fórmulas de derivación - M. en C. Manuel Ivan Casillas del Llano
Anuncio
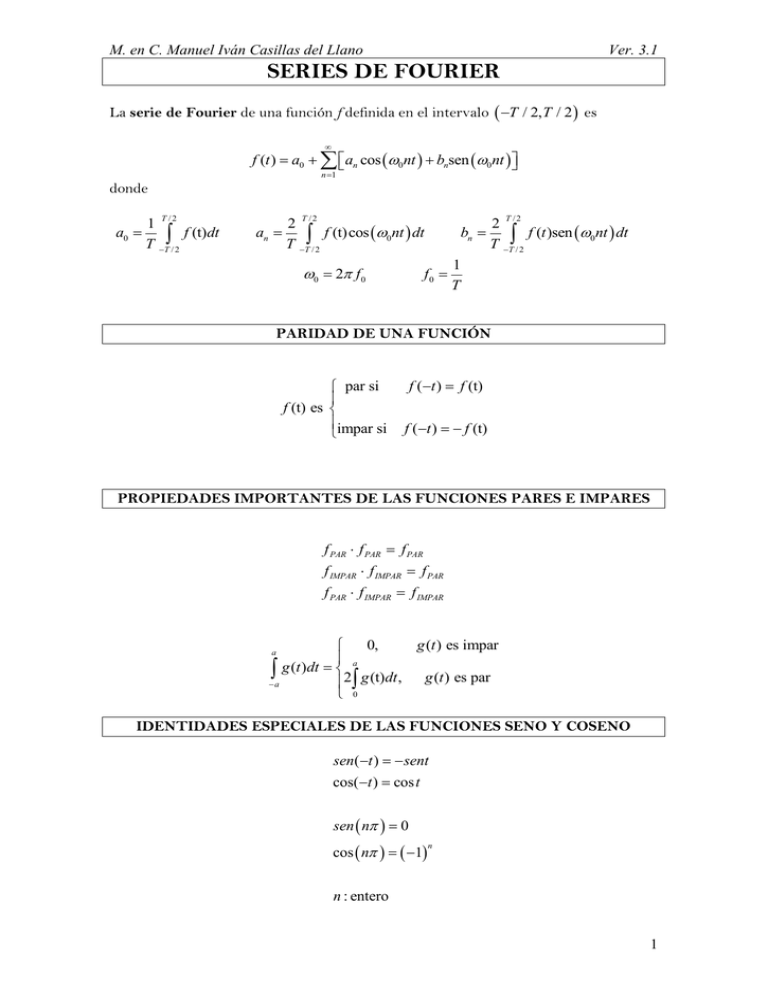
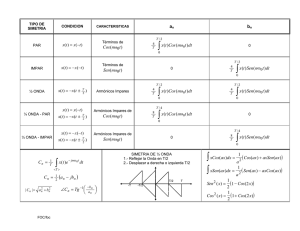
M. en C. Manuel Iván Casillas del Llano Ver. 3.1 SERIES DE FOURIER La serie de Fourier de una función f definida en el intervalo T / 2, T / 2 es f (t ) a0 an cos 0nt bnsen 0nt n 1 donde T /2 1 a0 f (t)dt T T/ 2 T /2 T /2 2 an f (t)cos 0nt dt T T/ 2 2 bn f (t )sen 0nt dt T T/ 2 1 f0 T 0 2 f0 PARIDAD DE UNA FUNCIÓN par si f (t) es impar si f (t ) f (t) f (t ) f (t) PROPIEDADES IMPORTANTES DE LAS FUNCIONES PARES E IMPARES f PAR f PAR f PAR f IMPAR f IMPAR f PAR f PAR f IMPAR f IMPAR 0, g (t ) es impar a g (t )dt 2 g (t)dt , g (t ) es par a 0 a IDENTIDADES ESPECIALES DE LAS FUNCIONES SENO Y COSENO sen(t ) sent cos(t ) cos t sen n 0 cos n 1 n n : entero 1