Present Progressive
Anuncio

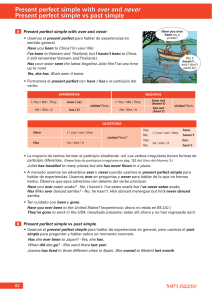
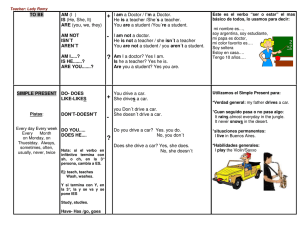
Present Progressive Structure: Affirmative: Subject + to be + verb (ing) + Complement. Negative: Subject + to be not + verb (ing) + Complement. Isn’t / Aren’t Positive Questions: To be + Subject + verb (ing) + Complement + ?. Negative Questions: To be not + Subject + verb (ing) + Complement + ? Isn’t / Aren’t Ways to use Present Progressive: 1.- We use Present Progressive to talk about actions that started in the past and continue in the present. An action that is happening right now. Usamos Present Progressive para hablar de acciones que empezaron en el pasado y continúan en el present. Una acción que está pasando ahora mismo. Ex: Joseph is cooking his lunch. Marta is talking on the phone. Tom and Lucia are seeing each other. We are going to school. 2.- We also use Present Progressive to talk about future plans, where we are going to focus. También usamos Present Progressive para hablar sobre planes futuros, donde nos enfocaremos. When we use Present Progressive to talk about future plans, we use the same general rule, but we add a time expression like: Cuando usamos Present Progressive para hablar de planes futuros, usamos la misma regla general, pero agregamos una expresión de tiempo, como: Tonight This weekend Tomorrow Next week In “X” hours. In the morning In the afternoon. At night Carly is going out tonight. Kent is leaving town tomorrow. Allison and Kate are traveling next week. We are finishing college in 2 months. Ex: “To Be”: The verb to be changes depending of the subject. If the subject is HE, SHE or IT, we use “IS”. If the subject is YOU, THEY or WE, we use “ARE”. But if the subject is I, we use “AM”. El verbo “to be” cambia dependiendo del sujeto. Si el sujeto es “HE”, “SHE” o “IT”, usamos “IS”. Si el sujeto es “YOU”, “THEY” o “WE”, usamos “ARE”. Pero sí el sujeto es “I”, usamos “AM”.