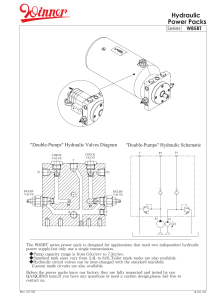
Forklift Trucks 18-25 tonnes Publ. no UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual in original MAINTENANCE MANUAL DCF 180–250 A Foreword B Safety C Preventive maintenance 0 Complete machine 1 Engine Maintenance Manual 2 Transmission DCF 180–250 3 Driveline/axle 4 Brakes 5 Steering 6 Suspension 7 Load handling 8 Control system 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories 10 Common hydraulics 11 Common electrics 12 Common pneumatics D Error codes E Schematics F Technical data G Terminology and index A:1 A Foreword Contents A Foreword Foreword ............................................................................................................ A:3 About the maintenance manual ...................................................................... A:3 General ...................................................................................................... A:3 Conditions .................................................................................................. A:3 Storage....................................................................................................... A:3 About the machine version......................................................................... A:3 Copyright .................................................................................................... A:3 Reading instructions ....................................................................................... A:4 Warning information ................................................................................... A:4 Important information ................................................................................. A:4 Read operator's manual ............................................................................. A:4 Read maintenance manual ........................................................................ A:4 Maintenance manual's content................................................................... A:5 Function group structure ............................................................................ A:6 Product alternatives and optional equipment ............................................. A:6 Machine card.............................................................................................. A:7 Function descriptions ................................................................................. A:7 About the documentation .............................................................................. A:10 The documentation's parts ....................................................................... A:10 Ordering of documentation....................................................................... A:10 Feedback .......................................................................................................A:11 Form for copying .......................................................................................A:11 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB A:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 A Foreword – Foreword A:3 A Foreword About the maintenance manual General Thank you for selecting Cargotec as your machine supplier. We hope that we will meet your expectations. The maintenance manual contains information about how the machine should be maintained for maximal operating reliability and service life as well as troubleshooting information for fast correction of any malfunctions. Conditions The instructions are based on use of general tools available in stores. All lifting devices, e.g., straps, slings, ratchet blocks, etc., must meet governing national regulations for lifting devices. Cargotec will not accept any responsibility for modifications performed without permission from Cargotec or in the event of the use of lifting devices, tools or work methods other than those described in this manual. Storage NOTE The maintenance manual shall be accessible to service personnel. About the machine version The information in this publication corresponds to the machine's design and appearance when delivered from Cargotec. There may be differences due to customisation of the machine. Cargotec reserves the right to change specifications and equipment without prior notification. The information in the manual is valid at the time of publication. DANGER External equipment may only be used if it is approved by Cargotec. Risk of fatal accidents and property damage! Only used equipment approved by Cargotec. Copyright Cargotec Sweden AB Duplication of the content in this manual, in whole or in part, is strictly prohibited without written permission from Cargotec Sweden AB. Duplication by any means such as copying, printing, etc., is prohibited. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB A:4 A Foreword – Reading instructions Reading instructions Warning information Warnings inform of potential hazards that, if warnings are not heeded, may result in personal injury or product damage. DANGER Situation that may lead to severe personal injury or fatality if the rule is not followed. WARNING Situation that may lead to personal injury if the rule is not followed. CAUTION Situation that may lead to product damage if the rule is not followed. Important information Important information is indicated by NOTE, and is provided to facilitate the work process, handling or increase understanding of the information. NOTE Information that is important without being related to safety. Read operator's manual 000262 The symbol to the left is used in certain cases on the machine and refers to important information in the operator's manual. Read the operator's manual 001128 Read maintenance manual The symbol to the left is used in certain cases on the machine and refers to important information in the maintenance manual. Read the maintenance manual UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 A Foreword – Reading instructions A:5 Maintenance manual's content The information in the maintenance manual is divided into function groups (0-12) to facilitate searching for information. The manual is divided in 20 sections A-C, 0-12, D-G. The sections with letters contain specific information that applies to several function groups and is not bound to a function, e.g., section "F Technical data". This is described in greater detail in the table below. For more information about function groups, see Function group structure, page A:6. A Foreword General information about the maintenance manual's purpose, content and reading instructions as well as survey for feedback of views and eventual inaccuracies. B Safety Keep in mind for your safety. C Preventive maintenance General information about preventive maintenance of the machine. 0 Complete machine 1 Engine 2 Transmission 3 Driveline/Axle 4 Brakes 5 Steering Technical description, description of the machine's functions with schematic drawings and explanatory texts for the included components. 6 Suspension Overviews with the components' position on the machine. 7 Load handling Work instructions for preventive maintenance. 8 Control system Work instructions for checking and adjusting. 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories 10 Common hydraulics 11 Common electrics 12 Common pneumatics D Error codes Error code information is found in the Workshop manual and Operator's manual. E Diagrams Wiring diagrams and hydraulic diagrams are found in the Workshop manual. F Technical data Technical data, conversion tables, information for conversion of units. G Terminology and index General terminology and abbreviations, explanations of terms and abbreviations that may appear in the manual, index for headings in the manual. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB A:6 A Foreword – Reading instructions Function group structure The information in the manual is divided in a structure of functions at different levels, based on the machine's design and use, called function groups. The upper level (called main group) determines group, e.g., group 7 Load handling. The second level (called two-digit) determines function, e.g., 7.2 Lifting/lowering. The third and fourth levels are used to break down functions into smaller parts (components). The function groups' structure for main group and two-digit group level are common for all machines from Cargotec, e.g., 4.3 Power-assisted brake system. Machine-unique adaptations of function groups are done at the third and fourth group level, e.g., 4.3.9 Wheel brake and 4.3.9.1 Disc pack. This means that some function groups (headings) will be left out of the documentation for certain machines since the machine does not have that particular function or component. In turn, this means that the function groups' numbering may 'skip', e.g., the three-digit heading level 4.8.7 Oil cooler may be included for some machines but not for others. The idea is that the function groups are intended to work as a search term to find different types of information between different sections and manuals. The information under a function group is divided into smaller sections according to the type of content, e.g., description or change. The maintenance manual and workshop manual contain different information. The maintenance manual only includes information needed for preventive maintenance as well as simpler troubleshooting. The workshop manual includes more in-depth information and repair instructions. References between sections in the same manual are indicated with section and group number, e.g., "see section 4 Brakes, group 4.3.9 Wheel brake". References within a section are indicated with a page number, e.g., "see Sensor fuel level, description page 24". References are not given between Maintenance manual and Workshop manual. If more information is desired for a function group, the primary recommendation is to search under the same function group in the other manual. Product alternatives and optional equipment The information in the manual is divided in modules. For product alternatives and optional equipment, handling of the modules differs depending on if it is the one or the other that is described, see below. Special equipment is not described in the manual. If you're uncertain about what equipment the machine should have, use the machine card to decide which information applies, see Machine card, page A:7. Product alternatives 000264 Product alternatives Symbol indicating optional equipment Product alternatives are such options that exclude certain standard equipment (e.g., engine alternative). Equivalent information for different product alternatives is described in separate sections following each other under the same function group. To indicate that there are different alternatives, the supplement "Product alternative" is used in the heading together with a simple description of which alternative is described, e.g., "(Product alternative Climate control unit ECC)". In addition, alternatives that are optional are marked with the symbol for optional equipment. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 A Foreword – Reading instructions A:7 Optional equipment Optional equipment are options that can be added to the standard equipment to obtain additional or improved functions. Information for optional equipment is described in separate sections with the standard equipment as starting point. Description of the optional equipment describes how the standard function is affected by the option as well as which additional components are added. Machine card NOTE If the machine has been modified after delivery the information on the machine card may be lacking or incorrect. IMPORTANT Changes done on the machine shall be reported to Cargotec so that the machine card can be updated. A new updated machine card is sent on the request of the customer. The machine card indicates of which drawings the machine consists, in many cases these can be associated to options and product alternatives. For more information on handling product alternatives and optional equipment, see Product alternatives and optional equipment, page A:6. The machine card is supplied with the spare parts catalogue and should be in the cab. The machine card is divided in the same function groups as the spare parts catalogue, maintenance manual, and workshop manual. For practical reasons, the machine card only uses the first and second level of the function group index. The function groups are written in groups of four characters, e.g., group 0107 corresponds to group 1.7 Cooling system in the manual. For more information about how the machine card is used for ordering spare parts, see the parts catalogue's foreword. If the information on the machine card does not help, contact Cargotec. NOTE All documents that accompany the machine are non-registered documents and there will be no notification of changes. Function descriptions Function descriptions are schematic overviews that describe how a function works as well as which components and signals work together. The function descriptions describe the function in a logical flow from input signal to desired output signal. Most functions require that pre-determined conditions are fulfilled for that function to be activated. In these cases the conditions are listed above the figure. Function descriptions use symbols to illustrate components such as valves, sensors, etc. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB A:8 A Foreword – Reading instructions 1 8 7 2 6 5 3 014779 4 Example of function description 1. Hydraulic force (solid double line) 6. 2. Flag diagnostic test, indicates that the signal can be checked with diagnostic test, see section 8 Control system, group 8.4 Diagnostics Flag pressure check connection (Check point), indicates that there is a measuring outlet for checking the pressure signal 7. Electric power (solid single line) 3. Illustration of function, (lifting/lowering) 8. Electric signal (dashed single line) 4. Component list 5. Position number in illustration, reference to component list UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 A Foreword – Reading instructions Symbol explanation function descriptions 1 2 3 4 5 Symbol explanation function descriptions The following symbols are used in function descriptions, the symbols are based on standard symbols used in wiring and hydraulic diagrams. 6 7 8 9 A:9 M 10 1. Electric control signal 2. Electric force 3. Hydraulic control signal 4. Hydraulic force 5. Hydraulic motor 6. Hydraulic oil pump with variable displacement 7. Hydraulic oil pump with fixed displacement 8. Electric motor 9. Accumulator 10. Disc brake 11. Filter 11 12. Radiator 12 13. Bulb 14. Control system, two control units with CAN-bus D790-1 13 15. Restriction 14 16. Adjustable restriction D797-F 17. Inductive position sensor 15 16 17 18 18. Electrically controlled servo valve 19. Thermal bypass valve 19 °C 21 °C 23 Pa 20. Temperature-controlled switch 21. Temperature sensor 20 °C 22 22. Pressure sensor 23. Pressure-controlled switch Pa 24. Hydraulic cylinder 25. Double-acting hydraulic cylinder 24 26. Spring brake cylinder 27. Valve block 25 28. Shuttle valve 26 27 28 29 014726 29. Non-return valve Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB A:10 A Foreword – About the documentation About the documentation The documentation's parts The documentation for the machine consists of the following parts: Operator's manual The operator's manual is delivered with the machine in the cab. Documentation kit Maintenance manual and spare parts catalogue with machine card are delivered to the machine as a separate documentation kit. Supplementary documentation Supplementary documentation can be ordered for the machine. • Workshop manual • Supplier documentation for engine, transmission and drive axle. Ordering of documentation The documentation is ordered from the dealer for Cargotec. Always specify publication number when ordering. For publication number, see the machine card. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 A Foreword – Feedback A:11 Feedback Form for copying Cargotec's ambition is that you who work with maintenance of Kalmar machines shall have access to correct information. Your feedback is important to be able to improve the information. Copy this form, write down your views and send it to us. Thanks for your help! To: Cargotec Sweden AB Technical Documentation Torggatan 3 SE-340 10 Lidhult SWEDEN Fax: +46 372 263 93 From: Company / Sender: .......................................................................................................................................... Telephone: .......................................................................................................................................................... E-mail: ................................................................................................................................................................. Date: .................................... - .................. - .................. Manual information Name / Publication number: ............................................................................................................................. Section / page number: ...................................................................................................................................... Suggestions, views, remarks, etc. ............................................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................................. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB A:12 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 B:1 B Safety Contents B Safety Safety.................................................................................................................. B:3 General safety information.............................................................................. B:3 Safety concerns everyone!......................................................................... B:3 A near accident is a warning! ..................................................................... B:3 Safety instructions........................................................................................... B:4 General ...................................................................................................... B:4 Service position .......................................................................................... B:4 Hydraulic system, depressurising............................................................... B:5 Oils ............................................................................................................. B:5 Fuel system ................................................................................................ B:6 AdBlue........................................................................................................ B:7 Clothing, etc. .............................................................................................. B:8 Several mechanics on the same machine.................................................. B:8 Working under machine ............................................................................. B:8 Lifting heavy components .......................................................................... B:9 Vibrations ................................................................................................... B:9 Noise ........................................................................................................ B:10 Solvents ................................................................................................... B:10 Fire and explosion risks.............................................................................B:11 Fluid or gas under pressure ..................................................................... B:13 Coolant ..................................................................................................... B:13 Refrigerant ............................................................................................... B:14 Air pollution .............................................................................................. B:14 Tensioned springs .................................................................................... B:15 Electric motors ......................................................................................... B:15 Rotating components and tools................................................................ B:15 Tyres and rims.......................................................................................... B:16 Lifting equipment ...................................................................................... B:16 Spare parts............................................................................................... B:18 Non-ionised radiation ............................................................................... B:19 Environment.................................................................................................. B:20 General .................................................................................................... B:20 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB B:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 B Safety – Safety B:3 B Safety General safety information Safety concerns everyone! The safety information concerns everyone who works with the machine! Persons who do not follow the safety instructions in this manual must make absolutely sure that the work is performed without risks of personal injury, without risks of machine damage, or property damage! Remember to: • follow the instructions in this manual • be trained for the work in question • follow local laws, safety rules and regulations • use the correct equipment and tools for the job • wear the correct clothes • use common sense and be careful. Do not take any risks! Cargotec has in this publication documented and warned for situations and risks that may occur in connection with using as well as service or repairs of the machine during normal circumstances. Therefore, it is very important that all who work with the machine, or carry out repairs or service work, acquaint themselves with and act according to the information in the Maintenance Manual and Operator's Manual. A near accident is a warning! An incident is an unforeseen event where neither a person, the machine, nor property is damaged. However, incidents indicate that there is a risk of injury and actions must be taken to avoid injury risks. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB B:4 B Safety – Safety instructions Safety instructions General Read, consider and follow the safety instructions below before starting to work in the machine: • Service position, page B:4 • Hydraulic system, depressurising, page B:5 • Oils, page B:5 • Fuel system, page B:6 • AdBlue, page B:7 • Clothing, etc., page B:8 • Several mechanics on the same machine, page B:8 • Working under machine, page B:8 • Lifting heavy components, page B:9 • Vibrations, page B:9 • Noise, page B:10 • Solvents, page B:10 • Fire and explosion risks, page B:11 • Fluid or gas under pressure, page B:13 • Coolant, page B:13 • Refrigerant, page B:14 • Air pollution, page B:14 • Tensioned springs, page B:15 • Electric motors, page B:15 • Rotating components and tools, page B:15 • Tyres and rims, page B:16 • Lifting equipment, page B:16 • Spare parts, page B:18 • Non-ionised radiation, page B:19 Service position General General Service position is used for service, maintenance and other situations when the machine needs to be secured. 014404 Service position means: Machine with forks and trolley in completely lowered position UDCF06.01GB • Machine parked, that is, applied parking brake. • Forks and trolley in completely lowered position. • Engine off. • System voltage off (with battery disconnector). Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 B Safety – Safety instructions B:5 Hydraulic system, depressurising 1 Machine in service position, see Service position, page B:4. 2 Depressurise the hydraulic system by opening the drain valve on the accumulator charging valve. NOTE Keep the accumulator drain valve open as long as work is in progress. NOTE After the work has been finished, close the drain valve and tighten the lock ring. Oils The following safety instructions shall be followed for work when handling oils. WARNING Warm and pressurised oil. Always depressurise the hydraulic system before starting work in the system. The hydraulic system is pressurised and its oil can cause personal injury. Avoid skin contact with the oil, use protective gloves. Hot oil may cause burns, rashes and irritation! Oil may also be corrosive to mucous membranes in, e.g., eyes, skin, and throat. IMPORTANT Always clean the area around components and connections before loosening them. Dirt in oil systems causes increased wear, which results in material damage. Always take actions to avoid spills. Where a container cannot be used for draining, use a pump or hose for safe handling. Always check that plugs seal tight before collection containers are moved. Handle all oil as environmentally hazardous waste. Oils freely released cause damage to the environment and may also start fires. Waste oils/fluids shall always be handled and taken care of by companies that are authorised for this work. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB B:6 B Safety – Safety instructions Fuel system The following safety instructions shall be followed for work when handling fuel. DANGER Pay attention to the risk of fire when working on the fuel system. Work on the fuel system shall be avoided when the engine is warm since fuel can spill on hot surfaces and may ignite. Ensure that naked flames, sparks or red-hot/glowing objects have been extinguished before starting work on or in the vicinity of the fuel system. Do not smoke in the vicinity of the machine when work on the fuel system is in progress. WARNING The engine's fuel system operates at very high pressure. The pressure is so high that the jet can damage the skin, which results in serious injuries. Risk of personal injury. Use protective gloves and protective safety goggles, avoid skin contact with fuel. If a component is to be loosened, hold a rag over the coupling as protection and collect the fuel. Fuel may be corrosive to mucous membranes in, e.g., eyes, skin, and throat. CAUTION Always clean the area around components and connections before loosening them. Dirt in the fuel system can cause malfunctions and engine stops in unwanted situations, as well as increased wear and material damages. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 B Safety – Safety instructions B:7 IMPORTANT Always take actions to avoid spills. Where a container cannot be used for draining, use a pump or hose for safe handling. Always check that plugs and connections seal tight before moving collection containers. Handle the fuel as environmentally hazardous waste. Fuel freely released causes damage to the environment and may also start fires. Fuel shall always be handled and taken care of by companies that are authorised for this work. AdBlue The following safety instructions shall be followed for work when handling AdBlue. CAUTION AdBlue can irritate the skin and eyes and when inhaled. Health hazard! Handle with care and avoid contact with skin, use gloves. In the event of contact with skin and spillages on clothing, rinse the skin with large amounts of water and replace contaminated clothing and gloves. In the event of contact with eyes, rinse thoroughly with water for several minutes and seek medical advice if necessary. In the event of inhalation, breath fresh air and seek medical advice if necessary. CAUTION AdBlue spilled onto hot components evaporates quickly. Irritation of eyes and respiratory system. Turn your face away. Evaporated AdBlue can harm mucus membranes in, for example, the eyes and throat. In the event of contact with eyes, rinse thoroughly with water for several minutes and seek medical advice if necessary. In the event of inhalation, breath fresh air and seek medical advice if necessary. IMPORTANT Avoid spilling AdBlue on the ground and in watercourses. Spillages on the ground must be absorbed with sand or other absorbent, non-combustible material. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB B:8 B Safety – Safety instructions Clothing, etc. Clothes should be in good repair. Remove loose, hanging items (e.g., tie, scarf). Do not wear clothes with wide sleeves, pant legs, etc. Remove jewellery as it may conduct electricity and get caught in moving parts. Long hair should be put up securely since it may otherwise get caught in moving parts. Be careful when working with a welder or open flame since hair is flammable. Several mechanics on the same machine WARNING If several mechanics are working on the same vehicle, be extra careful so that accidental movements do not injure another person. Communicate so that everyone knows where everyone is and what they are doing. Risks Work with wheels or axle suspension, mountings, etc., may result in components on the other side moving and causing damage or injury. Movements performed from the operator's station, e.g., all movement of lifting equipment, may cause severe personal injuries. Safety actions • Make sure that the machine's lifting equipment is completely lowered or secured in another way. • Move the battery disconnector to position zero and remove the key. • Be aware of the risks when several persons work around the vehicle. • Make your co-workers aware of what you're working with. • Do not work with drive wheels on the machine's both sides at the same time. Working under machine Working under the cab Loose objects must not be present in cabs that are to be tilted. The cab must always be tipped to its end position and secured with the stop device. When the work does not allow the cab to be tilted to its end position, or for work with cab suspension, the cab must always be secured with the stop device. On machines with vertically adjustable cab the cab must be secured in the raised position with the intended lock. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 B Safety – Safety instructions B:9 Working under frame A raised vehicle may not, for any reason, be supported or lifted in parts that belong to the wheel suspension or steering. Always support under the frame or wheel axle. Risks Mechanical or hydraulic tools and lifting devices can fall over or accidentally be lowered due to malfunctions or incorrect use. Safety actions • Use axle stands and supports that stand securely. • Lifting tools should be inspected and type approved for use. Lifting heavy components WARNING Careless handling of heavy components may lead to serious personal injury and material damage. Use type approved lifting tools or other devices to move heavy components. Make sure that the device is sturdy and intact. Risks Unsuitable lift slings, straps, etc. may break or slide. The centre of gravity of the component can change during the course of the work, and the component may then make unexpected movements which may cause severe personal injuries and material damage. A component lifted with lifting equipment can start to turn if the centre of gravity changes. A component lifted using an overhead crane may start to swing back and forth, which can cause severe crushing injuries or material damage. Safety actions Lift with lifting device. Use lifting tools or other devices, especially when such items are available for certain jobs. See the workshop manual for methods. If lifting must be performed without lifting device: • Lift near the body. • Keep your back vertical. Raise and lower with your legs and arms, do not bend your back. Do not twist your body while lifting. Ask for assistance - before lifting. • Wear gloves. They're often good protection to reduce crushing and cutting injuries to fingers. • Always use protective shoes. Vibrations Use of vibrating tools, e.g. impact nut runner or grinder, for an extended period of time may cause injuries as vibration is transmitted from tool to hands. Most of all when fingers are cold. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB B:10 B Safety – Safety instructions Safety actions • Use heavy gloves to protect against the cold and transfer of vibrations. • Switch between work duties to give the body time to rest. • Vary work position and grip so that the body is not stressed in only one position by the vibrations. Noise Noise louder than 85 dB (A) lasting for longer than 8 hours is deemed to damage hearing. (Limit values may differ between different countries.) High tones (high frequency) is more damaging than low tones at the same sound level. Noise in the form of impulse sounds may also be damaging, e.g., hammer blows. Risks Hearing damage may occur at noise levels higher than the limit value. In severe cases, damage may be permanent. Safety actions • Use hearing protection. Make sure that it's tested and protects against the right noise level. • Limit noise with noise-absorbing dividers, for example, noise-absorbing materials in roof and on walls. Solvents Fluids that (unlike water) dissolve grease, paint, lacquer, wax, oil, glue, rubber, etc., are called organic solvents. Examples: Naphtha, gasoline, thinner, alcohols, diesel, xylene, trichloroethylene, toluene. Many solvents are flammable. Risks Products with solvents give off vapours that may cause dizziness, headache, and nausea. They may also cause irritation of mucous membranes in the throat and respiratory tracts. If dissolvent comes into direct contact with the skin it can dry and crack. Higher risk of skin allergies. Solvents may also cause injuries if they penetrate the skin and are absorbed by the blood. If the body is continuously exposed to solvents, the central nervous system may be injured. This manifests itself as trouble sleeping, depressions, nervousness, poor memory, and general tiredness. Continuous inhalation of gasoline and diesel vapours is suspected of causing cancer. Safety actions UDCF06.01GB • Avoid inhaling solvent fumes by providing good ventilation, or wearing a fresh-air mask or respiratory device with a suitable filter for the toxic gases. • Never leave a solvent container without tight-sealing lid. • Use solvents with a low content of aromatic compounds. This reduces the risk of injuries. • Avoid skin contact. • Use protective gloves. • Make sure that work clothes are solvent-resistant. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 B Safety – Safety instructions B:11 Fire and explosion risks DANGER The operator's safety may not be jeopardised in case of fire. If possible, take the following actions at the slightest sign of fire: 1. Stop the machine and turn the start key to stop position. 2. Leave the cab. 3. Turn off the system voltage with the battery disconnector. 4. Call the fire department. 5. Try to put out the fire. If this is not possible, leave the machine and the danger area. DANGER Smoke from a fire may be very toxic. Smoke anaesthetises, suffocates, and kills! Smoke from fires, even small amounts, can damage lungs and respiratory organs. Avoid inhaling smoke gases, do not stand in the smoke. Use breathing protection when putting out a fire and working with burnt materials. Examples of flammable and explosive substances are oils, gasoline, diesel fuel oil, organic solvents (lacquer, plastics, cleaning agents), rustproofing agents, welding gas, gas for heating (acetylene), high concentration of dust particles consisting of combustible materials. Rubber tyres are flammable and cause explosive fires. Risks Examples of causes of ignition are welding, cutting with a welding torch, smoking, sparks from grinding machines, contact between hot machine parts and flammable materials, heat generation in rag drenched with oil or paint (linseed oil), and oxygen. Oxygen cylinders, lines, and valves shall be kept free from oil and grease. Fumes from, e.g., fuel are heavier than air and may "run" down into a sloping plane, or down in a grease pit, where welding flames, grinding sparks or cigarette glow may cause an explosion. Evaporated gasoline explodes very forcefully. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB B:12 B Safety – Safety instructions Special cases Gas oil with added gasoline has a reduced flash point. Risk of explosion already at room temperature. Explosion risk for heated gas oil is higher than for gasoline. When changing oil in the engine, hydraulic system and transmission, keep in mind that the oil may be hot and can cause burn injuries. Welding on or near machine. If diesel and or other oils have leaked out and been absorbed by rags, absorbent agents, paper or other porous material, glowing welding sparks can cause ignition and explosive fires. When a battery is being charged, the battery electrolyte's water is divided into oxygen and hydrogen gas. This mixture is very explosive. The risk of explosion is especially high when a booster battery or a rapid-charge device is used since this increases the risk of sparks. In today's machines there are a lot of electronics. When welding, all control units must be unplugged and the electric power must be turned off with the battery disconnector. Powerful welding currents may otherwise short-circuit the electronics, destroy expensive equipment, and may cause an explosion or fire. Never weld on painted surfaces (remove paint, preferably by blasting at least 10 cm around the welding or cutting point). Use gloves, breathing protection, and protective safety glasses. Also, never weld near plastic or rubber materials without first protecting them from the heat. Paint, plastic, and rubber generate many substances when heated, and these may be hazardous to health. Be careful with machines that have been exposed to intense heat or fire. Safety actions DANGER Remains of fuel, oils, grease, and other flammable materials on the engine or in the engine compartment are fire hazards. Risk of fire! Remove remains of flammable materials from the engine compartment as soon as they are discovered, be extra thorough with hot surfaces such as the exhaust system, manifold, or turbo. If leaks of oil, fuel, or coolant are detected, find the cause and solve the problem before starting the engine. UDCF06.01GB • Make a habit of performing a visual check of the engine and engine compartment before starting the engine and after operation, when the engine has been stopped. This ensures fast detection if anything abnormal has happened or is about to occur. Pay special attention to oil, fuel, or coolant leaks, loose bolts, worn or poorly tensioned drive belts, loose connections, damaged hoses, and electrical cables. The inspection only takes a few minutes and may prevent serious problems and expensive repairs. • Store hazardous substance in approved and sealed container. • Make sure that there is no ignition source near flammable or explosive substances. • Make sure that ventilation is adequate or there is an air extraction unit when handling flammable substances. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 B Safety – Safety instructions B:13 Fluid or gas under pressure Lines with high pressure may be damaged during work and fluid or gas may jet out. There may be high pressure in a line even if the pump has stopped, therefore gas or fluid may leak out when the connection for the hose is loosened. A gas cylinder exposed to outside forces may explode, e.g., if it falls on a hard surface. Gas may flow out from damaged valves. Risks Risk of damage/injuries in connection with work on: • Hydraulic systems (e.g., working hydraulics and brake system). • Fuel system. • Changing tyres. • Climate control unit (air conditioning). Safety actions • Use protective goggles and protective gloves. • Never work in a pressurised system. • Never adjust a pressure limiting valve to a higher pressure than the manufacturer's recommendations. • A hydraulic hose that swells, e.g., at a connection, shows that it is about to rupture. Replace it as soon as possible! Check the connections thoroughly. • Use fluid when checking for leaks. • Never blow clothes clean with compressed air. • Failed pressure accumulators shall first be drained of pressure and then punctured before being discarded (to avoid risk of explosion). Carefully drill a hole with 3 mm diameter after draining the pressure. • Never feel with your hands to check for any leaks. A fine jet from a hydraulic hose may have such high pressure that it easily cuts through, e.g., a hand, causing very severe injuries. Coolant The coolant in the machine’s cooling system consists of water, anti-corrosion compound and anti-freeze fluid, for example, ethylene glycol. Coolant must not be drained into the sewer system or directly onto the ground. Risks The cooling system is at high pressure when the engine is warm. Hot coolant may jet out and cause scalding in case of leaks or when the cap on the expansion tank (filling point) is opened. Ingesting ethylene glycol and anti-corrosion compound is dangerous and hazardous to health. Safety actions • Use protective gloves and safety glasses if there is a risk of splashing or spraying. • First open the cap for the filling point, to release the high pressure. Be careful. Hot steam and coolant may jet out. • If possible, avoid working on the cooling system when the coolant is hot. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB B:14 B Safety – Safety instructions Refrigerant Refrigerant is used in the machine’s air conditioning system. Work on the air conditioning system must be performed by accredited/authorised and trained personnel according to national legislation and local regulations. Risks The air conditioning operates at high pressure. Escaping refrigerant can cause frostbite injuries. Refrigerant that is heated (e.g., when repairing leaking climate/AC system), generates gases that are very dangerous to inhale. Safety actions • Follow special instructions and equipment for refrigerant according to the manual when working on the air conditioning unit. Any person doing the work must have special accreditation. (Note national legislation and local regulations!) • Use protective gloves and safety glasses if there’s a risk of leaks. • Make sure that heat-producing sources or objects are not close by (cigarette glow, welding flame). Air pollution Air pollution is the pollution in the air around us and that are regarded as hazardous to health. Certain pollutants are more prevalent in some environments. The following health-hazardous air pollution is especially prominent in workshops: • Carbon monoxide (fumes) is found in exhaust gases. Odourless and therefore extremely dangerous. • Nitrogen oxides (nitrous gases) are present in exhaust fumes. • Welding smoke especially hazardous to health when welding on oily surfaces, galvanised or lacquered materials. • Oil mist for example, when applying anti-corrosion agent. • Grinding dust and gases generated when grinding and heating plastics, lacquer, anti-corrosion agents, lubricants, paint, etc. • Isocyanates are present in certain paints, fillers, adhesives and foam plastics used on machines. Risks Sulphuric acid mist is corrosive and injures the respiratory tracts. (Generated when heating certain plastics and paints.) Isocyanates may be released in the form of vapour, dust (or may be found in aerosol) when cutting, grinding, or welding. May cause mucous membrane irritation with asthma-like symptoms and impaired lung function. Even brief exposures to high concentrations may cause problems with persistent hypersensitivity. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 B Safety – Safety instructions B:15 Safety actions • Make sure of adequate ventilation with fresh air when welding, battery charging and other work when hazardous gases are generated. • Use suitable protective gloves and breathing protection when there is risk of oil mist. Make sure that the protection is oil-resistant. • Apply oil-resistant protective lotion to unprotected skin. • Make sure that an eyewash station is in the immediate vicinity when working with corrosive substances. • Avoid unnecessary operation of the machine inside the workshop. Connect air extraction to the exhaust pipe so that exhausts are led out from the workshop. Tensioned springs Examples of tensioned springs: 1. Torque springs in, e.g., pedals. 2. Return spring (cup springs) in parking brake cylinder. 3. Lock rings 4. Gas springs Risks If a tensioned spring releases, it is shot out by the spring force and can also take adjoining parts with it. Small springs can cause eye injuries. Parking brake springs are tensioned with high force and can cause very severe accidents if they are accidentally released in an uncontrolled manner. Gas springs and gas-charged shock absorbers are tensioned with high force and can cause very severe accidents if they are accidentally released in an uncontrolled manner. Safety actions • Use safety glasses. • Lock rings should be of a suitable type and in good condition. • Follow the instructions in this and other manual when performing maintenance and changing parts and components. • Always use recommended tools. Electric motors Safety actions Always turn off the battery disconnector when working on electric motors. Always block the machine’s wheels, make sure that the parking brake is activated and that the gear selector is in neutral position before starting any work on the machine. Rotating components and tools Examples of rotating components and tools: • Cooling fan • Drive belts • Propeller shafts • Drills • Grinding machines Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB B:16 B Safety – Safety instructions Risks Rotating components, e.g., fans or shafts, can cause severe injuries if touched. Drills, lathes, grinders or other machines with rotating parts can cause severe accidents if clothes or hair get caught and are wound up in the machine. Safety actions • Do not use gloves when working with a drill. • Remove loose, hanging clothing, scarf or tie. • Never use clothing with wide sleeves or pant legs. • Make sure that clothing is intact and in good condition. • Long hair should be gathered up in a hair-net or similar. • Remove large or loose hanging jewellery from hands, arms and neck. Tyres and rims DANGER Tyres are to be considered as pressurised containers. Handling incorrectly, they are a fatal hazard. Parts can be thrown with explosive force and may cause severe injuries. Never repair damaged tyres, rims, or lock rings. Tyre changes shall be performed by authorised personnel. Risks Dismantling wheels: Tyres, rims, and lock rings may be ejected. Inflating tyres: Tyres, rims, or lock rings may be ejected. Safety actions • Always deflate the tyre before starting to work on the wheel. • Check that tyres, rims, and lock rings are free from damage. Never repair damaged rims or lock rings. • Wheels shall be inflated on the machine or in a protective device, designed and dimensioned so that it can handle or dissipate a shock wave from a tyre explosion as well as catch the ejected parts. • Use protective screen and safety glasses. Lifting equipment When working on the machine in general, and with the machine's lifting equipment in particular, the greatest care must be taken with regard to securing the mast and carriage. Get into the habit of always keeping the carriage lowered to the lowest position when working on the machine. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 B Safety – Safety instructions B:17 Risks If the machine's lifting equipment is not lowered or secured, there is a risk of crushing. Risk of crushing is extra high when depressurising the hydraulic system, see Hydraulic system, depressurising, page B:5. Safety actions Do not start work until the carriage is fully lowered. If the nature of the work requires the carriage to be raised, it must be secured in some way. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB B:18 B Safety – Safety instructions Spare parts WARNING For safety reasons, the following spare parts may only be replaced by genuine spare parts: UDCF06.01GB • Brake valve • Drive axle • Valve for mini-wheel/joystick control • Steering valve (Orbitrol) • Steering valve incl. priority valve • Steering axle • Steering cylinder • Rim • Solid wheels • Control valve, hydraulic servo • Mast, carriage • Lift cylinder incl. load control valve • Separate load control valve • Lifting chains • Chain tightener and shaft • Forks, fork carrier • Lift cylinder • Tilt cylinder • Twistlock • Control breaker (for hydraulic function) • Emergency switch • Hydraulic cylinder, cab tilt • Accumulator • Tilt valve • Main valve load handling • Accumulator charging valve • All control units Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 B Safety – Safety instructions B:19 Non-ionised radiation WARNING Extra equipment such as two-way radio, RMI, telephone, etc. may emit non-ionised radiation. Risk of interference with active or non-active medical products. Use a two-way radio, RMI, telephone, etc., when no persons with active or non-active medical products are nearby. NOTE When persons with active or non-active medical products are not nearby, then telephone and two-way radio may be used in the cab. Equipment should not be used when operating or load handling since this reduces your concentration as operator. Cargotec does not assume any responsibility for extra equipment not installed by Cargotec or according to installation instructions approved by Cargotec. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB B:20 B Safety – Environment Environment General Our global environment is significantly affected by the world's ever-increasing industrialisation. Nature, animals, and humans are exposed daily to great risks in connection with handling of chemicals in various forms. Still there are no environmentally safe chemicals, e.g., oils and coolants, on the market. Therefore, all who handle, perform service, or repair machines must use the tools and methods that are necessary to protect the environment in an environmentally correct way. By following the simple rules below, you will contribute to protecting our environment. Recycling Well-planned recycling of the machine is the starting point for finishing the life cycle and making use of materials for re-use in new products. According to calculations by Cargotec, the machine can be recycled to more than 90% by weight. Environmentally hazardous waste Components such as batteries, oils and other chemicals, and other materials that may constitute environmentally hazardous waste, must be handled and taken care of in an environmentally safe and sound manner. Discarded batteries contain substances hazardous to personal health and the environment. Therefore, handle batteries in an environmentally safe manner and according to national regulations. Oils and fluids Oils freely released cause damage to the environment and may also start fires. When emptying and draining oils or fuel, take actions to prevent unnecessary spills. Waste oils and fluids must always be taken care of by an authorised disposal company. Pay close attention to oil leaks and other fluid leaks! Take immediate action to seal any leaks. Air conditioning system The refrigerant in the air conditioning unit for the cab contributes to the greenhouse effect if it escapes into the open air. Special training is required for all service work on the air conditioning unit. Many countries also require certification by an authority for such work. When scrapping an air conditioning unit, the refrigerant shall be taken care of by a certified company. Working in a contaminated area The machine shall be equipped for work within a contaminated area (polluted environment or health-hazardous area) before starting the work. Also, special local instructions apply for handling and service work on such a machine. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 B Safety – Environment B:21 Declarations The machine does not contain asbestos. The machine contains lead in batteries and electrical wiring. Some models have cast lead counterweights. If the machine is equipped with air conditioning, refrigerant of the type R134a and an amount between 1-3 kg is used. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB B:22 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 C:1 C Preventive maintenance Contents C Preventive maintenance Preventive maintenance ................................................................................... C:3 Preventive maintenance, general ................................................................... C:3 Preventive maintenance, work instructions..................................................... C:3 Check and service log..................................................................................... C:4 50h-check ....................................................................................................... C:5 Service schedule............................................................................................. C:7 Washing ........................................................................................................ C:14 Lubricating 500h ........................................................................................... C:15 Lubricating 1000h ......................................................................................... C:20 Checking for cracks ...................................................................................... C:24 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:3 C Preventive maintenance Preventive maintenance, general It’s very important that preventive maintenance is performed according to recommended intervals. Preventive maintenance should be performed by Cargotec, or by a service organisation authorised by Cargotec. CAUTION Service intervals shall be followed. This is to maintain the machine's safety and to fulfil warranty and service agreements! Use spare parts and fluids approved by Cargotec to fulfil the warranty. Preventive maintenance, work instructions 1 For a new machine it is very important to check-tighten the wheel nuts during the first work week until they are seated properly. This should be done at an interval of 4–5h (up to approx. 40–50h). 2 For a new machine, perform the checking action after 50 hours of operating time, see 50h-check, page C:5. Note completed 50h-check in the service log, see Check and service log, page C:4. 3 Regular service shall be performed according to service schedule, see Service schedule, page C:7. The service schedule shall be followed to ensure high machine reliability and safety. Note completed service in the service log, see Check and service log, page C:4. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:4 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance Check and service log Model: Serial number: Completed maintenance Operating hours Actions 50h 50h-check 500h 500h service 1000h 1000 service 1500h 500h service 2000h 2000h service 2500h 500h service 3000h 1000 service 3500h 500h service 4000h 2000h service 4500h 500h service 5000h 1000 service 5500h 500h service 6000h 2000h service 6500h 500h service 7000h 1000 service 7500h 500h service 8000h 2000h service 8500h 500h service 9000h 1000 service 9500h 500h service 10000h 2000h service UDCF06.01GB Operating hours Date Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 Signature C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:5 50h-check On a new machine, the following checks shall be performed after 50 operating hours. The checks are performed to increase reliability and safety. In addition to the following checks, lubrication should also take place in accordance with the 500h-service, see Lubricating 500h, page C:15. 1 Engine Reference Bolted joints, attachments, mountings, hose clamps, wear and chafing of hoses, cable harnesses, etc. Sealing check oil, coolant, exhaust system Fuel prefilter, water draining Section 1 Engine, group 1.2.3 Fuel prefilter Air filter indicator, check Operator's manual Air filter main cartridge, inspection Air filter safety cartridge, inspection Drive belt tension, check Section 1 Engine, group 1.7.5 Cooling fan Coolant level, check Operator's manual Oil and oil filter, change Section 1 Engine, group 1.8 Lubrication system Oil pressure 2 Transmission Leakage check Oil and oil filter, change Section 2 Transmission, group 2.6 Transmission oil, changing. 3 Driveline/Axle Mounting propeller shaft, check-tightening Section 3 Driveline/Axle, group 3.2 Propeller shaft Mounting drive axle, inspection Section 3 Driveline/Axle, group 3.3 Drive axle 4 Brake system Leakage check Power-assisted brake, function check Parking brake, function check Operator's manual Section 10 Common hydraulics Group 10.3.2 Accumulator 5 Steering Sensor steering wheel reading mini-wheel/joystick control, function check Section 5 Steering, group 5.2.11 Sensor steering wheel reading 6 Suspension Steering axle suspension, checking Section 6 Suspension, group 6.2.1 Steering axle cradle Tyres and rims, check Section 6 Suspension, Group 6.3.1 Tyres Wheel nuts, check-tightening 7 Load handling Hose connections, checking the O-ring seal. Check-tightening in the event of leaks. For additional attachments, see the manufacturer's instructions. 8 Control system Check that there are no active error codes Section 8 Control system, group 8.3 Error codes Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:6 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories Hose fittings, air conditioning (ECC Electric Climate Control), check-tightening Air conditioning system, performance tests Section 9 Frame, body, cab, and accessories, group 9.4 Air conditioning. Counterweights, checking Section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, group 9.13.4 Counterweights 10 Common hydraulics Hose connections, check-tightening in the event of leakage Leakage check Section 10 Common hydraulics, group 10.5.2 Main valve Hydraulic oil filter, changing Section 10 Common hydraulics, group 10.6.8 Hydraulic oil filter Oil level, check Section 10 Common hydraulics, group 10.6.9 Hydraulic oil 11 Common electrics Batteries, check UDCF06.01GB Section 11 Common electrics, group 11.3.1 Start battery Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:7 Service schedule Service shall be performed every 500h. Actions are divided into 500h, 1000h and 2000h service. Actions for 500h service are performed between 1000h and 2000h service, which means at 500h, 1500h, 2500h, etc. Actions for 1000h service are performed at odd thousands of operating hours: 1000h, 3000h, 5000h, etc. Actions for 2000h service are performed at even thousands of operating hours: 2000h, 4000h, 6000h, etc. After service is performed, make a note in the check and service log, see Check and service log, page C:4. In the column for service below, the following abbreviations are used: R = replace C = check or inspection L = lubrication h= operating hour CAUTION Lubrication intervals are based on normal handling and environment and are subject to the use of the recommended grades and quantities. In other conditions, e.g. cold, hot, dusty, we recommend halving the intervals. The lubrication interval must never exceed 12 months. Service Object, action 500h, 1500h, 2500h, etc. 1000h, 3000h, 5000h etc. 2000h, 4000h, 6000h etc. C C Comment Reference C Check and remove remains of flammable materials in the engine compartment, pay extra attention to hot surfaces such as exhaust system, manifold, or turbo. If leaks of oil, fuel, or coolant are detected, find the cause and solve the problem. Section B Safety C C Visual check in connection with greasing. L L Lubricating 500h, page C:15 L L Lubricating 1000h, page C:20 0 complete machine Checking cleanliness and leakage Attachments (stub axles) Lubricating 500h Lubricating 1000h Checking for cracks L C* * Check every 4000h or every year. Checking for cracks, page C:24 1 Engine Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:8 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance Service Object, action Bolted joints, attachments, mountings, etc. 500h, 1500h, 2500h, etc. 1000h, 3000h, 5000h etc. 2000h, 4000h, 6000h etc. C C C Fuel tank Fuel prefilter C R Comment Reference C Clean if necessary. Section 1 Engine, group 1.2.1 Fuel tank R Drain water/impurities. Section 1 Engine, group 1.2.3 Fuel prefilter Change filter earlier if error code is displayed. R R Change filter earlier if error code is displayed. Section 1 Engine, group 1.2.4 Fuel filter AdBlue tank C Cleaning Section 1 Engine, group 1.2.12 AdBlue tank AdBlue filter R Fuel filter Valve clearance C Section 1 Engine, group 1.2.13 AdBlue filter First check after 500 h, then every 1500 h. NOTE After engine replacement or engine overhaul check/adjust after 250 h. Performed by service shop authorised by Volvo Penta. Section 1 Engine, group 1.6.1 Air cleaning system Air filter main cartridge C/R C/R C/R Checking indicators, change when indicated. Air filter safety cartridge C C/R C/R Changed every other time main cartridge is changed. Air filter, hood C R R Washed every 500 operating hours. Filter change every 1000 operating hours. Section 1 Engine, group 1.6.1 Air cleaning system Exhaust system C C C Sealing check Section 1 Engine, group 1.6.3 Exhaust system C C Sealing check Section 1 Engine, group 1.6.4 Intercooler C C External check and cleaning. Section 1 Engine, group 1.7.4 Radiator and expansion tank Charge-air hoses Radiator C NOTE Do not use high pressure wash. Drive belts C/R C/R Belt tensioner Coolant R Section 1 Engine, group 1.7.5 Cooling fan C C C C / R* Level check. * Change after 5000 h or once every two years. For volume and quality, see section F F Technical data. Coolant, freezing point UDCF06.01GB C C C For volume and quality, see section F F Technical data. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 Section 1 Engine, group 1.7.7 Coolant C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:9 Service Object, action 500h, 1500h, 2500h, etc. 1000h, 3000h, 5000h etc. 2000h, 4000h, 6000h etc. Turbo C Injectors C* Comment * Every 3000 h. Reference NOTE Performed by service shop authorised by Volvo Penta. Engine oil R R R Engine oil filter R R R R R For volume and quality, see section F F Technical data. Section 1 Engine, group 1.8 Lubrication system R At each transmission oil change. Section 2 Transmission, group 2.6.4 Oil filter R Change transmission oil every 1000h or every year. Section 2 Transmission, group 2.6 Lubrication system 2 Transmission Transmission oil filter Transmission oil C Also change on indication from the filter monitor. Transmission, calibration C C Calibration of transmission is recommended every 1,000 operating hours. Section 2 Transmission, group 2.8 Control system C C Section 3 Driveline/Axle, group 3.2 Propeller shaft C C Section 3 Driveline/Axle, group 3.3 Drive axle C R R Section 3 Driveline/Axle, group 3.3 Drive axle Power-assisted brake C C C Brake pedal and pedal assembly C C C Section 4 Brakes, group 4.1.1 Brake pedal Brake pressure, checking C C C Section 4 Brakes, group 4.3.6 Distribution block C/R C/R C/R Link arms C C C Sensor steering wheel reading mini-wheel/joystick C C C Steering axle suspension C C Suspension in the frame. Section 6 Suspension, group 6.2.1 Steering axle cradle Wheel spindle, check C C Clearance in wheel suspension shall be checked. Max. 0.25 mm. Section 6 Suspension, group 6.2.2 Wheel spindle 3 Driveline/Axle Propeller shaft C Drive axle Drive axle oil 4 Brake system Parking brake Function check. Check pad thickness, change when needed. Section 4 Brakes, group 4.5.4.2 Parking brake pads Checking the bearings and lock screws for the shafts. Section 5 Steering, group 5.2.6 Link arm 5 Steering Section 5 Steering, group 5.2.11 Sensor steering wheel reading control 6 Suspension Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:10 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance Service Object, action 500h, 1500h, 2500h, etc. Wheel hub, checking 1000h, 3000h, 5000h etc. 2000h, 4000h, 6000h etc. *) C Comment Reference Check bearing pre-load. Section 6 Suspension, group 6.2.3 Wheel hub *) Check the first time after 1000 h, then every 2000 h. Tyres and rims C C C Damage, wear and pressure, change as needed. Section 6 Suspension, group 6.3 Tyres and rims Wheel nuts C C C Check-tighten. Section 6 Suspension, group 6.3 Tyres and rims C* * Checking for cracks, every 2,000 hours and in connection with tyre changes. Section 6 Suspension, group 6.3.2 Rim C C Check that the welds are intact and check the bearings. Section 7 Load handling, group 7.2.6 Mast C C Check for damage. Section 7 Load handling, group 7.2.8 Chains Rim 7 Load handling Mast suspension Lifting chains C Tension chain when needed. Support roller C C C Section 7 Load handling, group 7.2.14 Support roller and 7.2.15 Top support roller Side shift cylinder C C C Section 7 Load handling, group 7.4.4 Side shift cylinder Tilt cylinder C C C Lifting forks C C C C C Calibrating the scales Section 7 Load handling, Group 7.10.1 Electric scales Attachment C C Damage Section 7 Load handling, group 7.10.5 Side lift attachment Twistlocks C C/R Check for cracks every other year or every 4000 operating hours. Section 7 Load handling, group 7.10.5 Side lift attachment Scales Check that the welds are intact and check the bearings. Section 7 Load handling, group 7.7.5 Tilt cylinder Section 7 Load handling, group7.9.1 Lifting forks Replace every 10,000 operating hours. Reset time counter for twistlocks after replacement. Sensors C C C C C C Section 7 Load handling, group 7.10.5 Side lift attachment 8 Control system Service indicator, reset UDCF06.01GB A special code is required in addition to the service code. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 Section 8 Control system, group 8.2.4 Service indicator C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:11 Service Object, action 500h, 1500h, 2500h, etc. 1000h, 3000h, 5000h etc. 2000h, 4000h, 6000h etc. C C C Function check C C C Checking function. Comment Reference 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories Instruments and controls Air conditioning unit Function check of drive belt Section 9 Frame, body, cab, and accessories, group 9.4 Air conditioning. Section 1 Engine, group 1.7.5 Cooling fan Fresh air filter C/R R R Depending on the external environment. Certain models have washable prefilters. Fine filters are changed when necessary. Condenser C C C Clean when needed. NOTE! Not high-pressure washer. Section 9 Frame, body, cab, and accessories, group 9.4.4 Fresh air filter Section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, Group 9.4.9 Condenser unit C/R C/R C/R Windshield wipers C C C Lighting and audible signals C C C Communication equipment C C C Roof window C C Check damage, change when needed. Section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, Group 9.9 Glass/windows/mirrors Cab frame C C Check rust damage, deformation or cracks. Section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, group 9.10 Cab frame C C Check doors' mounting points. Section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, Group 9.10.2 Doors C C Check mountings, isolators and bolted joints. Section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, group 9.10.3 Cab undercarriage C C Check the pin for the cab and the lift cylinder's mounting. Section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, group 9.10.3 Cab undercarriage Moisture filter Hinges for doors and cover lids C Cab undercarriage Hydraulic tilting of the cab C Checking, change if indication is grey. Section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, group 9.4.21 Moisture filter Incl. flushing. Section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, Group 9.5 Wiping and cleaning of windows See separate subcontractor information Section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, Group 9.10.4 Cab tilting Frame C C Check for any deformation and rust damage as well as cracks in welded joints. Non-slip plate for cab steps and on cab floor C C Check and replace non-slip plate in poor condition. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:12 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance Service Object, action 500h, 1500h, 2500h, etc. Counterweight mounting/box Central lubrication C 1000h, 3000h, 5000h etc. 2000h, 4000h, 6000h etc. C C Section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, Group 9.13.4 Counterweights C C Section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, group 9.14 Central lubrication Paint/coatings C Comment Check the machine's painted surfaces for stone chips and scratches Reference Section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, group 9.15 Paint/coatings Repair damage immediately to avoid corrosion. Safety decals C C C Check that safety decals are legible, securely fastened, and not damaged. Clean dirty decals and replace decals as needed. See Operator's manual, section 3 Overview, group 3.2 Signs Hydraulic pressure, checking C C C Accumulator C C C Check the precharge pressure. Section 10 Common hydraulics Group 10.3.2 Accumulator C C External check and cleaning. Section 10 Common hydraulics, group 10.6.2 Hydraulic oil cooler 10 Common hydraulics Cooler for hydraulic oil Section 10 Common hydraulics NOTE Do not use high pressure wash. Breather filter hydraulic oil tank Hydraulic oil filter UDCF06.01GB C/R R R R R Change at indication. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 Section 10 Common hydraulics, group 10.6.7 Breather filter hydraulic oil tank Section 10 Common hydraulics, group 10.6.8 Hydraulic oil filter C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:13 Service Object, action 500h, 1500h, 2500h, etc. 1000h, 3000h, 5000h etc. Hydraulic oil 2000h, 4000h, 6000h etc. C/R Comment Reference Checked with oil sample. Section 10 Common hydraulics, group 10.6.9 Hydraulic oil • If oil sample OK after 2000h, operate for a further 1000h and take new oil sample. • If oil sample OK after 3000h, operate for a further 1000h and change oil. Note! Max. 4000h change interval. Additive: Lubrizol should be added when changing hydraulic oil. Concentration 3%. For volume, see section F Technical data. 11 Common electrics Position sensors C C C Should be free from grease and dirt, clean as needed. Fuses C C C Check that fuses are intact, change if needed. Section 11 Common electrics, group 11.2.2 Fuses Batteries C C C Clean when needed. Section 11 Common electrics, group 11.3.1 Start battery Check the electrolyte level. Battery cable C C C Test-run C C C After test-run C C C Section 11 Common electrics, group 11.3.1 Start battery Test-run the machine and check the following: • Instruments • Brakes • Gearshifting • All load handling functions • Communication equipment • Steering • Any noise Check the following after test-run: • Sealing (no leakage) • Fluid levels Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:14 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance Washing CAUTION High-pressure washing of sensitive components can lead to short-circuiting and may cause malfunctions. Product damage! Do not use high-pressure washing on cab, radiator, battery compartment, electric components, control units, connectors, cable splices, cylinder seals, stub axles, axle/shaft seals, and chains. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:15 Lubricating 500h 1 Turn off the engine and turn off the system voltage. 2 Clean the area around each grease cup before greasing. 3 Lubricate the machine's lubrication points with lubricant in accordance with the recommendation, see section F Technical data. Also do a visual check of all lubricated mounts. IMPORTANT On machines with central lubrication, check that the central lubrication's lubrication points are lubricated, see section 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories, group 9.14 Central lubrication. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:16 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance 6 5 14 14 2 2 15 15 7 3 4 8 2 3 9 10 1 13 12 11 Lubrication points, lubricating grease Pos. Lubrication points Reference 1 Cab lock Cab lock, page C:17 2 Hinges doors Hinges doors, page C:17 3 Key lock door/engine cover Key lock door/engine cover, page C:17 4 Pedal assembly, brake pedal Brake pedal, page C:17 5 Slide plates. Mast, page C:19 6 Mast top support rollers, if applicable. 7 Chain wheel 8 Lifting chains 9 Support rollers and fork wheels, forks Support rollers, forks, page C:18 10 Side shift cylinder Side shift cylinder, page C:17 11 Support rollers Mast, page C:19 12 Mast wheel 13 Mast mount 14 Link arm Link arm, page C:18 15 Tilt cylinder Tilt cylinders, page C:18 16 Side lift attachment UDCF06.01GB (not positioned in the figure) Side lift attachment, page C:20 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 014458 9 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:17 Cab lock 1 Tilt the cab. 2 Lubricate the cab locks with lubricating grease. Hinges doors 3 Lubricate the door's hinges with lubricating grease. If necessary, lift the door to facilitate lubrication. Lubricate the mechanism in the hood. Key lock door/engine cover Lubricate the key locks on doors and hood with lock oil. 007874 4 Brake pedal 5 Lubricate the brake pedal's hinge with grease. 6 Wipe off excess grease. Lubrication points brake pedal Side shift cylinder 7 Lubricate the side shift cylinder with lubricating grease. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:18 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance Support rollers, forks 8 Lubricate the support rollers and fork wheels with lubricating grease. Link arm 1 9 Lubricate the link arms' bearings with lubricating grease. 3 007869 2 4 1. Lubrication point, upper king pin bearing. 2. Lubrication point, inner link arm bearing 3. Lubrication point, outer link arm bearing 4. Lubrication point, lower king pin bearing. Tilt cylinders 007871 10 Grease the tilt cylinder axles with lubricating grease. There is one lubrication point on each end of the tilt cylinder. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:19 Mast 4 11 Start the machine and raise the mast to facilitate access to lubrication points. 3 12 Turn off the engine. 4 13 Secure the mast in a way that ensures safety. 14 Lubricate slide plate (position 1), support rollers (position 2), chain wheel (position 4) and mast wheel (position 5), as well as top support rollers (position 3) if applicable, with lubricating grease, see section F Technical data. 15 Brush or spray the chains with chain oil. Make sure that the chains are well lubricated. 1 2 5 5 007275 2 Lubrication points for mast. Mast mount 16 Remove the load from the mast mountings in an appropriate manner. Unload using one of the following methods: – Fit a jack under the mast and lift so that the mast does not hang on the mast mounting. – Tilt the mast backwards, fit something under the mast that withstands the load and then tilt forwards. 007868 17 Lubricate the mast mounting with lubricating grease. Lubrication point, mast mounting. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:20 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance Side lift attachment 18 Lubricate all slide surfaces with slide grease (pos. 1) with attachment in max. extended position. 2 2 2 1 1 2 3 5 4 014772 5 19 Lubricate the hydraulic cylinders' shafts with lubricating grease (pos. 2). 20 Lubricate the twistlock cylinder's shaft with lubricating grease (pos. 3). 21 Lubricate the twistlocks with lubricating grease (pos. 4). 22 Lubricate the contact pins with lubricating grease (pos. 5). Lubricating 1000h UDCF06.01GB 1 Turn off the engine and turn off the system voltage. 2 Clean the area around each grease cup before greasing. 3 Lubricate the machine's lubrication points with lubricant in accordance with the recommendation, see section F Technical data. Also do a visual check of all lubricated mounts. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:21 3 3 2 2 1 014459 4 3 Lubrication points, lubricating grease Lubrication points Reference Lubricating 500h Lubricating 500h, page C:15 1 Hose wheels Hose wheels, page C:21 2 King pin bearing King pin bearing, page C:22 3 Wheel bearings, steering axle Wheel bearings, steering axle, page C:22 Turnable operator's station Turnable operator's station, gears and chain Electric connectors (not shown on diagram) Electric connectors, page C:23 4 5 6 Side lift attachment (not positioned in the figure) , page C:22 Side lift attachment, page C:23 Hose wheels 1 Remove the lock plate to release the hose wheel. 2 Remove the hose wheels. 3 Apply slide grease to the shaft. 4 Fit the hose wheels. 5 Fit the lock plate. 007876 Pos. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:22 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance King pin bearing 1 6 3 Lubricate the wheel spindle's bearings (upper and lower) with lubricating grease on both sides. If necessary, turn the wheels for better access. 4 007869 2 Wheel bearings, steering axle 7 Grease the wheel hub until grease comes out at the seal on the hub's inside. Lift the seal ring's lip with a small screwdriver to facilitate pressing out of air. Grease until grease comes out by the seal. NOTE 007862 Be careful so that the seal is not damaged. Turnable operator's station, gears and chain 8 UDCF06.01GB Remove the cover plate and clean and lubricate the gears with universal grease. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance 9 C:23 Remove the cover plate and clean and lubricate the chain with universal grease. Electric connectors 006645 10 Grease electric connectors with electric connector grease. Electric connector, example Side lift attachment 11 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 014771 1 12 Lubricate the rotary coupling (pos. 1) with lubricating grease. 13 Clean and lubricate the twistlocks with lubricating grease. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:24 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance Checking for cracks DANGER Welds in areas of high stress concentration must be checked in accordance with recommended intervals. The interval is calculated according to the machine being used for normal handling and on a level, smooth ground surface. For other handling or, e. g., rough surface, the interval should be shortened. If the welds show signs of cracking, take the machine out of operation immediately and contact Cargotec Support. 1 Turn off the engine and turn off the system voltage. 2 Clean every weld carefully before inspection. 3 Visually inspect for damage and cracks in the areas with high stress concentration, see Checkpoints, page C:26. Check the whole length of every weld. Welds where cracks are suspected following visual inspection are tested with magnetic particle inspection and liquid penetrant if appropriate in accordance with the following: a. The magnetic particle method is used to determine if there's a crack or not, and where it is. See Magnetic particle method, page C:24. b. Confirmed cracks are investigated further with penetrating fluid. See Checking cracks with penetrating fluid, page C:25. 001703 Magnetic particle method Rim 1 Blast the applicable area clean so that it is completely free of paint residue. 2 Test using magnetic particle inspection and the following equipment: • • • Equipment: Yoke Tiede Method: a Alternating current AC b Contrast colour Checking medium: a Wet b Colour (for example, Tiede Ferrolux) If no cracks are detected with the magnetic particle method, checking is finished and the applicable area is approved. If cracks are indicated, the crack should be investigated further with penetrating fluid. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:25 001704 Checking cracks with penetrating fluid 1 Clean the area with cleaning fluid part no. 923626.0668. 2 Spray penetrating fluid part no. 923626.0669 on the cleaned area and let dry 10 min. 3 Wash off penetrating fluid with cleaning fluid part no. 923626.0668. Thoroughly wipe off the cleaning fluid with a drying cloth and let any remaining cleaning fluid evaporate. Rim 1 2 4 Spray detection fluid part no. 923626.0670 on the area. 5 Let the sprayed area dry 1-2 hours. 6 Visually inspect the area. If the tested area does not show signs of linear or point-shaped cracks, it is approved. 001705 If the crack check indicates linear or point-shaped cracks, contact Cargotec Support. Examples of cracks 1. Linear crack 2. Pointed crack Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:26 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance Checkpoints Check the following welds carefully: 6 5 8 3 5 1 4 4 7 2 Checking for cracks Pos. Checkpoint Reference 1 Mast mount Mast mount, page C:26 2 Tilt mount Tilt mount, page C:28 3 Drive axle mount Drive axle mount, page C:28 4 Lifting forks Lifting forks, page C:29 5 Lifting equipment Lifting equipment, page C:29 6 Counterweight box Counterweight box mounting against the frame, page C:31 7 Steering axle mounts Steering axle mounts, page C:31 8 Mounting of frame beam to back piece Mounting of frame beam to back piece, page C:32 Mast mount 1 Mast mount in frame 009485 a) UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 014460 5 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:27 Welds between mast beam and mount tab. c) Mast mount in frame, bottom view d) Weld between mast beam and mount tab, bottom view. 009524 009523 009487 b) Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:28 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance Tilt mount 2 Tilt mount in mast. b) Tilt mount in frame. 