, hacemos, hacéis, hacen Preterite: hice, hiciste, hizo, hicimos, hicisteis, hicieron Future: haré, harás, etc. Conditional: haría, harías, etc. Present Subjunctive: haga, hagas, haga, hagamos, hagáis, hagan Commands: haz (tú), no hagas (neg. tú), haga (Ud.), hagamos (nosotros), hagan (Uds.) Past Participle: hecho ir Present Indicative: voy, vas, va, vamos, vais, van Imperfect: iba, ibas, iba, íbamos, ibais, iban Preterite: fui, fuiste, fue, fuimos, fuisteis, fueron Present Subjunctive: vaya, vayas, vaya, vayamos, vayáis, vayan Commands: ve (tú), no vayas (neg. tú), vaya (Ud.), vamos (nosotros), vayan (Uds.) Present Participle: yendo Past Participle: ido estar Present Indicative: estoy, estás, está, estamos, estáis, están Preterite: estuve, estuviste, estuvo, estuvimos, estuvisteis, estuvieron Present Subjunctive: esté, estés, esté, estemos, estéis, estén RECURSOS Gramática—resumen R33 GRAMÁTICA–RESUMEN decir haber Page 11 of 12 Irregular Verbs cont. reír (e→ i, i) oír Present Indicative: oigo, oyes, oye, oímos, oís, oyen Preterite: oí, oíste, oyó, oímos, oísteis, oyeron Present Subjunctive: oiga, oigas, oiga, oigamos, oigáis, oigan Present Participle: oyendo Past Participle: oído Present Indicative: río, ríes, ríe, reímos, reís, ríen Preterite: reí, reíste, rió, reímos, reísteis, rieron Present Subjunctive: ría, rías, ría, riamos, riáis, rían Present Participle: riendo Past Participle: reído like reír: sonreír poder (0→ ue) GRAMÁTICA–RESUMEN Present Indicative: puedo, puedes, puede, podemos, podéis, pueden Preterite: pude, pudiste, pudo, pudimos, pudisteis, pudieron Future: podré, podrás, etc. Conditional: podría, podrías, etc. Present Subjunctive: pueda, puedas, pueda, podamos, podáis, puedan Present Participle: pudiendo poner Present Indicative: pongo, pones, pone, ponemos, ponéis, ponen Preterite: puse, pusiste, puso, pusimos, pusisteis, pusieron Future: pondré, pondrás, etc. Conditional: pondría, pondrías, etc. Present Subjunctive: ponga, pongas, ponga, pongamos, pongáis, pongan Commands: pon (tú), no pongas (neg. tú), ponga (Ud.), pongamos (nosotros), pongan (Uds.) Past Participle: puesto querer (e→ ie) Present Indicative: quiero, quieres, quiere, queremos, queréis, quieren Preterite: quise, quisiste, quiso, quisimos, quisisteis, quisieron Future: querré, querrás, etc. Conditional: querría, querrías, etc. Present Subjunctive: quiera, quieras, quiera, queramos, queráis, quieran R34 RECURSOS Gramática—resumen saber Present Indicative: sé, sabes, sabe, sabemos, sabéis, saben Preterite: supe, supiste, supo, supimos, supisteis, supieron Future: sabré, sabrás, etc. Conditional: sabría, sabrías, etc. Present Subjunctive: sepa, sepas, sepa, sepamos, sepáis, sepan salir Present Indicative: salgo, sales, sale, salimos, salís, salen Future: saldré, saldrás, etc. Conditional: saldría, saldrías, etc. Present Subjunctive: salga, salgas, salga, salgamos, salgáis, salgan Commands: sal (tú), no salgas (neg. tú), salga (Ud.), salgamos (nosotros), salgan (Uds.) ser Present Indicative: soy, eres, es, somos, sois, son Imperfect: era, eras, era, éramos, erais, eran Preterite: fui, fuiste, fue, fuimos, fuisteis, fueron Present Subjunctive: sea, seas, sea, seamos, seáis, sean Commands: sé (tú), no seas (neg. tú), sea (Ud.), seamos (nosotros), sean (Uds.) Page 12 of 12 Irregular Verbs cont. tener Present Indicative: tengo, tienes, tiene, tenemos, tenéis, tienen Preterite: tuve, tuviste, tuvo, tuvimos, tuvisteis, tuvieron Future: tendré, tendrás, etc. Conditional: tendría, tendrías, etc. Present Subjunctive: tenga, tengas, tenga, tengamos, tengáis, tengan Commands: ten (tú), no tengas (neg. tú), tenga (Ud.), tengamos (nosotros), tengan (Uds.) like tener: mantener(se), obtener traer Present Indicative: vengo, vienes, viene, venimos, venís, vienen Preterite: vine, viniste, vino, vinimos, vinisteis, vinieron Future: vendré, vendrás, etc. Conditional: vendría, vendrías, etc. Present Subjunctive: venga, vengas, venga, vengamos, vengáis, vengan Commands: ven (tú), no vengas (neg. tú), venga (Ud.), vengamos (nosotros), vengan (Uds.) Present Participle: viniendo ver Present Indicative: veo, ves, ve, vemos, veis, ven Imperfect: veía, veías, veía, veíamos, veíais, veían Preterite: vi, viste, vio, vimos, visteis, vieron Present Subjunctive: vea, veas, vea, veamos, veáis, vean Past Participle: visto valer Present Indicative: valgo, vales, vale, valemos, valéis, valen Future: valdré, valdrás, etc. Conditional: valdría, valdrías, etc. Present Subjunctive: valga, valgas, valga, valgamos, valgáis, valgan Commands: val or vale (tú), no valgas (neg. tú), valga (Ud.), valgamos (nosotros), valgan (Uds.) RECURSOS Gramática—resumen R35 GRAMÁTICA–RESUMEN Present Indicative: traigo, traes, trae, traemos, traéis, traen Preterite: traje, trajiste, trajo, trajimos, trajisteis, trajeron Present Subjunctive: traiga, traigas, traiga, traigamos, traigáis, traigan Present Participle: trayendo Past Participle: traído venir