Chapter 12
Anuncio

Graficos Y Java 2D
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Introducción
Contextos y objetos gráficos
Colores
Fuentes
Pintar Líneas, Rectángulos y Óvalos
Pintar Arcos
Pintar Polígonos and Polilíneas
Java2D API
Ejemplo
1 Introducción
Capacidades gráficas de JAVA
-
Pintar figuras de 2D
-
Uso y control colores
-
Uso y control de fuentes
Java 2D API
-
Uso más sofisticado de primitivas de
dibujo en 2D
Uso de formar y polígonos 2D personalizados
Relleno de figuras con colores, gradientes,
patrones y texturas.
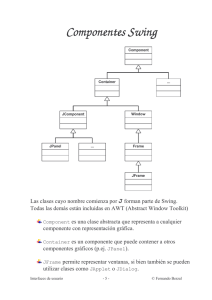
Jerarquía de algunas clases e interfaces del Java2D API.
Object
Color
Component
Font
FontMetrics
Graphics
Polygon
Clases e interfaces del Java2D API que aparecen en el
paquete java.awt
Graphics2D
interface
java.awt.Paint
BasicStroke
GradientPaint
TexturePaint
interface
java.awt.Shape
interface
java.awt.Stroke
Clases e interfaces del Java2D API que aparecen en
el paquete java.awt.geom
GeneralPath
Line2D
RectangularShape
Arc2D
Ellipse2D
Rectangle2D
RoundRectangle2D
1 Introducción
Sistema de coordenadas de JAVA
-
Identifica todos los puntos disponibles de
la pantallas
-
Origen de coordenadas (0,0) en la esquina
superior izquierda
-
Sistema de coordenadas compuestas por
componentes X e Y.
Sistema de coordenadas de Java. Unidad de medida en pixels.
2 Contextos y objetos gráficos
Contexto Graphics
-
Permite pintar en la pantalla.
– El objeto Graphics controla el contexto de
graficos
-
-
Controla como se pinta en la pantalla
La Clase Graphics es abstracta
No se puede instanciar
Contribuye a la portabilidad de Java
La el método paint de la lase Component
emplea el objeto Graphics
public void paint( Graphics g )
3 Colores
Clase Color
-
Define los métodos y las constantes para
manipular los colores.
-
Los colores se crean en base al esquema
de rojo/verde/azul (RGB).
Constantes de colores definidas en la clase Color
Métodos de la clase Color y métodos de relacionados de la
clase Graphics
1
// Fig. 12.5: ShowColors.java
2
// Demonstrating Colors.
3
import java.awt.*;
4
import javax.swing.*;
5
6
public class ShowColors extends JFrame {
7
8
// constructor sets window's title bar string and dimensions
9
public ShowColors()
10
{
11
super( "Using colors" );
12
Pinta la ventana cuando
13
setSize( 400, 130 );
comienza la ejecución de
14
setVisible( true );
la aplicación
15
}
16
17
// draw rectangles and Strings in different colors
El método setColor establece el color
18
public void paint( Graphics g )
19
{
de pintura en base a un color RGB
20
// call superclass's paint method
21
super.paint( g );
22
El método fillRect crea un rectángulo
23
// set new drawing color using integers
24
g.setColor( new Color( 255, 0, 0 ) ); relleno en el color de pintura actual.
25
g.fillRect( 25, 25, 100, 20 );
26
g.drawString( "Current RGB: " + g.getColor(), 130, 40 );
27
El método drawString escribe un
String en el color actual en las
coordenadas especificadas
28
29
51
// set new drawing color using floats
g.setColor( new Color( 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f ) );
30
g.fillRect( 25, 50, 100, 20 );
31
g.drawString( "Current RGB: " + g.getColor(), 130, 65 );
32
33
// set new drawing color using static Color objects
34
g.setColor( Color.BLUE );
35
g.fillRect( 25, 75, 100, 20 );
36
g.drawString( "Current RGB: " + g.getColor(), 130, 90 );
37
38
// display individual RGB values
Empleamos las constantes
39
Color color = Color.MAGENTA;
40
g.setColor( color );
la clase Color
41
g.fillRect( 25, 100, 100, 20 );
42
g.drawString( "RGB values: " + color.getRed() + ", " +
43
color.getGreen() + ", " + color.getBlue(), 130, 115 );
44
45
} // end method paint
46
47
// execute application
48
public static void main( String args[] )
49
{
50
ShowColors application = new ShowColors();
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
52
}
53
54 } // end class ShowColors
de
1
// Fig. 12.6: ShowColors2.java
// Choosing colors with JColorChooser.