009482 009481 a) Drive axle mount 3 Drive axle mount in frame 009483 a) UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:29 Lifting forks 4 NOTE 009480 There may be other variants of forks than those shown here. a) The fork's suspension bracket against the carriage beams. Mounting of support rollers. When checking fork material, see section 7 Load handling, group 7.9.1 Lifting forks. Fork upper mounting bracket, bottom view. 009529 b) Lifting equipment 5 NOTE There may be other variants of trolleys than those shown here. Trolley side's welds against the trolley beams. 009536 a) Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance b) Outer struts' welds against the trolley beams. c) Chain mounting in the trolley. 009535 C:30 009479 Also check the mounting pin to the chain and its split pin. d) Chain mounting in the mast. 009478 Also check the chain tightener, mounting pin to the chain and its split pin. e) The wheel pin welds in the trolley. 009530 Check the inner mast wheel pins as well. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance C:31 Counterweight box mounting against the frame 6 a) Counterweight box mounting against the frame, under rear mudguard. 009533 Angle the steering wheels on the ground for easier access. Steering axle mounts 7 a) Steering axle mounts in the frame. b) Steering axle mounts in the steering axle cradle. a 009525 b Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB C:32 C Preventive maintenance – Preventive maintenance Mounting of frame beam to back piece 8 Mounting of frame beam to back piece. b) Mounting of frame beam to back piece, bottom view. 009531 014766 a) UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 0:1 0 Complete machine Contents 0 Complete machine Complete machine..............................................................................................0:3 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 0:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 0 Complete machine – Complete machine 0:3 0 Complete machine Complete machine, description The Kalmar DCF 180-250 is a forklift truck. The machine has a lifting capacity of 18-25 tonnes depending on version. The engine is a six-cylinder, four-stroke diesel engine with direct injection. The transmission is hydro-mechanical with gears in constant mesh. It has three forward gears and three reverse gears. The engine's power is transmitted using a torque converter. The power transmission consists of propeller shaft and a rigid drive axle with hub reduction. The machine has front-wheel drive. The service brake is of the type disc brake in oil, which is integrated with the driving wheels' wheel hubs. The parking brake is of the disc brake type and acts on the drive axle's input shaft. The machine is steered with the rear wheels using a double-acting hydraulic cylinder. The steering axle is oscillation-mounted in the frame. The wheels are mounted on the hubs with nuts and washers. The drive axle has twin wheels, the steering axle has single wheels. The wheel rims are detachable. Load handling consists of components and functions for handling loads. Loads are lifted with forks secured to a carriage that is fitted on a mast. Load handling is divided into the functions lifting/lowering, tilt, side shift, spreading, levelling and load carrier. • Lifting/lowering is the function that lifts and lowers the fork carriage. • Side shift is for repositioning the forks in parallel at the same distance from each other laterally along the carriage. • Spreading is for adjusting the width between the forks on the carriage. • Tilt is for angling the load in the longitudinal direction of the machine by means of the mast. • Levelling is for angling the load in the lateral direction of the machine. • The load carrier is for holding or gripping the load. The control system includes functions to warn the operator of dangerous situations and faults. The control system has diagnostic options that facilitate troubleshooting. The frame supports the machine. Fitted on the frame are the engine, transmission, drive axle and steering axle, etc. On the sides of the frame are tanks for fuel, AdBlue and hydraulic oil. The cab has a central location and can be tilted laterally. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 0:4 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1:1 1 Engine Contents 1 Engine 1 Engine..................................................................................................................1:3 1.2 Fuel system......................................................................................................1:8 1.2.1 Fuel tank .....................................................................................................1:9 1.2.3 Fuel prefilter ................................................................................................1:9 1.2.4 Fuel filter ...................................................................................................1:12 1.2.12 AdBlue tank ...............................................................................................1:13 1.2.13 AdBlue filter ...............................................................................................1:15 1.6 Air intake and exhaust outlet..........................................................................1:18 1.6.1 Air cleaning system ...................................................................................1:19 1.6.3 Exhaust system .........................................................................................1:22 1.6.4 Intercooler .................................................................................................1:22 1.7 Cooling system ..............................................................................................1:24 1.7.4 Radiator and expansion tank ....................................................................1:24 1.7.5 Cooling fan ................................................................................................1:24 1.7.7 Coolant ......................................................................................................1:25 1.8 Lubrication system .........................................................................................1:30 1.9 Control system engine ...................................................................................1:33 1.10 Ignition/heating...............................................................................................1:34 1.11 Start/stop........................................................................................................1:35 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – Engine 1:3 1 Engine Engine, description The engine provides power for propulsion and the working hydraulics. The engines are low emission engines and meet emission regulations from the USA (California) and Europe. The new engines provide considerable improvement, not only for exhaust emissions but also for the power and torque curve. The machine is equipped with Volvo TAD761VE. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:4 1 Engine – Engine Engine alternative Volvo TAD761VE, function description Volvo TAD761VE is a straight 6-cylinder, 4-stroke turbocharged low-emission diesel engine with unit injectors and air-to-air intercooler. 0 I P II °C III 1 7 <° 10 . rpm kph <° 4 bar ECU790 EDU795 F 9 N R R 1 11 4 5 M 3 ECU794 UDS SENSORS 8 H2O 2 6 12 M 13 15 16 14 1. Ignition key lock (S144) 9. 2. Control unit engine (ECU794) 10. Sensor fuel level (B757) 3. Preheating coil (E800) 11. Control unit, transmission (D793) 4. Control unit general (ECU790) 12. Control unit SCR (UDS) 5. Starter motor (M654) 13. AdBlue pump 6. Electric components engine 14. Water valve 7. Accelerator pedal (B690) 15. Sensor exhaust temperature 8. Make-contact (closing switch) coolant level (B759) 16. Level and temperature sensor AdBlue UDCF06.01GB Control unit terminal (EDU795) Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 014282 ECU793 5 1 Engine – Engine 1:5 Engine, component location 5 4 6 3 7 2 8 9 1 20 18 16 14 12 10 014761 21 19 17 15 13 11 Volvo TAD761VE left-hand side (in the machine's direction of travel) 1. Sensor flywheel speed 12. Fuel filter 2. Crankcase ventilation 13. Sensor fuel pressure 3. Filling point engine oil 14. Control unit engine (D794) 4. Injector and preheating (6 pcs.) 15. Sensor oil pressure 5. Sensor coolant level (B757) 16. Oil plug 6. Sensor coolant temperature 17. Dipstick 7. Thermostat housing 18. Fuel prefilter 8. Alternator 19. Sensor water-in-fuel 9. Water pump 20. Water trap 10. Fuel pump 21. Sensor camshaft speed 11. Oil filter Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:6 1 Engine – Engine 4 3 2 5 1 6 7 11 014762 10 9 8 Volvo TAD761VE, right side (in the machine's direction of travel) 1. Expansion tank 7. Starter motor 2. Filling point coolant 8. Intercooler 3. Preheating of air after intercooler 9. Condenser 4. Sensor boost pressure and temperature 10. Transmission oil cooler 5. Sensor fuel pressure (fuel distribution pipe) 11. Radiator engine 6. Turbo UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – Engine 1 2 1:7 4 3 6 5 10 9 0 P I 8 II 7 014408 III Electric components machine 1. Control unit, steering (ECU792) 6. Control unit terminal (EDU795) 2. Control unit, hydraulics (ECU796) 7. Ignition key lock 3. Control unit general (ECU790) 8. Accelerator pedal 4. Fuel tank 9. Control unit, transmission (ECU793) 5. Sensor fuel level (B757) 10. Control unit engine (ECU794) Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:8 1 Engine – Fuel system 1.2 Fuel system Fuel system, description The fuel tank is located on the left-hand side of the machine and is equipped with a sensor for the fuel level. The amount of fuel in the tank is shown on an operating menu on the display in the cab. Fuel prefilter with water trap and fuel filter are on the engine. The water trap is equipped with electrical indication, an event menu appears on the display when the water trap must be emptied of water. For component locations see, see Engine, component location, page 1:5. WARNING The engine's fuel system operates at very high pressure. The pressure is so high that the jet can damage the skin, which results in serious injuries. Risk of personal injury. Use protective gloves and protective safety goggles, avoid skin contact with fuel. If a component is to be loosened, hold a rag over the coupling as protection and collect the fuel. Fuel may be corrosive to mucous membranes in, e.g., eyes, skin, and throat. Fuel system, bleeding NOTE Read safety recommendations for fuel system before starting work, see section B Safety. The fuel system must be bled after fuel filter replacement, if the fuel tank has been run dry or after long periods of operation for example. 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 1 2 Open the hand pump (position 1) by pressing it in and turning anticlockwise. 3 Bleed the fuel system by pumping the hand pump at least 250 times. Pump quickly to maintain the pressure in the pump. NOTE Bleeding is not complete until there is no resistance in the pump. Close the hand pump by pressing in and turning clockwise. 5 Start the engine and allow it to idle for about five minutes before increasing speed. 014767 4 1. Hand pump UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – Fuel tank 1:9 1.2.1 Fuel tank Fuel tank, cleaning NOTE Read safety recommendations for fuel system before starting work, see section B Safety. 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Empty the fuel tank of fuel. Use a pumping device. 3 Remove the drain plug from the fuel tank. 4 Rinse the fuel tank clean through the fuel filler hole. 5 Reinstall the drain plug. 2 1 014210 3 1. Fuel filler 2. Drain plug, under tank 3. Fuel tank 1.2.3 Fuel prefilter Fuel prefilter, draining condensation NOTE Read safety recommendations for fuel system before starting work, see section B Safety. NOTE Water traps must be emptied of water as necessary or at least every 50 operating hours. 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Close the fuel cock. 3 Place a container under the fuel prefilter. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:10 1 Engine – Fuel prefilter 4 Open the drain cock (position 1) on the underneath and allow the condensation water to run out. Close the cock when clean fuel without water runs out. 5 Remove the water trap (position 2) from the fuel filter by turning it clockwise. 6 Clean the water trap and refit it on the filter cartridge. 7 Close the drain cock and open the fuel cock. 8 Bleed the fuel system, see Fuel system, bleeding, page 1:8. 9 Turn on the system voltage and start the engine. Check that the filter seals tight. 2 014216 1 1. Drain cock 2. Water trap Fuel prefilter, replacement NOTE Read safety recommendations for fuel system before starting work, see section B Safety. UDCF06.01GB 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Clean the fuel prefilter and water trap. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – Fuel prefilter 3 1:11 Drain the fuel prefilter of fuel and water. See Fuel prefilter, draining condensation, page 1:9. 4 Remove the water trap (position 3) from the old filter. 5 Remove the fuel filter (position 2) from the filter holder, use a filter tool. Collect any fuel in a container. 6 Lubricate the gasket on the new fuel filter. 7 Install the new fuel prefilter on the filter holder. 2 1 014214 3 1. Wiring 2. Fuel prefilter 3. Water trap Tighten in accordance with the instructions on the filter. 8 Install a new O-ring on the water trap and lubricate with diesel oil. Install the water trap on the new fuel prefilter. 9 Bleed the fuel system, see Fuel system, bleeding, page 1:8. 10 Turn on the system voltage and start the engine. Check that the filter seals tight. 2 1 014215 3 1. Wiring 2. Fuel prefilter 3. Water trap Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:12 1 Engine – Fuel filter 1.2.4 Fuel filter Fuel filter, replacement NOTE Read safety recommendations for fuel system before starting work, see section B Safety. NOTE Do not fill the fuel filter with fuel prior to installation. There is a risk of contaminants entering the fuel system and causing malfunctions or damage. 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. NOTE The fuel filter is self-draining. Wait a few seconds after the engine has been switched off before removing the filter cover and filter insert. 1 2 2 Clean around the filter. 3 Remove the filter cover (position 1). 4 Remove the O-ring (position 2) and filter insert (position 3). 5 Fit a new filter insert and new O-ring. 6 Fit the filter cover, tighten to a torque of 25 Nm 7 Bleed the fuel system, see Fuel system, bleeding, page 1:8. 8 Start the engine and check sealing. 014217 3 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – AdBlue tank 1:13 1.2.12 AdBlue tank AdBlue tank, cleaning NOTE Read safety recommendations for AdBlue before starting work, see section B Safety. 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Remove the drain plug (position 1) on the underside of the AdBlue tank. Drain any remaining AdBlue into a container. 3 Replace the drain plug gasket and reinstall the plug, tighten to a tightening torque of 30 Nm. NOTE Remove the filler cap and filler pipe. 5 Lower the filler cap and filler pipe in a water bath. Let them remain for at least two minutes. 014225 4 014226 1 014224 Only use gaskets that can withstand AdBlue. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1 Engine – AdBlue tank 6 Detach and remove the tank connections. 7 Check the strainer on the connections. Clean when needed. 014227 1:14 NOTE 014228 Always replace a damaged strainer. 8 Flush the tank with hot water for at least ten minutes. 014229 Then check that the tank is completely drained of water. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – AdBlue filter Reinstall the tank connections. 014230 9 1:15 10 Reinstall the filler pipe. 014231 11 Fill the tank with AdBlue. Refit the filler cap. 1.2.13 AdBlue filter AdBlue filter, replacement NOTE Read safety recommendations for AdBlue before starting work, see section B Safety. CAUTION Wait at least two minutes after switching the engine off before removing the hoses for AdBlue so that the SCR system has time to drain and depressurise. 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Remove the plate covering the pump unit from below. The plate is placed under the battery compartment on the machine's left-hand side. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:16 1 Engine – AdBlue filter 3 Remove the connection for the heating element. NOTE 014232 Pull the connection straight out. 4 Drain any remaining AdBlue into a container. 014233 Place a container under the pump unit. Connect a plastic tube to the drain screw located on the filter holder. Open the screw and allow the remaining AdBlue solution to run down into the container. Remove the hose from the filter holder by pressing in the catches. 014234 5 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – AdBlue filter 6 1:17 Remove the filter holder (position 1) from the pump unit. Remove the filter insert (position 3). NOTE If the filter has been detached, it must be removed completely before being reinstalled, even if it is to be reused. 7 Install a new O-ring (position 2) in the new filter holder. Install a new filter insert in the filter holder. Install the filter insert and filter holder as one unit in the pump. Tighten the filter holder using a toque wrench. 3 NOTE Check that the drain valve is closed. 8 Install the hose to the filter holder. Check that the locks lock securely. 9 Reconnect the connection to the heating element. Check that the connection locks securely. NOTE Ensure that the connection is connected straight. 10 Start the engine and check sealing. 014236 1 014235 2 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:18 1 Engine – Air intake and exhaust outlet 1.6 Air intake and exhaust outlet Air intake and exhaust outlet, description There is an air cleaner on the machine. The air cleaner is equipped with an indicator that indicates when the air filter needs replacing. The air cleaner has two filter inserts, one main insert and a safety insert. The air cleaner is connected to the engine by the turbocharger. Volvo Stage 3B engines are equipped with SCR technology to reduce nitrogen oxides (NOx) in exhaust gases. SCR technology means that AdBlue is injected into the exhaust gases before it reaches the SCR catalyst. A sensor measures the exhaust gases' NOx levels. The SCR is located on the left-hand side of the machine. AdBlue contains deionised water mixed with 32.5% urea. The urea is broken down into ammonia, which reacts with NOx to create harmless nitrogen and water vapour. The exhaust system consists of pipe and silencer. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – Air cleaning system 1:19 Exhaust outlet, component location 4 5 3 2 1 7 6 11 8 9 014288 10 1. Control unit SCR (UDS) 7. Level and temperature sensor AdBlue 2. Silencer with integrated SCR catalyst 8. Exhaust pipe 3. Catalyst 9. AdBlue tank 4. End-pipe 10. Pump unit 5. Heat shield 11. Heating valve 6. Injector unit 1.6.1 Air cleaning system Air filter, hood, changing 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:20 1 Engine – Air cleaning system 2 Detach and remove the air filter holder. 3 Change the filter in the filter holder and refit the filter holder. Air filter, changing 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Fold up the hood. 3 Clean the outside of the air filter housing. C B A Position for air filter holder B Replacement indicator C Dust reservoir UDCF06.01GB 014077 A Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – Air cleaning system 4 Remove the cap from the air filter housing. 5 Remove the filter insert. 6 Clean the dust reservoir. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1:21 UDCF06.01GB 1:22 1 Engine – Exhaust system 7 Check the safety insert, change as needed. (The safety insert should be changed every other time the filter insert is changed). 8 Fit a new filter insert. NOTE The filter insert should be changed, not cleaned. 9 Fit the cover to the air cleaner casing. 10 Check that the hoses from the air filter housing (and other parts) are intact and sealed. 11 Reset the indicator. 1.6.3 Exhaust system Exhaust system, checking WARNING Hot exhaust system! Risk of burn injuries. Never touch the turbo, exhaust pipe, or muffler when the machine is in operation or has recently been turned off! 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Check the exhaust system's sealing and other wear. 3 Check that the exhaust system suspension is intact. 1.6.4 Intercooler Intercooler, checking 1 UDCF06.01GB Machine in service position, see section B Safety. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – Intercooler 2 1:23 Clean the intercooler with compressed air. NOTE Do not use high pressure wash. 1 Intercooler Charge-air pipe, checking 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Check the charge air pipes for visible cracks and other external damage. If the pipes are damaged or if connections leak, the boost pressure will be too low and engine power is reduced. 014249 1. Check the sealing and check that the intercooler's hoses and clamps are in good condition. 014471 3 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:24 1 Engine – Cooling system 1.7 Cooling system Cooling system, description The engine radiator is located together with the intercooler and the transmission oil cooler in one unit, a cooling unit. For component locations see, see Engine, component location, page 1:5. 1.7.4 Radiator and expansion tank Radiator, cleaning 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Clean the radiator with compressed air. NOTE Do not use high pressure wash. 3 Check that the cooling flanges are whole. 1.7.5 Cooling fan Drive belt, inspection Check after operating when the belts are warm. It should be possible to press down the drive belt approx. 3-4 cm between the belt pulleys. The drive belt has an automatic belt tensioner and does not need to be adjusted. Check the condition of the belts, replace if necessary, see Drive belt, replacement, page 1:24. IMPORTANT Always change a drive belt that looks to be worn or has cracks. Drive belt, replacement 1 UDCF06.01GB Machine in service position, see section B Safety. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – Coolant 1:25 2 Loosen the belt tensioner and lock it with a drift (position 1). 3 Remove the belt from the coolant pump (position 2) first. 4 Install the new belt. Let back the belt tensioner and check that the belt is positioned correctly in the grooves and is tensioned correctly. 2 014242 1 1.7.7 Coolant Coolant level, check WARNING The cooling system is pressurised. Steam or hot fluid may jet out. Risk of scalding and burn injuries! C B Open the filler cap very carefully when the engine is warm. Wait until the coolant has cooled before topping up. A Coolant should be filled in the system's expansion tank (position A). The coolant should be visible in the sight glass (position C) on the expansion tank. NOTE 014063 Open very carefully as hot coolant may jet up. A Position for coolant reservoir (expansion tank) B Filling point C Sight glass If the coolant level should become too low then an error code is shown in the control system's display (position 41). NOTE A low coolant level may cause engine damage or may cause the engine to stop. 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:26 1 Engine – Coolant 2 If needed, top up with ready-mixed recommended coolant. For volume and quality, see section F F Technical data. CAUTION Different types of coolant must not be mixed. Risk of engine damage and damage to the cooling system if different types of coolant are mixed. When changing and topping up coolant, only use coolant of the same type that was used before. IMPORTANT On machines with ECC or AC, it is of the utmost importance that the engine's cooling system be refilled with coolant that contains the correct mixture of anti-freeze fluid; otherwise there is a risk that the air conditioning will freeze up and fail during use. Coolant, changing Radiator performance is reduced due to deposits in the radiator and radiator ducts. Clean the system in conjunction with changing the coolant. WARNING The cooling system is pressurised. Steam or hot fluid may jet out. Risk of scalding and burn injuries! Open the filler cap very carefully when the engine is warm. Wait until the coolant has cooled before topping up. WARNING Glycol and anti-corrosion agents are hazardous to health. Health hazard! Handle with care. Avoid contact with skin, use protective goggles and protective gloves. In the event of contact with skin, wash the skin. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – Coolant 1:27 IMPORTANT Cleaning may not be performed if there can be a risk of freezing in the cooling system since the cleaning solution does not have anti-freeze properties. NOTE Read safety instructions for coolant before starting work, see section B Safety. NOTE Before draining, stop the engine and remove the filler cap. Draining 1 B A 014063 C Remove the filler cap from the cooling system's expansion tank. A Position for coolant reservoir (expansion tank) B Filling point C Sight glass Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:28 1 Engine – Coolant 2 Open all drain points. Drain the coolant from the radiator and engine block with drain hose. The drain nipples are under the radiator and on the right-hand side of the engine block. 3 Check that all coolant drains. NOTE There may be deposits inside the cock or the plug that must be cleaned; otherwise there is a risk that coolant may remain and cause freezing damage. 007394 Check whether the installation has additional cocks or plugs on the coolant line's lowest points. Allow the drain cocks or plugs to remain open and ensure that the heating knob is set to full heat during cleaning. Drain point engine. 4 Insert a hose in the filler hole in the expansion tank and flush with clean water, until the draining water is clear. 5 If there still are impurities after flushing for some time, cleaning with coolant can be performed. Otherwise continue with Cleaning with coolant, page 1:28. Cleaning with coolant 1 Fill the cooling system with 15-20 % concentrated coolant mixture. Only use recommended concentrated coolant mixed with clean water. 2 Drain the cooling system after 1-2 days of operation. NOTE In order to avoid dissolved materials getting into the cooling system, drain quickly, within 10 minutes, without the engine having been stationary for a long time. Remove the filler cap from the expansion tank and any lower radiator hose to increase the drain speed. 3 Immediately flush the system thoroughly with clean hot water to prevent dirt getting on the internal surfaces. Flush until clean water runs out. Make sure the heat control is at full heat during cleaning. 4 If impurities should remain after a long time of flushing, cleaning can be performed with radiator cleaning agent and after-treatment with neutraliser. NOTE Use only cleaning agent approved by the engine manufacturer. Carefully follow the instructions on the packaging. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – Coolant 1:29 Filling point 1 When the cooling system is completely free from impurities, close the drain cocks. CAUTION Different types of coolant must not be mixed. Risk of engine damage and damage to the cooling system if different types of coolant are mixed. When changing and topping up coolant, only use coolant of the same type that was used before. NOTE Only use recommended coolant. 2 Add coolant so that the level lies between the MIN and MAX markings. The engine must not be started until the system has been bled and filled fully. 3 Start the engine when the system is bled and completely filled. Open any bleeder valves some time after start, so that the trapped air can escape. Open all heat controls on the heater unit so that it is bled. 4 Stop the engine after about one hour and check the coolant level, top up if needed. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:30 1 Engine – Lubrication system 1.8 Lubrication system Lubrication system, description The engine's lubrication system is completely closed and has no connections to the machine. For component locations see, see Engine, component location, page 1:5. Oil and oil filter, change NOTE Read safety instructions for oil before starting work, see section B Safety. Run the engine until warm. 2 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 3 Remove the drain plug from the engine and drain the engine of oil. 4 Place a container under the oil filter. 5 Clean around the oil filter. 014238 1 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – Lubrication system 1 1:31 6 Carefully remove the filter cover (position 1). 7 Remove the O-ring (position 2) and filter insert (position 3). Allow the oil to drain from the filter into the container. 2 3 8 Fit the new filter insert and a new O-ring. 9 Fit the filter cover and tighten to a torque of 40+10 Nm. 10 When the oil has run out fit the oil plug with a new gasket. Tighten to a maximum torque of 55±10 Nm. NOTE Do not tighten the oil plug with higher tightening torque, the threads will be damaged. 11 Fill with engine oil to the correct level. Do not fill over MAX-level. For volume and quality, see section F Technical data. 12 Start the engine, let it idle. Check that the oil pressure is normal. 014237 13 Turn off the engine and check the oil level, see Oil level, check, page 1:32. Top up as needed. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:32 1 Engine – Lubrication system Oil level, check NOTE Read safety instructions for oil before starting work, see section B Safety. The engine's filler pipe (position B) and dipstick (position C) are under the engine hood. 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Check the oil level when the engine has been warmed up. Wipe off the dipstick before checking. The dipstick has two markings, MAX and MIN, and the oil level should be between them. NOTE On certain machines the oil dipstick is long. Wear gloves. A 3 Top up with new engine oil if necessary (position B). For volume and quality, see section F Technical data). 4 Fill - wait awhile - check on the dipstick. C B NOTE 014768 Work carefully when filling to prevent other fluids or particles from contaminating the oil, which means risk of engine damage. B A Location for filling and dipstick for engine oil B Filling point C Dipstick UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – Control system engine 1:33 1.9 Control system engine Control system engine, description The engine is controlled by a control system, for which the central unit is a control unit. Amongst other things the system consists of sensors, control unit and electric injectors. The sensors emit input signals to the control unit, which in turn controls the injectors. The control unit receives input signals on the engine's operating condition from the following components: • sensor camshaft speed • sensor flywheel speed • sensor coolant temperature • sensor boost pressure and temperature • sensor oil pressure • sensor water-in-fuel • sensor fuel pressure • sensor coolant level (B757) • accelerator pedal (B690) • control unit SCR (UDS) • control breaker • level and temperature sensor AdBlue • sensor exhaust temperature Based on the input signals the control unit controls: • main relay • preheating relay • starter motor (M654) • injector diesel • injector AdBlue • accelerator pedal actuator • fuel pump (MPROP) • control unit SCR (UDS) If serious malfunctions are detected by the control and monitoring system on the engine, then engine power is limited to protect the engine from further damage. The information from the sensors accurately advises the current operating conditions and allows the processor in the control unit to calculate the correct fuel quantity and check the engine condition. For more information about control unit engine, see section 11 Common electrics, group 11.5.3 Control units and supplier documentation engine. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:34 1 Engine – Ignition/heating 1.10 Ignition/heating Ignition/heating, description The engine features preheating of the induction air, for faster start at low temperatures. Preheating is activated when the ignition key is in position I. When preheating is activated the preheating symbol illuminates in the display. The ignition key lock sends signals to Control unit General (ECU790) which sends messages via CAN-bus drivetrain to Control unit engine (ECU794). For component locations see, see Engine, component location, page 1:5. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 1 Engine – Start/stop 1:35 1.11 Start/stop Start/stop, general The electrical system operates at 24 volts. The positive terminal is connected to a battery disconnector (A). A-D A D 1. When starting the gear selector must be in neutral position. 2. Turn the ignition key lock to position 1, the preheating is activated if the engine senses that it is required. The display shows the preheating symbol down at the left-hand edge. 3. Turn the ignition key lock to position 3, ECU790 sends a signal to the engine via the CAN bus. 4. The engine is stopped by the ignition key lock being turned to position 0. NOTE The battery disconnector must not be used as an emergency switch! C 014409 B A Battery disconnector B Knob for opening the battery cover C Position for main current on D Position for main current off There is a stop button on the engine that can be used to stop the engine in an emergency, e.g. if the engine cannot be stopped by other means. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 1:36 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 2:1 2 Transmission Contents 2 Transmission 2 2.3 2.6 2.7 2.8 Transmission ......................................................................................................2:3 Mechanical transmission..................................................................................2:6 Lubrication system ...........................................................................................2:7 Cooling system ..............................................................................................2:10 Control system transmission.......................................................................... 2:11 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 2:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 2 Transmission – Transmission 2:3 2 Transmission Transmission, function description The transmission transfers the engine power to the drive wheels (drive axle) via the drive shaft and also power to drive the hydraulic oil pumps for the hydraulic system. The machine is equipped with ZF 3WG171. The transmission is manual with torque converter. The transmission has three gears in each direction. The torque converter and transmission work together via a common hydraulic system. The torque converter is a hydraulic clutch placed between the engine's output shaft and the transmission's input shaft. The hydraulic oil pumps and the oil pump for control and lubrication of the transmission are fitted on the torque converter but directly connected to the torque converter input shaft, i.e. they are directly driven by the engine and are not affected by the torque converter. The gear position is selected by modulating pressure via electrical valves that are controlled by the transmission control unit (ECU793). The control unit uses sensors for pressure, temperature, and rpm to decide which gear position should be activated as well as solenoid valves to activate the gear. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 2:4 2 Transmission – Transmission Transmission, function description 3 F R 1 F N °< 20 R <° R 6 1 4 5 19 2 18 Pa ECU790 EDU795 16 17 UDS ECU794 8 14 ECU793 7 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 SENSORS 5 15 014410 4 1. Gear selector (S160) 11. Sensor output shaft speed (B758) 2. Control unit general (ECU790)) 12. Sensor temperature converter (B766) 3. Switch parking brake (S107) 13. Sensor engine speed (B753) 4. Oil pump transmission 14. Filter monitor 5. Oil filter transmission 15. Transmission oil cooler 6. Accelerator pedal (R690-1) 16. Control unit terminal (EDU795) 7. Control unit, transmission (D793) 8. Solenoid valves for travel direction and gear position in valve block transmission control (KV, KR, K1-K3) 18. Break contact (opening switch) declutch (S1039) 9. Sensor turbine speed (B751) 19. Switch for inching (S220-1) 17. Control unit engine (ECU794) 10. Sensor inner transfer shaft speed (B752) UDCF06.01GB 20. Brake pedal potentiometer (R690-2) Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 2 Transmission – Transmission 2:5 Transmission, component location 1 2 3 4 5 12 6 11 7 8 014461 10 9 1. Filter monitor 7. Sensor inner transfer shaft speed (B752) 2. Sensor engine speed (B753) 8. Oil drain plug 3. Output to oil cooler 9. Sensor output shaft speed (B758) 4. Sensor temperature converter (B766) 10. Oil filter transmission 5. Input from oil cooler 11. Oil filling 6. Sensor turbine speed (B751) 12. Transmission oil cooler Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 2:6 2 Transmission – Mechanical transmission 2.3 Mechanical transmission Mechanical transmission, description The transmission is built with all gears in constant mesh. It is shifted by hydraulic pressurising of clutch discs for each of the gears. The discs connect the input shaft with the main shaft or tubular shaft, depending on which gear has been selected. Shifting takes place without disengaging the transmission from the engine. The FORWARD and REVERSE clutches are electro-hydraulically modulated, which means that the clutch pressure is built up gradually. This allows for switching between FORWARD and REVERSE and vice versa whilst travelling at a speed that is lower than the set limit. Modulation also allows for smooth shifts between FORWARD and REVERSE. High modulation (i.e. smooth driving/intensive slippage between gears) gives high wear on the transmission and high oil temperature. Sensor for oil temperature gives a warning when the oil is hotter than 120 °C. If the oil temperature sensor indicates 125 °C the transmission stops working. There are three gears in each direction for the transmission. Disengaging the drive normally takes place at a certain brake pressure. The electronic gearshifting system is either manual or automatic. Using inching avoids the transmission being fully disengaged. For component locations see Transmission, component location, page 2:5. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 2 Transmission – Lubrication system 2:7 2.6 Lubrication system Lubrication system, description The transmission has its own lubrication system that is used for lubrication, control, and cooling of the transmission. The transmission oil cooler is located at the bottom in the cooling unit behind the engine, a thermostat in the cooler enables the oil to reach operating temperature faster. For component locations see Transmission, component location, page 2:5. Oil and oil filter, change NOTE Read safety instructions for oil before starting work, see section B Safety. NOTE Do not over-fill the transmission! NOTE It is recommended that the transmission is calibrated after changing the oil. 1 Operate and warm up the transmission oil. 2 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 3 Place a container under the transmission. 4 Remove the drain plug for transmission oil and let the oil drain into the receptacle. NOTE 014746 Make sure that the drain plug's washer seal is also removed. Drain plug transmission oil Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 2:8 2 Transmission – Lubrication system 5 Clean the area around the oil filter. 6 Change oil filter. Lubricate the O-ring on the new oil filter with transmission oil. Tighten to contact and then another one-third to one-half turn. 7 When the transmission oil has drained, fit the drain plug. NOTE 009416 Make sure that the washer for the oil plug is included. Oil filter transmission 8 Remove the oil dipstick for transmission oil and fill new transmission oil through the oil dipstick's filler pipe until the oil level is at the bottom marking on the oil dipstick marked "COLD". The oil dipstick has three marks. The lowermost, marked "COLD", is a rough estimate for cold transmission. The two uppermost are marked "HOT" and are marks for maximum, MAX, and minimum, MIN, oil level at operating temperature. The oil level must be between MIN and MAX. For volume and quality, see section F F Technical data. 9 Start the engine and let it idle. 10 Check that the drain plug for transmission oil seals tightly. 