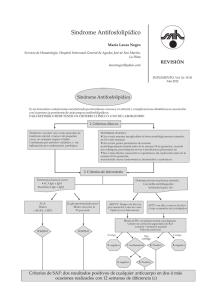
tiles) con sentimientos de autoimagen pobre, aislamiento y tristeza
Anuncio

Fig. 3. Es necesario fomentar el desarrollo de habilidades sociales para evitar el aislamiento. tiles) con sentimientos de autoimagen pobre, aislamiento y tristeza, aunque también puede cursar con conductas agresivas. Se han descrito algunos casos de trastornos psicóticos (crónicos o agudos), que raramente aparecen antes de la adolescencia. Es importante prestar toda la atención a la sintomatología aquí descrita para no diagnosticar erróneamente los problemas neuroconductuales como desórdenes psiquiátricos, puesto que en este caso las estrategias terapéuticas son radicalmente diferentes. 5. BIBLIOGRAFÍA BARTOLUCCI, G. y YOUNGER, J. (1994): “Tentative classification of neuropsychiatric disturbances in Prader-Willi syndrome”, Journal of Intellectual Disability Research 38(pt6): 621-9. 113 BORGHGRAEF, M., FRYNS, J.P., y BERGHE, V.D. (1990): “Psychological profile and behavioral characteristics, in 12 patients with Prader-Willi syndrome”, Genetic Counseling: 38, 141-150. BOYLE, I.R. (1994): “Psychiatric medication and Prader-Willi syndrome: Notes from the frontiers”, Prader-Willi Perspectives, 2(2): 4. CLARKE, D.J. (1993): “Prader-Willi syndrome and psychoses”, British Journal of Psychiatry 163: 680-684. CLARKE, D.J., BOER, H., CHUNG, M.C., STURMEY, P. y WEBB, T. (1996): “Maladaptive behavior in Prader-Willi syndome in adult life”, Journal of Intellectual Disability Research 40(2): 159-165. CLARKE, D.J., y WEBB, T. (1995): “Prader-Willi syndrome and psychotic symptoms: Report of a further case”, Irish Journal of Psychological Medicine 12(1): 27-9. CURFS, L.M.G. (1992): “Psychological profile and behavioral characteristics in the PraderWilli syndrome”, en SB Cassidy (ed.), Prader-Willi syndrome and Other Chromosome 15q Deletion Disorders, New York: Spring-Verlag (211-221). DYKENS, E., HODAPP, R., WALSH, K. y NASH, L. (1992a): “Profiles correlates and trajectories of Intelligence in Prader-Willi syndrome”, Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 31(6): 1125-1130. — (1992b): “Adaptive and maladaptive behavior in Prader-Willi syndrome”, Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 31(6): 1131-1136. DYKENS, E.M. y CASSIDY, S.B. (1995): “Correlates of maladaptive behavior in children and adults with Prader-Willi syndrome”, American Journal of Medical Genetics 60(6): 546-9. DYKENS, E.M., LECKMAN, J.F. y CASSIDY, S.B. (1996): “Obsessions and compulsions in Prader-Willi syndrome”, Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 37: 995- 1002. GABEL, S., TARTER, R.E., GAVALER, J., GOLDEN, W.L., HEGEDUS, A.M. y MAIER, B. (1986): “Neuropsychological capacity of Prader-Willi children: General and specific aspects of impairment”, Applied Research In Mental Retardation 7:459- 466. GREENSWAG, L.R. (1985): Sexuality for people with Prader-Willi syndrome: Is ignorance bliss? Proceedings of National Conference of Prader-Willi Syndrome Association, Windsor Locks, CT. GREENSWAG, L.R., SINGER, S., CONDON, N., BUSH, H., OMROD, S., MULLIGAN, M., y SHAW, P. (1995): “Residential options for Endividuals with Prader-Willi syndrome”, en Management of Prader-Willi Syndrome (2nd ed), Greenswag LR, & Alexander RC, eds. New York, Springer-Verlag 214-247. HELLINGS, J.A. y WARNOCK, J.K. (1994): “Self-Enjurious behavior and serotonin in PraderWilli syndrome”, Psychopharmacology Bulletin 30: 245-250. 114 HODAPP, R.M., DYKENS, E.M. y MASINO, L. (1997): “Stress and support en families of persons with Prader-Willi syndrome”, Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 27: 11-24. HALL, J. (1975): “Sexuality and the mentally retarded”, en R. Green (ed), Human sexuality: A Health practitioner’s text, Baltimore MD: Williams & Wilkens (181-195). MARSHALL, B.D. JR, WALLACE, C.J., ELDER, J., BURKE, K., OLIVER, T. y BLACKMAN, R. (1981): “A behavioral approach to the treatment of Prader-Willi syndrome”, en V.A. Holm, S.J. Sulzbacher & PL Pipes (Eds.) Baltimore: University Park Press, The Prader-Willi syndrome (185-199). MITCHELL, W. (1988: “Social skills training for Prader-Willi Syndrome”, en Greenswag L.R. & Alexander R.C. (Eds): Management of Prader-Willi Syndrome (165- 170), New York; Springer-Verlag. TAYLOR, R.L. (1988): “Cognitive and behavioral characteristics”, en M.L. Caldwell & R.L. Taylor (Eds), New York: Springer-Verlag, Prader-Willi syndrome: selected research and management issues (29-42). WHITMAN, B. y GREENSWAG, L. (1995): “Psychological and behavioral management”, en Management of Prader-Willi Syndrome (2nd ed.), Greenswag, L.R., Alexander, R.C., eds. New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 125-141. WHITMAN, B. y ACCARDO, P. (1987): “Emotional symptoms in Prader-Willi syndrome adolescents”, American Journal of Medical Genetics 28: 897-905. WOLFF, O. (1987): “Prader-Willi syndrome, psychiatric aspects”, Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine 80: 718-720. 115