3
import java.awt.*;
4
import java.awt.event.*;
5
import javax.swing.*;
6
7
public class ShowColors2 extends JFrame {
8
private JButton changeColorButton;
9
private Color color = Color.LIGHT_GRAY;
10
private Container container;
11
12
// set up GUI
13
public ShowColors2()
14
{
15
super( "Using JColorChooser" );
16
17
container = getContentPane();
18
container.setLayout( new FlowLayout() );
19
// set up changeColorButton and register its event handler
changeColorButton = new JButton( "Change Color" );
22
changeColorButton.addActionListener(
23
2
20
21
24
new ActionListener() { // anonymous inner class
25
26
// display JColorChooser when user clicks button
27
public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent event )
28
{
29
color = JColorChooser.showDialog(
30
ShowColors2.this, "Choose a color", color );
31
32
// set default color, if no color is returned
33
if ( color == null )
34
color = Color.LIGHT_GRAY;
35
36
// change content pane's background color
37
container.setBackground( color );
38
}
39
40
} // end anonymous inner class
41
42
); // end call to addActionListener
43
44
container.add( changeColorButton );
45
46
setSize( 400, 130 );
47
49
setVisible( true );
48
} // end ShowColor2 constructor
50
JColorChooser presenta
un diálogo para
seleccionar colores
static showDialog
muestra el cuadro de
diálogo
55
51
// execute application
52
public static void main( String args[] )
53
{
54
ShowColors2 application = new ShowColors2();
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
56
}
57
58 } // end class ShowColors2
ShowColors2.java
Fig. 12.7 HSB and RGB tabs
of the JColorChooser dialog
4 Fuente
Clase Font
-
Contiene métodos y constantes para el
control de las fuentes.
-
El constructor de la clase Font tiene tres
argumentos
Font name
– Monospaced, SansSerif, Serif, etc.
Font style
– Font.PLAIN, Font.ITALIC y Font.BOLD
Font size
-
Medido en puntos
Métodos y constantes relacionados con la clase Font
1
// Fig. 12.9: Fonts.java
2
// Using fonts.
3
import java.awt.*;
4
import javax.swing.*;
5
6
public class Fonts extends JFrame {
7
8
// set window's title bar and dimensions
9
public Fonts()
10
{
11
super( "Using fonts" );
12
13
setSize( 420, 125 );
14
setVisible( true );
15
}
16
17
// display Strings in different fonts and colors
18
public void paint( Graphics g )
19
{
20
// call superclass's paint method
El método setFont
21
super.paint( g );
22
23
// set font to Serif (Times), bold, 12pt and draw a string
24
g.setFont( new Font( "Serif", Font.BOLD, 12 ) );
25
g.drawString( "Serif 12 point bold.", 20, 50 );
establece la fuente a usar
Escribe el texto con la
configuración actual de
fuente
26
27
// set font to Monospaced (Courier), italic, 24pt and draw a string
28
g.setFont( new Font( "Monospaced", Font.ITALIC, 24 ) );
29
g.drawString( "Monospaced 24 point italic.", 20, 70 );
30
31
// set font to SansSerif (Helvetica), plain, 14pt and draw a string
32
g.setFont( new Font( "SansSerif", Font.PLAIN, 14 ) );
33
g.drawString( "SansSerif 14 point plain.", 20, 90 );
34
35
// set font to Serif (Times), bold/italic, 18pt and draw a string
36
g.setColor( Color.RED );
37
g.setFont( new Font( "Serif", Font.BOLD + Font.ITALIC, 18 ) );
38
g.drawString( g.getFont().getName() + " " + g.getFont().getSize() +
39
" point bold italic.", 20, 110 );
40
41
} // end method paint
42
43
// execute application
44
public static void main( String args[] )
45
{
46
Fonts application = new Fonts();
47
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
48
}
49
50 } // end class Fonts
Control de fuentes
Parámetros de medida y posición de
las Fuentes
-
Height - Altura
-
Descent (puntos por debajo de la linea
base)
-
Ascent (puntos por encima de la linea
base)
-
Leading (diferencia entre Ascent y
Descent)
Control y medidas
Fig. 12.11 FontMetrics and
Graphics methods for
obtaining font metrics
1
// Fig. 12.12: Metrics.java
2
// FontMetrics and Graphics Metrics.java
methods useful for obtaining font Line 22
Line 23
metrics.
