Guia 3
Anuncio
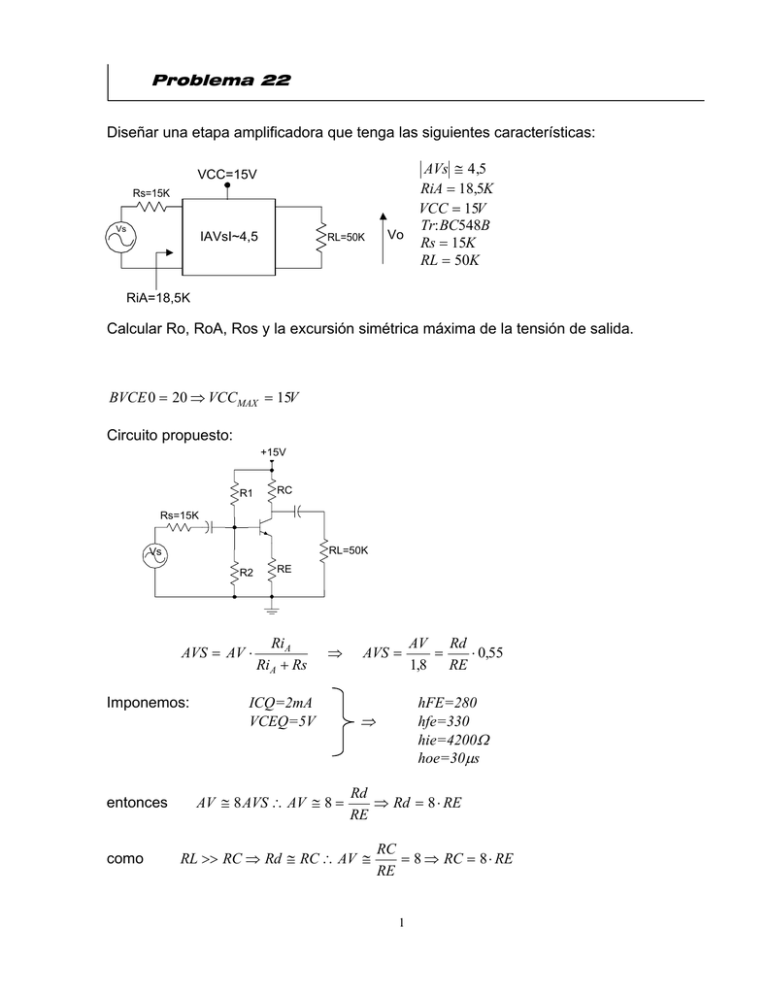
Problema 22 Diseñar una etapa amplificadora que tenga las siguientes características: VCC=15V Rs=15K Vs IAVsI~4,5 RL=50K AVs ≅ 4 ,5 RiA = 18,5K VCC = 15V Tr: BC548B Vo Rs = 15K RL = 50K RiA=18,5K Calcular Ro, RoA, Ros y la excursión simétrica máxima de la tensión de salida. BVCE 0 = 20 ⇒ VCCMAX = 15V Circuito propuesto: +15V R1 RC Rs=15K RL=50K Vs R2 AVS = AV ⋅ Imponemos: entonces como RE RiA RiA + Rs ⇒ ICQ=2mA VCEQ=5V AV ≅ 8 AVS ∴ AV ≅ 8 = AVS = AV Rd = ⋅ 0,55 1,8 RE hFE=280 hfe=330 hie=4200Ω hoe=30µs ⇒ Rd ⇒ Rd = 8 ⋅ RE RE RL >> RC ⇒ Rd ≅ RC ∴ AV ≅ RC = 8 ⇒ RC = 8 ⋅ RE RE 1 luego: VCC = VCEQ + ICQ ⋅ ( RC + RE ) ⇒ RE = VCC − VCEQ = 555Ω 9 ⋅ ICQ RC = 8 ⋅ RE = 4444Ω Para que RiA=18,5K: Ri = hie + RE ⋅ hfe ⇒ RE ⋅ hfe = 183150Ω ⇒ Ri = 187350Ω RiA = RB Ri = 18,5K ⇒ RB = 20526Ω Para la Ro: Ro ≅ 1 hfe ⋅ RE + ( RE hie) = 492 K ⋅ 1 + hoe ( Rs RB) + RE + hie Ro A = Ro RC ≅ RC = 4444Ω RoS = Ro Rd ≅ Rd = 4081Ω luego para hallar VBB: ICQ = VBB − VBE RB ⇒ VBB = ICQ ⋅ RE + + VBE = 1,96V RB hFE RE + hFE Para hallar R1 y R2: R1 ⋅ VBB = VCC ⋅ RB ⇒ R1 = VCC ⋅ RB = 157358Ω VBB 1 1 1 = + ⇒ R2 = 23605Ω RB R1 R 2 Valores estandarizados de los resistores: R1=150K R2=22K RC=4700Ω RE=560Ω Verificación: VBB = VCC ⋅ R2 = 1,92V R1 + R2 2 RB = R1 R2 = 19186Ω VCEQ = VCC − ICQ ⋅ ( RC + RE ) = 4,69V ICQ = ICQ = VBB − VBE = 2,18mA → hFE = 290 RE VBB − VBE = 1,95mA → hFE = 270 RB RE + hFE AV = − n= Rd ≅ 7,68 RE AVS = AV ⋅ Ri A ≅ 4,14 Ri A + Rs RE ≅6 RB hFE min Ri = hie + RE ⋅ hfe = 189000Ω Ri A = RB Ri = 17,5K Ro ≅ hfe ⋅ RE 1 + ( RE hie) = 500 K ⋅ 1 + hoe ( Rs RB) + RE + hie Ro A = Ro RC ≅ 4692Ω RoS = Ro Rd ≅ 4300Ω Para la máxima excursión de Vo: IC[mA] ICM Rd ' = Rd + RE RCD Q ICQ Vo∃ 0,25V RCE VCC VCEQ 3 ICQ . Rd’ VCE [V] VCE SAT = 0,25V VCEQ − VCE SAT < ICQ ⋅ Rd ' 4,44V < 9,48V Vo∃ = (VCEQ − VCE SAT ) ⋅ Rd = 3,9V Rd ′ 4 Problema 40 Calcular la AV y la máxima amplitud simétrica de la tensión de salida del amplificador de la figura. Suponer que los transistores son idénticos y tienen un hFE=100. Graficar la recta de carga dinámica de ambos transistores. +20V 100K 1K 100K hFE ≅ hfe = 100 T2 1K T1 Vs 10K 1K 1K AV = − gm ⋅ Rd y además 1K Vo gm = 1 hib gm = 40 ⋅ ICQ1 Averiguo las