11 Check the transmission oil level with the engine running at idle and top up to the marking for "COLD". 12 Run the transmission to operating temperature by driving the machine in all gears so that the transmission oil temperature is 80-90°C on the display. a Operating menu oil temperature a Transmission oil temperature b Battery voltage UDCF06.01GB b 006995 - + Use operating menu to check the transmission oil temperature (position a, upper horizontal row in display). 13 Check the transmission oil level and top up to the marking for maximum level, MAX. 14 Calibrate the transmission, see Transmission, calibration, page 2:12. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 2 Transmission – Lubrication system 2:9 Oil level, check NOTE Read safety instructions for oil before starting work, see section B Safety. The transmission oil filling pipe and dipstick are under the hood on the left-hand side of the machine. 1 Check the oil level with the engine idling, the transmission in neutral, and at operating temperature (approx. 80-90°C on the display). The dipstick has three marks. The lowermost, marked "COLD", is a rough estimate for cold transmission. The two uppermost are marked "HOT" and are marks for maximum, MAX, and minimum, MIN, oil level at operating temperature. The oil level must lie between MIN and MAX when the transmission is hot at idle in neutral. Wipe off the dipstick before checking. NOTE The oil dipstick is long. Wear gloves. Transmission oil dipstick and filling 2 Fill the transmission oil through the filler pipe, if necessary. For volume and quality, see section F F Technical data. 3 Fill - wait awhile - check the level marks on the oil dipstick. NOTE Work carefully when filling transmission oil to prevent other fluids or particles from contaminating the oil, which means risk of transmission damage. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 2:10 2 Transmission – Cooling system 2.7 Cooling system Cooling system, description The transmission is cooled by the lubrication system see Lubrication system, description, page 2:7. For component locations see Transmission, component location, page 2:5. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 2 Transmission – Control system transmission 2:11 2.8 Control system transmission Control system transmission, description Control unit transmission controls shifting based on signals from pressure, temperature, and speed (rpm) sensors. Gear selection takes place by activation of solenoid valves that distribute control pressure in the transmission, so that the selected gear gives the right speed. For component locations see section 11 Common electrics, group 11.5.3 Control units. In the event of a fault in the transmission, use the control unit's four different modes with reduced functionality in order to protect the transmission: Substitute clutch control, Limp-home and Transmission shutdown and ECU793 shutdown. SUBSTITUTE CLUTCH CONTROL mode Shown as an alarm in the KCS display if a fault arises. In this mode, the operator can use the machine as usual. On the other hand, shifting and changing direction are not under the control of normal modulating. The control unit uses the standard values for modulating the clutches. LIMP-HOME mode Shown as an alarm in the KCS display if a fault arises. In this mode, the operator can use one of the transmission gears in each direction, and in some cases only in one direction of travel. In order to continue driving in the event of a fault with the “Limp home” limitation the machine must be brought to a standstill, the gear selector moved to neutral before the gear can be selected again. TRANSMISSION-SHUTDOWN mode Shown as an alarm in the KCS display if a fault arises. In this mode, the transmission is permanently in the neutral position when the solenoid valves for the clutches and elements of power to the transmission are switched off. Park the machine and switch off the engine. ECU793-SHUTDOWN mode Shown as an alarm in the KCS display if a fault arises. In this mode, the transmission is permanently in the neutral position when all solenoid valves and all power to the transmission are switched off. Park the machine and switch off the engine. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 2:12 2 Transmission – Control system transmission Transmission, calibration DANGER Do not leave the machine during calibration. The machine may start to move. Stop the machine on level ground, select neutral, apply the parking brake. Run the engine at idle and check the oil level and that the transmission oil temperature is between 70-90 ºC. 2 To select the function to calibrate, first navigate to the service menu. Then press Enter. 3 Enter the code for calibration. 000056 1 The code is obtained from Cargotec Support. 1 23 4 5 000060 NOTE AUTOMATIC 2(2) GEAR SHIFT ECU793 CALIBRATION 5 Select CALIBRATION by scrolling with the arrow keys (1 and 2) and confirm with Enter. 6 Only shown when the engine is running. 007741 Select AUTOMATIC GEAR SHIFT ECU 793 by scrolling with the arrow keys (1 and 2) and confirm with Enter. 1(2) The signals for parking and declutch have been temporarily disconnected to make it possible to run “Heat mode”, the highest gear possible is always selected. 009098 CALIBRATION 4 007742 AUTOMATIC GEAR SHIFT ECU793 The code determines which service menu shall be activated (Service, Diagnostics, Initiation or Calibration). GEARBOX HEAT MODE ACTIVATE P-BRAKE! 7 CALIBRATION Increase the oil temperature in the transmission as follows: 009541 FWD<->NTRL 15S CYCLE! SELECTED GEAR F3 TEMPERATURE 70”C “Heat Mode” is a function for heating the transmission when the machine is stationary by using the parking brake to slow the machine and allowing the converter to heat the gearbox oil. A. Apply the parking brake so that the machine is stationary. B. Select direction of travel forward or backward and apply half to full throttle for 30 seconds. C. Engage neutral position and apply half throttle for 15 seconds, run the engine at idle. D. Repeat steps B and C until the oil is above 70 °C or maximum 90 °C. The temperature display starts to flash when calibration of the clutches can be started. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 2 Transmission – Control system transmission 009101 CALIBRATION >SELECT NEUTRAL >P-BRAKE ACTIVE >TEMP >70grC 8 Only shown when the engine is running. Press “Enter” to access the next menu. 9 The following requirements must be fulfilled in order to start calibration: Transmission in neutral position and parking brake activated. Check that all requirements are fulfilled and that the oil temperature is 70 ºC before proceeding to the next menu by pressing Enter. 009100 CALIBRATION 2(2) AUTOMATIC CLUTCH FILLING PARAMETER ADJUSTMENTS (AEB) 2:13 10 When the TCU has started the calibration the display shows information about the calibration process in clear text. Any error messages are also shown here. 009103 CALIBRATION STATUS K1 ADJUST! 11 During the calibration process engine speed is governed automatically to a preset value that is adapted to each respective transmission. After completion of calibration the following text is shown in the display: "ADJUSTMENT FINISHED SWITCH OFF IGNITION FOR 5 SECONDS!" 12 Only shown when the engine is switched off and inching is installed, this is an option. 2(2) INCH PEDAL 009104 CALIBRATION To able to see "CALIBRATION INCH PEDAL" requires that the engine is already switched off, otherwise this is not shown at all. --> Engine switched off = INCH PEDAL CALIBRATION Engine running = AEB CLUTCH CALIBRATION 13 When the TCU has started the calibration the display shows information about the calibration process in clear text. Any error messages are also shown here. PRESS PEDAL SLOW! 009105 CALIBRATION STATUS 14 Depress the pedal slowly and hold until the information in the display changes to "Release pedal slow!". Release the pedal slowly. If everything has worked the following is shown: ADJUSTMENT FINISHED SWITCH OFF IGNITION FOR 5 SECONDS!" Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 2:14 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 3:1 3 Driveline/Axle Contents 3 Driveline/Axle 3 3.2 3.3 Driveline/Axle......................................................................................................3:3 Propeller shaft..................................................................................................3:3 Drive axle .........................................................................................................3:4 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 3:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 3 Driveline/Axle – Driveline/Axle 3:3 3 Driveline/Axle Driveline/Axle, description The machine's power transmission consists of propeller shaft and drive axle with differential and hub reduction. 3.2 Propeller shaft Propeller shaft, description The propeller shaft transmits the engine power from the transmission to the drive axle. Propeller shaft, checking 1. Clean. • Check-tighten the retaining bolts at the mountings for the drive axle and transmission to 98 Nm (oil). • Check clearance in universal joints. 014778 1 • Propeller shaft Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 3:4 3 Driveline/Axle – Drive axle 3.3 Drive axle Drive axle, description The drive axle transmits the engine power to the wheels. After the drive axle's input shaft there is a differential that changes the gear ratio, distributes the power between the right and left drive wheel, and makes it possible for the drive wheels to have different speeds when cornering. The half shaft transmits the power from the differential to the wheel hubs. At the wheel hubs there are hub reductions that change the gear ratio between wheels and engine to reduce the stress on the half shaft. 1 2 3 014412 4 1. Hub reduction 2. Insert shaft 3. Differential 4. Drive axle housing Drive axle, checking UDCF06.01GB 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Check the drive axle's attachment to the frame so that there is no corrosion on structural elements (e.g., attaching bolts). Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 3 Driveline/Axle – Drive axle 3 Check-tighten the drive axle's attaching bolts (position A) to 1350 Nm. 4 Visually inspect the drive axle's welding seams (position A) at the mountings. 5 Check that the drive axles and hub reductions are sealed. Listen for noise. 6 Check the bolted joint to the parking brake caliper's attaching plate and brake disc. 7 Check whether the drive axles' wheel bearings have play by means of the following: A 014770 007804 A 3:5 – Lift the machine under the mast beam. Support under the drive axle in a secure way. – Check whether the drive axle's wheel bearings have play. Loose bearings should be adjusted, see the Workshop Manual. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 3:6 3 Driveline/Axle – Drive axle Drive axle oil, level check NOTE Read safety instructions for oil before starting work, see section B Safety. Equipment: Receptacle (30 l). 1 Position the machine so that the drain plug on one of the hub reductions is in the lowest position. 2 Turn off the engine and apply the parking brake. 3 Position a receptacle by the hub. Position a piece of sheet metal or similar in the wheel rim to lead any oil to the receptacle. 4 Remove the level plug. 5 Check that the oil level is at the lower edge of the filler hole. Top up as needed. 6 Fit the hub reduction's filler plug. NOTE Make sure that the sealing washer is fitted in place. Repeat steps 1 and 6 on the other hub. 007845 7 Drive axle oil, changing NOTE Read safety instructions for oil before starting work, see section B Safety. Equipment: Receptacle (30 l). 1 Position the machine so that the hub reductions' drain plugs at the wheels are in the lowest position. Wheel 1: move forwards or backwards to obtain the correct position. Wheel 2: lift the wheel from the ground (raise the machine under the drive axle) and rotate the wheel into the correct position. Lower the wheel. 2 Turn off the engine and apply the parking brake. 3 Place a receptacle under the differential carrier's drain plug. NOTE The drive axle has a capacity of approx. 44 l oil. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 3 Driveline/Axle – Drive axle 3:7 4 Remove the differential carrier's drain plug. 5 Position a receptacle by each hub. Position a piece of sheet metal or similar in the wheel rim to lead oil into the receptacle. 6 Remove the drain plug and the level plug. 7 Repeat steps 5 and 6 on the other hub. 8 When the oil has drained, fit the drain plugs. NOTE Make sure that the sealing washers are fitted in place. 007844 9 Fill one hub with oil until the oil level is at the lower edge of the filler hole. NOTE The oil is very viscous, fill the oil slowly. Check the level in stages so that the oil has time to settle. 10 Fit the hub reduction's filler plug. NOTE Make sure that the sealing washer is fitted in place. 007845 11 Repeat steps 9 and 10 on the other hub. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 3:8 3 Driveline/Axle – Drive axle 12 Remove the filler plug for the differential carrier. 13 Fill the differential with new oil until the oil is level with the filler hole. 14 Fit the differential carrier's filler plug. NOTE Make sure that the sealing washer is fitted in place. 15 Remove and clean the drive axle's ventilation. 007846 16 Clean the axle from oil spillage. 17 Remove the receptacles and pieces of sheet metal. Handle the oil as environmentally hazardous waste. 18 Test drive the machine for a short distance without load. 19 Check the oil level in hubs and differential carrier assembly. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 4:1 4 Brakes Contents 4 Brakes 4 Brakes..................................................................................................................4:3 4.1 Controls and instruments .................................................................................4:4 4.1.1 Brake pedal .................................................................................................4:4 4.3 Power-assisted brake system ..........................................................................4:5 4.3.6 Distribution block .........................................................................................4:8 4.5 Parking brake system ......................................................................................4:9 4.5.4 Parking brake unit ..................................................................................... 4:11 4.8 Temperature control, cleaning and hydraulic oil.............................................4:13 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 4:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 4 Brakes – Brakes 4:3 4 Brakes Brakes, general There are brakes to stop the machine. The brakes act on the drive axle (steering axle does not have brakes). The brake system is divided into three functions: • Power-assisted brake system, function description, page 4:5 • Parking brake system, function description, page 4:9 • Temperature control, cleaning and hydraulic oil, function description, page 4:13 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 4:4 4 Brakes – Controls and instruments 4.1 Controls and instruments 4.1.1 Brake pedal Brake pedal, checking and adjusting 1 Clean the floor around the brake pedal and check that nothing blocks movement of the brake pedal. 2 Check that the brake pedal returns all the way and that the clearance between the brake pedal and brake valve is 1–1.5 mm. If needed, adjust the brake pedal's stop bolt so that the clearance becomes correct. 3 Check that the pedal's travel is smooth. 4 Grease the pedal hinges with EP2 universal grease. 5 Check that the rubber on the pedal is intact and that the tread pattern isn't worn out. Change when needed. Stop bolt screw for adjusting clearance between brake pedal and brake valve. (Illustration shows loose brake pedal.) Brake pedal lubrication points. (Figure shows unattached brake pedal) UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 4 Brakes – Power-assisted brake system 4:5 4.3 Power-assisted brake system Power-assisted brake system, function description The power assisted brake system consists of a hydraulic oil tank, hydraulic oil pump, hydraulic oil filter, accumulator charging valve, accumulator, brake valve, pressure sensors, brake cylinder and wheel brake units. The hydraulic oil pump pumps oil (from the tank) which is cleaned in the oil filter. The accumulator charging valve directs pressure to the accumulator that stores the pressure or directs the oil through the wheel brake for cooling of the brake discs. The brake valve directs pressure from the accumulator to the brake cylinder. The brake cylinder compresses the discs in the brake units that brake the machine. Make-contact (closing switch) brake pressure emits a signal so that the brake light is switched on when the brake cylinder is pressurised. When the accumulator is charged, the accumulator charging valve directs oil through the drive axle's brake units; it cools the brakes and then directs the oil back to the tank. On machines with turnable operator's station there is an extra brake pedal for driving backwards. This brake pedal is connected in parallel with the brake pedal for driving forwards. A shuttle valve selects the strongest pressure signal and forwards it to the wheel brakes. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 4:6 4 Brakes – Power-assisted brake system ECU790 12,14 D <° 5 D 13b B Pa 10 P T D 16 13a Pa 11 4 Pa 9 C C 6 B 15 3 P 8 X ACC 7 T P B C 2 B 1. Hydraulic oil pump 10. Relay, brake light (K308-1) 2. Hydraulic oil filter 3. Accumulator charging valve 11. Break contact (opening switch), low accumulator pressure 4. Accumulator 12. Control unit general (ECU 790) 5. Brake valve 13. a. Break contact (opening switch), declutch (S220) 6. Distribution block b. Inching potentiometer 7. Brake cylinder 14. Control unit general (ECU 790) 8. Wheel brake 15. Brake valve 9. Make-contact brake lights (S216) 16. Shuttle valve UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 014413 1 4 Brakes – Power-assisted brake system 4:7 Power-assisted brake system, component location 1 2 6 3 4 7 5 8 11 10 9 014415 12 1. Hydraulic oil pump 7. Shuttle valve 2. Brake valve 8. Distribution block 3. Break contact (opening switch), low accumulator pressure 9. Wheel brake 4. Make-contact brake lights (S216) 5. Break contact (opening switch), declutch (S220) 6. Accumulator charging valve 10. Hydraulic oil filter 11. Hydraulic oil tank 12. Accumulator Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 4:8 4 Brakes – Distribution block 4.3.6 Distribution block Brake pressure, checking 1 Operate and warm up the machine so that the oil in the hydraulic system reaches operating temperature, at least 50 ºC. 2 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 3 Connect the pressure gauge to the measuring outlet on the distribution block, see also Power-assisted brake system, component location, page 4:7. 4 Start the engine and let it idle. 5 Depress the brake pedal and read the pressure. Compare with the permissible pressure on the pressure plate (located next to the cab tilting device for the machine). 6 Remove the pressure gauge and fit the protective cap on the measuring outlet. Measuring nipple, brake pressure on the distribution block UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 4 Brakes – Parking brake system 4:9 4.5 Parking brake system Parking brake system, function description The parking brake consists of a hydraulic oil tank, hydraulic oil pump, hydraulic oil filter, accumulator charging valve, accumulator, pressure sensors, parking brake valve and parking brake unit. The hydraulic oil pump pumps oil (from the tank) which is cleaned in the oil filter. The accumulator charging valve directs pressure to the accumulator that stores the pressure. The parking brake unit is released with pressure from the accumulator by means of the parking brake valve pressurising the parking brake caliper. Make-contact (closing switch) parking brake emits a signal so that the symbol for activated parking brake is shown when the parking brake is applied. rpm km/h 800 0 N 10 U 13 EDU795 F N R R 1 4 ECU790 5 D 4 10,12 D 5,11 9 C 8 Pa 6 ACC C 3 7 H P 2 T 1 014414 B 1. Hydraulic oil pump 8. Break-contact parking brake (S200) 2. Hydraulic oil filter 9. Relay parking brake (K314) 3. Accumulator charging valve 10. Control unit general (ECU 790) 4. Accumulator 11. Indicator light in switch, parking brake (S107) 5. Switch parking brake (S107) 12. Control unit general (ECU 790) 6. Solenoid valve, parking brake (Y642) 13. Control unit terminal (EDU 795) 7. Parking brake unit Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 4:10 4 Brakes – Parking brake system Parking brake system, component location 2 1 3 4 7 6 5 014416 8 1. Hydraulic oil pump 5. Parking brake unit 2. Accumulator charging valve 6. Hydraulic oil filter 3. Make-contact (closing switch) parking brake (S200) 7. Hydraulic oil tank 4. Solenoid valve, parking brake (Y642) 8. Accumulator UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 4 Brakes – Parking brake unit 4:11 4.5.4 Parking brake unit Brake shoe lining, changing 1 Machine in service position and blocked wheels. 2 Remove the cover from the brake caliper. Check that there is no oil inside the cover. 3 Loosen the lock nut. 4 Loosen the adjusting screw so that the brake pads become loose. 5 Remove the split pin and loosen the nut on the attaching bolt holding the parking brake caliper. 6 Pull out the attaching bolt so that the brake pads can be twisted out and removed. NOTE The bolt does not have to be removed. 7 Remove the parking brake pads. 8 Clean the brake disc with methylated spirit. 9 Fit the new parking brake pads. 10 Press back the attaching bolt. 11 Fit the nut and fit a new split pin. 12 Start the engine and let it idle. 13 Release the parking brake. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 4:12 4 Brakes – Parking brake unit 14 Adjust the adjustment screw so that the brakes are applied. 15 Turn back the adjusting screw so that the clearance between pad and disc becomes 0.5±0.1 mm. 16 Tighten the lock nut. NOTE To avoid turning the adjustment screw as well, it must be held still when tightening the lock nut. 17 Refit the cover on the caliper. 18 Check the function of the parking brake. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 4 Brakes – Temperature control, cleaning and hydraulic oil 4:13 4.8 Temperature control, cleaning and hydraulic oil Temperature control, cleaning and hydraulic oil, function description The wheel brakes are cooled when the hydraulic oil is pumped through the brake unit. The temperature control system consists of hydraulic oil tank, hydraulic oil pump, hydraulic oil filter, accumulator charging valve and wheel brake units. The hydraulic oil pump pumps oil (from the tank) which is cleaned in the oil filter. When the accumulator is charged, the accumulator charging valve directs oil through the drive axle's brake units; it cools the brakes and then directs the oil back to the tank. C C 4 P 2 T 5 3 002611 1 1. Hydraulic oil pump 4. Wheel brake 2. Hydraulic oil filter 5. Bypass valve in distribution block 3. Accumulator charging valve Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 4:14 4 Brakes – Temperature control, cleaning and hydraulic oil Temperature control, cleaning and hydraulic oil, component location 2 1 3 5 4 014417 6 1. Hydraulic oil pump 4. Wheel brake 2. Accumulator charging valve 5. Hydraulic oil filter 3. Bypass valve in distribution block 6. Hydraulic oil tank UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 5:1 5 Steering Contents 5 Steering 5 Steering ...............................................................................................................5:3 5.2 Power assisted system ....................................................................................5:4 5.2.6 Link arm ......................................................................................................5:9 5.2.11 Sensor steering wheel reading....................................................................5:9 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 5:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 5 Steering – Steering 5:3 5 Steering Steering, general The function steering means to steer the machine while operating. The machine is steered with the rear wheels by a power-assisted steering system. Joystick or mini-wheel steering is available as an option and means that the machine is steered electronically by a control in the driver seat armrest. On machines with turnable operator's stations, the steering reading is alternated with the directional control valve for the turnable operator's station when driving with the operator's station turned backward so that the steering wheel actuation and steering deflection are in agreement. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 5:4 5 Steering – Power assisted system 5.2 Power assisted system Power assisted system, function description The function power assisted system refers to steering the machine. The machine's steering is power-assisted with pressure from the hydraulic oil pump for steering and load handling. Steering consists of steering wheel, steering wheel shaft, steering valve, hydraulic oil pump, priority valve, steering cylinder, link arms and wheel spindles. The steering wheel (via the steering shaft) acts on the steering valve which in turn directs oil pressure from the hydraulic oil pump to the steering cylinder. The priority valve, located between the hydraulic oil pump and the steering valve, gives priority to oil supply for the steering valve ahead of load handling. The steering cylinder acts on the wheel spindles. The link arms are located between the steering cylinder and wheel spindles. 5 2 PP C P LS CF 6 T P LS L T R 3 4 7 014418 1 1. Hydraulic oil pump 5. Steering wheel 2. Priority valve 6. Steering valve 3. Shuttle valve 7. Steering cylinder 4. Shuttle valve UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 5 Steering – Power assisted system 5:5 Power-assisted system, turnable operator's station, function description On machines with turnable operator's stations, the steering reading is alternated with the directional control valve for the turnable operator's station when driving with the operator's station turned backward so that the steering wheel actuation and steering deflection are in agreement. 10 10 5 R D 2 PP C ECU790 6 P CF 11 P LS LS T 3 T 4 L R 8 1 7 7 D 014419 9 1. Hydraulic oil pump 8. Directional control valve 2. Priority valve 9. Steering cylinder 3. Shuttle valve 4. Shuttle valve 10. End position switch, seat forward (S720-1) and seat backward (S720-2) 5. Steering wheel 6. Steering valve 7. Solenoid valve steering forward (Y636-1) and steering backward (Y636-2) 11. Control unit (ECU 790) Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 5:6 5 Steering – Power assisted system Power-assisted system, mini-wheel/joystick control, function description Joystick control or mini-wheel steering means that the machine is controlled by an electrical control in the left armrest of the operator's seat. The electrical control sends signals to the control system. The steering cylinder is pressurised by a control valve that is also controlled by the control system. Joystick control and mini-wheel function in the same way, the difference is in the design of the control. NOTE The standard steering wheel always has priority over joystick control or mini-wheel steering. Joystick control or mini-wheel steering are disabled as soon as a steering wheel movement is made. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 5 Steering – Power assisted system 5:7 Condition Reference value Joystick control activated Voltage signal from switch mini-wheel/joystick steering. Steering wheel stationary No signal from sensor steering wheel reading. Speed Under 2 km/h (when activated) Control breaker Not activated 6 7 ECU790 8 9 ECU792 EDU795 5 D8 D4 10 4 C1 D7 D10 14 P 3 13 12 EF LS 2 11 Ps P Ts T T CL CR L R 014840 1 15 1. Hydraulic oil pump 9. 2. Shuttle valve 10. Sensor steering column (B770) Steering wheel 3. Shuttle valve 11. Steering valve 4. Feedback joystick control: Sensor, wheel angle (R807) 12. Steering control valve 5. Control unit terminal (EDU 795) 6. Control unit general (ECU 790) 7. Control unit, steering (ECU 792) 8. Potentiometer, joystick control (R825) mini-wheel (R825) 13. Solenoid valve, steering (Y615) 14. Priority valve 15. Steering cylinder Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 5:8 5 Steering – Power assisted system Power assisted system, component location 2 3 6 4 7 1 5 8 15 9 14 13 11 10 014421 12 12 1. Steering cylinder 8. Steering valve 2. Hydraulic oil pump 9. Steering valve (for joystick control/mini-wheel) 3. Steering control valve 10. Sensor steering wheel reading (B770) 4. Solenoid valve, steering (Y615) 11. Directional control valve 5. Priority valve (for joystick control/mini-wheel) 12. Solenoid valve (Y636-1 and Y636-2) 6. Priority valve 13. Hydraulic oil tank 7. Potentiometer, joystick control (R825) mini-wheel (B825) 14. Sensor (S720-1 and S720-2) UDCF06.01GB 15. Shuttle valve Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 5 Steering – Link arm 5:9 5.2.6 Link arm Link arm, checking 007918 Check the link arms' guide bearings, axles and the bolts that lock the link arms' axles. 5.2.11 Sensor steering wheel reading Sensor steering wheel reading, checking 1 (product option mini-wheel or joystick steering) Check that the joystick control and mini-wheel disconnect when the steering wheel is turned. Also check that the sensor for the steering wheel reading is secure in its bracket and that the multi-function levers are secure by unfastening the bottom of the steering wheel panel. 014420 2 1. Metal plate (with four gears) 2. Sensor steering wheel reading Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 5:10 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 6:1 6 Suspension Contents 6 Suspension 6 Suspension .........................................................................................................6:3 6.2 Suspension ......................................................................................................6:4 6.2.1 Steering axle cradle ....................................................................................6:4 6.2.2 Wheel spindle..............................................................................................6:5 6.2.3 Wheel hub ...................................................................................................6:5 6.3 Tyres and rims .................................................................................................6:7 6.3.1 Tyres .........................................................................................................6:19 6.3.2 Rim ............................................................................................................6:20 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 6:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 6 Suspension – Suspension 6:3 6 Suspension Suspension, description The machine's wheel suspension is made up of its tyres (with associated rims and bolts), steering axle with hubs, wheel spindles, and the steering axle's suspension in the frame. The drive axle belongs to the power transmission, see section 3 Power transmission, group 3.3 Drive axle. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 6:4 6 Suspension – Suspension 6.2 Suspension Suspension, description The steering axle cradle is mounted to the frame with two bushings, one at the leading edge and one at the trailing edge of the steering axle cradle. In the steering axle cradle there are two wheel spindles mounted on journalled shafts. The wheel spindle is flexible to enable steering. On the wheel spindles there are journalled wheel hubs where the wheels are mounted. Suspension, component location Suspension refers to: 4 2 5 1 • Steering axle cradle • Steering spindle • Wheel hub 11 10 9 8 7 1. Steering axle cradle 2. Attaching lug 3. Rubber damper 4. Tyres 5. Rim 6. Steering cylinder 7. Piston rod 8. Link arm 9. Wheel spindle 6 007811 3 10. Hub 11. Bolts 6.2.1 Steering axle cradle Steering axle cradle, checking UDCF06.01GB 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety, with transverse wheels. 2 Check that the bushings in the suspension are intact. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 6 Suspension – Wheel spindle 6:5 3 Measure the distance between the frame and the steering axle cradle. Note the measurement. 4 Lift the machine under the rear counterweight. NOTE Do not lift under the steering axle. 5 Again, measure the distance between the frame and the steering axle cradle. Note the measurement. 6 Calculate the difference between the two measurements. The difference may be max. 3 mm. If the difference is greater, the bushing must be replaced. 6.2.2 Wheel spindle Wheel spindle bearing, checking 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety, with transverse wheels. 2 Measure dimension A with a feeler gauge. Note the measurement. 3 Lift the machine under the rear counterweight. 4 Re-measure measurement A. 5 Calculate the difference between the two measurements. The difference must be max. 0.25 mm. If the difference is greater, shimming must be repeated, see Workshop manual. 007812 A 6.2.3 Wheel hub Wheel hub, checking Clean the hub covers on the control wheels. 2 Remove the hub cover. 3 Wipe off grease from hub cap and hub nut. Handle it as environmentally hazardous waste. 007859 1 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 6:6 6 Suspension – Wheel hub 4 Bend up the lock washer's tabs, remove the lock nut and the locking washer. 5 Torque the bearing nut as follows. A. Lube the thread on the spindle and the side of the nut that faces the bearing with oil SAE 80W/140 or equivalent. B. Tighten the nut while the wheel hub is being rotated. C. Rotate the wheel hub at least ten turns. D. Retighten the nut while the wheel hub is being rotated. 009177 E. Repeat points B-D until the nut cannot be tightened any further. F. Check the friction resistance in accordance with the following: The lower limit for zero play is obtained when the bearing is tensioned until no play is felt when the wheel is tilted. The upper limit can be checked with a spring balance, which gives maximum friction torque. The friction torque should be about 19 Nm. 510 mm 009580 Max 8 kg Wind a wire rope a few turns around the wheel bolts before the wheel is fitted and suspend with a spring balance. Read from the spring balance when the hub rotates. 6 Fit the lock washer and outer lock nut. 7 Tighten to at least 250 Nm or as tight as required to fold the locking washer into the closest groove. 8 Fill the bearing cap with grease and fit it. 9 Grease the wheel bearing with grease through the grease nipple. Lift the seal ring's lip with a small screwdriver to facilitate pressing out of air. Grease until grease comes out by the seal. NOTE Be careful so that the seal is not damaged. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 6 Suspension – Tyres and rims 6:7 6.3 Tyres and rims Tyres and rims, safety DANGER Always block wheels on the side of the axle that is not going to be worked on before placing the jack. Always secure the jack to prevent it from slipping out of position. Deflate the tyres before removing. Otherwise the lock ring and lock lugs can release and shoot off when the pressure changes. For twin tyres, both tyres must be deflated! The air should always be released through the valve. If this is not possible - drill holes in the tread to release the air. Damaged tyres may explode. Never stand in front of the tyre when deflating or inflating. Lock ring and lock lugs may release and shoot off when the pressure changes. Never install damaged tyres or rims. It's prohibited to repair rims with welding. It's prohibited to operate the machine if one of the tyres is flat. Wheels, tyres, and rims are dimensioned and selected for each machine type so that max. wheel loads and operating speeds are not exceeded. Therefore, changing of tyre dimension, tyre brand, tyre type, rim type, or rim brand is not permitted without approval from Cargotec. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 6:8 6 Suspension – Tyres and rims CAUTION When removing wheels, leave the wheel nuts in place after they have been loosened. If the wheel nuts are removed immediately the wheel may release from the hub. When removing drive wheels, make sure that the wheels are secured when removing the spacer rings. If the wheels move they may move the spacer rings, which may result in crushing injuries. When installing drive wheels, ensure that the clamps clamp straight on the spacer ring. Wheel nuts should be check-tightened after 4-5 operating hours. Always follow the tyre manufacturer's or other approved instructions when changing tyres. Never use a steel hammer to install or remove rim components. Instead, use a lead, brass, or plastic mallet. Keep tyre pressures at the prescribed level. Loosely inflated tyres impair stability and reduce the machine's capacity. Remove penetrating objects such as crushed glass, pieces of wood, metal filings, etc. Check if tyre wear is abnormal, this could indicate a mechanical fault. Rectify faults immediately and change damaged tyres. Tyre and rim system, description The tyres are the points of contact between the machine and the ground, and the tyres absorb unevennesses and provide suspension. The drive axle is exposed to high forces during operation, if the drive wheels' rolling circumference is different the stresses increase on the drive axle. It is important that the tyres on the drive axle are the same model, type and make, and have equal wear and proper inflation pressure. Tyres and rims, check Read the safety instructions before working with tyres and rim, see Tyres and rims, safety, page 6:7. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 6 Suspension – Tyres and rims 6:9 DANGER Never stand in front of the tyre when deflating or inflating! Lock ring and lock lugs may release and shoot off when the pressure changes. The air should always be released through the valve. If this is not possible - drill holes in the tread to release the air. Damaged tyres may explode. Do not exceed prescribed air pressure! When changing tyre or rim version, another air pressure may apply, contact Cargotec. 1 1 2 3 4 Check the rims. • Check that the spacer rings and clamps are installed correctly. • Check that there are no cracks in the rims' parts. In case of damage, the tyre and rim must be removed and checked. 007892 6 5 1. Inner rim 2. Outer rim 3. Inner spacer ring 4. Outer spacer ring 5. Clamp 6. Nut Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 6:10 6 Suspension – Tyres and rims 2 Check the air pressure in the tyres, see section Tyres, inflating, page 6:19. The pressure must be 1.0 MPa, inflate if necessary. 3 Check the tyres. • Check for uneven and fast wear, this is caused by mechanical defects such as, e.g., uneven brake action. Make sure that such defects are repaired immediately. • Remove penetrating objects such as crushed glass, pieces of wood, metal filings, etc. If the tyre is damaged, the wheel shall be dismantled and the tyre shall be changed, see Tyre, change, page 6:20. 4 If the tyres and rims have no defects, check-tighten the wheel nuts. Tighten crosswise to a torque of: 350 Nm. 013940 • Examples: The figure shows inflation of drive wheel. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 6 Suspension – Tyres and rims 6:11 Tyre and rim system, removing and fitting (drive axle) Read the safety instructions before working with tyres and rim, see Tyres and rims, safety, page 6:7. Removing 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Lift the machine under the mast or under the drive axle with a jack at the wheel in question. Support under the drive axle in a secure way. DANGER With double wheel fitting both tyres must be deflated otherwise the inner may explode when the outer is removed. Risk of tyre explosion! Fatal danger! Empty both tyres of air. