Glosario de fonética inglesa
Anuncio

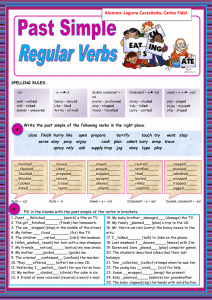
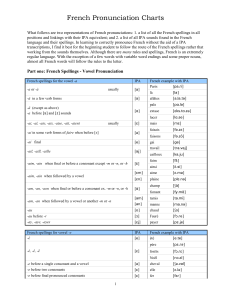
PHONETICS GLOSSARY English Word Transcription Spanish word Accent Acento Acoustic phonetics Fonética acústica Affricate Africada Allophone Alófono Alveolar Alveolar Alveolar ridge Amplitude of vibration Amplitud de vibración Articulatory phonetics Fonética articulatoria Assimilation Asimilación Meaning The way a person speaks, with differences in the sounds that can show the place a person comes from, or their social class. The study of the physical properties of speech sounds. Type of consonant consisting of a stop consonant followed by a fricative; for example, the initial sounds of child and joy. Also called affricative. Affricate consonants are /t / and /d /. A different form of the same sound or phoneme. Consonant pronuncied using the blade of the tongue close to the alveolar ridge. In English, alveolar consonants are /t/,/d/,/n/,/s/,/z/ y /l/. Anatomy phonetics ridge behind teeth: a hard ridge in the mouth immediately behind the roots of the teeth. The maximum displacement of a vibrating particle from its position of rest. The study of the way the vocal organs are used to produce speech sounds. Change of a sound in speech so that it becomes identical with or similar to a 1 Auditory phonetics Fonética auditiva Back vowel Vocal posterior neighbouring sound. The study of the way people perceive speech sounds. Vowel which is produced in the back of the tongue. Back vowels are [ ],[ ],[ ],[ ], [ ],[ ],[ ] and [ ]. Bilabial Bilabial Central vowel Vocal central Close (or high) vowel Close−mid vowel Consonant Vocal cerrada Consonant pronounced using both lips,by bringing both lips into contact with each other or by rounding them. English bilabials are /p/, /b/ and /m/. Vowel pronounced in the central position of the tongue. Central vowels are [ ], [ ], [ ] and [ ]. A vocal, or sometimes a whispered, sound modified by resonance in the oral passage, the peculiar resonance in each case giving to each several vowel its distinctive character or quality as a sound of speech.Close vowels are [i], [ ], [ ], [ ], [ ] and [u]. Vowel situated between close vowels and Vocal semicerrada open−mid vowels. Close−mid vowels are [e], [ ],[ ] and [ ]. Consonante Sound formed by stopping the air flowing through the mouth. The twenty two consonantic phonemes in English are: /p,b,,f,v,t,d,k,g,s,z, , ,,, 2 Dental / Dental Interdental Diphtong Diptongo Disyllabic Bisílaba Elision Elisión Falling intonation Entonación descendente Flap Formant (spectrum) Frequency Frequency range Fricative ,m, n,l,r,h/. Consonant that is formed by placing the tongue against the back of the top front teeth. Vowels where two vowel qualities can be perceived. A word composed of two syllables. Language omission of element of word: the omission of a vowel, consonant, or syllable while pronouncing or writing something, sometimes as a natural shortening. Intonation produced in statements, wh questions, question tags and commands. The intonation falls along the sentence. Articulation of consonants consisting of making a single tap be the tongue tip against the alveolar ridge, as in some pronunciations of /r/ or /d/. Any of several frequency regions of relatively great intensity in a sound spectrum, Formante (espectro) which together determine the characteristic quality of a vowel sound. The number of occurrences within a given time period. Frecuencia Sound frequency is measured in cycles per second. The point where vowel sounds are at their most distinctive and characteristic pitch. Fricativa 3 A consonant produced by the forcing of breath through a constricted passage. Also called spirant. In English, fricative consonants are: /f/, /v/, / /, / /, /s/, /z/, / / and / /. Front vowel Vocal anterior Glottis Glotis Grapheme Grafema Hard palate Paladar duro Homograph Homógrafa Homophone Homófona Intensity Intensidad Intonation Entonación Vowel produced in the front side of the tongue. The opening between the vocal chords at the upper part of the larynx. All of the letters and letter combinations that represent a phoneme. The front side of the palate. One of two or more words that have the same spelling but differ in