ÁLGEBRA 4°
TEORÍA DE EXPONENTES
Son definiciones y teoremas que estudian a los exponentes a través de operaciones de potenciación y
radicación.
POTENCIACIÓN
an = P
a: base, a R
n: exponente n Z
P: potencia P R
DEFINICIONES
1.
Exponente Natural
xn x . x . ..........
......x
; x R n Z+
n veces
x0 = 1
2.
Exponente Cero
3.
Exponente Negativo
x n
1
xn
; xR–{0}
; ; x R – {0} n Z+
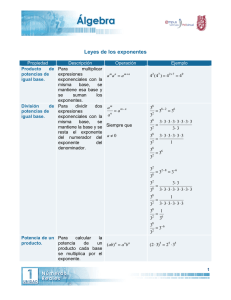
TEOREMAS
I)
BASES IGUALES
1.
Multiplicación
2.
División
am
am . an = am+n
am n ; a 0
an
II) EXPONENTES IGUALES
1.
Multiplicación
2.
División
an
an . bn = (ab)n
a n
bn b
; b0
III) EXPONENTE DE EXPONENTE
([ a]m )n P amnp
RADICACIÓN
n
a b
n: es el índice; n N n 2
a: es el radicando
b: es la raíz enésima
DEFINICIONES
n
x y yn x
; nN n2
(x R, además, cuando n es par, x 0)
1
( x) n x
; n0
n
m
n
(x) n ( x )m
n
xm
; n0
TEOREMAS
I)
RAÍZ DE UNA MULTIPLICACIÓN INDICADA
n
xy
n
x .
n
y
II) RAÍZ DE UNA DIVISIÓN
n x
y
n
n
x
;
y
y0
m n p
III) RAÍZ DE RAÍZ
x
m.n.p
x
CASOS ESPECIALES
m
m
xr .
xa
n
n
ys .
xb
p
p
zt
xc
m. n. p
m.n.p
xr.n.p . y s.p . zt
x( an b)p c
ECUACONES EXPONENCIALES
Son aquellas en las que la incógnita esta como exponente y también como base y exponente a la vez.
3x + 3x+1 + 3x+2 = 39
Ejm.:
x-x = 4
PROPIEDAD
1.
2.
Si:
am = an m = n
ax = bx a = b
Si:
a 0, 1, -1
a>0 b>0
Además: Si: x = 0 a b
3.
;
xx = aa x = a
EJERCICIOS RESUELTOS:
1. Simplificar:
E=
E=
(10) 5 (6) 5 (24)
E
(48) 2 (15) 4 (4) 3
(2.5)5 (2.3)5 23 .3
(24 .3)2 .(3.5)4 (22 )3
25 .55 .25 .35 .23 .3
28 .32 .34 .54 .26
213 .55 .36
5
E = 13 4 6 = 213−14 . 55−4 = 2−1 . 5 =
2 .5 .3
2
a) 5/2
b) 1/6
c) 5/6
d) 4/3
e) 3/8
2
1
1 1 1
E
2 4
125
81
1
3
2. Efectuar:
1
1
3
1
4
E = [ (4) + (125) + (81) ]
2
2
1
E = [ .16 + √125 + √81 ]
3
4
−
−
1
4
1
2
1
2
2
1
E = [8 + 5 + 3]−2
1
E = [16]−2
1
E=
1 2
[16]
1
E = √16
E=
1
4
a) 0.25
= 0.25
b) 1
c) 0.5
d) 4
e) 16
1
2
3. Resolver:
4x1 8x1 16x3
(22 )𝑥+1 . (23 )𝑥−1 = (24 )𝑥+3
(22 )𝑥+1 . (23 )𝑥−1 = (24 )𝑥+3
22𝑥+2 . 23𝑥−3 = 24𝑥+12
25𝑥−1 = 24𝑥+12
⇒ 5x – 1 = 4x + 12
x = 13
a) 13
b) 12
c) 11
d) 10
e) 9
EJERCICIOS PROPUESTOS:
155.143.24
J 4
6 .353.302
4. Simplificar :
a) 5
5.
b) 1
c) -1
d) -6
1
6. Efectuar : P 16 3
b)
3
c) 3
e) 4
0
2
5
3
0
b) 1
a) 1/2
d) 3
11 4
Calcular:
a) 0
c) 2
d)
6
2
3
e) 2
5
1
80
e) 2
x 3
x
7. Hallar “x” en: 25
225
a) 1
b) 3
c) -3
d) 4
e) -1
8
5
1
8. Resolver: 8 . 8 . 8 ........8 4 . 4 .......4
n veces
a) 4
b) 2
c) 8
(n 2) veces
d) -8
e) -2