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 6:12 6 Suspension – Tyres and rims 3 Release the air from the tyres by: Unscrewing the valve and releasing the air. b) If this does not work, undo the valve in the rim and release the air. c) If this does not work, break off, cut or saw off the valve pipe. d) If it is not possible to release the air via the valve connection, the tyre must be emptied by drilling a hole in the tyre's tread. Use a drill bit of a max. Ø 5 mm. 005123 014572 014573 014571 a) Loosen the inner drive wheel's valve from the bracket. 007881 4 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 6 Suspension – Tyres and rims 6:13 Secure the wheel with the lifting equipment, i.e. make sure that the wheel is positioned safely for lifting in the lifting equipment. 6 Remove all wheel nuts and clamps. 7 Remove the spacer ring. 007878 005124 5 Pull the wheel out a bit so that the spacer ring comes loose. NOTE The spacer ring weighs approx. 20 kg. Lift the outer wheel away and position it safely so that it does not fall or move. 9 Secure the inner drive wheel with lifting equipment. 007879 8 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 6:14 6 Suspension – Tyres and rims 10 Remove the spacer ring between the outer and inner drive wheel. NOTE The spacer ring weighs approx. 20 kg. 007880 11 Remove the inner drive wheel and position it safely so that it does not fall or move. Installing Make sure the mounting surfaces (location A) on the hub and wheel are clean and free from paint and grease. 2 Lift the inner wheel into place with lifting equipment. Turn the wheel so that the guide lug runs into the groove on the hub. This work is facilitated if the hub's groove is aligned towards the top and bottom. 3 Fit the inner spacer ring. 007882 1 NOTE 007880 The inner ring is not split. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 6 Suspension – Tyres and rims 6:15 Lift the outer wheel into place with lifting equipment. Turn the wheel so that the guide lug enters the groove on the hub. 5 Fit the outer spacer ring. 007883 4 NOTE 007884 The outer spacer ring is spit. Turn the ring so that the opening ends up directly opposite the groove on the hub. 6 Fit clamps and nuts on the wheel studs. Fit washers as well where applicable. NOTE Don not forget the bracket for the inner tyre's valve extender. Remove the lifting equipment. 8 Tighten the wheel nuts crosswise, start at the guide lugs and move outwards to prevent the spacer rings from aligning incorrectly. 9 Tighten the wheel nuts crosswise in turn with increasing torque to 350 Nm. 007878 7 10 Fill wheel with air, see Tyres, inflating, page 6:19. 11 Lower the axle and remove the jack. 12 Test-drive the machine and check that the wheels are secure. 007885 13 Check-tighten the wheel nuts crosswise to a torque of 350 Nm. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 6:16 6 Suspension – Tyres and rims Tyre and rim system, removing and fitting (steering axle) Read the safety instructions before working with tyres and rim, see Tyres and rims, safety, page 6:7. Removing 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Lift the machine under the steering axle at the wheel in question with a jack. Support under the steering axle in a secure way. 3 Release the air from the tyres by: Unscrewing the valve and releasing the air. b) If this does not work, undo the valve in the rim and release the air. 014573 014571 a) UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 6 Suspension – Tyres and rims 6:17 If this does not work, break off, cut or saw off the valve pipe. d) If it is not possible to release the air via the valve connection, the tyre must be emptied by drilling a hole in the tyre's tread. Use a drill bit of a max. Ø 5 mm. 005123 014572 c) 4 Secure the wheel with the lifting equipment, i.e. make sure that the wheel is positioned safely for lifting in the lifting equipment. 5 Remove all wheel nuts and clamps. 6 Remove the wheel and position it safely so that it does not fall or move. Installing Make sure the mounting surfaces on the hub and wheel are clean and free from paint and grease. 8 Lift the wheel into place with lifting equipment. 005124 7 Adjust the position of the wheel so that the steering pin passes over the notch in the hub and so that the wheel is lying against the hub. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 6:18 6 Suspension – Tyres and rims 9 Fit clamps and nuts on the wheel studs. Fit washers as well where applicable. 10 Remove the lifting equipment. 11 Fit the wheel. Tighten the wheel nuts crosswise in turn with increasing torque to 350 Nm. 12 Fill wheel with air, see Tyres, inflating, page 6:19. 13 Lower the axle and remove the jack. 14 Test-drive the machine and check that the wheels are secure. 000383 15 Check-tighten the wheel nuts crosswise to a torque of 350 Nm. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 6 Suspension – Tyres 6:19 6.3.1 Tyres Tyres, inflating Read the safety instructions before working with tyres and rim, see Tyres and rims, safety, page 6:7. DANGER Always follow the instructions for inflating tyres to avoid risk of accidents. Only use approved rim components. If the tyre has been completely deflated, the tyre must be dismantled and the rim checked for damage. Never install rim components by striking with a hammer while inflating. Never strike fully or partly inflated tyres or rim sets. Never inflate tyres before all parts are in place. Wheels shall be inflated on the machine or in a protective device, designed and dimensioned so that it can handle or dissipate a shock wave from a tyre explosion as well as catch the ejected parts. 013940 Do not exceed the prescribed tyre pressures which must be checked at ambient temperature. When changing tyre or rim version, another air pressure may apply, contact Cargotec. Plate for air pressure in tyres must be replaced with a plate that shows applicable pressure. Examples: The figure shows inflation of drive wheel. Never stand in front of the tyre when deflating or inflating. Lock ring and lock lugs may release and shoot off when the pressure changes. Check that all parts are in place when the tyre pressure is 30 kPa. NOTE An air filter and water trap should be installed on the line from the compressor that is used to inflate tyres to avoid rim corrosion. 1 Make sure that the lock ring and lock lugs are in the correct position before inflating. 2 Connect the compressor with a locking air-chuck to the nipple on the tyre. 3 Stand at an angle behind the tyre and remain there until inflating has been completed in order to prevent being hit by rim parts in the event of an explosion. 4 Inflate the tyre to prescribed pressure, see specifications. When changing tyre or rim version, another air pressure may apply, contact Cargotec. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 6:20 6 Suspension – Rim Tyre, change DANGER Changing tyres is complicated and dangerous work. FATAL DANGER! Leave tyre work to authorised personnel/tyre company. Check the rim in connection with tyre change, see Rim, check, page 6:20. 6.3.2 Rim Rim, check DANGER Perform the following checks to minimise risks of accidents for all split rims. Always use the right tyre size and a design corresponding to the manufacturer's rim type and size. Over-dimensioned tyres may not be used. Replace all damaged, worn or corroded rims or mounting parts. Dismantle the rim, see Tyre, change, page 6:20. 2 Carefully clean the outside of the rim edge with a steel brush. 3 Measure wear after the lock ring. 001703 1 The lock ring's wear on the tyre bead often gives a mark, A in the figure. The mark occurs between the lock ring's ends. Measure wear depth at point A using a steel ruler and sliding gauge. If wear exceeds 0.5 mm then the wheel rim, lock ring and the tapered rim must be discarded and replaced with new parts. A 001715 Max 0,5 mm UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 6 Suspension – Rim 4 6:21 Check the rim's diameter. Measure the rim edge's circumference (O) with a measuring tape and calculate the diameter (D). [D = Circumference (O) / 3.14] Compare the value of the diameter with specified min. measurement. If diameter is smaller, then the wheel rim, lock ring, and the tapered rim must be discarded and replaced with new parts. Information about min. diameter can be obtained from Cargotec. O 001701 D O. Circumference D. Diameter 5 Check for damage in the areas with high stress concentration. Checking is done in two steps: 1. The magnetic particle method is used to determine if there's a crack or not, and where it is. 2. Confirmed cracks are investigated further with penetrating fluid. 001702 Typical rim damages are circumference cracks, corrosive damage, rust, warping and wear. 001703 Magnetic particle method Rim 1 Blast the applicable area clean so that it is completely free of paint residue. 2 Test using magnetic particle inspection and the following equipment: • Equipment: Yoke Tiede • Method: • a Alternating current AC b Contrast colour Checking medium: a Wet b Colour (for example, Tiede Ferrolux) If no cracks are detected with the magnetic particle method, checking is finished and the applicable area is approved. If cracks are indicated, the crack should be investigated further with penetrating fluid. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 6:22 6 Suspension – Rim 001704 Checking cracks with penetrating fluid 1 Clean the area with cleaning fluid part no. 923626.0668. 2 Spray penetrating fluid part no. 923626.0669 on the cleaned area and let dry 10 min. 3 Wash off penetrating fluid with cleaning fluid part no. 923626.0668. Thoroughly wipe off the cleaning fluid with a drying cloth and let any remaining cleaning fluid evaporate. Rim 1 2 4 Spray detection fluid part no. 923626.0670 on the area. 5 Let the sprayed area dry 1-2 hours. 6 Visually inspect the area. If the tested area does not show signs of linear or point-shaped cracks, it is approved. 001705 If the crack check indicates linear or point-shaped cracks, contact Cargotec Support. Examples of cracks 1. Linear crack 2. Pointed crack UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7:1 7 Load handling Contents 7 Load handling 7 Load handling .....................................................................................................7:3 7.2 Lifting/lowering .................................................................................................7:4 7.2.6 Mast ............................................................................................................7:7 7.2.8 Chains .........................................................................................................7:8 7.2.14 Support roller...............................................................................................7:9 7.2.15 Top support roller ......................................................................................7:10 7.4 Side shift ........................................................................................................ 7:11 7.4.4 Side shift cylinder ......................................................................................7:13 7.5 Spreading.......................................................................................................7:14 7.7 Tilt ..................................................................................................................7:18 7.7.5 Tilt cylinder ................................................................................................7:22 7.8 Levelling.........................................................................................................7:23 7.9 Load carrier....................................................................................................7:27 7.9.1 Lifting forks ................................................................................................7:27 7.9.2 Coil ram .....................................................................................................7:29 7.10 Other functions...............................................................................................7:30 7.10.1 Scales .......................................................................................................7:30 7.10.5 Side lift attachment....................................................................................7:31 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Load handling 7:3 7 Load handling Load handling, general The load handling function refers to lifting, lowering, side shifting and tilting the load for example. 013929 Load handling has been divided into the following subfunctions: Lifting/lowering • Tilt • Side shift • Spreading • Levelling • Load carrier • Side lift attachment 013930 Lifting/lowering • 007916 Tilt 007910 Side shift 007917 Spreading Levelling Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:4 7 Load handling – Lifting/lowering 7.2 Lifting/lowering Lifting/lowering, description Lifting/lowering means that the mast's components are raised and lowered so that the fork carriage is raised and lowered. During lifting, the inner mast is raised with the lift cylinders. The chain that is secured in the carriage (and in the outer mast) runs over the chain wheel at the top of the mast. By these means the carriage is also lifted at the same time as the inner mast. . The The machine can be equipped with a special free-lift mast fork carriage is raised in two stages, first the free-lift stage and then the lifting stage. In the free-lift stage the fork carriage is raised to the top of the inner mast (machine transport height is not affected) In the lifting stage the inner mast is lifted to its max. position (machine transport height is affected). The free-lift cylinder and the lift cylinders are pressurised by the control valve for load handling. There are two versions of the lifting/lowering function, depending on how the function is controlled: • Hydraulic servo means that the control levers are supplied with hydraulic pressure, which controls the lifting/lowering function. • Electric servo means that the control levers are electrical and send voltage signals to the control system to control the lifting/lowering function. In order to absorb and dampen the pressure surges that arise when running on an uneven surface a piston accumulator is connected via a male stud branch tee between the control valve and the lift cylinders. The accumulator absorbs the pressure surges that arise when running on an uneven surface and in the event of a sudden stop of the lowering movement. This way the harmful impact on the hydraulic system and mechanical parts is reduced, while operator comfort is improved. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Lifting/lowering 7:5 Lifting/lowering, function description (hydraulic servo) 9 7 8 5 11 10 C 4 T C 6 PS B2 11 P EF P 10 P LS T A2 9 7 3 C C 2 12 014428 1 8 1. Hydraulic oil pump 7. Load control valve 2. Hydraulic oil pump 8. Load control valve 3. Shuttle valve 9. Lift cylinder 4. Priority valve 10. Load control valve 5. Control lever, lifting/lowering 11. Free-lift cylinder 6. Control valve load handling 12. Hydraulic oil filter Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:6 7 Load handling – Lifting/lowering Lifting/lowering, function description (electric servo) Condition Reference value Control breaker Not activated 11 9 6 ECU796 10 5 D D 13 12 7 T 8 B2 C 4 13 P EF 12 P LS T A2 P 11 9 3 C C 2 14 014427 1 10 1. Hydraulic oil pump 8. Control valve load handling 2. Hydraulic oil pump 9. Load control valve 3. Shuttle valve 10. Load control valve 4. Priority valve 11. Lift cylinder 5. Control lever lifting/lowering (R8071) 12. Load control valve 6. Control unit, hydraulics (ECU 796) 13. Free-lift cylinder 7. Solenoid valve, lift mast (Y6005) lower mast (Y6004) 14. Hydraulic oil filter UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Mast 7:7 Lifting/lowering, component location 3 4 5 2 1 6 8 7 9 14 10 11 13 1. Hydraulic oil pump for steering and load handling 8. Lifting mast 2. Hydraulic oil pump for lifting/lowering and tilt 9. Lift cylinder 3. Priority valve 10. Load control valve 4. Control valve load handling, hydraulic servo 11. Load control valve 5. Control valve load handling, electric servo 12. Free-lift cylinder 6. Solenoid valve, lift mast (Y6005) (electric servo) 13. Shuttle valve 7. Solenoid valve, lower mast (Y6004) (electric servo) 14. Hydraulic oil tank 014422 12 7.2.6 Mast Mast suspension, checking bearings 1 Raise and secure the trolley WARNING Never work under a trolley that is not secured. Risk of crushing! Secure the trolley properly before beginning work. 2 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7 Load handling – Chains 3 Make a marking on the mast. 4 Remove the load from the mast mountings in an appropriate manner. 5 Make a new marking on the mast. Measure the distance between the markings. The measurement should be max. 2 mm. 6 If the difference is greater, the bearings in the mast mountings must be replaced, see Workshop manual. 009520 7:8 7.2.8 Chains Lifting chains, checking and adjusting With the aim of increasing safety, the lifting chains should be checked regularly according to the following: The chains must be thoroughly cleaned over their entire length. The check is performed without a load on the forks. Wear checking The chain must not have extended more than 3%. Measure the length of the 25 links that first (and most often) travel over the chain wheel during lifting. This is where the extension is greatest. Compare with the value in the table. If the 3% limit is exceeded, the chains must be replaced. 2 P-measurement = the distance between 2 pins 005670 1 P-measurement [in] P-measurement [mm] 3/4 Measurement over 25 links [mm] New chain Max. measurement 19.05 476.25 490 1 25.4 635 654 1.1/4 31.75 793.75 817 1.1/2 38.1 952.5 981 2 50.8 1270 1308 On chains with up to 1 inch pitch, it is possible to use a special measuring tape intended to measure the wear. The measuring tape is marked with: • Zulässige Verlängerung = permitted lengthening. • Kette austauschen = chain must be replaced. The measuring tape can be ordered from Cargotec. Adjusting UDCF06.01GB 3 Check that the pins for the outer washers are securely fastened. 4 Check that the washers are free of visible cracks. 5 Check that the chain is free from mechanical damage. 6 Check that the chain is free of rust. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Support roller 7:9 7 Check that the chain bends easily over the pulley (does not jam when bending). 8 Place the machine on level surface with the mast vertical (0° tilt). 9 Lower the carriage to the bottom position. 10 Check that there is 10-20 mm of clearance between the underside of the forks and the ground. Adjust the position by tensioning or loosening the chains equally on the adjustment nut in the carriage. NOTE If the chain is slack when the carriage is in its lowest position, the chain must be tightened. 11 Adjust the chains so that the carriage is lifted evenly in the mast. • Loosen the locking washers (position 1) and remove the lower nut (position 2). • Lift the chain tightener (position 4) out of the carriage and remove the old locking washer. • Reinstall with new locking washer, chain tightener, locking washer and lower nut. Repeat on the other side. 3 NOTE 1 4 007850 2 Reinstall only new locking washers. • Adjust the nuts on each side to balance the carriage so that the distance between the carriage and mast is 10-20 mm. • Tighten the nuts with 2000 Nm and lock them with locking washers. • 1. Locking washer 2. Lower nut Test lift and check that the lifting chain stretches equally on each side so that the carriage is balanced. 3. Upper nut Repeat adjustments as needed. 4. Chain tightener 12 Lubricate the chains after completed inspection. 7.2.14 Support roller Support roller, checking Machine in service position. 2 Check that the support rollers run correctly and that all surfaces of the support rollers and contact faces against the mast have a normal appearance. 007851 1 Example of support roller Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:10 7 Load handling – Top support roller 7.2.15 Top support roller Support roller, checking See Support roller, checking, page 7:9. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Side shift 7:11 7.4 Side shift Side shift, description Side shift means moving the lifting forks sideways. Control valve, load handling, pressurises the side shift and spreading cylinders which extend the fork brackets on the fork carriage in relation to the mast. During side shift the rod side of one of the side shift and spreading cylinders is pressurised. The pressure from the piston side on the first cylinder is directed to the piston side of the second cylinder and compresses the second cylinder. With the spreading and side shift carriage the same hydraulic cylinders are used for side shift as for fork spreading. (If there is no spreading function then the cylinders are just for side shift, on the side shift carriage.) There are two versions of side shift, depending on how the function is controlled. • Hydraulic servo means that the control levers are supplied with hydraulic pressure, which controls the side shift. • Electric servo means that the control levers are electrical and send a voltage signal to the control system to control the side shift. Side shift, function description (hydraulic servo) 5 7 C 4 T C 6 PS B P EF P LS T A 8 3 C 2 9 014429 1 1. Hydraulic oil pump 6. Control valve load handling 2. Shuttle valve 7. Side shift cylinder 3. Shuttle valve 8. Side shift cylinder 4. Priority valve 9. Hydraulic oil filter 5. Control lever side shift Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:12 7 Load handling – Side shift Side shift, function description (electric servo) Condition Reference value Control breaker Not activated 6 ECU796 D 5 D 9 7 T B C 4 8 P EF P LS T A 3 10 2 C 11 014430 1 1. Hydraulic oil pump 2. Shuttle valve 7. Solenoid valve, side shift left (Y6020), side shift right (Y6021) 3. Shuttle valve 8. Control valve load handling 4. Priority valve 9. Side shift cylinder 5. Control lever side shift (R8073) 10. Side shift cylinder 6. Control unit, hydraulics (ECU 796) 11. Hydraulic oil filter UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Side shift cylinder 7:13 Side shift, component location 2 3 4 5 1 6 7 9 014423 8 1. Hydraulic oil pump for steering and load handling 2. Priority valve 3. Control valve load handling, hydraulic servo 4. Control valve load handling, electric servo 5. Solenoid valve, side shift left (Y6020) (electric servo) 6. Solenoid valve, side shift right (Y6021) (electric servo) 7. Side shift cylinder 8. Shuttle valve 9. Hydraulic oil tank 7.4.4 Side shift cylinder Side shift cylinder, checking 007849 Visually check that the cylinders are straight and that the mounting points and welding seams are intact. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:14 7 Load handling – Spreading 7.5 Spreading Spreading, description Spreading involves changing the relative distance between the lifting forks. Control valve side shift, spreading and levelling, pressurises the spreading cylinders which in turn move the forks. There is a flow distributor between the valve and the cylinders that ensures that the forks move uniformly even if the resistance on the forks should be different. With the spreading and side shift carriage the same hydraulic cylinders are used for side shift as for fork spreading. There are two versions of spreading, depending on how the function is controlled. • Hydraulic servo means that the control levers are supplied with hydraulic pressure, which controls the spreading. • Electric servo means that the control levers are electrical and send a voltage signal to the control system to control the spreading. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Spreading 7:15 Spreading, function description (hydraulic servo) 8 7 5 8 C 4 T 6 PS B P EF P LS T A 3 C 2 9 014431 1 1. Hydraulic oil pump 6. Control valve load handling 2. Shuttle valve 7. Flow distributor 3. Shuttle valve 8. Spreading cylinder 4. Priority valve 9. Hydraulic oil filter 5. Control lever, spreading Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:16 7 Load handling – Spreading Spreading, function description (electric servo) Condition Reference value Control breaker Not activated 10 6 ECU796 9 D 5 D 10 7 T 8 B C 4 P EF P T A LS 3 C 2 11 014432 1 1. Hydraulic oil pump 7. Solenoid valve, spreading inwards (Y6019) outwards (Y6018) 2. Shuttle valve 3. Shuttle valve 8. Control valve load handling 4. Priority valve 9. Flow distributor 5. Control lever, spreading (R8074) 10. Spreading cylinder 6. Control unit, hydraulics (ECU 796) 11. Hydraulic oil filter UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Spreading 7:17 Spreading, component location 2 3 4 5 1 6 7 8 10 014424 9 1. Hydraulic oil pump for steering and load handling 6. Solenoid valve, spreading outwards (Y6018) (electric servo) 2. Priority valve 3. Control valve load handling, hydraulic servo 7. Spreading cylinder 4. Control valve load handling, electric servo 8. Flow distributor 5. Solenoid valve, spreading inwards (Y6019) (electric servo) 9. Shuttle valve 10. Hydraulic oil tank Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:18 7 Load handling – Tilt 7.7 Tilt Tilt, description Tilt means the angling of the mast in relation to the machine. Control valve lifting/lowering and tilt pressurises the tilt cylinders which angle the mast in relation to the machine. Tilt is controlled with control lever, tilt. There are two versions of tilt, depending on how the function is controlled. • Hydraulic servo means that the control levers are supplied with hydraulic pressure, which controls the tilting. • Electric servo means that the control levers are electrical and send a voltage signal to the control system to control the tilting. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Tilt 7:19 Tilt, function description (hydraulic servo) 5 7 4 T C 8 6 B1 C PS 7 P EF P P 8 A1 LS T 3 C 2 9 014433 1 C 1. Hydraulic oil pump 6. Control valve load handling 2. Hydraulic oil pump 7. Load holding valve 3. Shuttle valve 8. Tilt cylinder 4. Priority valve 9. Hydraulic oil filter 5. Control lever, tilt Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:20 7 Load handling – Tilt Tilt, function description (electric servo) Condition Reference value Control breaker Not activated 6 ECU796 5 D D 9 7 4 T 10 B1 C 8 9 P EF P P T 10 A1 LS 3 C 2 11 014434 1 C 1. Hydraulic oil pump 7. Solenoid valve, tilt in (Y6011), tilt out (Y6010) 2. Hydraulic oil pump 8. Control valve load handling 3. Shuttle valve 9. Load holding valve 4. Priority valve 10. Tilt cylinder 5. Control lever tilt (R8072) 11. Hydraulic oil filter 6. Control unit, hydraulics (ECU 796) UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Tilt 7:21 Tilt, component location 3 4 5 2 1 6 7 11 8 014425 10 9 1. Hydraulic oil pump for steering and load handling 7. Solenoid valve, tilt in (Y6011) (electric servo) 2. Hydraulic oil pump for lifting/lowering and tilt 8. Tilt cylinder 3. Priority valve 9. Load holding valve 4. Control valve load handling, hydraulic servo 10. Shuttle valve 5. Control valve load handling, electric servo 11. Hydraulic oil tank 6. Solenoid valve, tilt out (Y6010) (electric servo) Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:22 7 Load handling – Tilt cylinder 7.7.5 Tilt cylinder Tilt cylinder, checking Visually check that the mounting points and welding seams are intact. Tilt mount, checking bearings NOTE There may be other variants of tilt cylinder mountings than those shown here. Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Make marks on the mast and frame when the mast is vertical. 3 Add blocks under the outer mast in order to unload the tilt mountings and tilt out to the maximum. Measure the distance to the marking. The measurement should be max. 2 mm. 4 If the difference is greater, the bearings in the tilt mounting must be replaced, see Workshop manual. 009521 009522 1 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Levelling 7:23 7.8 Levelling Levelling, description Levelling means that the load is angled in the horizontal direction. This enables the machine to handle loads on uneven ground surfaces. There are two different types of levelling, fork levelling and central levelling (with the central levelling carriage specified). For machines with fork levelling, one of the forks (right or left) is suspended via a hydraulic cylinder that moves the fork vertically through a sleeve secured to the carriage. With central levelling the front section of the fork carriage is levelled (turned) around the centre line of the carriage, four degrees up or down. There are two versions of levelling, depending on how the function is controlled. • Hydraulic servo means that the control levers are supplied with hydraulic pressure, which controls the levelling. • Electric servo means that the control levers are electrical and send a voltage signal to the control system to control the levelling. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:24 7 Load handling – Levelling Levelling, function description (hydraulic servo) 5 T 6 PS B C 4 P EF 7 P T A LS 3 C 2 8 014435 1 1. Hydraulic oil pump 5. Control lever, levelling 2. Shuttle valve 6. Control valve load handling 3. Shuttle valve 7. Load holding valve 4. Priority valve 8. Hydraulic oil filter UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Levelling 7:25 Levelling, function description (electric servo) Condition Reference value Control breaker Not activated 6 ECU796 D 5 D 7 T B C 4 8 P EF 9 P T A LS 3 C 2 10 014436 1 1. Hydraulic oil pump 6. Control unit, hydraulics (ECU 796) 2. Shuttle valve 7. Solenoid valve, levelling down (Y6022) up (Y6023) 3. Shuttle valve 8. Control valve load handling 4. Priority valve 9. Levelling cylinder 5. Control lever, levelling (R8075) 10. Hydraulic oil filter Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:26 7 Load handling – Levelling Levelling, component location 2 3 4 6 5 1 7 9 014426 8 1. Hydraulic oil pump for steering and load handling 2. Priority valve 3. Control valve load handling, hydraulic servo 4. Control valve load handling, electric servo 5. Solenoid valve, levelling down (Y6022) (electric servo) UDCF06.01GB 6. Solenoid valve, levelling up (Y6023) (electric servo) 7. Levelling cylinder 8. Shuttle valve 9. Hydraulic oil tank Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Load carrier 7:27 7.9 Load carrier Load carrier, general The load carrier is designed to lift a load when required. There are several ways to lift the load, such as: • Lifting forks, normal and inverted. • Coil ram • Side lift attachment 7.9.1 Lifting forks Lifting forks, component location 1 2 3 4 5 014438 6 7 1. Lifting fork 5. Lock pin 2. Support roller 6. Mobile lock hook 3. Inverted lifting forks 7. Lower mounting hook 4. Upper mounting hook Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:28 7 Load handling – Lifting forks Lifting forks, checking DANGER Damaged lifting forks must be changed. Repairs to lifting forks change their strength, which may lead to dropped loads and fatalities. 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Check the fork arms with regard to blade thickness, cracks and deformation. • Blade wear (at position a) must not exceed 10% (calculated from initial dimensions and measured 150 mm from the heel of the fork). • Visible cracks may not be present. Pay special attention to the fork heel. Surface cracks are generally no longer than 5 mm. If surface cracks are discovered, grind down approx. 0.5 mm and test with magnetic particle inspection to see if the crack is still visible. Testing must be performed by an approved company. a Check the forks' suspension mountings, e.g. clearance. 4 If the forks need repair - contact Cargotec or one of Cargotec's approved service personnel, who will determine whether the forks can be repaired. 007781 150 mm 3 NOTE Surface cracks and wear must not be dealt with using welding. 5 UDCF06.01GB Forks which have been hot-straightened must be heat treated again (carried out by an approved firm). Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Coil ram 7:29 7.9.2 Coil ram Coil ram, component location 2 1 014437 4 3 5 1. Coil ram 2. Upper mounting hook 3. Lock pin 4. Mobile lock hook 5. Lower mounting hook Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:30 7 Load handling – Other functions 7.10 Other functions 7.10.1 Scales Scales, description The scales function is available in two configurations. 1. Electric-hydraulic scales without indication in the display. 2. Electric-hydraulic scales with indication in the display and functions for taring and summation of the load. A pressure sensor in the lift cylinder measures the pressure and so estimates the weight of the load. The scales function can be used by other functions in the machine independently of the indication in the display. The accuracy depends on mast movement before measuring. The scales are very sensitive and are affected by several factors such as friction in the mast and fork carriage, oil temperature and bearings. The mast must be in a vertical position and the fork carriage centred. The fork carriage must be raised and then lowered to about 1 metre above the ground before calibration and weighing. If the system is calibrated after gentle lowering, and weighing is performed in the same way, then an accuracy of about 5% of the maximum load capacity is achieved. The weight is presented continuously on the display, in tonnes to one decimal place (e.g. 5.2 tonnes). Scales, calibration The scales on a machine equipped with complete scales are always adjusted and calibrated from the factory. For correct use of the scales they must be calibrated regularly against a known test weight. NOTE The mast should be in a vertical position and the fork carriage should be centred for weighing, calibration and taring. Operate the trolley up and down a few times to remove any mechanical tension. 2 Operate the machine for a few minutes before zero adjustment and weight calibration take place. 3 To select the function to calibrate, first navigate to the service menu. Then press Enter. 000056 1 4 Enter the code for calibration. The code is obtained from Cargotec Support. 1 23 4 5 000060 NOTE The code determines which service menu shall be activated (Service, Diagnostics, Initiation or Calibration). 5 Select SCALE by scrolling with the arrow keys (1 and 2) and confirm with Enter. 000803 SCALE UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Side lift attachment 6 SCALE WITHOUT LOAD 1(2) 600 600 (mV) above the ground. Reset to zero by pressing 7 in the menu 1 (2). Load with a known weight (preferably a frequently used loading weight or close to the machine's maximum load), adjust with 4 CALIBR and 5 000805 2(2) 4000 8000 KG 4000 8000 KG SCALE WITH LOAD Unload, operate the trolley up and lower it slowly to about 1 metre 000804 CALIBR 7:31 to the correct weight and lower the trolley slightly. Confirm the weight by pressing in the menu 2 (2). For the weight to be adjustable there must be a value in setup for maximum lifting capacity. 7.10.5 Side lift attachment Side lift attachment, description Side lift attachments are designed on the basis of simple, safe and fast handling, low weight and easy maintenance. Both corner boxes of the side lift attachment are telescopic and spring-mounted to the main beam, which allows levelling of 195 mm on each side for coupling tilting containers. A hydraulic cylinder between the attachment and carriage enables side shift. A hydraulic system ensures that the container is locked via twistlocks to the attachment before lifting. An electric safety system blocks locking and release of twistlocks unless the attachment is aligned properly in contact with the container. The system also prevents lifting unless twistlocks are either fully locked or released. A lamp panel shows contact, locked container or released container. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:32 7 Load handling – Side lift attachment Twistlocks, checking WARNING Dropped load. Fatal danger! Twistlocks hold the load during load handling and therefore it is crucial that twistlocks are checked according to instructions and replaced at the slightest sign of damage or wear. WARNING Make sure that the engine is off when working on the twistlocks. Twistlocks can be locked automatically if all sensors for contact are activated manually. 1 2 1 3 Check that the twistlocks function correctly. Lock and open the twistlocks, check that the indicator lights work, both in cab and on attachment. 2 Clean the twistlocks from any dirt. 3 Under the rubber cover for twistlocks: check pin, link arm and lock nut. 4 Clean the area around sensor contact. 5 Press in the contact pin so that the head is flush with the spreader beam's underside. Check the distance to sensor contact, the distance should be 5±1 mm. Adjust when needed NOTE 4 1. Sensor unlocked twistlock 2. Sensor contact 3. Sensor locked twistlock 4. Lock guide 5. Lift pin 6. Contact pin UDCF06.01GB 5 007922 6 The contact pin should move easily and spring back completely. 6 Check that the lock guide and lift pin can move freely. 7 Fit a pry bar between the lift pin (position 5) and the lock guide (position 4) and check the clearance, max. clearance: 1-1.5 mm. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7:33 8 Turn twistlocks to locked position and check wear of the lift pin. Replace the lift pin as required. 9 Repeat steps 1–8 on the other side. Max. 4 mm 002311 M in . 70 m m 7 Load handling – Side lift attachment Wear limits lift pin. Twistlocks, checking for cracks DANGER Material fatigue, reduced strength. Fatal danger! Change twistlocks that shows signs of cracks or other external damage, or twistlocks with more than 10 000 operating hours. 1 Remove the lift pins from the attachment. NOTE 002313 Twistlocks are heavy, be careful when removing. Area for checking for cracks on lift pin. 2 Check for cracks within the marked area on the lift pins without causing damage. 3 If the lift pins show signs of cracking, they must be replaced with new ones. 4 Install approved twistlocks. NOTE Use the new attaching nut and spherical bearing. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:34 7 Load handling – Side lift attachment 1 2 007782 Sensor contact, checking and adjusting 1 Check that the contact pins in the corner boxes can move freely up and down. The contact pins shall spring down when not loaded. 2 Check that the sensor is free of damage and dirt. 3 Turn the start key to position I and check that the light indicators on the sensor are turned off. 4 Lower the attachment onto a container and check that Indicator light contact is lit. 5 Lift the container a little bit so that the Indicator light contact is switched off. 6 With the container raised, check how much movement on the contact pins is needed to detect contact (light indicator on the sensor is lit). The movement should be 3–4 mm. 7 If necessary, loosen the lock nut and screw in/out the sensor until the distance between the sensor and the contact pin is 5±1 mm. Right side 1. Sensor contact 2. Contact pin 2 007919 1 Left side 1. Sensor contact 2. Contact pin UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 7 Load handling – Side lift attachment 7:35 Sensor twistlocks, checking and adjusting 1 Check that the sensors are free of damage and dirt. 2 Turn the start key to position I and check that the light indicator on the sensor for unlocked twistlock is lit. If necessary, loosen the lock nut and screw in/out the sensor until the distance between the sensor and the indicator plate is 5±1 mm. 3 Check that indicator light twistlocks open is lit. 4 Lower the attachment over a container and lock twistlocks. 5 Check that the light indicator on the sensor for locked twistlock is lit. 1 2 007783 If necessary, loosen the lock nut and screw in/out the sensor until the distance between the sensor and the indicator plate is 5±1 mm. 6 Check that indicator light twistlocks locked is lit. Right side 1. Sensor unlocked twistlock 2. Sensor locked twistlock 2 007920 1 Left side 1. Sensor unlocked twistlock 2. Sensor locked twistlock Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 7:36 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 8:1 8 Control system Contents 8 Control system 8 Control system ...................................................................................................8:3 8.2 Monitoring functions.........................................................................................8:6 8.2.3 Speed limitation...........................................................................................8:6 8.2.4 Service indicator..........................................................................................8:7 8.3 Error codes ......................................................................................................8:8 8.4 Diagnostics ......................................................................................................8:9 8.4.1 ECU 790....................................................................................................8:10 8.4.2 ECU 792.................................................................................................... 