Brain Tumors - Pages
Anuncio

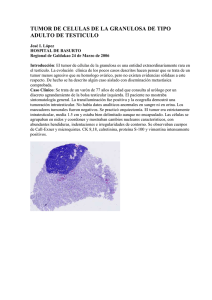
Brain Tumors A tumor that starts and grows in the brain is called a primary brain tumor. Primary brain tumors get their name from the type of cell or the part of the brain where they start growing. A secondary brain tumor is a cancer that has spread (metastatic) to the brain from another part of the body. There are many different types of brain tumors. Tumors are put into groups based on where they grow in the brain, the type of brain tissue that is affected and if the tumor is cancer (malignant) or not cancer (benign). Brain tumors can happen at any age and can cause different symptoms depending on their size and location. Glioma Tumors A common type of brain tumor in adults is a Glioma. The three most common types of gliomas are: • Astrocytoma • Oligodendroglioma • Oligoastrocytoma More on next page Learn more about your health care. © Copyright October 11, 2012. James Cancer Hospital & Solove Research Institute, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center - Upon request all patient education handouts are available in other formats for people with special hearing, vision and language needs, call (614) 293-3259. Tumores cerebrales Un tumor que comienza y crece en el cerebro se llama tumor cerebral primario. Estos reciben su nombre del tipo de célula o la parte del cerebro en donde comienzan a crecer. Un tumor cerebral secundario es un cáncer que se ha propagado (metastásico) al cerebro desde otra parte del cuerpo. Hay muchos tipos diferentes de tumores cerebrales. Los tumores se clasifican en grupos basándose en el lugar en el que crecen en el cerebro, el tipo de tejido cerebral que afecta y si el tumor es cáncer (maligno) o no lo es (benigno). Los tumores cerebrales pueden aparecer a cualquier edad y pueden causar diferentes síntomas dependiendo de su tamaño y ubicación. Tumores tipo glioma Un tipo común de tumor de cerebro en adultos es un glioma. Los tres tipos más comunes de gliomas son: • Astrocitoma • Oligodendroglioma • Oligoastrocitoma Sigue en la próxima página Aprenda más sobre los cuidados de su salud. Brain Tumors. Spanish. © Copyright October 11, 2012. James Cancer Hospital & Solove Research Institute, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center - Upon request all patient education handouts are available in other formats for people with special hearing, vision and language needs, call (614) 293-3259. 2 Glioma tumors develop roots that grow into the nearby normal brain tissue. The roots are unable to be seen with a MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or any other type of x-rays. Gliomas are unable to be cured with surgery because tumor cells that are not seen will remain after the tumor is removed. This type of tumor can spread to other areas of the brain. They rarely spread to other parts of the body. Treatment options for brain tumors may include: surgery, radiation or chemotherapy. Your doctor will talk with you about the type of treatment that is best for you. Grades of Gliomas Tumors are graded based on how the tumor cells look under a microscope. A piece of the tumor will be needed to determine the tumor grade. Grading is a system used to describe how abnormal or aggressive the tumor cells look. The lower the grade the more normal the tumor cells look. The higher the grade the more abnormal the cells look. With treatment, a brain tumor may grow back at some point in time. Types of Gliomas Astrocytoma Astrocytoma is the most common type of glioma. Astrocytomas are tumors that start in the “astrocytes” (star-shaped cells that make up the “glue-like” or supportive tissue of the brain). Grades of Astrocytoma tumors: • Grade I – Pilocytic Astrocytoma is an uncommon slow growing tumor that is found most often in children. • Grade II – Low Grade Astrocytoma is a low-grade glioma. This type of tumor usually affects younger adults. Although these tumors are low-grade and less aggressive, they can grow with or without treatment which may cause symptoms and harm to the brain. • Grade III – Anaplastic Astrocytoma is a high-grade tumor. This type of tumor grows faster and is more aggressive than grade II astrocytomas. 