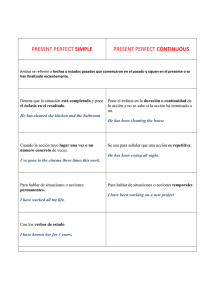
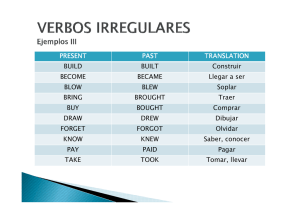
ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. UNIT 1 TENSES REVIEW PAST CONTINUOUS En la imagen podemos ver diferentes “sports and Leisure activities”, los cuales representan deportes y varias actividades que la gente realiza en su tiempo libre diferentes a su trabajo o actividades de obligación. Mira cada personaje en la imagen e identifica en el cuadro cual “leisure activity” estaban realizando. Usa el diccionario si es necesario. Respondiendo a la pregunta, y siguiendo los ejemplos dados (usando el pasado continuo) describe lo que estaban haciendo las personas en la imagen teniendo en cuenta la letra dada. WHAT WAS HE / SHE DOING YESTERDAY? (¿Qué estaba él / ella haciendo ayer?) A. B. F. G. He was sailing. (El estaba navegando) He was ………………………. He.……………………………. She……………………………. ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. WHAT WERE THEY DOING YESTERDAY? (¿Qué estaban ellos haciendo ayer?) C. They were doing yoga. (Ellos estaban haciendo yoga) D. They were s…………………… E. They were ……………………. H. They ………………………….. I. They …………………………… J. They were…………………….. Ahora escribe sobre las “Leisure Activities” que estuviste haciendo ayer, la semana pasada o el pasado fin de semana o año pasado, etc. Contestando a la pregunta correctamente y siguiendo el modelo de las anteriores oraciones. WHAT WERE YOU DOING YESTERDAY? (¿Qué estabas haciendo tú?) Example, I was visiting museums last week. (Ahora responde tú:) _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. De acuerdo al siguiente ejemplo, y teniendo en cuenta las anteriores imágenes, escribe un párrafo diciendo lo que la gente estaba haciendo en esos lugares como “leisure activities”. Usa el pasado continuo afirmativo y negativo. ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. PAST SIMPLE TENSE Como vimos anteriormente el pasado continuo lo usamos para mencionar una acción que sucedió en un lapso de tiempo determinado (tú estabas bailando: acción que sucede durante un lapso de tiempo determinado, acción que no ha terminado aún). En cuanto al pasado simple, éste es usado para mencionar una acción que sucedió en el pasado y ya terminó (yo te vi: acción que ya terminó) en el momento en que se habla o se usa la oración. REVIEW SIMPLE PAST – REGULAR VERBS (-ED) Affirmative Form 1. You arrived home at 7 p.m 2. She worked a lot in her art project. 3. I traveled to New York last year 4. They watched a very interesting TV program yesterday. Negative Form 1. You didn´t arrive at home at 3 p.m. 2. She didn´t work a lot in an office 3. I didn´t travel to Nice last year. 4. They didn´t watch a reality show yesterday. ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. Interrogative form Did I arrive late? Did she work in her project yesterday? Did you travel to the United States last year? Did they watch a good TV show last night? Short Answers Yes, you did. Yes, she did. Yes, I did. Yes, they did. / No, you didn´t. / No, she didn´t. / No, I didn´t. / No, they didn´t. REVIEW SIMPLE PAST – IRREGULAR VERBS (from the list). Para aquellos verbos que aparecen en la lista (adjunto en el curso) no es posible agregarles –ED para formar el pasado como en los anteriores casos. Estos verbos (en la lista Irregular Verbs) tienen su propia forma para el presente y otra para el pasado. Veamos ejemplos. verb Begin Eat Sleep feel Get home Past form began ate slept felt Got home Affirmative Form 1. You slept so much last night. 2. She broke a chair 3. I felt so nervous by the exam. 4. They found their lost book in the box. 5. The police caught him after committing the crime. Meaning Comenzar Comer Dormir Sentir Llegar a casa ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. Negative Form 1. You didn´t sleep so much last night. 2. She didn´t break a chair 3. I didn´t feel so nervous by the exam. 4. They didn´t find their lost book in the box. 5. The police didn´t catch the criminal. Interrogative Form 1. Did You sleep so much last night? 2. Did She break a chair? 3. Did I feel so nervous by the exam? 4. Did They feel their lost book in the box? Puedes revisar la lista de verbos irregulares en la plataforma. PRACTICE Mira las siguientes imágenes y menciona lo que hicieron los personajes en su pasado fin de semana. Usa el pasado simple, verbos irregulares y regulares en forma afirmativa para todos las imagines. Luego adiciona oraciones negativas para los numerales 4, 5, 12, 15 (usa la lista pues son irregulares). Los demás admiten –ed para el pasado. Example, 1. She watched television and she ate popcorn last night. ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE Vs PAST SIMPLE TENSE Cuando narramos diferentes actividades que ocurrieron en el pasado, podemos usar las dos formas del pasado “past continuous” y “Simple Past” combinadas en oraciones. Para esto debemos identificar cual acción sucede y termina (past simple) y cual sigue sucediendo en un lapso de tiempo del pasado narrado (past continuos) como en los ejemplos anteriormente presentados. Mira las imágenes en las cuales suceden dos acciones. Identifica las acciones y escribe incorrecta, sigue el modelo dado. para la oración que esta correcta y X para la oración ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. WRITTEN PROJECT George es un estudiante de la universidad. Su gemelo Kurt es un disc jockey en un club. Escribe en un párrafo acerca de lo que ellos estaban haciendo el pasado sábado, usando la información en la siguiente tabla. Example, George was getting up while Kurt was driving home. __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. Lee el siguiente material de apoyo para comprensión del pasado simple. Y completa los ejercicios a y b. ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. EXERCISE A ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. EXERCISE B ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS Para estudiar el tiempo perfecto continuo, lo veremos en comparación con el tiempo presente perfecto simple. Es importante notar que en inglés hay 2 distinciones en el uso del tiempo perfecto. PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE Este es usado en los siguientes casos: Para una acción terminada en el pasado Una acción que no termina cuando se está mencionando sobre ella. Para una acción que comenzó en el pasado y continúa en el presente y podría continuar en el futuro. Examples, -I have taken the exam. He terminado mi examen. -He has already finished his soup. Ha terminado su sopa. -Karen has lived here for 5 years. Ha vivido aquí por 5 años (aún vive aquí). -Juan and Peter have studied in the same class since 1999. Ellos han estudiado en la misma clase desde 1999. (y aún están en la misma clase). PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS OR PROGRESSIVE Este es usado para los siguientes casos: Para describir una acción que inicio en el pasado y continua en el presente pero además continuará en el futuro. Para hacer énfasis en que aún se continuará realizando la acción que inicio en el pasado. Examples, -I have been writing this report for days. He estado escribiendo este reporte por días. (Seguirá escribiéndolo pues no termina). -We have been dating since 2015. Hemos estado saliendo desde 2015. (Seguirán saliendo juntos). Para describir acciones que ocurren en lapsos cortos de tiempo dentro del mismo día, se usa con mayor frecuencia el presente perfecto continuo o llamado también progresivo. -My Little dog has been sleeping for hours. -Hector has been living here since 2001. ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. A menudo encontramos palabras como FOR, ALL y SINCE acompañando estos tiempos perfectos. Las dos primeras indican la duración de la acción, mientras que SINCE indica el momento en el cual inicia la acción. -Mi perrito ha estado durmiendo POR horas. -Héctor ha estado viviendo aquí DESDE 2001. También encontramos otras palabras que indican el momento como: Already Yet Still Ever Never En cuanto a la estructura de este tiempo veamos en el cuadro sus cambios para cada sujeto en la forma afirmativa, negativa e interrogativa. Notemos la diferencia en el auxiliar HAVE/HAS cuando se habla en tercera persona (he, she, it). PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS OR PROGRESSIVE - affirmative I have been working since 1998. You have been traveling for days. He / she has been eating for hours. It has been raining since 2 p.m we have been studying together for 3 years. you have been watching television all the day. they have been playing soccer all the morning. PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS OR PROGRESSIVE - negative I haven´t been working since 1998. You haven´t been traveling for days. He / she hasn´t been eating for hours. It hasn´t been raining since 2 p.m We You haven´t been haven´t been studying together for 3 years. watching television all the day. They haven´t been Playing soccer all the morning. ESING – English III – Lic. Mary Jimena Santacruz B. PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS OR PROGRESSIVE - interrogative have I been working since 1998? have you been traveling for days? has he / she been eating for hours? has have have have it been we been you been they been raining since 2 p.m? studying together for 3 years? watching television all the day? playing soccer all the morning? Now you can practice using the following exercises in the link. Read the explanation and complete the exercises in the page of the British Council. https://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/es/intermediate-grammar/present-perfect-simple-and-present-perfect-continuous