3
import java.awt.*;
4
import javax.swing.*;
5
Set font to SansSerif 12-point bold
6
public class Metrics extends
Obtain FontMetrics
JFrame {
object for current font
7
8
// set window's title bar
String and dimensions
9
public Metrics()
25
Use FontMetrics to
obtain ascent, descent,
height and leading
Metrics.java
g.drawString( "Ascent: " +
metrics.getAscent(), 10, 55 );
Repeat same process for
Lines 25-28
italic font
26
g.drawString( "Descent:Serif
" 14-point
Lines 30-37
+ metrics.getDescent(), 10, 70 );
27
g.drawString( "Height: " +
metrics.getHeight(), 10, 85 );
28
g.drawString( "Leading: "
+ metrics.getLeading(), 10, 100 );
29
30
Font font = new
Font( "Serif", Font.ITALIC, 14 );
31
metrics =
g.getFontMetrics( font );
Metrics.java
5 Pintar Líneas, Rectángulos y Óvalos
Clase Graphics
-
Provee métodos para pintar líneas,
rectángulos y óvalos
Todos lo métodos de pintar estas figuras
requieren el ancho y alto que ocuparan
Existen los métodos para pintar figuras con o
sin rellene (draw* y fill*)
Métodos de la clase Graphics para pintar líneas,
rectángulos y óvalos
Métodos de la clase Graphics para pintar líneas,
rectángulos y óvalos
1
// Fig. 12.14: LinesRectsOvals.java
2
// Drawing lines, rectangles and ovals.
3
import java.awt.*;
4
import javax.swing.*;
5
6
public class LinesRectsOvals extends JFrame {
7
8
// set window's title bar String and dimensions
9
public LinesRectsOvals()
10
{
11
super( "Drawing lines, rectangles and ovals" );
12
13
setSize( 400, 165 );
14
setVisible( true );
15
}
16
17
// display various lines, rectangles and ovals
18
public void paint( Graphics g )
19
{
20
super.paint( g ); // call superclass's paint method
21
22
g.setColor( Color.RED );
23
g.drawLine( 5, 30, 350, 30 );
24
25
g.setColor( Color.BLUE );
26
g.drawRect( 5, 40, 90, 55 );
27
g.fillRect( 100, 40, 90, 55 );
47
28
29
g.setColor( Color.CYAN );
30
g.fillRoundRect( 195, 40, 90, 55, 50, 50 ); Draw filled rounded rectangle
31
g.drawRoundRect( 290, 40, 90, 55, 20, 20 );
32
Draw (non-filled) rounded rectangle
33
g.setColor( Color.YELLOW );
34
g.draw3DRect( 5, 100, 90, 55, true );
Draw 3D rectangle
35
g.fill3DRect( 100, 100, 90, 55, false );
36
Draw filled 3D rectangle
37
g.setColor( Color.MAGENTA );
38
g.drawOval( 195, 100, 90, 55 );
Draw oval
39
g.fillOval( 290, 100, 90, 55 );
40
Draw filled oval
41
} // end method paint
42
43
// execute application
44
public static void main( String args[] )
45
{
46
LinesRectsOvals application = new LinesRectsOvals();
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
48
}
49
50 } // end class LinesRectsOvals
Altura y anchura del arco necesario para construir
RoundedRectangle
Medidas para construir un óvalo en base al rectángulo que lo
contiene
6 Pintar Arcos
Arco
-
Porción de un óvalo
-
Se miden en grados
-
Barre (Sweeps) el número de grados que
indique el ángulo de arco
-
Sweep empieza en el inicio de medida de
los ángulos
Barre en sentido contrario a las agujas del
reloj si el ángulo es positivo
Barre en sentido de las agujas del reloj para
ángulos negativos.