8:11 8.4.4 ECU 796.................................................................................................... 8:11 8.4.5 Last alarms (latest alarm).......................................................................... 8:11 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 8:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 8 Control system – Control system 8:3 8 Control system Control system, general In many cases the machine's functions are controlled electrically. The signals that control the machine are monitored to warn the operator or limit the machine's functions in case of certain dangerous situations or if there are malfunctions in the machine. The function control system is divided into the following functions: • Monitoring functions • Error codes • Diagnostics • Settings • Software Monitoring functions describe the machine’s monitoring functions that warn the operator or limit the machine’s functions in the event of a dangerous situation. Error codes notify operators and mechanics when malfunctions have been detected. Diagnostic test is tool for performing service and troubleshooting with menus in the machine’s display. Settings is the tool for setting and adapting the machine’s functions. The software creates the functions in the control system. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 8:4 8 Control system – Control system Control system, description B The machine is equipped with an electronic system used for controlling and monitoring certain of the machine's different functions. C The system provides information to the operator in the form of alarm information and operating information. The information is presented on the steering wheel panel's display (position B). The function keys are used to navigate in the display menus for service and troubleshooting, for example. F N R R 2 4 5 3 007801 1 A A Function keys B Display C Alarm indicator Function keys Function keys R 4 UDCF06.01GB 2 5 The function keys (position A) are used to navigate in the menu system for information, setting and diagnostic menus. 3 000693 1 They are also used to enter values into the system and to confirm error codes. • Function key 1 : Scroll anticlockwise in menu system as well as enter value 1. • Function key 2 enter value 2. • Function key 3 R : cancel selection of menu or procedure in progress and confirm the error codes displayed. Also acts as a shortcut to the operating menus if held depressed for a short time. • Function key 4 : enter value 4, for gradual settings adjustment and gradual decrease of values in menus (counts down when the function key is held down, counts faster if held down longer). • Function key 5 : enter value 5, for gradual settings adjustment and gradual increase of values in menus (counts up when the function key is held depressed, counts faster if held down longer). • Function key 6 : confirms selection of menu and confirms value entered (stored in memory). 1 2 : Scroll clockwise in menu system as well as 3 4 5 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 8 Control system – Control system Operating menus 8:5 Operating menus 50 When the machine is started the operating menu is shown with engine speed, speed, clock, current gear (gear positions 1-3 are not shown with inching or declutch), as well as fuel level. This menu is shown until another menu is selected or an event-controlled menu is shown(e.g., in case of error code type "WARNING" and "STOP"). Menus are selected using the function keys for arrow right and arrow left. Each press of the key changes the display to the next menu. To quickly return to the original display hold the function key for Reset (R) depressed. U This section describes the information that can be obtained from the different operating menus. The figures show example data. -/+ - + NOTE The availability of the menus is dependent on the machine's equipment. + 014087 The following operating menus are available to aid the operator: Examples of available operating menus Service menu • Operating menu • Operating menu engine • Operating menu transmission and electrical system • Operating menu service interval • Operating menu scale • Operating menu joystick control/mini-wheel • Operating menu trip computer • Operating menu statistics • Operating menu service 000056 Service menu The service menu is the gateway to the machine's diagnostic system. Different parts of the Service menus are made available by pressing "Enter" and entering different codes. The code to access the diagnosis menus is 11111, while the code to access the settings menus requires special authority (contact Cargotec in the event of any questions). The different service menus are: • Error codes, description, page 8:8. • Diagnostics, general, page 8:9. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 8:6 8 Control system – Monitoring functions 8.2 Monitoring functions Monitoring functions, general The machine is equipped with a number of control functions to increase safety during load handling: • Speed limitation • Service indicator 8.2.3 Speed limitation Speed limitation, description Speed limitation prevents the machine's speed from exceeding a preset value by controlling the engine speed. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 8 Control system – Service indicator 8:7 8.2.4 Service indicator Service indicator, resetting Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Navigate first to the service menu and press Enter. 3 Enter code for resetting service indicator. 000056 1 The code is obtained from Cargotec Support. 1 23 4 5 000060 NOTE The code determines which service menu shall be activated (Service, Diagnostics, Initiation or Calibration). 500h TO NEXT SERVICE PRESS ENTER TO CONFIRM! Reset the service indication by pressing Enter. 000808 4 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 8:8 8 Control system – Error codes 8.3 Error codes Error codes, description When a malfunction occurs in the machine error messages (error codes) are generated by the control unit in question that is sending the error code via the CAN-bus to control unit EDU 795 that shows the error codes on the display and stores the error codes. Explanation of error codes is found in Operator's manual and Workshop manual. Error code indication 41 Error code indication 42 Error code is indicated with illuminated indicator for active error codes (position 42). Error codes are divided into three error code levels, depending on how serious they are. The error code levels are indicated as follows: • B STOP is indicated with a STOP sign in the display together with a fixed red light from the indicator for the control system (position 42). Error code with level STOP is shown automatically in the display. • WARNING is indicated with a warning triangle in the display, together with a fixed red light from the indicator for the control system (position 42). Error code with level WARNING is shown automatically in the display. • INFORMATION is indicated with an adjustable wrench in the display together with fixed red light from the indicator for the control system (position 42). 007192 Error code with level INFORMATION is shown automatically on display. B. Symbol error code level 41. Display for control system (KCS) 42. Indicator for control system (KCS) Error code display Error code display 307 004257 Error code information is displayed with display images and symbols that give an indication about the nature of the error arising. Example of automatic display figure The error code and figure can be removed temporarily with the Reset (R) function key and then they disappear from the display. If the error code is active then the indication returns in the display within 1-3 minutes. If the error code is the information type and is removed with Reset (R) then it is not displayed again until the system is restarted. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 8 Control system – Diagnostics 8:9 8.4 Diagnostics Diagnostics, general The machine has built-in functions for troubleshooting called diagnostic test. The diagnostic test consists of several menus that are shown in the display. The menus are grouped according to control unit for faster access. 000916 DIAGNOSTICS The following pages show compilations of the diagnostic menus. The workshop manual has a more detailed description of each diagnostic menu. The diagnostic test is divided into the following groups: • Control unit ECU 790, ECU 790, menu overview, page 8:10. • Control unit ECU 792, ECU 792, menu overview, page 8:11. • Control unit ECU 796, ECU 796, menu overview, page 8:11. • Error code history, Last alarms, description, page 8:11. The diagnostic test varies between the different control units as to what type of diagnostics can be carried out, but the following alternatives are possible: • View inputs - means that the inputs can be checked (digital and analogue). • View outputs - means that the outputs can be checked (digital and analogue). • Control outputs - means that the outputs can be checked and controlled (digital and analogue). Diagnostics, operating instructions To choose diagnostics, do the following: 1 Navigate to the service menu. 2 Press 3 Enter the code for diagnostics (11111). 000056 . 000060 1 23 4 5 4 Select Diagnostics by pressing . 000916 DIAGNOSTICS Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 8:10 8 Control system – ECU 790 5 Main option for diagnostic test is now shown on the display. Choose which control unit shall be investigated using the function keys 1 DIAGNOSTICS ECU790 and 2 and confirm with . Only accessible control units on the machine are displayed. Each diagnostic function comprises a sequence of a number of diagnosis menus. The first diagnosis menu for the selected diagnosis group appears in the display. Select the next diagnosis menu using 1 DIAGNOSTICS ECU792 and 2 . DIAGNOSTICS ECU793 DIAGNOSTICS ECU796 007891 LAST ALARMS 8.4.1 ECU 790 ECU 790, menu overview DIAGNOSTICS ECU 790 DIAG ECU 790 DIAG ECU 790 2(3) VIEW OUTPUTS DIAG ECU 790 3(3) CONTROL OUTPUTS 007886 VIEW INPUTS 1(3) UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 8 Control system – ECU 792 8:11 8.4.2 ECU 792 ECU 792, menu overview DIAGNOSTICS ECU 792 DIAG ECU 792 DIAG ECU 792 1(3) 2(3) VIEW OUTPUTS 3(3) CONTROL OUTPUTS 007887 VIEW INPUTS DIAG ECU 792 8.4.4 ECU 796 ECU 796, menu overview DIAGNOSTICS ECU 796 DIAG ECU 796 DIAG ECU 796 1(3) 2(3) VIEW OUTPUTS 3(3) CONTROL OUTPUTS 007890 VIEW INPUTS DIAG ECU 796 8.4.5 Last alarms (latest alarm) Last alarms, description A history of the latest error codes generated can be viewed under this menu. If the same error code is generated several times then this is counted with a counter and the number of faults is shown in the display. The date and time for when the error code was last generated is also displayed. 000995 LAST ALARMS Select diagnostics and Last alarms in accordance with Diagnostics, operating instructions, page 8:9. This display indicates if Last alarms is selected. Press function key to proceed. The 10 latest error codes are displayed in chronological order (with error code number, number of error codes and the date and time for the last error code of this type received). LAST ALARMS 1(13) ALARM NUMBER 354 COUNTER 11 16.01.2007 10:58 009350 If only one error code is saved then there is only the menu for that fault and the last menu “Clear all alarms”. Accordingly, the number of menus under Last alarms is dynamic. Max. number of error codes saved is 10. 1 Latest active error codes (1, latest) in chronological order. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 8 Control system – Last alarms (latest alarm) LAST ALARMS 6(13) ALARM NUMBER 384 COUNTER 1 16.01.2007 10:58 LAST ALARMS 7(13) ALARM NUMBER 601 COUNTER 3 16.01.2007 10:58 LAST ALARMS 8(13) ALARM NUMBER 610 COUNTER 1 16.01.2007 10:58 LAST ALARMS 9(13) ALARM NUMBER 900 COUNTER 1 16.01.2007 10:58 UDCF06.01GB 4 Latest active error codes (4) in chronological order. 5 Latest active error codes (5) in chronological order. 6 Latest active error codes (6) in chronological order. 7 Latest active error codes (7) in chronological order. 8 Latest active error codes (8) in chronological order. 9 Latest active error codes (9) in chronological order. 009353 009352 009351 Latest active error codes (3) in chronological order. 009354 LAST ALARMS 5(13) ALARM NUMBER 380 COUNTER 6 16.01.2007 10:58 3 009355 LAST ALARMS 4(13) ALARM NUMBER 364 COUNTER 2 16.01.2007 10:58 Latest active error codes (2) in chronological order. 009356 LAST ALARMS 3(13) ALARM NUMBER 361 COUNTER 3 16.01.2007 10:58 2 009357 LAST ALARMS 2(13) ALARM NUMBER 358 COUNTER 8 16.01.2007 10:58 009358 8:12 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 8 Control system – Last alarms (latest alarm) 8:13 LAST ALARMS 12(13) GEARBOX ALARM 1(X) SPN: 5490 FMI: 11 PRESS (+) FOR NEXT 11 Latest active error codes (11) for the engine. In the event of more than one error code, scroll through the codes by pressing function 009360 key 5 . 12 Latest active error codes (12) for the transmission. In the event of more than one error code, scroll through the codes by pressing function key 5 . 009361 LAST ALARMS 11(13) ENGINE ALARM 1(X) SPN: 110 FMI: 10 PRESS (+) FOR NEXT 009359 10 Latest active error codes (10) in chronological order. LAST ALARMS 10(13) ALARM NUMBER 1200 COUNTER 2 16.01.2007 10:58 13 Clear all error codes (only possible with service code). This menu is shown if there is one or more error codes. Clear all error codes by pressing on the function key (Yes = ). 009362 13(13) CLEAR ALL ALARMS? YES = ENTER This menu and function deletes the last active error codes under "Last Alarms" and also the engine and transmission alternatives and their control units that support the deletion of inactive error codes, so-called DM3 in the J1939 CAN standard. 14 Shown if there are no error codes, and after reset. If there are no error codes from the KCS system, only menus 11-13 are shown. 13(13) 009364 NO ALARMS Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 8:14 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9:1 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories Contents 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories ...................................................................9:3 9.1 Controls and instruments .................................................................................9:5 9.2 Safety and emergency equipment .................................................................9:10 9.3 Seats.............................................................................................................. 9:11 9.4 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning ........................................................9:12 9.4.4 Fresh air filter ............................................................................................9:19 9.4.9 Condenser unit ..........................................................................................9:20 9.4.21 Moisture filter.............................................................................................9:20 9.5 Wiping and cleaning of windows....................................................................9:22 9.6 Lighting system ..............................................................................................9:23 9.7 Signalling system ...........................................................................................9:24 9.8 Entertainment and communication ................................................................9:25 9.9 Glass/windows/mirrors...................................................................................9:26 9.10 Construction and suspension of cab..............................................................9:27 9.10.1 Cab frame .................................................................................................9:27 9.10.2 Doors.........................................................................................................9:28 9.10.3 Cab undercarriage ....................................................................................9:28 9.10.4 Cab tilting ..................................................................................................9:29 9.11 Cab interior ....................................................................................................9:31 9.12 Frame.............................................................................................................9:32 9.13 Body structure................................................................................................9:33 9.13.4 Counterweights .........................................................................................9:33 9.14 Central lubrication ..........................................................................................9:35 9.15 Paint/coatings ................................................................................................9:37 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Frame, body, cab and accessories 9:3 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories Frame, body, cab and accessories, description The machine consists of frame, body and cab. The frame (chassis) is the machine's structural part and is made of high-strength steel. The body consists of fenders, hood and other parts mounted on the frame. The cab is built separately and isolated from the frame using heavy-duty rubber dampers. Operator's seat, steering wheel and controls for hydraulics can be adjusted for optimal individual operating position. Effective insulation gives a minimum of vibrations and a low sound level. The machine is equipped with heating and ventilation, air condition is available as an option. WARNING Each case of mechanical damage to the cab can involve risks as the strength is changed. Consequently, making holes in load bearing parts is forbidden. Risk of personal injury. Contact Cargotec for recommendations. WARNING Never work underneath a cab that is not tilted over its balance point or secured in another way. Risk of crushing injury. Always tilt the cab as much as possible. At maximum tilting angle (on a horizontal surface) align the cab's centre of gravity so that it does not risk tilting back. WARNING The hood may be slippery. Danger of slipping. It is forbidden to walk on the hood when it has no anti-slip protection or is not level. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:4 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Frame, body, cab and accessories WARNING The strength of the roof window can be substantially reduced by exposure to substances that contain aromatic hydrocarbons, ketones, esters, or chlorinated hydrocarbons. Low strength! Danger! Check the outside surface of the roof window at regular intervals. Clean only with windscreen washer fluid or a mild cleaning agent. Rinse thoroughly with plenty of lukewarm water. Replace a damaged roof window immediately if it is cracked or scratched! CAUTION All reworking of the roof window is forbidden (e.g. making holes, cutting or widening existing holes). Risk of material damage. Small cracks in the material around screw holes for example indicate that the strength of the roof window is affected and it must be replaced immediately. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Controls and instruments 9:5 9.1 Controls and instruments Cab overview Spirit Delta 1 2 3 4A 5 F N R R 14 1 4 2 3 5 7A 6 13 12 11 10 9 8 1 Left-hand dashboard panel 2 Gear and travel direction selector 3 Steering wheel panel 4A Steering wheel 4B Joystick or mini-wheel 5 Multi-function lever 6 Parking brake 7A Control for load handling 7B Alternative control for load handling 8 Arm rest 9 Driver's seat 10 Accelerator pedal 11 Brake pedal 12 Brake pedal 13 Electronic box with fuses and relays 14 Hour meter Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 014486 7B 4B UDCF06.01GB 9:6 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Controls and instruments Left-hand dashboard panel 31 30 32 Left-hand dashboard panel 33 19 .. 26 27 28 29 15 Control for heating 16 Control for fan 17 Control for defroster/cabin 18 Control for cooling AC 19 Switch for recirculation/fresh air (Only for heater unit with cooling AC) 18 20 17 16 Switch for extra work lights 15 32 33 19 .. 26 AU TO M O D E 34 21 Switch for work lights on mast 22 Switch for extra work lights 23 Switch for extra work lights 24 Switch for revolving beacon 25 Switch for warning beacon 26 Switch for headlights 27 Switch for seat heating 27 28 29 (The switch may be on the driver's seat.) 006908 31 30 Switch for cooling AC 28 Left-hand dashboard panel, upper with heater and lower with air conditioning 29 Switch for central lubrication Switch for short-stop heater 30 Spare 31 Spare 32 Spare 33 Socket for 12/24V 34 Air conditioning ECC See section Air conditioning ECC. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Controls and instruments Steering wheel panel 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 9:7 Steering wheel panel There is a buzzer integrated below the steering wheel panel (not visible). It is activated if: • starting attempts are made with a gear engaged and parking brake not activated • the parking brake is not activated when the operator leaves the driver's seat • the machine has low coolant level, low brake pressure or a parking brake fault • an error code is generated, at which point a short sound signal is emitted F N R R 45 Steering wheel panel 2 4 5 46 3 47 48 49 006903 44 1 35 Spare 36 Warning lamp, replace air filter 37 Indicator light for tilt control 38 Warning lamp for low battery charge 39 Indicator light for high beam 40 Indicator light for direction indicators 41 Display for control system, KCS 42 Alarm indicator for control system, KCS 43 Ignition key lock 44 Switch for turnable driver's seat 45 Switch for engagement and disengagement of alternative direction of travel selector 46 Switch for inching 47 Function keys for control system, KCS 48 Switch for windscreen wiper, rear 49 Switch for windscreen wiper, roof Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:8 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Controls and instruments Right-hand dashboard panel Right-hand dashboard panel 007728 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 Right-hand dashboard panel 51 Switch for disengaging reverse alarm 52 Switch for raising/lowering the driver's seat 53 Switch for extra work lights 54 Switch for electrically heated rear view mirrors 55 Spare 56 Spare 57 Spare 58 Spare 59 Spare Control for load handling For more controls for load handling and associated functions, see section Load handling. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Controls and instruments 9:9 Operating menus, overview 50 U 1. Operating menu 2. Operating menu engine 3. Operating menu transmission and electrical system 4. Operating menu service interval 5. Operating menu scale 6. Operating menu fuel consumption 7. Operating menu joystick control/mini-wheel 8. Operating menu service -/+ - + 014087 + Examples of available operating menus Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:10 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Safety and emergency equipment 9.2 Safety and emergency equipment General A good working environment has safety and emergency equipment to make the operator's work safe. The machine may be equipped with the following: 8 2 11 9 8 7 1. Reverse alarm 2. Revolving beacon/flashing beacon The revolving beacon is also vertically adjustable. 3. Horn 4. Electrically powered loud horn 5. Fire extinguisher A fire extinguisher is normally located on the left front fender, but may also be located on the right front fender or inside the cab. 014439 If the machine is supplied with a fire extinguisher, it should be of the type ABE in accordance with EN 3 part 1, 2, 4 and 5. With such a fire extinguisher, it is possible to extinguish fires in both solid organic materials and fluids. Adapted fire extinguishing equipment can be ordered from Cargotec. 1, 8 6 10 3 5 4 9 8 6. Seat belt 7. Buzzer in cab to indicate alarm or forgotten action, e.g. if the operator leaves the driver's seat without first applying the parking brake. 8. Camera with monitor Used to provide improved rearward vision when manoeuvring and/or load handling with the machine. The monitor is usually located inside the cab by the front right-hand door pillar. 9c 9. 9a External rear view mirrors : Used to provide increased visibility for operating and load handling. 9a shows a glimpse of the area in front of the machine 9b shows blocked area at the side/behind the machine 9c shows a glimpse of the area behind the machine 10. Control breaker for load handling (servo circuits, only at electric servo controls for load handling). 9b UDCF06.01GB 014440 11. Grating for roof window Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 . 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Seats 9:11 9.3 Seats Seats, general The function of the seat is to give the operator a good sitting position and contribute to a good working environment. The cab's seat has several adjustment features and meets high comfort requirements. The machine can be equipped with turnable or reversible driver's seat . NOTE Other alternative driver's seats may be installed. Seats, description (product alternative Bege) The seat has the following equipment: 1 2 3 4 5 8 mechanical adjustment • armrest right • seat belt, 2-point • seat belt, 3-point • armrest left • seat heating • head restraint • air suspension • integrated horizontal suspension (disengageable) • ventilated seat and backrest cushion (air-vent). The seat requires compressed air. The option includes an externally mounted compressor on the underside of the cab . 006825 6 • 7 Controls Bege 1. Adjustable lower back (lumbar) support 2. Adjustable arm rest, right 3. Adjustable arm rest, left 4. Adjustable tilt, backrest 5. Adjustable suspension position 6. Adjustable seat angle 7. Adjustable seat height 8. Longitudinal adjustment Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:12 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Heating, ventilation and air conditioning 9.4 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning Heating, ventilation and air conditioning, function description A standard equipped truck has a heater unit (cabin/defroster) that is connected to the engine's cooling system and which provides heat when the engine is warm. The heater unit consists of a fan and heater elements for heating the air. The air is distributed through integrated ducts in the cab's interior equipment and can be directed towards e.g. defroster or floor. Air conditioning, ECC (Electronic Climate Control, electronic control of cooling, dehumidifying and heating) is available as an option Air conditioning includes the parts presented in the illustration and ensures that the operator's cab climate is as comfortable as possible. Air conditioning function is to: F 2 4 D C E 1. Fluid reservoir/receiver dryer 2. Evaporator 3. Fan 4. Expansion valve 5. Condenser 6. Compressor A High-pressure gas B High-pressure fluid C Low-pressure fluid D Low-pressure gas E Heat, cab air F Cooled air to cab G Outdoor air for removal of heat UDCF06.01GB • dehumidify the air when it is humid • clean the air from impurities • cool the air when it is warm • defrost (defroster function) B 1 000762 G warm the air when it is cold The unit's fan is controlled in steps 0-I-II-III (with the fan control). For air conditioning ECC the fan is steplessly variable 0-100 %. A 5 • The unit is controlled with switches and controls on the dashboard panel. E 3 6 . Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Heating, ventilation and air conditioning 9:13 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning, component location 3 4 5 6 7 2 AU TO MO DE 8 10 9 11 1 12 13 21 20 19 17 16 15 14 014446 18 1. Condenser 12. Heat exchanger, heating 2. Moisture filter 13. Engine, recirculation 3. Sight glass 14. Expansion valve 4. Pressure switch 15. Sensor, deicing ECC 5. Sensor, outside temperature ECC 16. Heat exchanger, cooling 6. Sensor, temperature air conditioning ECC 17. Fresh air filter 7. Control for heater unit 18. Fan 8. Air conditioning ECC 19. Water valve, standard heating 9. Fine filter 20. Water valve ECC 10. Engine, air distribution 21. Compressor 11. Sensor, after heat exchanger ECC Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:14 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Heating, ventilation and air conditioning Air conditioning unit General recommendations for work on the air conditioning unit CAUTION Authorisation is required to perform repairs on the climate control unit. Check/performance test of air conditioning unit NOTE The air conditioning does not work at temperatures below approx. 0 ºC since the pressure in the refrigerant circuit is too low. If the pressure in the refrigerant circuit becomes too low the low pressure switch cuts off power supply to the compressor's magnet clutch, which means that the air conditioning stops working. Should be performed during continuous operation every week from early spring to late autumn as well as in winter during long periods of high humidity. In winter, during cold and dry periods of low operation, the compressor should be run for a few minutes every week so that the rubber hoses, couplings, gaskets and axle seals are lubricated. 1. Check that the condenser is not clogged – clean condenser fins with compressed air as needed. 2. Check that the compressor turns on and off without error. 3. Check that the drain for the cooling element's condensation water is not clogged. 4. Check that there is no refrigerant leakage. In case of leakage, oil and gas often form a dusty, dirty spot. 5. Start the engine and engage the cooling function with setting on maximum cooling. With ECC: Select Cool Mode and temperature at min. Let the engine run at min. 1,500 rpm. (At temperatures below approx. 0 ºC, the cooling function will not start due to low pressure in the system.) 6. With AC: Set fan control to position I or II. With ECC: Set fan to medium speed. UDCF06.01GB 7. After running for 10 minutes, check that there are no bubbles visible in the moisture filter's sight glass. (Bubbles should occur only when the compressor starts and stops). 8. Place a thermometer by the air vent closest to the evaporator. After 5-10 minutes, the temperature should be under 10 ºC. (Deviations in the measurement result can occur if the performance test is conducted when the ambient temperature is below approx. 18 ºC). If bubbles occur, subsequent filling should be done by an expert. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Heating, ventilation and air conditioning 9:15 Check the temperatures on the hoses and similar items as follows: 1. Check that the hoses and components on the pressure side keep a roughly even temperature by feeling them with your hand. NOTE In the event of a stop in one of cooling circuit's components, and during long-term operation, certain parts (possibly hoses before the condenser) can be very hot. Risk of burn injuries. 2. All hoses and components on the pressure side (from the compressor to the expansion valve) should be warm. 3. All hoses and components on the suction side (from the evaporator to the compressor) should be cold. 4. Check the expansion valve. Frost or cold temperatures on the intake side indicate that it is defective or clogged and that circulation is limited or stopped on the pressure side. 5. Check that the compressor engages and disengages normally. Run the cab fan at low speed and let the compressor work at high rpm. When the temperature in the air vents nozzles is close to 0 ºC, the compressor cuts out via the thermostat or ECC and cuts in again when the temperature has increased approx. 3-7 ºC. (If the compressor does not cut out, there is a risk of the evaporator icing up and cooling performance decreasing.) WARNING If there is a rupture of a cooling hose or leakage on the plant – turn off the unit immediately. It is dangerous to allow refrigerants to come in contact with skin or eyes. Never release refrigerant in a closed rum; the gas can cause asphyxiation in, for example, pits. Never weld on or near a closed cooling system. Empty refrigerant during repairs on the air conditioning. Work may only be performed on the refrigerant circuit by an accredited company. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:16 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Heating, ventilation and air conditioning Checking refrigerant quantity WARNING Electric fans can injure hands. Risk of personal injury. Avoid placing hands near the cooling fans when the engine is running. An estimation of the correct amount of refrigerant can be checked using the sight glass. Normally it should not be possible to see bubbles when the air conditioning system is operating. Bubbles may appear if the system contains the wrong amount of refrigerant, in connection with the compressor stopping and starting, and if the condenser is defective or at very high ambient temperature. It is easiest to confirm bubbles if you observe the sight glass at the same time as the compressor starts. Then bubbles are usually seen from a few seconds after the compressor has started, until the system starts to work normally. NOTE Reliable checking of refrigerant quantity through the sight glass can only be performed when the ambient temperature is above approx. 15 ºC. On the left-hand side of the condenser is a sight glass on the line to the evaporator. In the centre of sight glass is a coloured point for moisture indication. Normally the indication is GREEN. If the indication shows YELLOW then there may be moisture in the system (may occur if the system is not properly evacuated before filling refrigerant or if refrigerant has leaked). Sight glass inspection 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Start the engine and let it idle. 3 Switch on the air conditioning with max. cooling and fan. 4 Check that no bubbles are visible in the sight glass on the particle and moisture filter. 013669 Bubbles in the glass means that the quantity of refrigerant is incorrect or that the condenser is defective, clogged by, e.g., dust, or that the ambient temperature is very high. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Heating, ventilation and air conditioning 9:17 Action in the event of leakage in the system 1 Turn off the air conditioning. 2 Check the cooling plant and pinpoint leaks. For this purpose, use special leak detection equipment. If there still is refrigerant left, the remaining refrigerant amount shall be evacuated and then measured. 3 Rectify faults, seal leaks by replacing gaskets, hoses, etc. 4 Fill with the correct quantity of R-134a refrigerant in accordance with the following points when all faults have been rectified. 5 The following work requires special filling equipment. 6 Connect the suction pressure gauge's blue hose to the service valve on the compressor's suction side marked with S, SUC or SUCTION. 7 Connect the pressure gauge's red hose to the service valve on the compressor's pressure side marked with D, DIS or DISCHARGE. 8 Connect the hoses to the fluid reservoir. 9 Connect the yellow filler and vacuum hose to the nitrogen tube. Open the cock on the tube and then the cock on the pressure side. Open the valve on the cylinder and then the valve on the pressure side. Now the gas flows through the system and back to the suction side of the compressor, which can be seen on the blue pressure gauge which slowly indicates a pressure equivalent to the pressure in the cylinder (see red pressure gauge). (If the blue pressure gauge does not move then there is a stop in the system.) Turn off the valve on the pressure side and then the cock on the tube. 10 Now the system contains a mix of nitrogen gas and air. This gas amount is enough to indicate a leak. 11 Conduct leakage detection of all hose nipples and other connections by applying leakage indicator around all sealing surfaces and check whether gas bubbles arise. 12 Loosen the yellow hose from the nitrogen tube and connect it to the vacuum pump. 13 Start the vacuum pump and open the cock on the suction side very carefully, otherwise the oil is blown out of the vacuum pump. Then, open the cock on the pressure side, use vacuum suction for at least 30 minutes. Preferably longer. 14 First close both cocks on the pressure gauge set. Then turn off the vacuum pump. Work in this order, otherwise the air will rush back. Wait approx. 15 min and check on the pressure gauges that the vacuum does not change. 15 Move the yellow hose to the refrigerant tube and open the cock on the tube. 16 Bleed the yellow hose by unloading the service connection at the manometer set until pure gas flows out. 17 Open the cock on the suction side and allow the gas to flow around until the pressure gauges indicate the same pressure as in the tube. 18 Start the compressor and set the cooling thermostat and fan to max. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:18 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Heating, ventilation and air conditioning 19 Open the cock on the pressure side and let the compressor suck from the tube. Observe the sight glass. At the beginning the fluid is mixed with a lot of bubbles. The longer the compressor is allowed to run in intake mode, the less bubbles there will be, and the clearer the fluid will be. If the bubbles suddenly disappear the cooling thermostat has probably cut out. Bypass the thermostat using a cable directly from the connection 24 V or wait until the thermostat cuts in again. Continue until the correct refrigerant amount has been reached. NOTE Directly bypassing the compressor's coupling magnet can lead to compressor damage caused by incorrect refrigerant quantity. Close the cock on the suction side and then the cock on the tube. Disconnect the service hoses from the compressor and install the protective caps. Check for leaks according to step 11 or with a special leak detector. 20 In case of overfilling, the pressure and temperature increase slowly until the high-pressure monitor cuts off the current to the compressor's electromagnet. This is due to the refrigerant rushing around in the system without being evaporated or condensed in the condenser. The result is that the cold in the cooling coil is lost and high heat is generated in the condenser. In addition, a steady stream of bubbles can be seen in the sight glass. Return to point 2. 21 In the event of underfilling or a lack of refrigerant, bubbles appear in the sight glass - return to step 2. Compressor cooling oil 1 At delivery, the compressor is filled with cooling oil. Under normal conditions the oil should not be changed or refilled. In the event of suspected incorrect oil quantity, see the instruction: "When replacing the compressor." 2 In the event of refrigerant loss there may also be oil loss, because about 25% of the oil volume is taken up by the refrigerant. Recommended oil types that may be used are shown in the section F Technical data. When replacing the compressor The compressor is filled with cooling oil when delivered. When changing cooling compressor, change the oil as follows: UDCF06.01GB • Drain the defective compressor of oil and measure the quantity. • Then drain the new compressor of oil and refill with the same amount that was drained from the defective compressor. For oil volume in the system, see section F Technical data. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Fresh air filter 9:19 9.4.4 Fresh air filter Fresh air filter, cleaning and replacement The fresh air filter is also available as an option for the Spirit Delta cab with AC or ECC . 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Remove the filter insert. 3 Wash the filter insert with hot water and dishwashing detergent or replace the filter when necessary. 4 Fit the filter. Fine filter, air conditioning unit, replacement. Fine filter is always available in combination with AC or ECC. 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Loosen the bolts and remove the air conditioning unit's front cover (under the wiper motor). 