GASTROENTERITIS POR SHIGELLA EN ADULTOS Etiología
Anuncio

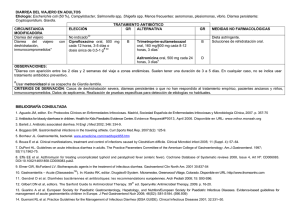
GASTROENTERITIS POR SHIGELLA EN ADULTOS Etiología: Shigella spp (S. dysenteriae,....) CIRCUNSTANCIA MODIFICADORA Gastroenteritis aguda leve Formas moderadas y graves, ancianos, manipuladores de alimentos, sanitarios# ELECCIÓN TRATAMIENTO ANTIBIÓTICO GR ALTERNATIVA No indicado* Ciprofloxacino oral, 500 mg, cada 12 horas, 3 días 7,17,22 Infección aguda en Ciprofloxacino oral 500 mg, § inmunodeprimidos cada 12 horas, 7-10 días 7,17,22 OBSERVACIONES: *Se indica tratamiento sintomático. # A D GR Trimetroprim-sufametoxazol oral, 160 mg/800 mg cada 12 horas, 3 días 7,17,22 D Azitromicina oral, 1 g, dosis única17 D MEDIDAS NO FARMACOLÓGICAS Dieta astringente. Soluciones de rehidratación si es necesario. D En casos graves o pacientes con factores de riesgo, el tratamiento específico debe guiarse por antibiograma. § La duración del tratamiento en pacientes con VIH no debería ser inferior a 2 semanas, especialmente en pacientes con CD4 muy bajos. CRITERIOS DE DERIVACIÓN: Infección prolongada, infección severa que no responde a antibióticos BIBLIOGRAFÍA CONSULTADA 1. Aguado JM, editor. En: Protocolos Clínicos en Enfermedades Infecciosas. Madrid, Sociedad Española de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica, 2007. p. 357-75 2. Antibiotics for bloody diarrhoea in children. Health for Kids Paediatric Evidence Centre. Evidence Request#P0013, April 2006. Disponible en URL: www.mihsr.monash.org 3. Barlett J. Antibiotic associated diarrhea. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 334-9. 4. Boggess BR. Gastrointestinal infections in the traveling athlete. Curr.Sports Med.Rep. 2007;6(2): 125-9. 5. Bonheur JL. Gastroenteritis, bacterial. www.emedicine.com/med/topic855.htm 6. Bouza E et al. Clinical manifestations, treatment and control of infections caused by Clostridium difficile. Clinical Microbiol infect 2005; 11 (Suppl. 4): 57–64. 7. DuPont HL. Guidelines on acute infectious diarrhea in adults. The Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Am.J.Gastroenterol. 1997; 92(11):1962-75. 8. Effa EE et al. Azithromycin for treating uncomplicated typhoid and paratyphoid fever (enteric fever). Cochrane Database of Systematic reviews 2008, Issue 4, Art Nº: CD006083. DOI:10.1002/14651858.CD006083.pub2. 9. Elmer GW, McFarland LV. Biotherapeutic agents in the treatment of infectious diarrhea. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2001 30:837-54 10. Gastroenteritis – Acute (DiseasedexTM). In: Klasko RK, editor. Drugdex® System. Micromedex, Greenwood Village, Colorado. Disponible en URL: http://www.thomsonhc.com 11. Gendrel D et al. Diarrhées bactériennes et antibiotiques: les recommandations européennes. Arch Pediatr 2008; 15: S93-S96. 12. Gilbert DN et al, editors. The Sanford Guide to Antimicrobial Therapy. 39th ed. Sperryville: Antimicrobial Therapy, 2009. p. 16-20. 13. Guarino A et al. European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition/European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases. Evidence-based guidelines for management of acute gastroenteritis children in Europe. J Ped Gastroenterol Nutr 2008; 46(S2): S81-S184. (596.939) 14. Guerrant RL et al. Practice Guidelines for the Management of Infectious Diarrhea (IDSA GUIDE). Clinical Infectious Diseases 2001; 32:331–50. 15. Guía Práctica de la Organización Mundial de Gastroenterología: Diarrea Aguda. Marzo, 2008. Disponible en URL: www.worldgastroenterology.org 16. Gurguí M, Moreno A, Sitges-Serra A, Blames M. http://Protocolos%20Clínicos%20S_E_I_M_C_archivos/proto9.htm. Peritonitis y otras infecciones intraabdominales. Protocolos Clínicos SEIMC. Disponible en: 17. Gutiérrez I et al. Gastroenteritis infecciosa en el adulto. Boletín de Uso Racional del Medicamento. Servicio Cántabro de Salud. Nº2, 2007. 