Ángulos positivos y negativos
Positive angles
Negative angles
90°
180°
90°
0°
270°
180°
0°
270°
Métodos de la clase Graphics para el pintado de arcos
1
8
20
// Fig. 12.19: DrawArcs.java
2
// Drawing arcs.
3
import java.awt.*;
4
import javax.swing.*;
5
6
public class DrawArcs extends JFrame {
7
// set window's title bar String and dimensions
9
public DrawArcs()
10
{
11
super( "Drawing Arcs" );
12
13
setSize( 300, 170 );
14
setVisible( true );
15
}
16
17
// draw rectangles and arcs
18
public void paint( Graphics g )
19
{
super.paint( g ); // call superclass's paint method
21
22
// start at 0 and sweep 360 degrees
23
g.setColor( Color.YELLOW );
24
g.drawRect( 15, 35, 80, 80 );
25
g.setColor( Color.BLACK );
Draw
26
g.drawArc( 15, 35, 80, 80, 0, 360 );
DrawArcs.java
Lines 24-26
first arc that
sweeps 360 degrees and
is contained in rectangle
28
29
30
31
32
34
35
36
37
38
40
41
43
44
46
47
27
// start at 0 and sweep 110 degrees
g.setColor( Color.YELLOW );
Draw second arc that
g.drawRect( 100, 35, 80, 80 );
sweeps 110 degrees and
g.setColor( Color.BLACK );
g.drawArc( 100, 35, 80, 80, 0, 110 );
is contained in rectangle
33
// start at 0 and sweep -270 degrees
g.setColor( Color.YELLOW );
g.drawRect( 185, 35, 80, 80 );
Draw third arc that
g.setColor( Color.BLACK );
sweeps -270 degrees and
g.drawArc( 185, 35, 80, 80, 0, -270 );
is contained in rectangle
39
// start at 0 and sweep 360 degrees
g.fillArc( 15, 120, 80, 40, 0, 360 );
Draw fourth arc that is filled, has starting
42
angle 0 and sweeps 360 degrees
// start at 270 and sweep -90 degrees
g.fillArc( 100, 120, 80, 40, 270, -90 );
45
Draw fifth arc that is filled, has starting
// start at 0 and sweep -270 degrees
angle 270 and sweeps -90 degrees
g.fillArc( 185, 120, 80, 40, 0, -270 );
48
49
} // end method paint
Draw sixth arc that is filled, has starting
50
angle 0 and sweeps -270 degrees
55
51
// execute application
52
public static void main( String args[] )
53
{
54
DrawArcs application = new DrawArcs();
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
56
}
57
58 } // end class DrawArcs
7 Pintar Polígonos y Polilíneas
Clases Polygon
-
Polígonos
-
Figuras de varios lados
Polilíneas
Series de puntos conectados
Métodos Graphics para pintar poligonos y métodos de la
clase Polygon
Métodos Graphics para pintar poligonos y métodos de la
clase Polygon
1
// Fig. 12.21: DrawPolygons.java
2
// Drawing polygons.
