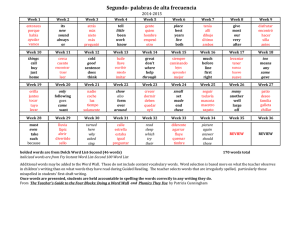
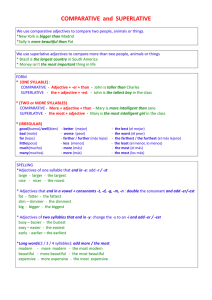
Irregular Comparisons Some adjectives have comparative forms that
Anuncio

Irregular Comparisons Some adjectives have comparative forms that are irregular. Adjective or Adverb Comparative bueno/a; bien good mejor better malo/a; mal bad peor worse grande big mayor bigger pequeño/a small menor smaller joven young menor younger viejo/a old mayor older When “grande” and “pequeño” are used to talk about size, the regular forms are used: EX: más grande El carro de mi padre es más grande que el tuyo. When “grande” and “pequeño” refer to age, the irregular forms are used: EX: Yo soy menor que tú. I am younger (smaller) than you. Superlatives Superlatives are used to express the highest or lowest degree of a quality. EX: the best the worst the longest The construction for superlatives is as follows: el /la /los /las + noun + más / menos + adjective **The noun is always preceded by a definite article. ** The word “de” is the same as “in” or “of” in English. **The noun can be omitted if the person, place, or thing referred to is clear. EX: El pollo asado es el plato más delicioso del restaurante. The roasted chicken is the best dish of the restaurant. Es el más delicioso del menú. It’s the best on the menu. + de There are irregular superlative forms. Adjective Superlative bueno/a good el/la mejor the best malo/a bad el/la peor the worst grande big el/la mayor the biggest pequeño/a small el/la menor the smallest joven young el/la menor the youngest viejo/a old el/la mayor the eldest **”Mejor” and “peor” generally precede the noun. Es la mejor clase. **”Mayor” and “menor” generally follow the noun when referring to age. Ella es mi hermana mayor. Absolute superlatives The absolute is the equivalent of “extremely”, “super” in English. To form the absolute of most adjectives and adverbs, drop the final vowel (if there is one) and add: -ísimo/a/os/as EX: mucho = muchísimo Some of the absolutes have spelling changes. rico = riquísimo largo = larguísimo feliz = felicísimo joven = jovencísimo trabajador = trabajadorcísimo