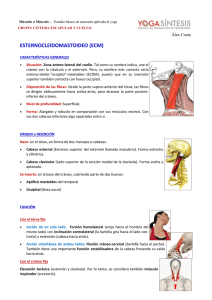
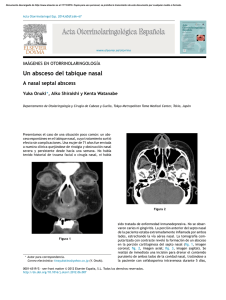
1. NERVIO OPTICO 2. QUIASMA CENTRAL 3. QUIASMA LATERAL 4. CINTILLAS OPTICAS Se afectan todas las fibras de los cuatro cuadrantes de la retina. Hay un ANOPSIA TOTAL DEL OJO AFECTADO La afectación central del quiasma (tumor hipofisario) da lugar a una HEMIANOPSIA BITEMPORAL por afectación de las fibras de la retina nasal de ambos ojos (ceguera nasal). Solamente afectación de las fibras de la retina temporal homolateral (aneurisma carótida interna). HEMIANOPSIA NASAL HOMOLATERAL. Lesión de las fibras de la retina temporal homolateral y nasal contralateral. HEMIANOPSIA NASAL HOMOLATERAL Y TEMPORAL CONTRALATERAL, hay incongruencia de los defectos del campo visual (no hay similitud en forma, tamaño y profundidad). 5. RDIACIONES SUPERIORES Se afectan el fascículo de la retina temporal superior homolateral y nasal superior contralateral. CUADRANTANOPSIA NASAL INFERIOR HOMOLATERAL Y TEMPORAL INFERIOR CONTRALATERAL. 6. RADIACIONES INFERIORES Lesión del fascículo de la retina temporal inferior homolateral y nasal inferior contralateral. Cuadrantanopsia nasal superior homolateral y temporal superior contralateral. 7. CORTEZA OCCIPITAL 8. RETINA HEMIANOPSIA NASAL HOMOLATERAL Y TEMPORAL CONTRALATERAL hay congruencia de los defectos de campo visual (similitud en forma, tamaño y profundidad) Escotoma central en concéntrico periférico mapa, circular,