Revenue Statistics 2015 - Spain
Anuncio

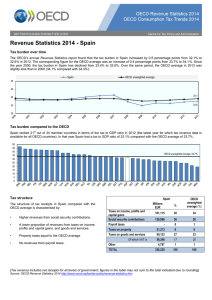
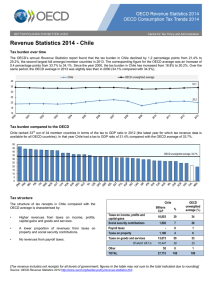
Revenue Statistics 2015 - Spain Tax burden over time The OECD’s annual Revenue Statistics report found that the tax burden in Spain increased by 0.5 percentage points from 32.7% to 33.2% in 2014. The corresponding figures for the OECD average were an increase of 0.2 percentage points from 34.2% to 34.4%. Since the year 2000, the tax burden in Spain has declined from 33.4% to 33.2%. Over the same period, the OECD average in 2014 was slightly above that in 2000 (34.4% compared with 34.2%). Spain % 34.2 33.8 33.5 33.5 33.4 33.0 33.4 33.3 OECD - unweighted average 33.6 32.7 32.8 33.8 33.3 34.1 34.1 33.9 33.4 36.5 36.1 35.3 34.3 32.3 29.8 29.9 32.1 31.3 34.2 34.4 32.7 33.2 Tax burden compared to the OECD th Spain ranked 19 out of 34 OECD countries in terms of the tax to GDP ratio in 2013 (the latest year for which tax revenue data is available for all OECD countries). Spain had a tax to GDP ratio of 32.7% compared with the OECD average of 34.2%. In 2012 Spain th ranked 20 out of 34 OECD countries in terms of the tax to GDP ratio. 47.6 45.0 44.7 43.9 43.7 42.8 42.5 40.5 38.4 38.4 OECD - unweighted average, 34.2% 36.8 36.7 36.5 35.9 34.5 34.4 34.3 32.9 32.7 31.9 31.8 31.4 30.6 30.5 30.4 30.3 29.3 29.0 27.5 26.9 25.4 24.3 20.0 19.7 Tax structure OECD comparison² 29 22 The structure of the tax revenues in Spain shows the following percentage breakdown 118,486 35 10 - 0 * 35% from social security contributions th (10 highest in the OECD) Taxes on property 23,125 7 14 Taxes on goods and services 96,392 28 24 Taxes on income, profits and capital gains Social security contributions Payroll taxes Of which VAT is Millions EUR 100,850 % 61,013 18 23 Other¹ 4,281 1 * TOTAL 343,134 100 29% from taxes on income, profits and capital gains nd (22 in the OECD) 28% from taxes on goods and services th (24 in the OECD) Tax revenue includes net receipts for all levels of government; figures in the table may not sum to the total indicated due to rounding 1. Includes income taxes not allocable to either personal or corporate income 2. The country with the highest share being number 1 and the country with the lowest share being number 34 Source: OECD Revenue Statistics 2015 http://www.oecd.org/tax/tax-policy/revenue-statistics.htm Tax structure compared to the OECD The structure of tax receipts in Spain compared with the OECD average is characterised by; • • • Higher revenues from social security contributions and taxes on property. A lower proportion of revenues from, taxes on income, profits and capital gains, goods and services and value added taxes. No revenues from payroll taxes. OECD - Average Spain % 34 35 29 26 7 Social security contributions 6 1 1 0 Taxes on income, profits and capital gains 14 10 19 18 Taxes on payroll Taxes on property Taxes on goods and services (excluding VAT/GST) 1 Other Value added taxes VAT rates The Spanish standard VAT³ rate is 21%, which is above the OECD average. The average VAT/GST standard rate in the OECD was 19.2% on 1 January 2015, up from 17.6 on 1 January 2009. Reduced VAT rates of 4% and 10% apply to many goods and services. In the last six years, 21 of the 34 OECD countries have raised their standard VAT/GST rate at least once. In line with this trend, Spain increased its standard VAT from 16% to 18% in 2010 and to 21% in 2012. The reduced VAT rate of 7% was increased to 8% in 2010 and to 10% in 2012. OCDE, unweighted average, 19.2% 15 8 8 10 16 17 18 18 19 19 20 20 20 20 20 21 21 21 21 22 22 23 23 23 23 24 24 25 25 25 27 10 5 3. VAT refers to value added tax and goods and services tax (GST) Source: OECD Tax Database 1st January 2015 Contacts David Bradbury Centre for Tax Policy and Administration Head, Tax Policy and Statistics Division David.Bradbury@oecd.org OECD Revenue Statistics Maurice Nettley Centre for Tax Policy and Administration Head, Tax Data & Statistical Publications Maurice.Nettley@oecd.org VAT rates Stéphane Buydens Centre for Tax Policy and Administration VAT Policy Advisor Stephane.Buydens@oecd.org