Fotosíntesis
Anuncio

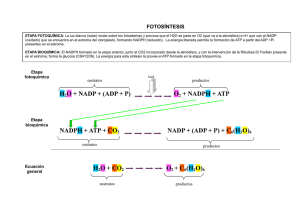
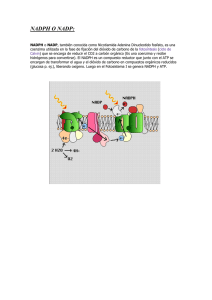
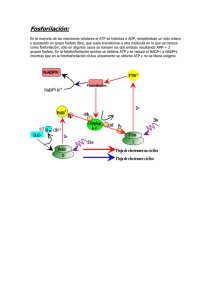
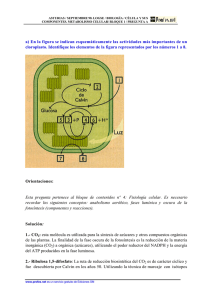
FOTOSINTESIS RESPIRACION FOTOSINTESIS RESPIRACION Mitocondria Cloroplasto ESTRUCTURA CLOROPLASTO ESTRUCTURA MITOCONDRIA H+ Espacio Intermembranoso Membrana Baja [H+] Espacio Tilacoidal Cadena transporte Electrones ATP sintasa Key Alta[H+] Difusion Estroma Matrix ADP + P i ATP H+ FOTOSINTESIS Leaf cross section Vein Mesophyll Estoma Chloroplast CO2O2 Mesophyll cell 5 µm Outer membrane Thylakoid Thylakoid EstromaGranum space Intermembrane space Inner membrane 1 µm Luz Luz Reflejada Cloroplasto luz Absorbida Grana Luz Transmitida FOTOSINTESIS Productos: 12 H2O 6 CO2 Reactivos: C6H12O6 6 H2O 6 O2 H2O LUZ REACCIONES LUMINCAS Chloroplast H2O Light LIGHT REACTIONS ATP NADPH Chloroplast O2 H2O CO2 Light NADP+ ADP + Pi LIGHT REACTIONS CALVIN CYCLE ATP NADPH Chloroplast O2 [CH2O] (sugar) e– Estado Excitado Calor Foton Clorofila II molecula Foton (fluorescente) Ground state Excitation of isolated chlorophyll molecule Thylakoid Photosystem Photon Thylakoid membrane Light-harvesting complexes Reaction center STROMA Primary electron acceptor e– Transfer of energy Special chlorophyll a molecules Pigment molecules THYLAKOID SPACE (INTERIOR OF THYLAKOID) H2O CO2 H2O Light NADP+ ADP NADP+ ADP CALVIN CYCLE LIGHT REACTIONS ATP NADPH O2 NADPH [CH2O] (sugar) O2 Light Pq e– e– e– P680 [CH2O] (sugar) Primary acceptor Energy of electrons Energy of electrons Primario aceptor H2O CALVIN CYCLE LIGHT REACTIONS ATP 2 H+ + 1/ 2 O 2 CO2 Light 2 H+ + 1/ 2 O 2 Light H2O e– Cytochrome complex Pc e– e– P680 ATP Fotosistema II (PS II) Fotosistema II (PS II) H2 O CO2 Light NADP+ ADP CALVIN CYCLE LIGHT REACTIONS ATP NADPH O2 [CH2O] (sugar) Primary acceptor Primary acceptor e– Pq Energy of electrons 2 H+ H2O e– Cytochrome complex + 1/2 O2 Light Fd e– e– NADP+ reductase Pc e– e– NADPH + H+ P700 P680 Light ATP Fotosistema II (PS II) NADP+ + 2 H+ Fotosistema I (PS I) H2 O CO2 Light NADP+ ADP CALVIN CYCLE LIGHT REACTIONS ATP NADPH ESTROMA (Low H+ concentration) O2 [CH2O] (sugar) Cytochrome complex Photosystem II Light 2 Photosystem I Light NADP+ reductase H+ NADP+ + 2H+ Fd NADPH + H+ Pq H2O THYLAKOID SPACE (High H+ concentration) 1/2 Pc O2 +2 H+ 2 H+ To Calvin cycle Thylakoid membrane ESTROMA (Low H+ concentration) ATP synthase ADP + Pi ATP H+ Light reactions Calvin cycle H2O CO2 Light NADP+ ADP + Pi RuBP Photosystem II Electron transport chain Photosystem I ATP NADPH 3-Phosphoglycerate G3P Starch (storage) Amino acids Fatty acids Chloroplast O2 Sucrose (export) H2O CO2 Input Light (Entering one CO2 at a time) 3 NADP+ ADP CALVIN CYCLE LIGHT REACTIONS ATP Phase 1: Carbon fixation NADPH Rubisco O2 [CH2O] (sugar) 3 P P Short-lived intermediate 3 P P 6 P 3-Phosphoglycerate Ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) 6 ATP 6 ADP 3 ADP 3 CALVIN CYCLE 6 P ATP P 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate 6 NADPH Phase 3: Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor (RuBP) 6 NADP+ 6 Pi P 5 G3P 6 P Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) 1 P G3P (a sugar) Output Glucose and other organic compounds Phase 2: Reduction Dado que en el ciclo de Calvin se necesita mas moléculas de ATP que de NADPH2 y como La fotofosforilacion fotosintetica es la producción de ATP en los cloroplastos reacciones activadas por la luz ; esto puede tener lugar vía dos sistemas , no ciclico y ciclico. •En la fosforilación no ciclica el ATP se genera en un sistema de transferencia electrónica “abierto” junto con desprendimiento de O2, a partir de agua yNADPH2 a partir de NADP. •En la fosforilación cíclica el ciclo de electrones es un sistema “cerrado” y el ATP es el único producto formado. Primary acceptor Primary acceptor Fd Fd NADP+ Pq NADP+ reductase Cytochrome complex NADPH Pc Fotosistema I Fotosistema II ATP