3
import java.awt.*;
4
import javax.swing.*;
5
6
public class DrawPolygons extends JFrame {
7
8
// set window's title bar String and dimensions
9
public DrawPolygons()
10
{
11
super( "Drawing Polygons" );
12
13
setSize( 275, 230 );
14
setVisible( true );
15
}
16
17
// draw polygons and polylines
18
public void paint( Graphics g )
19
{
int arrays specifying
20
super.paint( g ); // call superclass's paint method
21
Polygon polygon1 points
22
int xValues[] = { 20, 40, 50, 30, 20, 15 };
23
int yValues[] = { 50, 50, 60, 80, 80, 60 };
24
Polygon polygon1 = new Polygon( xValues, yValues, 6 );
Draw polygon1 to screen
25
26
g.drawPolygon( polygon1 );
27
28
29
53
int xValues2[] = { 70, 90, 100, 80, 70, 65, 60 };
int yValues2[] = { 100, 100, 110, 110, 130, 110, 90 };
30
int arrays specifying
31
g.drawPolyline( xValues2, yValues2, 7 );
Polyline points
32
33
int xValues3[] = { 120, 140, 150, 190 };
34
int yValues3[] = { 40, 70, 80, 60 };
Draw Polyline to screen
35
36
g.fillPolygon( xValues3, yValues3, 4 );
Specify points and draw (filled)
37
38
Polygon polygon2 = new Polygon();
Polygon to screen
39
polygon2.addPoint( 165, 135 );
40
polygon2.addPoint( 175, 150 );
41
polygon2.addPoint( 270, 200 );
42
polygon2.addPoint( 200, 220 );
43
polygon2.addPoint( 130, 180 ); Method addPoint adds pairs of
44
x-y coordinates to a Polygon
45
g.fillPolygon( polygon2 );
46
47
} // end method paint
48
49
// execute application
50
public static void main( String args[] )
51
{
52
DrawPolygons application = new DrawPolygons();
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
54
}
55
56 } // end class DrawPolygons
8 Java2D API
Java 2D API
-
Proporciona capacidades gráficas avanzas
2D
•
java.awt
•
java.awt.image
•
java.awt.color
•
java.awt.font
•
java.awt.geom
•
java.awt.print
•
java.awt.image.renderable
-
Usa la clase java.awt.Graphics2D
12.8 Java2D API
Java 2D formas
-
Paquetes java.awt.geom
• Ellipse2D.Double
• Rectangle2D.Double
• RoundRectangle2D.Double
• Arc3D.Double
• Lines2D.Double
1
// Fig. 12.22: Shapes.java
// Demonstrating some Java2D shapes.
3
import java.awt.*;
4
import java.awt.geom.*;
5
import java.awt.image.*;
6
import javax.swing.*;
7
8
public class Shapes extends JFrame {
9
10
// set window's title bar String and dimensions
11
public Shapes()
12
{
13
super( "Drawing 2D shapes" );
14
15
setSize( 425, 160 );
16
setVisible( true );
17
}
18
19
// draw shapes with Java2D API
20
public void paint( Graphics g )
21
{
22
super.paint( g ); // call superclass's paint method
23
Graphics2D g2d = ( Graphics2D ) g; // cast g to Graphics2D
25
2
24
Shapes.java
// draw 2D ellipse filled with a blue-yellow gradient
Use GradientPaint to
g2d.setPaint( new GradientPaint( 5, 30, Color.BLUE, 35, 100,
fill shape with gradient
28
Color.YELLOW, true ) );
29
g2d.fill( new Ellipse2D.Double( 5, 30, 65, 100 ) );
Fill ellipse with gradient
30
31
// draw 2D rectangle in red
32
g2d.setPaint( Color.RED );
Use BasicStroke to draw
33
g2d.setStroke( new BasicStroke( 10.0f ) );
2D red-border rectangle
34
g2d.draw( new Rectangle2D.Double( 80, 30, 65, 100 ) );
35
36
// draw 2D rounded rectangle with a buffered background
37
BufferedImage buffImage = new BufferedImage( 10, 10,
BufferedImage produces
38
BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB );
image to be manipulated
39
40
Graphics2D gg = buffImage.createGraphics();
41
gg.setColor( Color.YELLOW ); // draw in yellow