origin, meaning, and sometimes pronunciation, such as fair (pleasing in appearance) and fair (market). One of two or more words, such as night and knight, that are pronounced the same but differ in meaning, origin, and sometimes spelling. The magnitude of sound. The use of pitch in speech to create contrast and variation. Consonant Labio−dental Labio−dental Larynx Laringe articulated with the lower lip and upper teeth. Labio−dental consonats are /f/ and /v/. The expanded upper end of the windpipe or trachea, connected with the hyoid bone or 4 Lateral Lateral Liaison Liaison Lip Labios Minimal pair Par mínimo Monophthong (pure vowel) Vocal pura Monosyllabic Monosílaba Mouth Boca Nasal Nasal cartilage. It contains the vocal cords, which produce the voice by their vibrations,when they are stretched and a current of air passes between them. The larynx is connected to the pharynx by the glottis. Consonant produced by making a partial closure bye the blade of the tongue against the alveolar ridge, in such a way that the air stream is able to flow around the sides of the tongue. The lateral consonant is /l/. Pronunciation of the usually silent final consonant of a word when followed by a word beginning with a vowel. Either of two fleshy folds that surround the opening of the mouth. Words differing in just one sound, a pair of words or other linguistic expressions that are the same except for one sound, for example, bit and pit. Vowel with a single perceived auditory quality, made by a movement of the tongue towards one position in the mouth. A word which has only a syllable. The organ considered as the speech language. It consists of lips, teeth, alveolus, palate, velum and tongue. 5 Consonant articulated by lowering the soft palate so that air resonates in the nasal cavities and passes out the nose, as in the pronunciation of the consonants /m/, /n/ and Neightbour sounds Nose Occlusion Open (or low) vowel / /. The sounds that are next Contexto lingüístico to a different one. The organ that cooperates with mouth in breath and Nariz pronunciation. It makes possible the pronunciation of nasal consonants. Closure at some point in the vocal tract that Oclusión o cierre blocks the flow of air in the production of an oral or nasal stop. Vowel produced at the front of the mouth, in the lowest point that is theoretically possible Vocal abierta for the body of the tongue to reach. They are [a], [ ], [ ] and [ ]. Opening Apertura Open−mid vowel Vocal semiabierta Palatal Palatal Palato−alveolar Palato−alveolar Articulated with the tongue in a low position, as the vowel / / in far. Vowel situated between close−mid vowels and open vowels. Open−mid vowels are [ ], [ ], [ ] and [ ]. Consonant which is pronuncied by raising the front of the tongue close to the hadrd palate, as in /j/. Consonant pronuncied by using the blade (and sometimes the tip) of the tongue towardds the 6 roof of the mouth, as in the consonants / /, / /, / / and Phoneme Fonema Phonetic alphabet Pharynx Faringe Phonetics Fonética Phonology Fonología Plosive Oclusiva Polysyllabic Polisílaba Post−alveolar Post−alveolar / /. The smallest meaningful sound in a language. The English phonemes are represented in the Phonetic Alphabet. System of letters and symbols that are used to represent the individual sounds of a language. The passage to the stomach and lungs; in the front part of the neck below the chin and above the collar bone. The study of the sound systems of languages, and of the general properties displayed by these systems. It only studies the contrasts in sound (the phonemes) which make differences of meaning within language. The science or doctrine of the elementary sounds uttered by the human voice in speech, including the various distinctions, modifications and combinations of tones. Of, relating to, or being a speech sound produced by complete closure of the oral passage and subsequent release accompanied by a burst of air, as in the sound /p/ in pit or /d/ in dog. A word which has more than two syllables. 