18. Handbook of antimicrobial therapy. 18th ed. New Rochelle: The Medical Letter, 2008. p. 62-5. 19. Infectious Diseases Society of Taiwan; Taiwan Surgical Society of Gastroenterology; Medical Foundation in Memory of Dr. Deh-Lin Cheng; Foundation of Professor Wei-Chuan Hsieh for Infectious Diseases Research and Education; CY Lee’s Research Foundation for Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Vaccines. Guidelines for antimicrobial therapy of intraabdominal infections in adults. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2008;41: 279-81. 20. López-Brea M et al. Tratamiento de las infecciones gastrointestinales. En: García Rodríguez JA et al, editores. Antimicrobianos en Medicina. 2ª ed. Barcelona: Sociedad Española de Quimioterapia, 2006. p. 429-42. 21. Luther J, Higgins PD, Schoenfeld PS, Moayyedi P, Vakil N, Chey WD. Empiric quadruple vs. triple therapy for primary treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: Systematic review and metaanalysis of efficacy and tolerability. Am.J.Gastroenterol. 2010; 105(1): 65-73. 22. Mensa J et al. Guía de terapéutica antimicrobiana. 18 ed, 2009. 23. Musher DM et al. Contagious Acute Gastrointestinal Infections. N Engl J Med 2004;351:2417-27. 24. Pawloswski SW et al. Diagnosis and treatment of acute or persistent diarrhea. Gastroenterology 2009; 136(6): 1874-86. 25. Pillai A et al. Probióticos para el tratamiento de la colitis relacionada con el Clostridium difficile en adultos (Revisión Cochrane traducida). En: La Biblioteca Cochrane Plus, 2008 Número 4. Oxford: Update Software Ltd. Disponible en: http://www.update-software.com. (Traducida de The Cochrane Library, 2008 Issue 3. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.). 26. Prescilla RP. Gastroenteritis. Medscape: emedicine, Jan 2009. Disponible en URL: http://emedicine.mescape.com 27. Prine PRH, Kiruvbah VD, Sushil MJ, Venkatesan SV. Antibiotic therapy for Shigella dysentery. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, Issue 1. Art. No.: CD006784. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006784.pub3. 28. Sabol VK et al. Diarrhea: applying research to bedside practice. AACN.Adv.Crit Care. 2007; 18(1): 32-44. 29. Seif S et al. Traveller’s diarrhoea. Lancet Infect Dis 2005; 5: 349–60. 30. Sociedad Española de Medicina Familiar y Comunitaria. Guía Terapéutica en Atención Primaria basada en la selección razonada de medicamentos. 4ª edición. Barcelona: SEMFYC; 2010. 31. Tellado JM et al. Pautas de tratamiento antibiótico empírico de las infecciones intraabdominales. Rev Esp Quimioterap 2005; 18(2): 179-86. 32. Ternhag A, Asikainen T, Giesecke J, Ekdahi K. A meta-analysis on the effects of antibiotic treatment on duration of symptoms caused by infection with Campylobacter species. Clin Inf Dis 2007;44:696-700 33. Thaver D, Zaidi AKM, Critchley JA, Azmatullah A, Madni SA; Bhutta ZA. Fluorquinolones for treating typhoid and paratyphoid fever (enteric fever). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2008, Issue 4, Art Nº: CD004530. DOI:10.1002/14651858.CD004530.pub3. 34. Thielman NM et al. Acute Infectious Diarrhea. N Engl J Med 2004;350:38-47. 35. Tratamiento erradicador de Helicobacter pylori. Recomendaciones de la II Conferencia Española de Consenso. Medicina Clínica. 2005; 125(8): 301-16. 36. Welsh A, editor. National Collaborating Centre for Women’s and Children’s Health. Diarrhoea and vomiting caused by gastroenteritis, diagnostic, assessment and management in children younger than 5 years. London: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Clinical Guideline, April 2009. 37. World Gastroenterology Organisation (WGO). WGO practice guideline: acute diarrhea. Munich, Germany: World Gastroenterology Organisation (WGO). 2008: 28 p.