3 Remove the filter insert. 4 Replace the filter when necessary. 5 Fit the filter insert. NOTE Make sure that the filter insert is fitted in accordance with the arrow marking. 6 Fit the front cover. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:20 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Condenser unit 9.4.9 Condenser unit Condenser unit, checking 1. Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Check that the condenser's fins are not clogged with dust that prevents air flow. 3 Clean the fins with compressed air. 014466 1 1 Condenser 9.4.21 Moisture filter Moisture filter, checking 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Start the engine and let it idle. 3 Check the colour of the indicator on the moisture filter. Blue indication = moisture filter ok. 009183 Grey or pink indication = change moisture filter (see Moisture filter, changing, page 9:21). Indicator moisture filter UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Moisture filter 9:21 Moisture filter, changing WARNING Personal injury, environmental damage. Read the safety instructions for refrigerant, see section B Safety. 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Drain the air conditioning of refrigerant R134a, with the intended draining equipment. IMPORTANT 009183 Working on the air conditioning requires special authorisation. 3 Disconnect hoses and cabling from the moisture filter. 4 Disconnect the moisture filter pressure switch from the moisture filter. 5 Change the moisture filter. 6 Fit the pressure switch and connect the hoses to the moisture filter. 7 Leak test and refill the machine with refrigerant R134a, using the intended equipment. For volume, see section F Technical data. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:22 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Wiping and cleaning of windows 9.5 Wiping and cleaning of windows Wiping and cleaning of windows, description On the cab there are wipers for the front windshield, rear window, and roof window. The function is to clean the windows and maintain good visibility from the cab. 3 The wiper arm is attached to the wiper motor's shaft over a splined taper. The shaft is made of hardened steel and the wiper arm's bracket is made of a mild die cast material. When installing it is important to make sure that the splines are free from metal burrs or similar. Also, the nuts shall be tightened so tight that the splines are pressed into the bracket and work like drive flanges. Hold the wiper arm firmly when installing so that the torque is not transmitted to the motor as it may be damaged (16–20 Nm tightening torque). 2 001878 1 1. Wiper, front 2. Wiper, roof 3. Wiper, rear Wipers, checking Check that: UDCF06.01GB 1. the motors are operating normally and without noise. 2. the wiper arms are pressing the wiper blades against the windows. Replace them if they show signs of damage or significant wear. 3. the wiper blades are intact. Replace them if they are damaged or worn. 4. the washer function distributes washer fluid over the windows satisfactorily. If necessary, fill the washer fluid and adjust the washer nozzles. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Lighting system 9:23 9.6 Lighting system Lighting system, component location The function of the lighting is to increase safety during operation and load handling. NOTE It is important to use the correct bulb type for each area. See section F Technical data. The following lighting is available: 6,10,12,14,15 8 7 9 13 11,12 1,2,3,4 16 014447 3,4,5 1. Rear light, red 10. Extra work lights, cab roof, rear edge, 2 lamps 2. Brake lights 11. Mast work lights, 2 lamps 3. Direction indicators 12. Extra work lights, cab roof, rear edge, 2, 4 or 6 lamps 4. Running lights 5. Headlights 13. Extra work lights, cab roof, front edge, 2 lamps 6. Back-up light, white 14. Extra work lights for container handling, 4 lamps 7. Adjustable searchlight 15. Extra work lights for container handling, cab roof, rear edge, 4 lamps 8. Revolving beacon 9. Interior lighting 16. Extra work light between the tilt cylinders, 1 lamp Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:24 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Signalling system 9.7 Signalling system Signalling system, component location The function of the signals is to increase safety during operation and load handling. This can take place with light and sound. The machine has the following signal systems: NOTE It is important to use the correct bulb type for each area. See section F Technical data. 7 4 8 5, 6 3, 5 014448 2 1 1. Horn 5. Direction indicators 2. Electrically powered loud horn 6. Reverse alarm 3. Flashing hazard lights 7. Back-up lights 4. Revolving beacon 8. Buzzer in cab UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Entertainment and communication 9:25 9.8 Entertainment and communication Entertainment and communication, description For information and description of equipment, see supplier's documentation for each product. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:26 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Glass/windows/mirrors 9.9 Glass/windows/mirrors Glass/windows/mirrors, description Tempered safety glass is standard on all trucks. Tinted windows and laminated glass are available as an option. Roof windows are a safety feature and are therefore always made of polycarbonate plastic. C E The mirrors are all the convex type. The inner rear view mirror is fitted in all machines. Outer rear view mirrors are available as an option, both with and without electrical heating. A As an option the machine can be equipped with a back-up (reversing) camera and a screen in the cab to improve visibility. 007792 B D Overview, glass windows. A Side windows B Windscreen (front window) C Roof window D Rear window E Side windows, front Roof window, checking Check that the roof window is not damaged or cracked. If the roof window is defective, change it immediately. WARNING The strength of the roof window can be substantially reduced by exposure to substances that contain aromatic hydrocarbons, ketones, esters, or chlorinated hydrocarbons. Low strength! Danger! Check the outside surface of the roof window at regular intervals. Clean only with windscreen washer fluid or a mild cleaning agent. Rinse thoroughly with plenty of lukewarm water. Replace a damaged roof window immediately if it is cracked or scratched! UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Construction and suspension of cab 9:27 9.10 Construction and suspension of cab Design and suspension, description The cab has a flat floor with a bracket for the operator's seat. It is suspended in the cab undercarriage via heavy-duty rubber dampers located on the cab's underside. This is to minimise vibrations from the frame to the cab. Each damper has a rubber bushing and a bolt. 1 3 4 1. Cab frame 2. Door 3. Cab suspension 4. Cab undercarriage 003206 2 9.10.1 Cab frame Cab frame, checking 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Check the cab frame with regard to rust damage, deformation or cracks. Rectify if necessary. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:28 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Doors 9.10.2 Doors Doors, checking Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Visually inspect the door's mounting points. 3 Check the door's locking mechanism with regard to function and wear. 4 Lubricate the door hinges if necessary. 006914 1 9.10.3 Cab undercarriage Cab undercarriage, checking Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Check that the welding seams at the cab's mounting points are intact and free of visible cracks. 3 Check that the dampers are intact. Replace damaged dampers. 4 Check that the bolted joints are tightened, that the locking devices function (are not damaged) and that the brackets are undamaged. Take appropriate action if necessary. 006913 1 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Cab tilting 9:29 9.10.4 Cab tilting Cab tilting, description The cab can be tilted up to a certain inclination, above its equilibrium position, articulated around the suspension on the left-hand side, by means of a hydraulic cylinder. The hydraulic oil pressure is generated by a hand-operated pump with an integrated switch valve for up or down tilting. There are locking devices on the mounting on the right-hand side which secure the cab to the frame and they can be easily released for tilting the cab. Electric tilting of the cab is available as an option. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:30 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Cab tilting Tilting the cab WARNING Never work underneath a cab that is not tilted over its balance point or secured in another way. Risk of crushing injury. Always tilt the cab as much as possible. At maximum tilting angle (on a horizontal surface) align the cab's centre of gravity so that it does not risk tilting back. A, B, D C The cab must always be tilted over the equilibrium position. If the space is insufficient laterally then the cab must always be secured against accidental lowering by means of a brace. C Preparation: A • Set the gear and travel direction selector in neutral. • Tilt the mast forward and lower the forks. • Apply the parking brake. • Check that there is nothing loose in the cab. • Close the doors. Tilting B 1. Turn both lock handles (position C) so that they reach their outer position to loosen the cab from the frame. 2. Set the pump valve (position B) in the right-hand position. 3. Fit the pump rod in its bracket (position A). 4. Pump until the cab has reached the end-position. Lowering D 1. Set the pump valve (position B) in the left-hand position. 2. Fit the pump rod in its bracket (position A). 3. Pump all the way until the cab rests on the frame. 4. Turn both lock handles (position C) so that they reach their inner position to lock the cab to the frame. 013939 Electric tilting A. Pump rod bracket B. Pump valve C. Lock handle (figure shows open position) 1. Turn both lock handles (position C) so that they reach their outer position to loosen the cab from the frame. 2. Set the pump valve (position B) in the right-hand position. 3. Use the control buttons (position D) to raise the cab to the end position. Press both buttons simultaneously. Electric lowering D. Control buttons UDCF06.01GB 1. Set the pump valve (position B) in the left-hand position. 2. Use the control buttons (position D) to lower the cab until it makes contact with the frame. Press both buttons simultaneously. 3. Turn both lock handles (position C) so that they reach their inner position to lock the cab to the frame. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Cab interior 9:31 9.11 Cab interior Cab interior, description The cab is designed for best operator comfort. On the dashboard panels there are grouped switches, controls, warning and indicator lights to give the operator a good working environment. Recyclable material is used for all parts. • Dashboard panels • Interior plastic parts • Interior textile/fabric parts • Insulation Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:32 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Frame 9.12 Frame Frame, description The frame consists of two longitudinal frame sides cut from steel plate. Fenders, footsteps, tanks and counterweights are bolted to the frame. The frame contains mounting points for the steering axle and cab. Bolted to the frame are brackets for engine, transmission, drive axle and the fuel and hydraulic tanks, see under each respective function. The fenders are bolted or welded to the frame, depending on machine model. The space in the frame's rear part is used for counterweights, the number and size of which are adapted to the machine in question. 5 3 6 2 4 1 014449 7 1. Frame front section 5. Drive axle mount 2. Frame rear section 6. Steering axle mounts 3. Beam pair 7. Mast mount 4. Mounting, rear fenders Frame, checking UDCF06.01GB 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Inspect for deformation and rust damage, as well as cracks in the welded joints. Rectify as necessary. See section C Preventive maintenance. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Body structure 9:33 9.13 Body structure Body, safety WARNING The hood may be slippery. Danger of slipping. It is forbidden to walk on the hood when it has no anti-slip protection or is not level. Body, description The body's function is a part of the frame. There are fenders to deflect dirt, footsteps and handrail to facilitate access on the frame, engine hood to deflect dirt and objects from the engine compartment and a counterweight to balance the machine's lifting capacity. 1 2 4 014450 3 5 1. Fenders, front 2. Fenders, rear 3. Hood 4. Counterweight 5. Battery compartment 9.13.4 Counterweights Counterweights, checking DANGER The counterweights are factory fitted and are adapted according to the machine's characteristics. The machine's operating characteristics are changed! Never change the number of counterweights. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Counterweights 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety, with transverse wheels. 2 Visually inspect that the counterweights are positioned properly and that the mounts and welding seams are intact and free of visible cracks. 3 Check the bolted joints. 014451 9:34 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Central lubrication 9:35 9.14 Central lubrication Central lubrication, description Central lubrication (replaces manual lubrication) is available in different variants. The alternatives are: • Manual central lubrication, hand pumping lubricant at a lubrication point which is then spread to all selected lubrication points. • Automatic central lubrication lubricates selected lubrication points automatically during operation at pre-programmed time intervals. It is also possible to select the number of lubrication points as follows: • Total 14 lubrication points: 8 on the steering and 6 on the mast (the only alternative with manual central lubrication). • Total 18 lubrication points: 8 on the steering and 6 on the mast and 4 on the carriage. • Total 23 lubrication points: 8 on the steering and 6 on the mast and 9 on the carriage (with central levelling carriage). Automatic central lubrication is built up of the following components: 1 • Pump unit, with lubricant reservoir. • Distribution block, that distributes and portions the grease between the different lubrication points. The distribution block lubricates one point at a time. If a point cannot be lubricated properly, e.g. in the event of a line blockage, the following points will not be lubricated. The grease is forced out through the safety valve on the pump unit. 2 3 • Lines, between main unit and distribution block as well as distribution block and grease nipples. • Grease nipples, at lubrication points. On the pump unit it is possible to adjust the lubrication interval's frequency and duration. 007935 The central lubrication is supplied with voltage when the parking brake is released. 1. Pump unit 2. Safety valve 3. Distribution block NOTE Central lubrication does not lubricate all lubrication points, some still need to be lubricated during preventive maintenance. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:36 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Central lubrication Central lubrication, checking 1 1 Check that no grease has been forced out through the safety valve (position 2). If grease is pushed out through the safety valve, this means that there is a system blockage. Locate the blocked line by feeling the connections at the distribution block. A blocked hose remains pressurised and the connection becomes firm. 2 3 NOTE 4 If several distribution blocks are connected in series, a clogged line will be pressurised all the way to the first distribution block. 2 Turn the start key to position I. 3 Operate the pump manually and check that the indicator pin (position 3) moves in and out on the distribution blocks. To operate the pump, loosen the cover and press in switch manual operation (position 5). If the indicator pins do not move even when the pump is running, troubleshoot the pump unit. NOTE 5 007941 The system can be lubricated manually through the grease nipple on the distribution block. Overview of central lubrication. Example figure. 1. Lubricant nipple, filling point, lubricating grease 2. Safety valve 3. Indicator pin 4. Lubricant nipple, manual lubrication of the system 5. Switch, manual operation UDCF06.01GB 4 Fill grease in the pump unit through the filler nipple (position 1), see section F Technical data. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories – Paint/coatings 9:37 9.15 Paint/coatings Paint/surface finish, description The machine is finished with a paint that is applied by brush or spray. For colour code (RAL), see machine card. Check the machine often for stone chips, impact damage, and scratches to the paintwork, repair these immediately to avoid corrosion on the underlying metal. Only use touch-up paint for minor stone chip damage and scratches, major damage to paintwork should be repaired by a paint shop. NOTE Before performing touch-ups, the surface area must be carefully cleaned. For information on other surface and material colours, contact Cargotec. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 9:38 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 10:1 10 Common hydraulics Contents 10 Common hydraulics 10 Common hydraulics .........................................................................................10:3 10.2 Safety valves..................................................................................................10:9 10.3 Tanks and accumulators ..............................................................................10:10 10.3.2 Accumulator ............................................................................................ 10:11 10.4 Pumps..........................................................................................................10:12 10.5 Hoses, pipes and valves ..............................................................................10:13 10.6 Temperature control, cleaning and hydraulic oil...........................................10:14 10.6.2 Hydraulic oil cooler ..................................................................................10:15 10.6.7 Breather filter hydraulic oil tank ...............................................................10:16 10.6.8 Hydraulic oil filter .....................................................................................10:16 10.6.9 Hydraulic oil.............................................................................................10:20 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 10:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 10 Common hydraulics – Common hydraulics 10:3 10 Common hydraulics Common hydraulics, description Hydraulic functions that are common to several of the machine's main functions are found under the function common hydraulics. For example, the hydraulic oil pumps that supply load handling, steering, the brake system and certain cab functions with hydraulic pressure. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 10:4 10 Common hydraulics – Common hydraulics Pressure plate On the machine there is a pressure plate with the most important pressure information (stamped in). The pressure plate is located on the right-hand side of the frame in front of the cab steps. Pressure levels vary with the equipment and therefore they are unique to each machine. When checking pressure the pressures must correspond with the pressure plate. 2 3 4 1 5 6 014760 7 1. Precharge pressure, accumulators 5. Servo pressure, load handling functions 2. Steering pressure 6. Pressure for lifting/lowering and tilt 3. Hydraulic pressure, accumulators 7. Pressure for steering and load handling 4. Max. brake pressure UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 10 Common hydraulics – Common hydraulics 10:5 Hydraulic pressure, checking NOTE Read safety instructions for oil before starting work, see section B Safety. Servo pressure for control levers (PS) Operate and warm up the machine so that the hydraulic oil reaches operating temperature, approx. 50 ºC. 2 Turn off the engine. 3 Connect a pressure gauge (0–25 MPa) to the measuring outlet PS on control valve, load handling. 4 Start the engine and check the servo pressure. Compare to the pressure plate. 5 Switch off the engine and remove the pressure gauge and fit the protective cap on the measuring outlet. 6 To adjust the hydraulic pressure, see Workshop Manual DCF 180–250. 014473 1 Pump pressure for steering and load handling 1 Operate and warm up the machine so that the hydraulic oil reaches operating temperature, approx. 50 ºC. 2 Turn off the engine. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 10:6 10 Common hydraulics – Common hydraulics 3 Connect a pressure gauge (0–25 MPa) to the measuring outlet on the priority valve. 4 Start the engine and let it idle. 5 Check the standby pressure for one pump at a time as follows: Hydraulic oil pump for steering and load handling: 3.0 MPa Hydraulic oil pump for lifting/lowering and tilt: 2.8 MPa Settings apply to standard machine, certain machines may have higher standby pressure. For correct standby pressure, see pressure plate. However, the difference in pressure between the different pumps must always be maintained. 014473 6 Increase engine speed to approx. 1800 rpm and move the tilt function to relief (overflow). Tilt in the mast to the max. position and continue requesting max. tilt in with the control lever. This will move the tilt function to relief (overflow). Check the max. pressure on the hydraulic oil pump for lifting/lowering and tilt. The pressure should match the value on the pressure plate. 7 Increase engine speed to approx. 1800 rpm and turn to max. steering right or left and continue to activate the function. Check the max. pressure on the hydraulic oil pump for steering and load handling. The pressure should match the value on the pressure plate. 8 Switch off the engine and remove the pressure gauge and fit the protective cap on the measuring outlet. 9 To adjust the hydraulic pressure, see Workshop Manual DCF 180–250. Steering pressure Operate and warm up the machine so that the hydraulic oil reaches operating temperature, approx. 50 ºC. 2 Turn off the engine. 3 Connect a pressure gauge (0–25 MPa) to the measuring outlet at the priority valve. 4 Start the engine and increase engine speed to approx. 1200 rpm. 5 Turn the steering wheel to full deflection and read the pump pressure during steering wheel movement. Compare this to the control pressure on the hydraulics plate. 6 Switch off the engine and remove the pressure gauge and fit the protective cap on the measuring outlet. 7 To adjust the hydraulic pressure, see Workshop Manual DCF 180–250. 014475 1 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 10 Common hydraulics – Common hydraulics 10:7 Pump pressure, brake system Operate and warm up the machine so that the oil in the brake system reaches operating temperature, at least 50 ºC. 2 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 3 Depressurise the hydraulic system, see section B Safety. 4 Connect a pressure gauge (0–25 MPa) to the measuring outlet for pump pressure on the accumulator charging valve. 5 Start the engine and let it idle. 6 Close the drain valve on the accumulator charging valve and check the pump pressure during charging. 014477 1 Measuring outlet pump pressure NOTE Check that the accumulator drain valve is completely closed and tighten the lock ring. During charging the pressure should increase to 20.5±1.0 MPa before the accumulator charging valve switches to cooling. The pressure drops when the accumulator charging valve switches to cooling. 014476 7 Close the accumulator charging valve Check the pressure during cooling. During cooling the pressure should be max. 0.10–0.15 MPa at max. engine speed. 8 Turn off the engine. 9 Depressurise the hydraulic system, see section B Safety. 10 Remove the pressure gauge and fit the protective cap on the measuring outlet. 11 Close the drain valve on the accumulator charging valve. NOTE Check that the accumulator drain valve is completely closed and tighten the lock ring. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 10:8 10 Common hydraulics – Common hydraulics Checking accumulator charging Depressurise the hydraulic system, see section B Safety. 2 Connect a pressure gauge (0–25 MPa) to the measuring outlet for accumulator pressure on the accumulator charging valve. 3 Start the engine and let it idle. 4 Close the drain valve on the accumulator charging valve. 014478 1 Measuring outlet accumulator pressure NOTE Check that the accumulator drain valve is completely closed and tighten the lock ring. 5 Check that the pressure rises slowly to 20.5±1.0 MPa. 6 Brake repeatedly and check at which pressure the accumulator charging valve switches to charging. 014476 The valve shall switch to cooling at 15.5±0.5 MPa. Close the accumulator charging valve 7 Depressurise the hydraulic system, see section B Safety. 8 Remove the pressure gauge and fit the protective cap on the measuring outlet. 9 Close the drain valve on the accumulator charging valve. NOTE Check that the accumulator drain valve is completely closed and tighten the lock ring. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 10 Common hydraulics – Safety valves 10:9 10.2 Safety valves Safety valves, component location NOTE The valve shall be closed during operation and is opened to depressurise the machine. 1. Accumulator drain valve with opening knob and lock ring. 014452 1 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 10:10 10 Common hydraulics – Tanks and accumulators 10.3 Tanks and accumulators Tanks and accumulators, component location A. Sight glass B. Breather filter C. Filling point B C A UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 10 Common hydraulics – Accumulator 10:11 10.3.2 Accumulator Accumulator, checking 1 Start the machine and allow it to idle (until the accumulator charging valve switches to cooling). 2 Switch off the engine and turn the start key to position l. 3 Apply and release the brake several times, and count the number of times that the brake can be applied before the error code for low brake pressure is shown in the display. It should be possible to apply the brake at least 8 times before the error code for low brake pressure is shown. If the error code for low brake pressure is shown earlier then the accumulator is probably faulty and should be investigated further. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 10:12 10 Common hydraulics – Pumps 10.4 Pumps Pumps, general The machine's hydraulics are supplied from three pumps. Two of them for load handling/steering, and one for the brake system. 1 2 3 1. Pump 1 supplies steering and control valve load handling. The priority valve ensures that there is always pressure for steering, the residual flow goes to control valve load handling. 2. Pump 2 supplies lifting/lowering and tilt via control valve load handling. 3. The fixed brake oil pump supplies the brake system's brake and cooling circuit over an accumulator charging valve, see section 4 Brakes. 014442 The pumps are assembled into a pump bank which is mounted to the transmission's power take-off. Hydraulic oil pumps in standard version. 1. Hydraulic oil pump for steering and load handling 2. Hydraulic oil pump for lifting/lowering and tilt 3. Hydraulic oil pump for brake system UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 10 Common hydraulics – Hoses, pipes and valves 10:13 10.5 Hoses, pipes and valves Hoses, pipes and valves, component location 1 2 014453 3 1. Priority valve 2. Accumulator charging valve 3. Shuttle valve Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 10:14 10 Common hydraulics – Temperature control, cleaning and hydraulic oil 10.6 Temperature control, cleaning and hydraulic oil Temperature control, cleaning and hydraulic oil, function description The return oil from control valve load handling is filtered through the hydraulic oil filter in the hydraulic oil tank. A high pressure filter fitted after the brake system's hydraulic oil pump also cleans the oil. The cooling system lowers the temperature of the machine's hydraulic oil. The cooling system consists of a hydraulic oil cooler with separate temperature-controlled electric fan fitted in the wheel brakes' cooling circuit. Return oil from the accumulator charging valve is led via the wheel brakes and is cooled in the hydraulic oil cooler. An electric cooling fan increases the air flow through the cooler when the temperature needs to be reduced. A thermal bypass valve leads the hydraulic oil past the cooler directly to the tank if the temperature is below 55 °C. When the oil temperature above 65 °C all the oil is led through the cooler. The temperature sensor starts the electric fan if the oil temperature is above than 60 °C and switches off the fan when it is below 50 °C. C C 4 P T 5 3 °C 7 2 10 6 9 M 8 014454 1 1. Hydraulic oil pump 2. High-pressure filter 3. Accumulator charging valve 4. Wheel brake 5. Distribution block 6. Thermal bypass valve UDCF06.01GB 7. Make-contact (closing switch) hydraulic oil temperature (S240-1) 8. Relay (K359) 9. Cooling fan (M668) 10. Radiator Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 10 Common hydraulics – Hydraulic oil cooler 10:15 Temperature control, cleaning and hydraulic oil, component location 2 1 3 10 5 11 6 4 8 014455 7 9 1. Hydraulic oil pump, brake system 7. Tank heater 2. High-pressure filter 8. Thermal bypass valve 3. Accumulator charging valve 9. Make-contact (closing switch) cooling fan 4. Hydraulic oil filter 10. Hydraulic oil cooler 5. Breather filter hydraulic oil tank 11. Cooling fan 6. Hydraulic oil tank 10.6.2 Hydraulic oil cooler Hydraulic oil cooler, cleaning 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 Clean the hydraulic oil cooler (position A) using compressed air. Blow away dust and other loose dirt. 014456 A Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 10:16 10 Common hydraulics – Breather filter hydraulic oil tank 10.6.7 Breather filter hydraulic oil tank Breather filter hydraulic oil tank, changing 2 4 1 Turn off the engine and turn off the main electric power. 2 Clean the area around the filter housing. 3 Remove the filter housing. Press down and turn approx. 1/8 turn clockwise. 2 1 4 Replace the filter insert. Handle the filter insert as environmentally hazardous waste. 5 Fit the filter housing. Press down and turn approx. 1/8 turn anticlockwise. 6 Reset the filter indicator by pressing down the button in the middle on the glass centred on the filter insert. 014457 3 1. Cover plate for oil filter 2. Filling point hydraulic oil 3. Sight glass hydraulic oil 4. Breather filter hydraulic oil tank 10.6.8 Hydraulic oil filter High-pressure filter, changing A high-pressure filter is fitted in the engine compartment. NOTE Read safety instructions for oil before starting work, see section B Safety. IMPORTANT Ensure cleanliness around the filter and filling point when working on the hydraulic tank. Dirt particles may cause machine damage. Receptacle for hydraulic oil (5 l). 1 Machine in service position, see section B Safety. 2 UDCF06.01GB Tilt the cab. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 10 Common hydraulics – Hydraulic oil filter 10:17 3 Clean the filter cover externally. 4 Place a receptacle under the hydraulic oil filter. 5 Drain the oil in the filter by loosening the drain plug on the underside of the filter. 6 Remove the top of the filter cover. 7 Remove the filter insert. Handle the filter insert as environmentally hazardous waste. 8 Fit the small O-ring, which is located in the packaging, onto the new filter. In case of doubt, compare with the old filter insert. 9 Fit the new filter insert in the filter holder. NOTE Use only original filters. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 10:18 10 Common hydraulics – Hydraulic oil filter 10 Fit a new support ring (white) and O-ring (black), which are located in the packaging with the new filter, in the groove on the filter cover. 011772 NOTE It is important to fit the support ring under the O-ring as illustrated. 11 Lubricate the filter cover (on the side) with universal grease EP2. 12 Fit the top of the filter cover. 13 Start the engine and check that there are no leaks. 14 Turn off the engine. 15 Remove the receptacle. Handle the oil as environmentally hazardous waste. 16 Check the hydraulic oil level, see Hydraulic oil, level check, page 10:20. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 10 Common hydraulics – Hydraulic oil filter 10:19 Hydraulic oil filter, changing NOTE Read safety instructions for oil before starting work, see section B Safety. IMPORTANT Ensure cleanliness around the filter and filling point when working on the hydraulic tank. Dirt particles may cause machine damage. 2 4 1 Turn off the engine and turn off the main electric power. 2 Remove the cover plates (position 1) over the hydraulic oil filters. 3 Lift up the filter unit and place it in the receptacle. Let the hydraulic oil drain. 4 Part the filter unit and remove the filter insert. Handle the filter insert as environmentally hazardous waste. Note position of the parts. 5 Clean the filter holder's parts. Be especially thorough with the magnetic rod. 6 Fit the new filters and assemble the filter units. 7 Install the filter units and cover plates. Tighten the bolts crosswise. 8 Check the oil level, see Hydraulic oil, level check, page 10:20. 2 1 014457 3 1. Cover plate for oil filter 2. Filling point hydraulic oil 3. Sight glass hydraulic oil 4. Breather filter hydraulic oil tank Magnetic rod Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 10:20 10 Common hydraulics – Hydraulic oil 10.6.9 Hydraulic oil Hydraulic oil, level check NOTE Check the hydraulic oil level with the trolley completely lowered and the mast tilted completely inward. 1 Machine in service position, section B Safety. 2 Check the oil level in the hydraulic tank. The oil level should be visible in the sight glass. Fill oil as required. For oil grade, see section F Technical data. Hydraulic oil, checking The condition of the hydraulic oil must be checked by means of oil samples aimed at avoiding unnecessary wear and unnecessary oil changes. The intervals for oil samples are presented in the service schedule. Oil samples are taken in accordance with the instructions from the relevant institution or oil supplier. Threshold value for efficient oil is 18/14 in accordance with SS-ISO 4406 “Hydraulic fluid power - Fluids - Method for coding the level of contamination by solid particles”. Hydraulic oil, changing NOTE Read safety instructions for oil before starting work, see section B Safety. IMPORTANT Ensure cleanliness around the filter and filling point when working on the hydraulic tank. Dirt particles may cause machine damage. 1 UDCF06.01GB Machine in service position, see section B Safety. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 10 Common hydraulics – Hydraulic oil 2 2 Remove the filler cap and pump out the hydraulic oil in a collection container. 3 When most possible oil has been pumped out. Place a container under the hydraulic oil tank's drain plug and drain the last hydraulic oil. 4 Fit the drain plug when the oil has drained. 4 2 10:21 1 NOTE Make sure that the drain plug's washer seal is also removed. 5 If the hydraulic oil filters are to be changed, change them before filling the tank with oil, see Hydraulic oil filter, changing, page 10:19. 6 Fill new hydraulic oil in the filler holes on the filter's cover plates. This filters the oil and protects the hydraulic system from contamination. 014457 3 1. Cover plate for oil filter 2. Filling point hydraulic oil 3. Sight glass hydraulic oil 4. Breather filter hydraulic oil tank Fill oil until the oil level is in the middle of the sight glass. For volume and quality, see section F F Technical data. CAUTION Do not overfill! Leakage and environmental damage! The hydraulic oil level is checked when all hydraulic cylinders are in the retracted position. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 10:22 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 11:1 11 Common electrics Contents 11 Common electrics 11 Common electrics ............................................................................................11:3 11.2 Electrical protection........................................................................................ 11:4 11.2.2 Fuses ........................................................................................................ 11:5 11.3 Batteries......................................................................................................... 11:8 11.3.1 Start battery............................................................................................... 11:8 11.4 Alternator ..................................................................................................... 11:10 11.5 Distribution of electricity ............................................................................... 11:11 11.5.1 Voltage feed ............................................................................................ 11:11 11.5.2 Electronic box.......................................................................................... 11:12 11.5.3 Control units ............................................................................................ 11:14 11.6 Communication ............................................................................................ 11:16 11.6.1 CAN bus .................................................................................................. 11:16 11.6.2 Redundant CAN-bus ............................................................................... 11:16 11.6.3 CAN-bus drivetrain .................................................................................. 11:16 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 11:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 11 Common electrics – Common electrics 11:3 11 Common electrics Common electrics, general Electrical functions that are common to several of the machine's main functions are found under the function common electrics. For example, voltage feed and CAN-bus. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 11:4 11 Common electrics – Electrical protection 11.2 Electrical protection Electrical protection, component location 1 1. Circuit fuses, electronic box cab 2. Main fuses 3. Battery disconnector 4. Control breaker 4 2 014462 3 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 11 Common electrics – Fuses 11:5 11.2.2 Fuses Fuses, checking IMPORTANT Risk of cable damage and fire in cable harnesses! Always use fuses with the correct ampere rating. The electrical system has two main circuits (30 and 15-voltage), see Distribution of electricity, general, page 11:11. The main circuits are fused several times with main fuses and circuit fuses. Main fuses Main fuses The main fuses divide the machine's voltage feed into smaller parts to maintain as many functions as possible in case of damage to cables harnesses. The machine's electrical system has main fuses in the battery compartment on the frame, 4 x 25 A. Disconnects all electrical power. When checking and replacing the main fuse: 1 Disconnect the system voltage with the battery disconnector (position 2). 2. Remove the plastic cover. 3. Check and replace fuses if necessary. The fuses are 25 A. 4. Reconnect the system voltage. 014463 2 1. 1. Main fuses (25 A) 2. Battery disconnector Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 11:6 Circuit fuses 11 Common electrics – Fuses Circuit fuses The circuit fuses are grouped in fuse holders that are located in the electronic box in the cab. The electronic box is located behind the driver's seat in the cab. Adjacent to the electronic box is a fuse plate describing the various fuses. B C D 007482 A Fuses A. Fuse holder F58-1 B. Fuse holder F58-2 C. Fuse holder F58-3 D. Fuse holder F58-4 When checking and replacing fuses: 1. Disconnect the system voltage with the battery disconnector. 2. Remove the cover of the electronic box. 3. Remove the cover from the fuse holder. 4. Check that the fuses are intact. Change when needed. Measure and check if necessary. The fuse plate provides information on each fuse. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 11 Common electrics – Fuses Fuses, power supply engine 11:7 Fuses, power supply engine When checking and replacing fuses: 1. Power supply engine. 