EJERCICIOS PROGRMACION C++ 1. Muestre en pantalla el
Anuncio

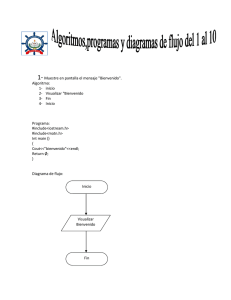
EJERCICIOS PROGRMACION C++ 1. Muestre en pantalla el mensaje “Bienvenido” PROGRAMA COMPLETO Inicio Muestre Bienvenido Fin Inicio Visualizar Bienvenido Fin # include <iostream.h> # include <math.h> Int main () Cout <<“Bienvenido”; Return 0 2. Muestre en pantalla el mensaje “Small Basic No Tiene Misterios” PROGRAMA COMPLETO Inicio Muestre en Pantalla “Small Basic No Tiene Misterios” Fin Inicio Visualizar “Small Basic No Tiene Misterios” Fin # include <iostream.h> # include <math.h> Int main () Cout <<“Small Basic No Tiene Misterios”; Return 0 3. Muestre en pantalla la suma de 100 y 120 PROGRAMA COMPLETO Inicio A= 100, B= 120, Suma= 0 Suma= A+B Visualizar suma en pantalla fin Inicio A= 100 B= 120 Suma= 0 Suma= A+B Visualizar Suma Fin # include <iostream.h> # include <math.h> Int main () Int A= 100, B= 120, Suma= 0 Suma= A+B; Cout <<“La Suma es: “<<Suma; Return 0; 4. Muestre en pantalla el producto de 50 y 51 PROGRAMA COMPLETO Inicio A= 50, B= 51, producto = 0 Producto= A*B Visualizar Producto Fin Inicio A= 100 B= 120 Producto= 0 Producto= A+B Visualizar Producto Fin # include <iostream.h> # include <math.h> Int main () Int A= 50, B= 51, Producto= 0 ; Producto= A*B Cout <<“El Producto es:” <<Producto; Return 0 5. Guarda en la variable X el número 23, y en la Y el 24 y en la variable Z 25 visualizar suma en pantalla. PROGRAMA COMPLETO Inicio X= 23, Y= 24, Z= 25, Suma 0 Suma= X+Y+Z Fin Inicio X= 23 Y= 24 Z= 25 Suma= 0 Suma= X+Y+Z Visualizar Suma # include <iostream.h> # include <math.h> Int main () Int X= 23, Y= 24, Z= 25, Suma= 0 Suma= X+Y+Z ; Cout <<“La Suma es:” <<Suma; Return 0 Fin 6. Guarde en la variable X el numero 10, en la variable Y el numero 11, en la variable Z el numero 12 calcule su producto y guárdelo en la variable llamada producto y muestre en pantalla el valor del producto PROGRAMA COMPLETO Inicio X= 10, Y= 11, Z= 12, producto= 0 Producto= X*Y*Z Visualizar producto Fin Inicio X= 10 Y= 11 Z= 12 Producto= 0 Producto= X*Y*Z Visualizar Producto Fin # include <iostream.h> # include <math.h> Int main () Int X= 10, Y= 11, Z= 12, Producto= 0 ; Producto= X*Y*Z Cout <<“El producto es:; <<Producto ; Return 0 7. Pida al usuario dos números enteros que se guarden en las variables A y B y muestre su suma en pantalla. PROGRAMA COMPLETO Inicio A= 0, B= 0, Suma= 0 Ingrese primer número Ingrese segundo número Suma= A+B Visualizar Suma Fin Inicio A= 0 B= 0 Suma= 0 Ingrese primer número Ingrese segundo número Suma= A+B Visualizar Suma Fin # include <iostream.h> # include <math.h> Int main () Int A= 0, B= 0, Suma= 0 Cout << “ingrese primer numero”; Cin a; Cout <<“ingrese segundo numero”; Cin >> b; Suma= A+B Cout <<“La suma es:” << Suma; Return 0; 8. Pida al usuario dos numero enteros guárdelos en las variables N1 y N2 y muestre su producto. PROGRAMA COMPLETO Inicio N1= 0, N2= 0, Producto= 0 Producto= N1*N2 Visualizar en pantalla Fin Inicio N1= 0 N2= 0 Producto= 0 Producto= N1*N2 Visualizar Producto Fin # include <iostream.h> # include <math.h> Int main () Int N1= 0, N2= 0, Producto= 0 Cout <<”ingrese primer numero”; Cin >>N1 Cout <<”ingrese segundo numero”; Cin >>N2 Producto= N1*N2 Cout <<”El producto es:” <<producto; Return 0 9. Pida al usuario dos numero reales que se guarden en las variables Dato 1 y Dato 2 y muestre en pantalla el resultado de dividir Dato 1 entre Dato 2 PROGRAMA COMPLETO Inicio Dato1=0, dato2=0, D=0 Ingresar primer número Ingresar segundo número D=dato1/dato2 Visualizar D Fin Inicio Dato 1= 0 Dato 2= 0 D=0 Ingrese primer número Ingrese segundo número D= Dato 1/ Dato 2 Visualizar División # include <iostream.h> # include <math.h> Int main () Int dato 1= 0, dato 2= 0, D= 0; Cout <<”ingrese primer numero”; Cin >> dato 1; Cout <<”ingrese segundo numero”; Cin >> dato 2; D=dato1/dato2 Cout <<”la división es:” << D; Return 0 ; Fin 10. Pida al usuario 2 números reales que se guarden en las variables Dato 1 y Dato 2. Si dato 2 es mayor deberá mostrar un mensaje de error, en caso contrario mostrar en pantalla el resultado de dividir Dato 1 y Dato 2 PROGRAMA COMPLETO Inicio Dato 1= 0, Dato 2=0, D= 0 Ingresar primer número Ingresar segundo número Si Dato 1= 0 entonces Visualizar el mensaje de error Regresar al paso 4 Caso contrario D= dato1/dato2 Visualizar División Fin Inicio Dato 1= 0 Dato 2= 0 D=0 Ingrese primer número Ingrese segundo número Si Dato 2=0 Visualizar mensaje de error D= dato1/dato2 Visualizar D Fin # include <iostream.h> # include <math.h> Int main () Int dato 1= 0, dato 2= 0, D= 0 Cout <<”ingrese primer numero”; Cin >> dato 1; Cout <<”ingrese segundo numero”; Cin >> dato 2; If (dato 2= 0); Cout <<”Visualizar mensaje error”; Else; D= dato1/dato2 Cout <<”la división es:” <<D; Return =0;