42
gg.fillRect( 0, 0, 10, 10 ); // draw a filled rectangle
43
gg.setColor( Color.BLACK ); // draw in black
44
gg.drawRect( 1, 1, 6, 6 ); // draw a rectangle
Draw texture into
45
gg.setColor( Color.BLUE ); // draw in blue
BufferedImage
46
gg.fillRect( 1, 1, 3, 3 ); // draw a filled rectangle
47
gg.setColor( Color.RED ); // draw in red
48
gg.fillRect( 4, 4, 3, 3 ); // draw a filled rectangle
49
26
27
50
// paint buffImage onto the JFrame
Use BufferedImage as texture
51
g2d.setPaint( new TexturePaint( buffImage,
for painting rounded rectangle
52
new Rectangle( 10, 10 ) ) );
53
g2d.fill( new RoundRectangle2D.Double( 155, 30, 75, 100, 50, 50 ) );
54
Use Arc2D.PIE to
55
// draw 2D pie-shaped arc in white
56
g2d.setPaint( Color.WHITE );
draw white-border
57
g2d.setStroke( new BasicStroke( 6.0f ) );
2D pie-shaped arc
58
g2d.draw( new Arc2D.Double( 240, 30, 75, 100, 0, 270, Arc2D.PIE ) );
59
60
// draw 2D lines in green and yellow
61
g2d.setPaint( Color.GREEN );
62
g2d.draw( new Line2D.Double( 395, 30, 320, 150 ) );
63
Draw solid green line
64
float dashes[] = { 10 };
65
66
g2d.setPaint( Color.YELLOW );
67
g2d.setStroke( new BasicStroke( 4, BasicStroke.CAP_ROUND,
68
BasicStroke.JOIN_ROUND, 10, dashes, 0 ) );
69
g2d.draw( new Line2D.Double( 320, 30, 395, 150 ) );
Draw dashed yellow line
70
71
} // end method paint
that crosses solid green line
72
77
73
// execute application
74
public static void main( String args[] )
75
{
76
Shapes application = new Shapes();
application.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE );
78
}
79
80 } // end class Shapes
Shapes.java
1
// Fig. 12.23: Shapes2.java
// Demonstrating a general path.
3
import java.awt.*;
4
import java.awt.geom.*;
5
import javax.swing.*;
6
7
public class Shapes2 extends JFrame {
8
// set window's title bar String, background color and dimensions
10
public Shapes2()
11
{
12
super( "Drawing 2D Shapes" );
13
14
getContentPane().setBackground( Color.WHITE );
15
setSize( 400, 400 );
16
setVisible( true );
17
}
18
19
// draw general paths
20
public void paint( Graphics g )
21
{
22
super.paint( g ); // call superclass's paint method
23
x-y coordinates that
24
int xPoints[] = { 55, 67, 109, 73, 83, 55, 27, 37, 1, 43 };
25
int yPoints[] = { 0, 36, 36, 54, 96, 72, 96, 54, 36, 36 };
26
2
9
comprise star
GeneralPath is a shape
27
Graphics2D g2d = ( Graphics2D ) g;
28
GeneralPath star = new GeneralPath(); // create GeneralPath object
constructed from straight
29
lines and complex curves
30
// set the initial coordinate of the General Path
Shapes2.java
31
star.moveTo( xPoints[ 0 ], yPoints[ 0 ] );
32
33
// create the star--this does not draw the star
Line 28
34
for ( int count = 1; count < xPoints.length; count++ )
Create star
35
star.lineTo( xPoints[ count ], yPoints[ count ] );
36
Lines 31-37
37
star.closePath(); // close the shape
38
Lines 42-50
39
g2d.translate( 200, 200 ); // translate the origin to (200, 200)
40
41
// rotate around origin and draw stars in random colors
42
for ( int count = 1; count <= 20; count++ ) {
43
g2d.rotate( Math.PI / 10.0 ); // rotate coordinate system
44
45
// set random drawing color
46
g2d.setColor( new Color( ( int ) ( Math.random() * 256 ),
47
( int ) ( Math.random() * 256 ),
48
( int ) ( Math.random() * 256 ) ) );
49
Draw filled, randomly colored
50
g2d.fill( star ); // draw filled star
51
}
star 20 times around origin
Shapes2.java