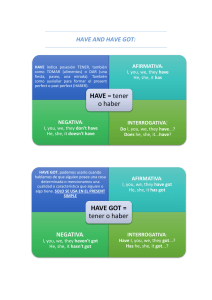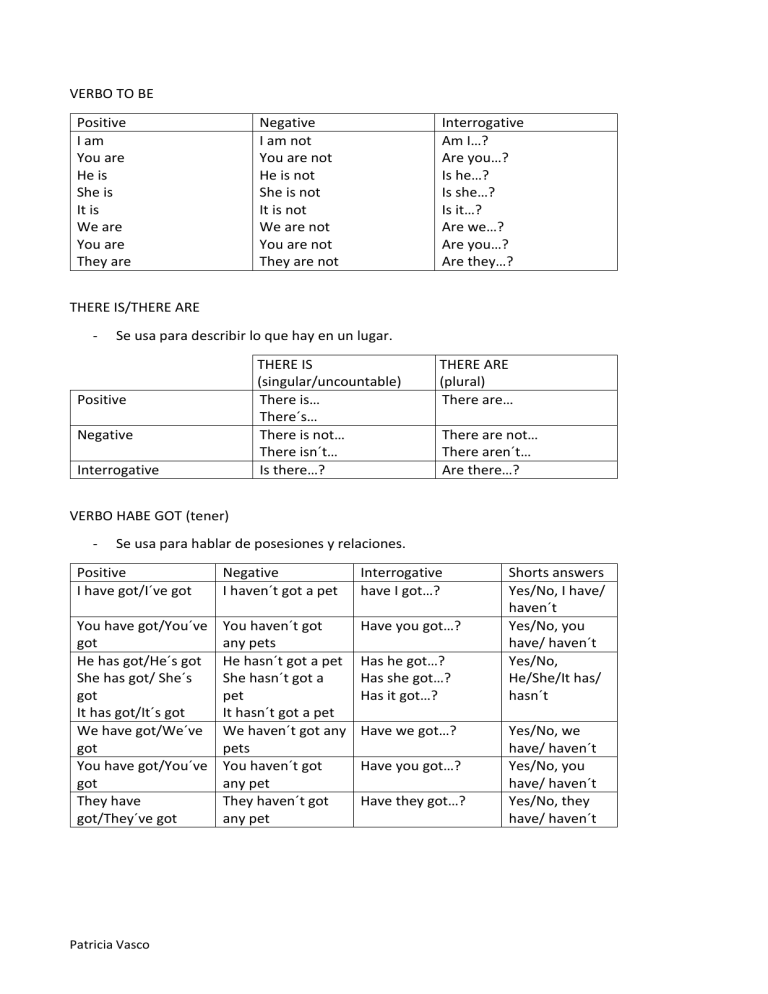
VERBO TO BE Positive I am You are He is She is It is We are You are They are Negative I am not You are not He is not She is not It is not We are not You are not They are not Interrogative Am I…? Are you…? Is he…? Is she…? Is it…? Are we…? Are you…? Are they…? THERE IS/THERE ARE - Se usa para describir lo que hay en un lugar. THERE IS (singular/uncountable) There is… There´s… There is not… There isn´t… Is there…? Positive Negative Interrogative THERE ARE (plural) There are… There are not… There aren´t… Are there…? VERBO HABE GOT (tener) - Se usa para hablar de posesiones y relaciones. Positive I have got/I´ve got Negative I haven´t got a pet Interrogative have I got…? You have got/You´ve got He has got/He´s got She has got/ She´s got It has got/It´s got We have got/We´ve got You have got/You´ve got They have got/They´ve got You haven´t got any pets He hasn´t got a pet She hasn´t got a pet It hasn´t got a pet We haven´t got any pets You haven´t got any pet They haven´t got any pet Have you got…? Patricia Vasco Has he got…? Has she got…? Has it got…? Have we got…? Have you got…? Have they got…? Shorts answers Yes/No, I have/ haven´t Yes/No, you have/ haven´t Yes/No, He/She/It has/ hasn´t Yes/No, we have/ haven´t Yes/No, you have/ haven´t Yes/No, they have/ haven´t PRESENT SIMPLE - Se usa para hablar sobre cosas que son ciertas y para hablar sobre hábitos y rutinas. Los verbos en el presente simple para “I, you, we and they” son iguales. Pero para “he, she and it” se añade: -es, -s or -ies. Positive I live You live He lives She lives It lives We live You live They live Negative I don´t live You don’t live He doesn’t live She doesn’t live It doesn’t live We don’t live You don’t live They don’t live Interrogative Do I live? Do you live? Does he live? Does she live? Does it live? Do we live? Do you live? Do they live? PAST SIMPLE - Se usa para hablar de acciones completas en el pasado. Se usan estas expresiones: “ yesterday, last night/week/month/year, on Monday, in October, an hour/two weeks/ three years ago, in 2013, an hour/two months later”. En los verbos regulares se añade -ed; en los irregulares se pone en past simple. Positive I lived Negative I did not live Interrogative Did I live…? You lived You did not live Did you live…? He lived She lived It lived We lived He did not live She did not live It did not live We did not live Did he live…? Did she live…? Did it live…? Did we live…? You lived You did not live Did you live…? They lived They did not live Did they live…? Patricia Vasco Shorts answers Yes/No, I don/don’t Yes/No, you don/don’t Yes/no, he/she/it does/doesn’t Yes/No, we don/don’t Yes/No, you don/don’t Yes/No, they don/don’t PRESENT CONTINOUS - Se usa para hablar de cosas que están en progreso en ese mismo momento. Se usan expresiones de tiempo como: now, right now and at the moment. Para las preguntas, algunas veces se usan particulas interrogativas: what, who, were, how, etc. Los verbos acabados en: -e, se quita la -e final y se añade -ing. Vocal (i, a, o) y consonante (m,p,t), se añade doble consonate antes de añadir -ing. -l, se pone doble -l (travel-travelling) -ie, se camabia la -ie por -ying (lie- lying) Positive I am playing Negative I´m not playing Interrogative Am I playing? You are playing You aren´t playing Are you playing? He is playing She is playing It is playing We are playing He isn´t playing She isn´t playing It isn´t playing We aren’t playing Is he playing? Is she playing? Is It playing? Are we playing? You are playing You aren’t playing Are you playing? They are playing They aren´t playing Are they playing? Shorts answers Yes, I am No, I´m not Yes, you are No, you aren´t Yes, he/she/it is No, he/she/it isn´t Yes, we are No, we aren’t Yes, you are No, you aren´t Yes, they are No, they aren´t PAST CONTINOUS - Se forma con “was/were” y el verbo en -ing. Se usa para describir una acción que está en progreso de tiempo en el pasado. Positive Negative was Was not (wasn´t) studying were Were not (weren´t) studying I/He/She/It We/You/They Yes/no questions Was I/He/She/It Were We/You/They studying studying Yes/No I/He/She/It Yes/No We/You/They Information questions What were Where was Patricia Vasco you she doing living three years ago? in 2009? Was/wasn´t Were/weren´t FUTURE SIMPLE - Se usa para predicciones