2 Los tumores glioma desarrollan raíces que crecen cerca del tejido cerebral normal. Las raíces no se pueden ver con una resonancia magnética o cualquier otro tipo de radiografía. Los gliomas no pueden curarse con cirugía porque las células tumorales que no se ven permanecerán después de retirado el tumor. Este tipo de tumor puede propagarse a otras áreas del cerebro. Rara vez se propagan a otras partes del cuerpo. Las opciones de tratamiento para los tumores cerebrales pueden incluir: cirugía, radiación o quimioterapia. Su médico hablará con usted sobre el mejor tipo de tratamiento para usted. Grados de gliomas Los tumores se clasifican basándose en cómo se ven las células tumorales con el microscopio. Se necesitará un trozo de tumor para determinar el grado del tumor. La clasificación por grados es un sistema usado para describir qué tan anormales o agresivas se ven las células tumorales. Cuanto más bajo el grado, más normal se ven las células tumorales. Cuanto más alto el grado, más anormales se ven las células tumorales. Aun con el tratamiento, un tumor cerebral puede volver a crecer más adelante. Tipos de gliomas Astrocitoma El astrocitoma es el tipo más común de glioma. Los astrocitomas son tumores que comienzan en los “astrocitos” (células con forma de estrella que forman el tejido de soporte “como pegamento” del cerebro). Grados de tumores astrocitoma: • Grado I – El astrocitoma pilocítico es un tumor de crecimiento lento poco común que se encuentra con frecuencia en niños. • Grado II – El astrocitoma de bajo grado es un glioma de grado bajo. Este tipo de tumor generalmente afecta a adultos más jóvenes. Aunque estos tumores son de bajo grado y menos agresivos, pueden crecer con o sin tratamiento, lo que podría causar síntomas y dañar el cerebro. • Grado III – El astrocitoma anaplásico es un tumor de grado alto. Este tipo de tumor crece más rápidamente y es más agresivo que los astrocitomas de grado II. 3 • Grade IV – Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) – This is the most common type of astrocytoma. This tumor can affect people of any age, but are most often found in older adults. It is a more aggressive and serious type of brain tumor. Treatment is needed to control the growth of the tumor. Oligodendroglioma An Oligodendroglioma brain tumor starts growing in the oligodendrocytes (cells that cover and protect the nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord). There are only two grades of Oligodendroglioma tumors: • Grade II Oligodendroglioma This type of tumor usually affects younger adults. Although these tumors are low-grade and less aggressive, they can grow with or without treatment which may cause symptoms and harm to the brain. • Grade III Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma This type of brain tumor is not common. It can develop at any age but it is most often found in middle-aged adults. This type of tumor is more aggressive and serious than lower grade tumors. Treatment is needed to control the growth of the tumor. Oligoastrocytoma An oligoastrocytoma is known as a “mixed” glioma brain tumor. It is made up of two types of cells, astrocytes and the oligodendrocyte These cells grow together and form this type of tumor. Talk to your doctor or others on your health care team if you have questions. You may request more written information from the Library for Health Information at (614) 293-3707 or email: health-info@osu.edu. 3 • Grado IV– El glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) es el tipo más común de astrocitoma. Este tumor puede afectar a personas de cualquier edad, pero se encuentra con más frecuencia en adultos mayores. Es un tipo de tumor cerebral más agresivo y grave. Es necesario el tratamiento para controlar el crecimiento del tumor. Oligodendroglioma Un tumor cerebral oligodendroglioma comienza a crecer en el oligodendrocito (una célula que cubre y protege las células nerviosas del cerebro y la médula espinal). Existen solo dos grados de tumores oligodendroglioma: • Oligodendroglioma grado II Este tipo de tumor generalmente afecta a adultos más jóvenes. Aunque estos tumores son de grado bajo y menos agresivos, pueden crecer con o sin tratamiento, lo que podría causar síntomas y dañar el cerebro. • Oligodendroglioma anaplásico grado III Este tipo de tumor cerebral no es común. Se puede desarrollar a cualquier edad pero se encuentra con más frecuencia en adultos de mediana edad. Este tipo de tumor es más agresivo y grave que los tumores de menor grado. Es necesario el tratamiento para controlar el crecimiento del tumor. Oligoastrocitoma Un oligoastrocitoma se conoce como un tumor cerebral glioma “mixto”. Está compuesto de dos tipos de células, astrocitos y el oligodendrocito. Estas células crecen juntas y forman este tipo de tumor. Hable con su médico u otras personas de su equipo de cuidados de salud si tiene preguntas. Puede solicitar más información por escrito de la Biblioteca de Información de Salud llamando al (614) 293-3707 o por correo electrónico a: health-info@osu.edu.