La Armada hasta finalizar el siglo XIX The Navy until the end of the
Anuncio

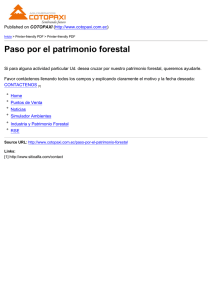
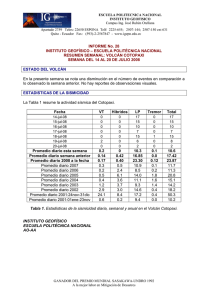
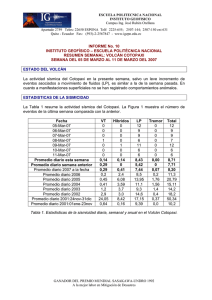
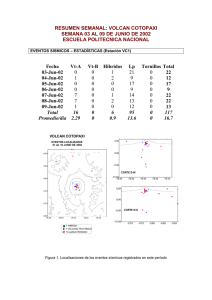
90 La Armada hasta finalizar el siglo XIX The Navy until the end of the XIX century Para el año 1886 la flota se componía del “Nueve de Julio”, el “Huacho” (“Seis de Diciembre”) y los vapores “Sucre” y “Jaramijó”. El “Huacho” y el “Sucre” se vendieron en pública subasta. In 1886 the fleet had the following vessels: War steamships “Nueve de Julio”, “Huacho” former (”Seis de Diciembre”) and the passenger steamships “Sucre” and “Jaramijo”. The “Huacho” and “Sucre” were sold at auction. En ese año el Gobierno adquirió el vapor “Chaihuin”, al que se lo llamó crucero “Cotopaxi”. El 23 de marzo de 1887 se adquirió por contrato la cañonera “Tungurahua”, la que vino de Inglaterra y arribó a Guayaquil el 8 de enero de 1888. In that year the government purchased the merchant steamship “Chaihuin”, which was renamed Cruiser “Cotopaxi”. On 23 March, 1887, the gunboat “Tungurahua” was bought by contract. It came from England and arrived in Guayaquil on 8 January, 1888. Durante la administración del doctor Antonio Flores no se pudo restablecer todavía la Escuela Náutica, pero a bordo de la cañonera “Tungurahua” y el crucero “Cotopaxi” hacían su instrucción cuatro guardiamarinas en cada buque. During the government of Dr. Antonio Flores, the Nautical Academy could not reopen yet, but four midshipmen received their instruction aboard the gunboat “Tungurahua” and the Cruiser “Cotopaxi”. Crucero “Cotopaxi”. Cruiser “Cotopaxi”.