del futuro. Si no estas seguro puedes usar “i think/ i don´t think” con will. Positive Negative Interrogative I will come I won´t come Will I come in? You will come You won´t come Will you come in? He will come She will come It will come He won´t come She won´t come It won´t come Will he come in? Will she come in? Will it come in? Won´t he come in? Won´t she come in? Won´t it come in? Yes, He/She/It will No, He/She/It won´t We will come We won´t come Will we come in? Won´t we come in? Yes, we will No, we won´t You will come You won´t come Will you come in? Won´t you come in? Yes, you will No, you won´t They will come They won´t come Will they come in? Won´t they come in? Patricia Vasco Interrogative negative Won´t I come in? Shorts answers Yes, I will No, I won´t Won´t you come in? Yes, You will No, You won´t Yes, they will No, they won´t PRESENT PERFECT - Se usa para hablar sobre experiencias del pasado. La hora exacta en la que paso no se conoce o no interesa. La forma del presente prefecto es con “have/has” y el verbo en “past participle” para los verbos irregulares, para los regulares se añade -ed. Se usan las expresiones: “for, since, already, yet, ever, never, just…” Se usa “never” en las declaraciones. Es decir, se usa para referirnos a que nunca hemos hecho eso hasta ahora. Se usa “ever” en las preguntas. Es decir, se usa para referirnos a que en cualquier momento hasta ahora También se puede usar “before” en las preguntas. Significa lo mismo que “ever”. Positive I have played Negative I haven’t played Interrogative Have I played? You have played You haven’t played Have you played? He has played She has played It has played We have played He hasn’t played She hasn’t played It hasn’t played We haven’t plated Has he played? Has she played? Has it played? Have we played? You have played You haven’t played Have you played? They played They haven’t played Have they played? Shorts answers Yes, I have No, I haven’t Yes, you have No, you haven’t Yes, he/she/it has No, he/she/it hasn’t Yes, we have No, we haven’t Yes, you have No, you haven’t Yes, they have No, they haven’t PAST PERFECT - Se utiliza para expresar una acción pasada anterior a otra pasada. Se utilizan las expresiones: “for, since, already, yet, ever, never, just…” Positive I had decided You had decided He had decided She had decided It had decided We had decided You had decided They had decided Patricia Vasco Negative I hadn’t decided You hadn’t decided He hadn’t decided She hadn’t decided It hadn’t decided We hadn’t decided You hadn’t decided They hadn’t decided Interrogative Had I decided? Had you decided? Had he decided? Had she decided? Had it decided? Had we decided? Had you decided? Had they decided? EXPRESIONS PREFECT PERFECT AND PAST PERFECT - - - - - - - For: *recordamos que la palabra a/an es igual a uno Se traduce por “desde hace/durante” Va seguido de un número Expresiones de for: “for ages: desde hace mucho tiempo” y “for a while: durane un tiempo” Since: Se traduce por “desde” Va seguido de una fecha: “un dia: Monday, Tuesday…” “un mes: July, August…” “un año: 2015, 2005…” “una hora: 22:23, 10:30…” “un momento en el tiempo: desde que maría murió…” Already: Significa “ya” Va delante del participio pasado No puede ir ni en preguntas ni en frases negativas Yet: Significa “ya” Va siempre al final de la frase “have you seen miguel yet?” Va siempre en preguntas y negativas En las frases negativas significa “todavía no” Ever: Significa “alguna vez” Va delante del participio pasado Va en frases afrimativas En las frases negativas y en las superlativas significa “nunca” Never: Significa “nunca” Va delante del participio pasado Va en frases afirmativas Just: Significa “acabar de” Va delante del participio pasado Patricia Vasco THE PASSIVE - Los verbos van en past participle. Positive I am known Negative I am not known Interrogative Am i known? You are known You aren´t known Are you known? He is known She is known It is known We are known He isn´t known She isn´t known It isn´t known We aren´t known Is he known? Is she known? Is it known? Are we known? You are known You aren’t known Are you known? They are known They aren’t known Are they known? Patricia Vasco Shorts answers Yes, i am No, i am not Yes, you are No, you aren´t Yes, he/she/it is No, he/she/it isn´t Yes, we are No, we aren´t Yes, you are No, you aren’t Yes, they are No, they aren’t