7 Consonant pronuncied by using the tongue tip close to just behind the alveolar ridge, as in /r/. Tiempo/ Rate Cantidad Received pronunciation Pronunciación recibida Retroflex Rhythm Rising intonation Roll or Trill Segmental phoneme Ritmo Interval in which sounds are produced. The way Standard English is spoken; without regional variations. Standard English and RP are widely used in the media and by public figures, so it has prestige status and is regarded by many as the most desirable form of the language. Sound pronounced using the tongue tip curled back to well behind the alveolar ridge. For some accents, the pronunciation of /r/ is this way. The pattern of sound that characterizes a language, dialect, or accent. Intonation in Yes/No questions and in short pauses, that consists in Entonación starting lower and ascendente finishing with a louder intonation. Sound made by vibrating vocal organs: a sound or consonant made by two vocal organs vibrating rapidly against each other, for example, the tip of the tongue vibrating against the ridge behind the front teeth. Fonema segmental Phoneme that can be isolated, such as vowels, consonants, diphtongs, triphtongs 8 Semi−vowel Semivocal Soft palate (velum) Paladar blando (velo del paladar) Spectrograph Espectrógrafo Speech Habla Standard English Inglés estándar Stress Acento Strong form Forma fuerte Suprasegmental phoneme Fonema suprasegmental Syllable Sílaba and semivowels. A vocal sound with short duration which slides quickly towards another vowel that is the centre of the syllable. The back side of the palate. A machine used to measure the frequency of the sounds. The faculty of uttering articulate sounds or words; the faculty of expressing thoughts by words or articulate sounds; the power of speaking. The variety of English that is held to be 'correct' in the sense that it shows none of the regional or other variations that are considered by some to be ungrammatical, or non−standard English. Phonetics emphasis on syllable: the emphasis placed on a particular sound or syllable by pronouncing it more loudly or forcefully than those surrounding it in the same word or phrase. Form that is used when the word is said in isolation or when is being emphasized. Phoneme that cannot be isolated,such as rhythm, stress and intonation. A unit of spoken language consisting of a single uninterrupted sound formed by a vowel, diphthong, or syllabic consonant alone, or by any of these 9 Timbre Timbre Tone Tono Tongue Lengua Transcription Transcripción Triphthong Triptongo Uvula Úvula Velar Velar Vocal chords Cuerdas vocales sounds preceded, followed, or surrounded by one or more consonants./One or more letters or phonetic symbols written or printed to approximate a spoken syllable. In auditive phonetics, the characteristic that helps us to recognize the quality of a sound. The quality of a person´s voice The movable fleshy organ attached to the bottom of the inside of the mouth of humans and most animals, used for speech. A phonetic representation of speech using special symbols. Vowels in which three vowel qualities can be perceived. A small fleshy V−shaped extension of the soft palate that hangs above the tongue at the entrance to the throat. Consonant spoken with the back of the tongue close to, or in contact with, the soft palate (velum). Velar consonants are /k/, /g/ and / /. Throat membranes that produce sounds: a pair of fibrous sheets of tissue that span the cavity of the voice box (larynx) and produce sounds by vibrating. Muscles tighten the cords, narrowing the gap between them, and as air is expelled from 10 Voiced consonant Voiceless consonant Vowel the lungs they vibrate. Consonant pronounced with vibration of vocal chords, by passing air Consonante sonora across them to create audible vibrations, as the sound /s/ in the word his. Consonant pronounced without vibration of vocal cords, without passing air across the Consonante sorda vocal cords and creating audible vibrations, as in the /s/ sound in the word hiss. Sound articulated with a relatively open configuration of the vocal tract: no part of the mouth is closed, and none of the vocal organs comoe so close together that we can hear the Vocal sound of the air passing betwenen them. English vowels are / /, / /, /e/, / /, / /, / /, / /, / /,/ /, / / and / /. Weak form Forma débil Forms which are normal in connected speech: peripheral vowels are replaced by those of a more central quality, and ome consonants may be elided. 11