2. Power supply 2 Disconnect the system voltage with the battery disconnector. 2. Remove the cover from the fuse. 3. Check and replace the fuse if necessary. 014274 1 1. after-treatment system. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 11:8 11 Common electrics – Batteries 11.3 Batteries 11.3.1 Start battery Battery, component location The batteries, two connected in series, are located behind a cover lid on the machine's rear left-hand side (by the fuel tank). 014464 The battery's negative terminal is connected to the frame and the positive terminal is connected to the battery disconnector. Start battery, checking WARNING Battery electrolyte contains corrosive sulphuric acid. Risk of corrosive injuries! Hazardous to health! Use protective safety goggles and protective work gloves when working with batteries. Remove immediately any electrolyte on the skin. Wash with soap and plenty of water. If electrolyte has splashed in the eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and contact a doctor immediately. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 11 Common electrics – Start battery 1 11:9 Check the battery's acid gravity with a hydrometer. In a fully charged battery the acid gravity should be 1.28 g/cm3. If the acid gravity is lower than 1.24 at +20 °C then the battery must be charged. NOTE A discharged battery freezes at -5 °C. NOTE If the acid gravity differs between the batteries they must be charged separately. 2 The fluid level should be level with the top of the round white plastic ring that is visible down in the battery when the cover is unscrewed. NOTE Use only distilled water if topping up is necessary. 3 Check that the batteries are clean on the top to prevent leakage currents between cells, which can cause reduced battery capacity. 014464 Wipe clean with a cloth and clean warm water without detergent. 4 Check that the battery's terminals are free from dirt. If needed, lube the battery terminals with terminal grease. Battery cables, checking DANGER Check that the battery cables are correctly clamped and free from damage. Fire hazard! Risk of personal injury! Repair or replace damaged clamps and check that no machine parts wear or chafe against the battery cables. Change damaged battery cables. The following battery cables should be checked for clamping, risk of rubbing and damage to the battery cables. Rectify incorrect clamping and risks of rubbing. Change battery cables that show signs of damage. Diesel-powered machines • Plus-cable between battery and battery disconnector. • Plus-cable between battery disconnector and starter motor. • Plus-cable between starter motor and alternator. • Plus-cable between battery disconnector and main fuses. • Plus-cable between starter motor and preheating relay. • Plus-cable between preheating relay and preheating coil. • Ground cable between battery and frame. • Ground cable between engine and frame. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 11:10 11 Common electrics – Alternator 11.4 Alternator Alternator, component location 014036 The alternator is fitted on the engine. Location is dependent on engine alternative. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 11 Common electrics – Distribution of electricity 11:11 11.5 Distribution of electricity Distribution of electricity, general This section describes distribution of electric power and communication between control units. Electric power distribution describes the foundation of the electrical system and the network of control units The system's communication has three main parts: • Voltage feed of control units • Redundant CAN bus communication (no control unit can drop out without the system losing all function) See CAN-bus, description, page 11:16. • CAN bus communication for drivetrain (the drivetrain has its own communication system) See CAN-bus drivetrain, description, page 11:16. 11.5.1 Voltage feed 11.5.1.1 Battery voltage, 30-voltage Battery voltage, 30-voltage, description The voltage before the ignition key lock is normally called 30-voltage. This is always approx. 24 V, even if the ignition is switched off (ignition key in position 0). 11.5.1.2 Ignition voltage, 15 volts Ignition voltage, 15 volts, description The voltage after the ignition key lock is normally called 15-voltage. This is at 24 V, only if the ignition is switched on (ignition key in position 1). Otherwise this voltage is 0 V. 11.5.1.3 Frame connections Frame connections, description Power supply takes place with cable harnesses (cables) which are routed across the machine. Communication takes place via twinned pair signal cable (30 rpm). Grounding points, description A grounding point in the frame acts as main ground, including for the starter motor. From there the ground is routed to a common point in the electronic box to which all current consumers' grounds are connected. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 11:12 11 Common electrics – Electronic box 11.5.2 Electronic box Electronic box, component location 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 10 11 12 13 14 15 007759 9 16 Electronic box 1. Relay, intermittent wipers 10. Bolts, holders and straps 2. Relay, ignition 11. Socket, relay 5-pin 3. Relays 12. Socket, relay 9-pin 4. Fuse holder F58-2 13. Flasher unit, 200 W, 24 V 5. Fuse holder F58-3 14. Mini relay 6. Fuse holder F58-4 15. Fuse holder F58-1 7. Fuse holder 16. Cable terminal, washer and screw 8. Sleeve block with 9 pins 17. Fitting plate 9. Circuit board with diodes UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 17 11 Common electrics – Electronic box 1 2 3 11:13 4 5 6 7 8 10 11 12 13 14 15 008571 9 16 17 Electronic box, machine with turnable driver's seat. 1. Relay, intermittent wipers 10. Bolts, holders and straps 2. Relay, ignition 11. Socket, relay 5-pin 3. Relays 12. Socket, relay 9-pin 4. Fuse holder F58-2 13. Flasher unit, 200 W, 24 V 5. Fuse holder F58-3 14. Mini relay 6. Fuse holder F58-4 15. Fuse holder F58-1 7. Fuse holder 16. Cable terminal, washer and screw 8. Sleeve block with 9 pins 17. Fitting plate 9. Circuit board with diodes Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 11:14 11 Common electrics – Control units 11.5.3 Control units Control units, general A B C D Part of the machine's different functions is managed by the control system KCS, see section 8 Control system, where each control unit is allotted responsibility for a number of functions. Control units ECU 790, ECU 792 and ECU 796 have indicator lamps that can be used to check basic information on control unit status. ECU 796 ECU 790 The indicator lamps have the following significations: 0007760 ECU 792 A ECU 792 B ECU 796 C ECU 790 D Electronic box Table Indicator lamps ECU 790 and ECU 792 Green (Power) Battery voltage OK. Green (System) Internal 5 VDC OK Yellow (Mode) Software check, flashes 0.5Hz if the program is OK, flashes 5 Hz if no program is loaded, fixed light if in setup mode Red (Status) Illuminates if a fault arises. Table Indicator lamps ECU 796 All LEDs illuminate with fixed light for 3 seconds when starting up. UDCF06.01GB Green Power, fixed light at 22-28 VDC, flashing if outside limits Yellow CAN bus communication and application OK Red Flashes if the supply voltage for the PWM card is under 12 VDC. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 11 Common electrics – Control units 11:15 Control units, position 1 2 4 3 6 014465 5 1. Control unit, steering (ECU 792) 4. Control unit terminal (EDU 795) 2. Control unit, hydraulics (ECU 796) 5. Control unit, transmission (ECU 793) 3. Control unit general (ECU 790) 6. Control unit engine (ECU 794) Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB 11:16 11 Common electrics – Communication 11.6 Communication Communication, general The machine's communication is handled by a so-called CAN bus system. The CAN bus system consists of control units connected together to form a network. ECU 792 1 ECU 790 EDU 795 The idea with the network is to share information. Signal values are sent out by the control unit that, e.g., is connected to a sensor, other control units can use the signal for their functions. ECU 796 The network consists of control units and segments. Segment is the CAN-bus between control units. ECU 794 1. Segment 2. CAN-bus drivetrain 007764 2 ECU 793 11.6.1 CAN bus CAN-bus, description The CAN-bus consists of two twisted cables (twisted pair). 11.6.2 Redundant CAN-bus Redundant CAN-bus, description ECU 790 CAN R CAN L EDU 795 CAN R CAN L Redundant CAN-bus means that each control unit has two connections for communication. The CAN-bus is connected in series between the control units. This means that the CAN-bus can handle loss of a segment. If several segments fail, then one or some control units lose contact with the network and work independently, often with limited capacity to perform their task. ECU 796 CAN R CAN L 007765 High+/Low- ECU 792 Signals can be checked with diagnostic menu. Principle illustration redundant CAN-bus 11.6.3 CAN-bus drivetrain CAN-bus drivetrain, description The communication with Control unit engine (ECU 794) and Control unit transmission (ECU 793) is separated from the redundant CAN-bus. EDU 795 ECU 794 ECU 793 007766 Signals can be checked with diagnostic menu. Principle illustration CAN-bus drivetrain UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 D:1 D Error codes D Error codes Error codes See Workshop manual DCF 180-250, section D Error codes. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB D:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 E:1 E Diagrams E Diagrams Diagrams See Workshop manual DCF 180-250, section E Diagrams. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB E:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 F:1 F Technical data Contents F Technical data Technical data.................................................................................................... F:3 Data .................................................................................................................F:3 Volumes ...........................................................................................................F:4 Specifications for lifting capacity and dimensions............................................F:6 Oils and lubricants, recommendation...............................................................F:8 Tightening torques, recommendations...........................................................F:10 Tightening torque, ORFS connections ...........................................................F:11 Tightening torque, connections for air conditioning unit.................................F:12 Unit explanations ...........................................................................................F:13 Conversion SI-units........................................................................................F:14 Conversion table, length ................................................................................F:15 Conversion table, area...................................................................................F:15 Conversion table, volume ..............................................................................F:15 Conversion table, weight................................................................................F:15 Conversion table, pressure ............................................................................F:16 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB F:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 F Technical data – Technical data F:3 F Technical data Data Machine weights and dimensions vary with equipment installed on the machine and are described in detail in the product specification and spec. sheet for the relevant machine. 0 complete machine Volvo TAD761VE Guaranteed sound power level in accordance with 2000/14/EC and 2005/88/EC including measurement uncertainty 1.5 dB. LWA 109 dB(A) 1 Engine Volvo TAD761VE Output in accordance with ISO 3046 (marked output) Torque ISO 3046 160 kW between 1300-2200 rpm 1180 Nm at 1200 rpm Max. rpm 1800 rpm Number of cylinders 6 cylinders Alternator, power 3360 W System voltage, voltage capacity 2 Transmission 24 V (2x12 V / 145 Ah) ZF 3WG171 No. of gears, forward - reverse 3 – 3 3.3 Driveline/Axle, drive axle Kessler Drive axle, type D91 4 Brakes Footbrake system - wheels affected Wet Disc Brake - drive wheel Parking brake system - wheels affected Spring brake - drive wheel 5 Steering Steering system Hydraulic servo 6 Wheels Dimension, front and rear 14.00x24 Tyre pressure, also see pressure plate 1.0 MPa Tyre type, front and rear Air filled. Spare and replacement tyres must be of a brand approved by Cargotec. 9 Cab Equivalent sound pressure level in cab according to EN12053 with measurement uncertainty σR = 2.5 dB. Measuring value with standard engine. LpAz 72 dB(A) Whole-body vibration in accordance with EN13059 with measurement uncertainty k = 0.3 x measured value. 0.4 - 0.7 m/s2 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB F:4 F Technical data – Technical data 9.6 Lighting system Instruments 3 Ba7s Indicator lamps 1.2 W2x4.6d Interior lighting 10 S8.5 Rear lights 5 BA15s Brake lights 21 BA15s Direction indicators 21 BA15s Rear lights, brake lights & direction indicators - Replace complete 5 SV8,5 - Replace complete Headlights (during high, low beam) 75/70 P43t-38 (H4) Back-up lights 70 PK22s (H3) Work light bulb 70 PK22s (H3) 35 D1S Xenon tube. Cartridge and ballast are replaced complete. - Replace complete 70 PK22s (H1) LED Running lights Running lights LED Work light, Xenon Work lighting LED Revolving beacon Volumes Any deviation from this table must be supported with written approval from Cargotec. 1.2 Engine, fuel system Fuel tank, volume Fuel quality 280 l Diesel according to: EN590, ASTM D 975 No 1–D, ASTM D 975 No 2–D. AdBlue tank, volume Quality 15 l AdBlue, according to ISO standard 22241. 1.7 Engine, cooling system Coolant volume 35 l Coolant filling Volvo Penta Coolant VCS, ready-mixed CAUTION Different types of coolant must not be mixed. Risk of engine damage and damage to the cooling system if different types of coolant are mixed. When changing and topping up coolant, only use coolant of the same type that was used before. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 F Technical data – Technical data F:5 1.8 Engine, lubrication system Oil type, quality See Oils and lubricants, recommendation, page F:8. 27 l Oil volume incl. filter 2.6 Transmission, lubrication system Oil type See Oils and lubricants, recommendation, page F:8 Oil volume 28 l 3.3 Driveline/Axle, drive axle Oil grade See Oils and lubricants, recommendation, page F:8. Oil volume, differential 30 l Oil volume, hub reduction 2x4 l 9 Frame, body, cab and accessories R134a Refrigerant air conditioning Volume refrigerant 2200 g (see sign for air conditioning) Lubricant air conditioning ZXL100PG Volume, lubricant 0.32 l Volume, washer fluid 2.5 l 10 Common hydraulics Oil grade See Oils and lubricants, recommendation, page F:8. Oil additive Lubrizol 3% Volume hydraulic oil tank 270 l Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB F:6 F Technical data – Technical data Specifications for lifting capacity and dimensions a b H5 A1 100 100 H4 H3 b V1 V B T1 H6 H2 H8 R1 R2 L3 L L2 S L4 T2 L1 DCF 180-12LB DCF 200-12LB DCF 220-12LB DCF 250-12LB 18 20 22 25 Lifting capacity Classification (kg x 103) 1200 Centre of gravity distance (L4 [mm]) Dimensions Truck length without forks (L [mm]) 6070 6320 Truck width (B [mm]) 3050 Height, basic machine (H6 [mm]) 3270 Seat height (H8 [mm]) 2150 Axle distance (L3 [mm]) 4000 4250 Distance drive axle - fork front shank surface (L2 [mm]) 1070 Track (front - rear) (T [mm]) 2200 - 2140 Minimum turning radius, outer (R1 [mm]) 5500 Slewing radius, inner (R2 [mm]) 550 Ground clearance, min [mm] 300 Height for cab tilting, max. (T1 [mm]) 3800 Width for cab tilting, max. (T2 [mm]) 3700 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 014780 a F Technical data – Technical data DCF 180-12LB Minimum track width for 90° stacking with forks (A1 [mm]) Kerb weight [kg x 10 3] DCF 200-12LB F:7 DCF 220-12LB 9170 28.5 Axle load pressure front, (without load) [kg] 29.8 DCF 250-12LB 9470 31.2 15000 32.9 15500 Axle load pressure front, (with classified load) [kg] 43200 46300 49500 53800 Axle load pressure rear, (without load) [kg] 13500 14800 16200 17400 Axle load pressure rear, (with classified load) [kg] 3300 3500 3700 4100 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB F:8 F Technical data – Technical data Oils and lubricants, recommendation Cargotec's stated service intervals in the maintenance manual are conditional on oil selection according to the following table. The table states recommended viscosity for different oil types and grades depending on outdoor temperature. Any deviation from this table must be approved in writing by Cargotec, and may mean changed service intervals. Oil type, quality °C -30 -20 -10 0 +10 +20 +30 +40 +50 °F -22 -4 +14 +32 +50 +68 +86 +104 +122 1.8 Engine, lubrication system SAE 15W/40 VDS-3 SAE 5W/30 2.6 Transmission, lubrication system API: CD/CE/CF-4/CF/CG-4/ CH-4/CI-4/SF/SG/SH/SJ/SL SAE 10W, 10W/30, 10W/40 SAE 15W/30, 15W/40 SAE 20W/20, 20W/40 ACEA: Categories A, B, E SAE 30 3.3 Driveline/Axle, drive axle Hypoid oil, API GL-5 and MIL-L-2105B SAE 80W140 SAE 80W90 SAE 90 SAE 85W140 10 Common hydraulics Hydraulic oil AV 32 SS 155434 Hydraulic oil AV 46 HVLP 46 DIN 51524 Hydraulic oil HLP 68 ISO - LHV 46 ISO 6743/4 UDCF06.01GB ISO - LHM 68 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 F Technical data – Technical data F:9 NOTE Oil filters shall always be changed in connection with oil change. The change interval for engine oil is conditional on the sulphur content in the fuel not exceeding 0.5%. *) API CH-4 or CI-4 are approved for markets outside the EU/EES. ACEA = Association des Constructeurs Européenne d'Automobiles API = American Petroleum Institute VDS = Volvo Drain Specification Grease Use a universal grease type EP according to NLGI Grade 2 (EP2) for all lubrication points except for lifting equipment and slide plates. For lifting equipment, use a universal grease type EP according to NLGI Grade 2 (EP2) with 3-5% Molybdenum disulfide intermix. For slide plates, use lubricants approved by Cargotec. Order from Cargotec Parts department. 0.65 kg cartridge for grease gun, part no. 923110.0360, and 5 kg can, part no. 923595.0003. NOTE Select grease grade according to relevant climate. Electrical connector grease Use electrical contact grease part no. 923836.0552. Sealant silicone Use silicone part no. 923107.0308. Silicone adhesive Use silicone adhesive part no. 923854.0100. Coolant Only use ready-mixed recommended coolant. Select mixture of the coolant that is adapted for correct temperature. CAUTION Different types of coolant must not be mixed. Risk of engine damage and damage to the cooling system if different types of coolant are mixed. When changing and topping up coolant, only use coolant of the same type that was used before. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB F:10 F Technical data – Technical data Tightening torques, recommendations The tightening torques in the following table are recommendations when tightening bolts and nuts. When torquing using a machine, for example, bolt runner, the tightening torque should be reduced by approx. 5%. For soft materials (lower hardness than 200 HB), use washer under both bolt head and nut. As an alternative, use flange bolt or flange nut. Tighten to the prescribed torque without stopping. Recommended tightening torque varies depending on surface treatment. Certain combinations of bolts and nuts require lubrication according to the following table. State Nut Screw Lubrication 1 untreated untreated oil 2 bright galvanised untreated or bright galvanised dry or oil 3 hot-galvanised untreated dry or oil 8.8 Quality 10.9 12.9 1 2 3 1 1 M81 27 Nm 24 Nm 30 Nm 39 Nm 46 Nm M101,25 54 Nm 48 Nm 61 Nm 78 Nm 91 Nm M121,25 96 Nm 85 Nm 108 Nm 135 Nm 162 Nm M161,5 230 Nm 205 Nm 260 Nm 323 Nm 388 Nm M181,5 330 Nm 294 Nm 373 Nm 466 Nm 559 Nm M4 3.2 Nm 2.9 Nm 3.6 Nm 4.6 Nm 5.5 Nm M5 6.4 Nm 5.7 Nm 7.2 Nm 9.1 Nm 11 Nm M6 11 Nm 9.8 Nm 12.5 Nm 16 Nm 19 Nm M8 26 Nm 24 Nm 30 Nm 38 Nm 45 Nm M10 52 Nm 47 Nm 59 Nm 74 Nm 89 Nm M12 91 Nm 81 Nm 103 Nm 128 Nm 154 Nm M16 220 Nm 198 Nm 250 Nm 313 Nm 375 Nm M20 430 Nm 386 Nm 490 Nm 620 Nm 732 Nm M24 750 Nm 668 Nm 848 Nm 1050 Nm 1270 Nm M30 1480 Nm 1317 Nm 1672 Nm 2080 Nm 2500 Nm 1/4 12.5 Nm 11.1 Nm 14.1 Nm 17.6 Nm 20 Nm 5/16 25 Nm 22.3 Nm 28.3 Nm 35 Nm 42 Nm 3/8 44 Nm 39 Nm 50 Nm 62 Nm 73 Nm 7/16 70 Nm 62 Nm 79 Nm 100 Nm 118 Nm 1/2 107 Nm 95 Nm 121 Nm 151 Nm 178 Nm 9/16 153 Nm 136 Nm 173 Nm 216 Nm 255 Nm 5/8 210 Nm 187 Nm 237 Nm 298 Nm 353 Nm 3/4 370 Nm 390 Nm 418 Nm 524 Nm 619 Nm State Fine M-thread M-thread UNC-thread UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 F Technical data – Technical data F:11 8.8 Quality 10.9 12.9 7/8 594 Nm 528 Nm 671 Nm 839 Nm 990 Nm 1 889 Nm 791 Nm 1005 Nm 1260 Nm 1480 Nm 1 1/8 1260 Nm 1120 Nm 1424 Nm 1780 Nm 2100 Nm 1 1/4 1760 Nm 1565 Nm 1990 Nm 2490 Nm 2940 Nm 1 3/8 2320 Nm 2065 Nm 2620 Nm 3280 Nm 3870 Nm 1 1/2 3060 Nm 2720 Nm 3455 Nm 4320 Nm 5100 Nm Tightening torque, ORFS connections Pipe and hose coupling Pipe diameter Tightening torque mm Nm inch 6 1/4 8 5/16 10 3/8 12 1/2 14 - 15 - 16 5/8 18 3/4 20 - 22 7/8 25 1" 28 - 30 - 32 1"1/4 35 - 38 1"1/2 23-25 33-38 51-57 80-90 120-130 150-170 180-200 200-240 Wrench size Tightening torque mm Nm inch 17 11/16 23-25 22 13/16 33-38 24 15/16 51-57 36 1 3/8 120-130 41 1 5/8 150-170 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB F:12 F Technical data – Technical data Goods coupling UNF-UN Metric-ISO BSSP Thread (inch) Tightening torque (Nm) Thread (mm) Tightening torque (Nm) Thread (inch) Tightening torque (Nm) 7/16-20 21 10x1 20 1/8-28 20 1/2-20 27 12x1.5 35 1/4-19 35 9/16-18 40 14x1.5 45 3/8-19 70 3/4-16 78 16x1.5 55 1/2-14 100 7/8-14 110 18x1.5 68 3/4-14 190 1"1/16-12 180 20x1.5 80 1"-11 300 1"3/16-12 230 22x1.5 98 1"1/4-11 330 1"5/16-12 285 26x1.5 170 1"1/2-11 400 1"5/8-12 320 27x2 180 1"7/8-12 400 33x2 310 42x2 330 48x2 400 Tightening torque, connections for air conditioning unit O-ring coupling cooling coils Hose diameter Thread Tightening torque mm inch inch Nm 6 1/4" 7/16" 7-13 Nm 10 3/8" 5/8" 14-20 Nm 10 3/8" 11/16" 14-20 Nm 12 1/2" 3/4" 14-26 Nm 16 5/8" 7/8" 27-41 Nm 19 3/4" 1 1/16" 34-46 Nm 3/8" 7-13 Nm Pressure switch 7/16" The above values should be considered guidelines and may vary depending on installation. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 F Technical data – Technical data F:13 Unit explanations Unit Abbreviation Newton metre Nm Kilopond metre kpm Kilopascal kPa Megapascal MPa Kilowatt kW Kilojoule kJ British thermal unit Btu Calorie ca Inch in Feet ft Yard yd Mile mile Centimetre cm Meter m Kilometre km Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB F:14 F Technical data – Technical data Conversion SI-units SI-unit Conversion factor Non-SI Conversion factor SI Nm x 10.2 = kg cm x 0.8664 = lb in Nm x 0.74 = lbf ft x 1.36 = Nm Nm x 0.102 = kg m x 7.22 = lb ft kPa x 4.0 = in.H2O x 0.249 = kPa kPa x 0.30 = in.Hg x 3.38 = kPa kPa x 0.145 = psi x 6.89 = kPa bar x 14.5 = psi x 0.069 = bar kp/cm 2 x 14.22 = psi x 0.070 = kp/cm2 N/mm 2 x 145.04 = psi x 0.069 = bar MPa x 145 = psi x 0.00689 = MPa kW x 1.36 = hp (cv) x 0.736 = kW kW x 1.34 = bhp x 0.746 = kW kW x 0.948 = Btu/s x 1.055 = kW W x 0.74 = ft lb/s x 1.36 = W kJ x 0.948 = Btu x 1.055 = kJ J x 0.239 = calorie x 4.19 = J m/s2 x 3.28 = ft/s2 x 0.305 = m/s2 m/s x 3.28 = ft/s x 0.305 = m/s km/h x 0.62 = mph x 1.61 = km/h Torque Pressure (Pa = N/ m2) Power (W = J/s) Energy (J = Nm) Speed and acceleration Horsepower/torque Bhp x 5252 rpm= TQ (lb ft) TQ x rpm 5252 = bhp Temperature °C = (°F – 32)/1.8 °F = (°C x 1.8) + 32 Flow factor l/min (dm3 /min) UDCF06.01GB x 0.264 = US gal/min x 3.785 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 = litre/min F Technical data – Technical data F:15 Conversion table, length Unit cm m km in ft yd mile cm 1 0.01 0.00001 0.3937 0.03281 0.01094 0.000006 m 100 1 0.001 39.37 3.2808 1.0936 0.00062 km 100000 1000 1 39370.7 3280.8 1093.6 0.62137 in 2.54 0.0254 0.000025 1 0.08333 0.02777 0.000015 ft 30.48 0.3048 0.000304 12 1 0.3333 0.000189 yd 91.44 0.9144 0.000914 36 3 1 0.000568 mile 160930 1609.3 1.6093 63360 5280 1760 1 1 mm = 0.1 cm - 1 mm = 0.001 m Conversion table, area Unit cm2 m2 km2 a ft2 yd2 in2 cm2 1 0.0001 - 0.000001 0.001076 0.000012 0.155000 m2 10000 1 0.000001 0.01 10.764 1.1958 1550.000 km2 - 1000000 1 10000 1076400 1195800 - a 0.01 100 0.0001 1 1076.4 119.58 - ft2 - 0.092903 - 0.000929 1 0.1111 144.000 yd2 - 0.83613 - 0.008361 9 1 1296.00 in2 6.4516 0.000645 - - 0.006943 0.000771 1 1 ha = 100 a – 1 mile2 = 259 ha = 2.59 km2 Conversion table, volume Unit cm3 = cc m3 l in3 ft3 yd3 cm3 = ml 1 0.000001 0.001 0.061024 0.000035 0.000001 m3 1000000 1 1000 61024 35.315 1.30796 dm3 (l) 1000 0.001 1 61.024 0.035315 0.001308 in3 16.387 0.000016 0.01638 1 0.000578 0.000021 ft3 28316.8 0.028317 28.317 1728 1 0.03704 yd3 764529.8 0.76453 764.53 46656 27 1 1 gal (US) = 3785.41 cm3 = 231 in3 = 0.83267 gal (UK) Conversion table, weight Unit g kg t oz lb g 1 0.001 0.000001 0.03527 0.0022 kg 1000 1 0.001 35.273 2.20459 t 1000000 1000 1 35273 2204.59 oz 28.3495 0.02835 0.000028 1 0.0625 lb 453.592 0.45359 0.000454 16 1 1 ton (metric) = 1.1023 ton (US) = 0.9842 ton (UK) Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB F:16 F Technical data – Technical data Conversion table, pressure Unit kp/cm2 bar Pa=N/m2 kPa lbf/in2 lbf/ft2 kp/cm2 1 0.98067 98066.5 98.0665 14.2233 2048.16 bar 1.01972 1 100000 100 14.5037 2088.6 Pa=N/m2 0.00001 0.001 1 0.001 0.00015 0.02086 kPa 0.01020 0.01 1000 1 0.14504 20.886 lbf/in2 0.07032 0.0689 6894.76 6.89476 1 144 lbf/ft2 0.00047 0.00047 47.88028 0.04788 0.00694 1 kg/cm2 = 735,56 Dry (mmHg) = 0.96784 atm UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 G:1 G Terminology and index Contents G Terminology and index Terminology and index .....................................................................................G:3 Terminology..................................................................................................... G:3 Index ............................................................................................................... G:7 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB G:2 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 G Terminology and index – Terminology and index G:3 G Terminology and index Terminology Explanations Term Description AC Air Conditioning Heater unit with manual control of heating, cooling, dehumidifying and air flow. Accumulator Reservoir that stores (accumulates) pressure for i.e. hydraulic functions. Attachment Part of the machine that grabs the load when lifting. Anti-corrosion agent Prevents oxidation, in simple terms, rustproofing. Working hydraulics All load handling functions, e.g. lift and lower, tilt, side shift, spreader and levelling. Axle distance Distance between drive axle and steering axle. Bar Unit for measuring pressure. Battery disconnector Cuts off current from battery. Central lubrication An automatic system for the lubrication of a preset number of lubrication points. Daily inspection The actions that should be performed daily to ensure the machine’s functionality. Decitonne Tenth of a tonne, measure of the machine's lifting capacity. Displacement The oil volume that the pump can supply per pump revolution. Display "Window" showing digital information on steering wheel panel in cab. Operating hours Number of hours machine has been in operation, shown on hour meter in cab. Drive axle Driving axle that receives the torque from the drivetrain. Drivetrain Parts in machine involved in power transmission; engine, torque converter, transmission, propeller shaft and drive axle with differential and hub reduction. ECC Electric Climate Control. Air conditioning with automatic control of heating, cooling, dehumidifying and air flow. ECU Electronic Control Unit. EDU Electronic Display Unit. Electrolyte level Fluid level in battery cells. Electric servo Load handling hydraulic components receive control signals from electro-mechanical controls. Expansion tank Tank for coolant. Fixed displacement Non-adjustable volume (capacity) of a pump. FlexCab Safety cage with a strong frame structure. Lined. FlexGuard Safety cage with a strong frame structure. Open. FMI Fault Message Identifier. Forks Lifting gear that lifts the load. Fork bracket Brackets for forks, mounted on the trolley. Main fuse Located by battery. Cuts the power to all systems in the whole machine. Hydraulic oil Oil for hydraulic system. See specifications in operator's manual. Hydraulic oil pump Pump in hydraulic system. Hydraulic servo Load handling hydraulic components receive control signals from mechanical controls. Hydraulic system System that uses oil pressure to transmit power to different functions. Hanging load Lifted load. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB G:4 G Terminology and index – Terminology Term Description Indicator Manual "sensor", e.g., shows that a filter is clogged and needs to be replaced. KCS Kalmar Control System. An electronic control system that monitors and regulates certain systems in the machine that require KCS, e.g. certain engine and transmission alternatives. Piston rod Rod that is inserted into the piston's cylinder barrel and is acted on by hydraulic pressure. Refrigerant Fluid/gas in air conditioning. May only be handled by authorised trained person. LC Load centre. Lifting capacity Indicates machine's maximum lifting capacity. Lifting point Attaching point for lift device when lifting an object. Trolley Lifts the load, located on the mast. Low-emission engine Engine with low emissions of hazardous substances. Manufactured according to regulations. Solenoid valve An electro-magnetically controlled valve. See also proportional valve. Control valve Valves that can be used to control something, e.g. release pressure and thus lower a mast or a fork. Machine model Machine type. Indicated, for example: DCF 180-250. See also type designation. Environmental waste Used oils, filters, etc., must be handled according to governing national laws and regulations. Torque converter Hydraulic, variable clutch. Counterweight Weights adapted to the machine's lifting capacity to provide a balancing load during lifting. Hub reduction Type of final drive (often next to drive wheel) that reduces rpm and increases torque from the drivetrain. Pilot oil pressure A low control pressure to, for example, a valve. Planetary gear Type of transmission with gears in constant mesh. Product alternatives One of several alternatives is selected for a machine, e. g., engine alternative. Progressive steering Rapid steering wheel movements give larger steering deflection. Proportional valve An electro-magnetically controlled valve. If a current is applied, the valve is activated in proportion to the current's amplitude. In everyday language, a stepless valve, as opposed to an Off/On valve. On, e. g., the transmission's valve housing. Frame beam Supporting beams in the frame. Recirculation Circulation in a closed system. Serial number Unique machine designation. Available on machine plate. Service position How machine should be safely positioned before service may be started. Servo A small user movement results in a big machine movement, e.g. power steering. Servo pressure A low control pressure to control a higher pressure, for example, to a valve. Side shift Forks moved sidewards in parallel. Levelling Forks tilted, e. g. if a load is standing on an uneven surface. SmartLink Software for operating the KCS (Kalmar Control System). Spirit Delta Enclosed type of cab. SPN Suspect Parameter Number. Spreading Spreading the forks, e.g. changing the relative distance between the forks. Mast Carrier of the attachment and the load. Dust reservoir The air filter collects the coarsest particles in a dust reservoir, emptied automatically during operation. UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 G Terminology and index – Terminology G:5 Term Description Steering axle Wheel axle with steering. Buzzer Audible alarm to catch the operator’s attention. Option Optional equipment for machine. Tilt The mast is leaned forward or backward. Top lift Attachment. See attachment. Transmission oil Oil for transmission and torque converter. See specifications in operator's manual. Securing machine for transport Actions before transporting machine. Twistlocks Two or four lock pins, one in each corner of the attachment, pushed down into corresponding holes in the container and twisted to lock the container when lifting. Type designation Indicates type of machine and capacity. See also machine model. Maintenance Periodic maintenance actions so that machine functions safely and for long life. Variable pump Pump with adjustable flow rate. Variable displacement Adjustable volume (capacity) of a pump. Valve slide Moving part in the valve. Decides the oil's path. Wet brakes Brake discs in oil-bath. Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 UDCF06.01GB G:6 UDCF06.01GB Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 G Terminology and index – Index Index Error codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8:8, D:1 Exhaust system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1:22 A F About the documentation . . . About the maintenance manual . Accumulator . . . . . . . . . AdBlue filter . . . . . . . . . AdBlue tank . . . . . . . . . Air cleaning system . . . . . . Air intake and exhaust outlet . . Alternator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A:10 . A:3 10:11 . 1:15 . 1:13 . 1:19 . 1:18 11:10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11:8 11:11 . 9:33 . 4:4 . 4:3 10:16 B Batteries. . . . . . . . . . . Battery voltage, 30-voltage . . . Body structure . . . . . . . . Brake pedal . . . . . . . . . Brakes . . . . . . . . . . . Breather filter hydraulic oil tank . Feedback . . . . . . . . . . . Foreword . . . . . . . . . . . Frame . . . . . . . . . . . . . Frame connections . . . . . . . Frame, body, cab and accessories Fresh air filter . . . . . . . . . Fuel filter . . . . . . . . . . . Fuel prefilter . . . . . . . . . . Fuel system . . . . . . . . . . Fuel tank . . . . . . . . . . . Fuses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A:11 . A:3 . 9:32 11:11 . 9:3 . 9:19 . 1:12 . 1:9 . 1:8 . 1:9 . 11:5 G General safety information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B:3 Glass/windows/mirrors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9:26 H C Cab frame . . . . . . . . . . . . Cab interior . . . . . . . . . . . Cab tilting . . . . . . . . . . . . Cab undercarriage . . . . . . . . CAN bus . . . . . . . . . . . . CAN-bus drivetrain . . . . . . . . Central lubrication . . . . . . . . Chains . . . . . . . . . . . . . Coil ram . . . . . . . . . . . . . Common electrics . . . . . . . . Common hydraulics . . . . . . . . Communication. . . . . . . . . . Complete machine . . . . . . . . Condenser unit . . . . . . . . . . Construction and suspension of cab . Control system . . . . . . . . . . Control system engine. . . . . . . Control system transmission . . . . Control units . . . . . . . . . . . Controls and instruments . . . . . Coolant . . . . . . . . . . . . . Cooling fan . . . . . . . . . . . Cooling system . . . . . . . . . . Counterweights. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9:27 9:31 9:29 9:28 11:16 11:16 . 9:35 . 7:8 . 7:29 . 11:3 . 10:3 11:16 . 0:3 . 9:20 . 9:27 . 8:3 . 1:33 . 2:11 11:14 4:4, 9:5 . . 1:25 . . 1:24 1:24, 2:10 . . . 9:33 D Diagnostics . . . . . . Diagrams . . . . . . . Distribution block . . . . Distribution of electricity . Doors . . . . . . . . . Drive axle . . . . . . . Driveline/Axle . . . . . G:7 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning . Hoses, pipes and valves . . . . . . . . Hydraulic oil . . . . . . . . . . . . . Hydraulic oil cooler . . . . . . . . . . Hydraulic oil filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9:12 . 10:13 . 10:20 . 10:15 . 10:16 I Ignition voltage, 15 volts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11:11 Ignition/heating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1:34 Intercooler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1:22 L Last alarms (latest alarm) Levelling. . . . . . . . Lifting forks . . . . . . Lifting/lowering . . . . . Lighting system. . . . . Link arm . . . . . . . . Load carrier . . . . . . Load handling . . . . . Lubrication system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8:11 . . 7:23 . . 7:27 . . 7:4 . . 9:23 . . 5:9 . . 7:27 . . 7:3 1:30, 2:7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8:9 E:1 4:8 11:11 . 9:28 . 3:4 . 3:3 Mast . . . . . . . . . Mechanical transmission. Moisture filter . . . . . Monitoring functions. . . . 7:7 . 2:6 . 9:20 . 8:6 O Other functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7:30 E ECU 790 . . . . . . . . . . . ECU 792 . . . . . . . . . . . ECU 796 . . . . . . . . . . . Electrical protection . . . . . . . Electronic box . . . . . . . . . Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . Entertainment and communication Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8:10 8:11 8:11 11:4 11:12 . 1:3 . 9:25 B:20 P Paint/coatings . . . . . . . Parking brake system . . . . Parking brake unit . . . . . Power assisted system . . . Power-assisted brake system Preventive maintenance . . . Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9:37 . 4:9 . 4:11 . 5:4 . 4:5 . C:3 UDCF06.01GB G:8 G Terminology and index – Terminology Propeller shaft . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3:3 Pumps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10:12 R Radiator and expansion tank . Reading instructions . . . . Redundant CAN-bus . . . . Rim . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1:24 . . A:4 . 11:16 . . 6:20 S Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . Safety and emergency equipment. Safety instructions . . . . . . . Safety valves. . . . . . . . . . Scales . . . . . . . . . . . . Seats . . . . . . . . . . . . . Sensor steering wheel reading . . Service indicator . . . . . . . . Side lift attachment . . . . . . . Side shift . . . . . . . . . . . Side shift cylinder . . . . . . . . Signalling system . . . . . . . . Speed limitation . . . . . . . . Spreading . . . . . . . . . . . Start battery . . . . . . . . . . Start/stop . . . . . . . . . . . Steering . . . . . . . . . . . . UDCF06.01GB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B:3 9:10 B:4 10:9 7:30 9:11 5:9 8:7 7:31 7:11 7:13 9:24 8:6 7:14 11:8 1:35 5:3 Steering axle cradle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6:4 Support roller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7:9 Suspension . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6:3–6:4 T Tanks and accumulators . . . . . . . . . . Technical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Temperature control, cleaning and hydraulic oil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Terminology and index . . . . . . . . . . Tilt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Tilt cylinder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Top support roller . . . . . . . . . . . . . Transmission. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Tyres . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Tyres and rims . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10:10 . . . . . F:3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4:13, 10:14 . . . G:3 . . . G:3 . . . 7:18 . . . 7:22 . . . 7:10 . . . 2:3 . . . 6:19 . . . 6:7 V Voltage feed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11:11 W Wheel hub . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6:5 Wheel spindle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6:5 Wiping and cleaning of windows . . . . . . . . . . . 9:22 Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 G Terminology and index – Index Maintenance Manual DCF 180–250 G:9 UDCF06.01GB last page Cargotec improves the efficiency of cargo flows by offering solutions for the loading and unloading of goods on land and at sea – wherever cargo is on the move. Cargotec’s main daughter brands for cargo handling Hiab, Kalmar and MacGregor are global market leaders in their fields. Cargotec’s global network offers extensive services that ensure the continuous, reliable and sustainable performance of equipment. Cargotec Sweden AB Torggatan 3 SE-340 10, Lidhult, Sweden tel. +46 372 260 00 fax +46 372 263 90 www.cargotec.com