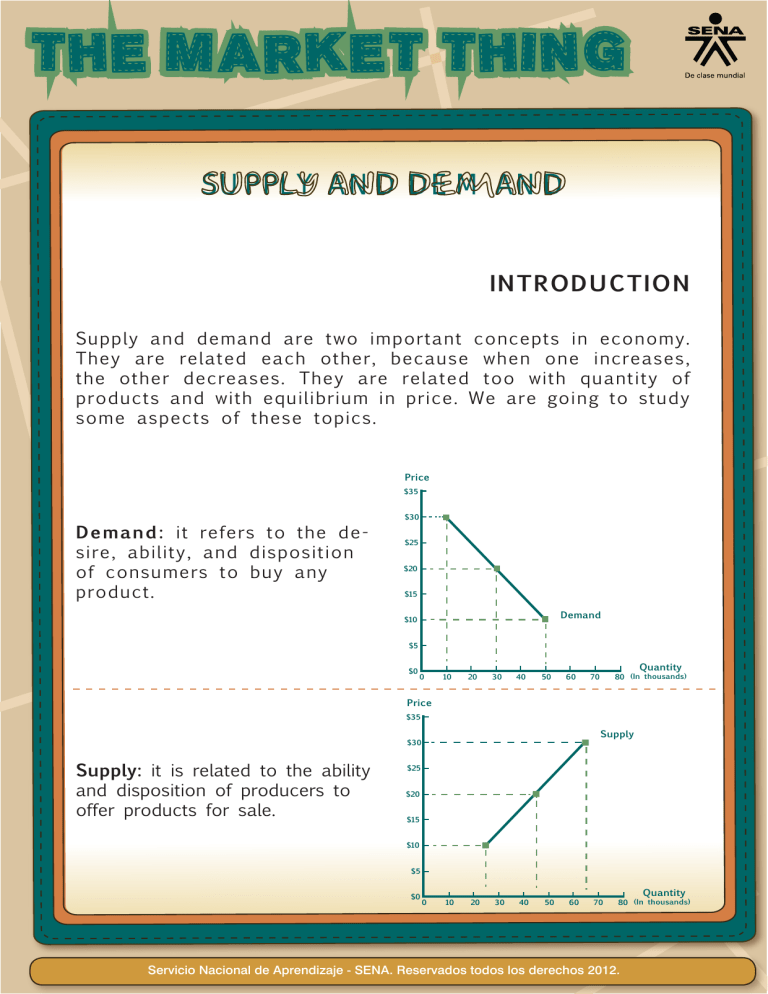
SUPPLY AND DEMAND INTRODUCTION Supply and demand are two important concepts in economy. They are related each other, because when one increases, the other decreases. They are related too with quantity of products and with equilibrium in price. We are going to study some aspects of these topics. Price $35 Demand: it refers to the desire, ability, and disposition of consumers to buy any product. $30 $25 $20 $15 Demand $10 $5 $0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Quantity 80 (In thousands) 70 Price $35 Supply $30 Supply: it is related to the ability and disposition of producers to offer products for sale. $25 $20 $15 $10 $5 $0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Quantity 80 (In thousands) Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje - SENA. Reservados todos los derechos 2012. In words of Janeen R. Adil, “Supply is the amount of goods and services there are to buy. Demand is how many people want to buy those goods and services” (2006, p. 4). 1. Tastes or preferences WHAT DO YOU TAKE INTO ACCOUNT TO DETERMINE THE DEMAND? Consumers may demand for an item one year and ignore it the next. 2. Number of consumers A large quantity of buyers carries to an increase in demand; a small quantity of buyers carries to a decrease (Franny Chan website). 3. Income When income rises, the quantity demanded will rise too. When income falls, the demand of that product will fall too (Franny Chan website). 4. Consumer expectations Purchasers are interested in satisfying their consumption regarding quality as the most important factor. Likewise, the lead price has an effect on the potential increase of the consumer´s final decision. 5. Price of related goods There are two kinds of related goods that can affect the demand: substitutes (for example, butter and margarine) and complementary (toys and batteries). Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje - SENA. Reservados todos los derechos 2012. WHAT FACTORS DETERMINE SUPPLY? 1. Price of goods The more expensive it will increase the amount that companies are willing to offer, the same way, the cheaper the product is, the lower the quantity supplied. 2. Production costs 3. Business objectives It depends on It’s not the same to produce for a market with higher expectations than produce for a market with lower ones. As greater the expectations are, the greater will be the offer from the companies. Cost of production factors Technology Laws of supply and demand According to David Besanko and Ronald R. Braeutigam, (2010, p. 37), the next are the laws of supply and demand: 1. Increase in demand + unchanged supply curve = higher equilibrium price and large equilibrium quantity 2. Decrease in supply + unchanged demand curve = higher equilibrium price and smaller equilibrium quantity 3. Decrease in demand + unchanged supply curve = lower equilibrium price and smaller equilibrium quantity 4. Increase in supply + unchanged demand curve = lower equilibrium price and large equilibrium quantity Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje - SENA. Reservados todos los derechos 2012. Marketing mix Supply and demand are two essential aspects in the market. Because the market is dynamic, marketing specialists use a variety of tools in order to achieve the goals of the company through combination or mixture (mix). These tools are known as the “Marketing Mix”, which refers to the kinds of marketing variables Remember: Marketing Mix sets out the marketing variables that your business needs to understand and control in order to achieve your overall business objectives. The four Ps of marketing mix PRICE PRODUCT Sizes Design Quality Returns Features Servicies Packaging Warranties Brand name Product variety Payment period Credit terms Allowances Price list Discounts Marketing mix variables (4P) PROMOTION Direct marketing Public relations Sales promotion Sales force Advertising PLACE Assortments Transport Locations Channels Coverage Inventory Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje - SENA. Reservados todos los derechos 2012. However, according to Larry Steven Londre (2007, pp. 5-9), the marketing mix has many variations and is formed by the 9PS (increasing marketing of 4ps by McCarthy). The next figure shows the nine Ps fo marketing mix: PASSION Feeling Emotions Devotion PRICE Payment period Credit terms Allowances Price list Discounts PRESENTATION PRODUCT Sizes Design Quality Returns Features Servicies Packaging Warranties Brand name Product variety PARTNERS Contract Suppliers Negotiations Alliances PROMOTION Marketing mix variables (9Ps) PLACE Assortments Transport Locations Channels Coverage Inventory Direct marketing Public relations Sales promotion Sales force Advertising PEOPLE/PROSPECT Community Individual characteristics Region or zone DISTRIBUTION Distribution Channel Coverage Assortments Locations Inventory Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje - SENA. Reservados todos los derechos 2012. The four Ps of marketing