corrientes de polarización: T1) RB = R1 R2 = 9,1K VBB = VCC ⋅ ICQ = R2 = 1,82V R1 + R2 VBB − VBE = 1mA RB RE + hFE VCEQ = VCC − IC ⋅ ( RC + RE ) = 18V T2) RB = 100 K VCC = ICQ = IC ⋅ RB + VBE + IC ⋅ RE hFE VCC − VBE = 9,65mA RB RE + hFE VCEQ = VCC − IC ⋅ ( RC + RE ) = 10,35V 223 Planteo el circuito dinámico: Rs RB1 Vs hib1 = hie2 hie1 ib.hfe1 RC1 RB2 RE RL ib2.hfe2 1 = 25Ω gm1 hib2 = hie1 = hib1 ⋅ hfe = 2,5K 1 = 2,6Ω gm2 hie2 = hib2 ⋅ hfe = 260Ω Ri2 = hie + ( RE ⋅ hfe) ( RL ⋅ hfe) = 260Ω + 50 K = 50260Ω Ri A = RB2 Ri2 = 33,3K Planteo de las ganancias: AV1 = − gm ⋅ Rd = − gm ⋅ ( RC Ri A2 ) = −39 Ri A = RB hie1 = 1,96 K AVs1 = AV ⋅ Ri A = −25,8 Ri A + Rs AVs2 = ( RE 2 RL) ⋅ hfe = 0,995 Vo = Vi2 hie + ( RE 2 RL) ⋅ hfe AVs = AVs1 ⋅ AVs2 = −25,7 IC[mA] IC[mA] RCE RCD RCD Q RCE Q ICQ VCEQ ICQ VCC VCE [V] Vo = ICQ ⋅ Rd = 0,97V VCEQ Vo = ICQ ⋅ Rd = 4,8V 224 VCC VCE [V] Problema 41 CA3086 ICQ4=1mA RC1=3K3 VCEQ4=-4,6V RL=10K VCC=VEE=6V RB=100Ω RE=2700Ω a) Determinar los valores de los componentes que faltan b) Encontrar el punto Q de todos los transistores c) Calcular la ganancia de modo diferencial del sistema, Rid y Ric VCC RE RC1 RB T1 T2 T4 RB Vs1 Vs2 RC4 RL R T3 a) T5 VEE ICQ4 6V ICQ4 = 1mA RE=2700 ICQ1 = -4,6V VCC − VC1T = 1mA RC1 VRE + VCEQ + VRC4 = VCC + VEE RC4 VRC4 = 4,7V -6V 225 ⇒ RC4 = VRC4 = 4700Ω ICQ4 Para fijar una corriente de 1mA que circule por T1 y T2 debemos calcular R: ICQ3 = 2mA ⇒ R= VEE − VBE = 2704Ω ≅ 2700Ω 2 ICQ3 ⋅ 1 + hFE b) T1: 6V 3,3V VCC − VRC1 − VCEQ1 = −0,7V RC1 VCEQ1 = VCC − VRC1 + 0,7V = 3,4V VCEQ1 -0,7V T2: 6V VCC − VCEQ2 = −0,7V VCEQ2 VCEQ2 = VCC + 0,7V = 6,7V -0,7V T3: -0,7V VEE = −VCEQ3 − 0,7V VCEQ3 VCEQ3 = −VEE + 0,7V = 5,3V -6V VR T5: VCEQ5 = VBE5 = 0,7V VCEQ5 -6V 226 c) Para hallar la Avds planteamos el circuito equivalente: hie12 T4 RB RC4 RC1 RL Rd Ri4 RB hie4 hie1 RC1 ibd.hfe1 RB Vd/2 Vod hie1 ib4.hfe4 RE hie4 RC1 ibd.hfe1 = 3500Ω RE Vd/2 Vd/2 1mA Rd ib4 Vos RE.hfe4 Rd ib4.hfe4 Ri4 AVds = Vos Vos Vod hfe12 ⋅ ( RC1 Ri4 ) Rd ⋅ hfe4 = ⋅ = ⋅ ≅ 53 Vd Vod Vd 2 ⋅ ( RB + hie12 ) (hie4 + RE ⋅ hfe4 ) Para hallar Rid: T1 T2 Rid = 2 ⋅ hie = 7000Ω TV Rid 227 Para hallar Ric: RB hie1 T1 2/hoe3 Ric hie T3 Ric = hie + 2 ⋅ 2hfe/hoe hfe ≅ 6,4 MΩ hoe donde 228 hoe3 = 3,12 ⋅ 10−5 A V