mix VARIABLES Product MEANING It´s the tangible object or service that can be offered to a market for acquisition, use or consumption that might satisfy a want or need. Price It´s is the amount a customer pays for the product. it includes Retail price/wholesale, discounts, quantity discounts, credit terms, sales and payment periods. Place/distribution It represents the location where a product or service can be purchased and the distribution channel. coverage, assortments, locations, inventory and transportation of the product or service. Promotion This refers to all of the communications that a company uses to increase knowledge about the product or service in addition to persuade the consumer to purchase (target segment). Passion Emotion, feelings. The emotions as distinguished from reason, a strong taste or devotion for some activity. Presentation It refers to the performances of presenting any of the 9P’s to your suppliers, customers, clients, or partners. A descriptive or persuasive account (Set forth for the attention of mind). People/prospect A product focusing on a specific target market based on demographic, geographic, psychographic and behavioral characteristics. Once the target market is chosen, the company can develop its marketing strategies to target this market. Partner The legal relationship between two parties, having specific rights and responsibilities as a common company. Planning To transform and develop marketing objectives to marketing strategies. Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje - SENA. Reservados todos los derechos 2012. To conclude about the marketing mix, 9ps are an extension of the 4ps, so we will continue to be based on the 4ps. BENCHMARKING Benchmarking is the procedure of determining who the best one is. It is an amount of the quality of company’s products, policies, programs, tactics, etc., and their contrast with standard measurements, or similar amounts of others. It is, also, the continuous systematic process for evaluating the companies that are recognized as best-in-class, for the following purposes: • • • Establishing priorities, target, goals Developing product and process objectives Meeting or surprising industry best practices Objectives of benchmarking • To define where and what improvements are requested • To investigate how other organizations reach their high performance levels • To use this information to improve the measurement of the results Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje - SENA. Reservados todos los derechos 2012. Process of benchmarking 1. Planning It is the plan for running the benchmarking investigation. 2. Analysis 3. Integration 4. Action After analyzing the information, it obtains a basis for comparison. Develop aims and incorporate them into the benchmarked process. It refers to the action plans necessary to achieve the objetives decided in step 3. Competition and its main aspects In benchmarking, it is necessary to take into account the next aspects: Product It is the thing produced by labor or effort. Price It refers to the quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services. Sales systems It is a set of principles, processes, strategies and tools that are put into place to bring the company results day-in and day-out. Payment systems It is used for transferring money include debit cards, credit cards, and e-commerce payment systems. Advertising Promotion Location It is a form of communication used to encourage or persuade an audience to continue or take some new action. It refers to the communications with the public in an attempt to influence them toward buying your products and/ or services. It is a place where something is or could be located. Organization It is a social unit of people systematically structured and managed to meet a need or to pursue collective goals on a continuing basis. Planimetry It is the measurement of plane surfaces; for example, the determination of, angles, horizontal distances and areas on a map. Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje - SENA. Reservados todos los derechos 2012. REFERENCES Adil, J. (2006). Supply and demand. Retrieved on May 20 2013, from http://books.google.com.co/books?id=8SxgIqc4BlcC&printsec=frontcover& dq=Janeen+r+adil&hl=es&sa=X&ei=ed6jUZ-jFY3m8gTMrYG4CQ&ved=0CEEQ 6AEwAw Besanko, D., and Braeutigam, R. (2010). Microeconomics. Reetrieved on May 8 2013, from http://books.google.com.co/books?id=978PKop7Cp8C &pg=PA37&dq=Laws+of+supply+and+demand&hl=es&sa=X&ei=OY2KUeX7B 6PO0gH04oCQBw&ved=0CE4Q6AEwBg#v=onepage&q=Laws%20of%20supply%20and%20demand&f=false Chan, F. (s/f). Determinants of demand. Fullerton College: Franny Chan website. Retrieved on May 18 2013, from http://staffwww.fullcoll.edu/ fchan/Micro/1determinants_of_demand.htm Londre, L. (2007). Several concepts. Retrieved on May 9 2013, from http://www.londremarketing.com/documents/LondreMarketingConsultingNinePs.pdf Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje - SENA. Reservados todos los derechos 2012.