Práctica 3. LABORATORIO
Anuncio

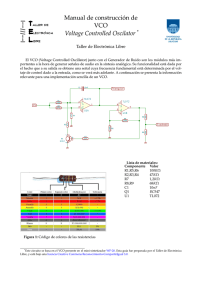
Práctica 3. LABORATORIO Electrónica de Potencia. 2004 Inversor de 50Hz controlado por ancho de pulso con modulación senoidal SPWM 1. Diagrama de Bloques El inversor que va a montar tiene el siguiente diagrama de bloques: ver apuntes de clase 2. Oscilador Para el oscilador usaremos uno de los operacionales que tiene el integrado MC 1458N. El oscilador es un amplificador realimentado positivamente para provocar la inestabilidad y, por lo tanto, la oscilación. Figura 1: Circuito oscilador senoidal. Determinar R y C para que oscile a 50Hz En la figura 1 se indica el montaje que debe realizar. La condición para que oscile es que: R2 ≥ 2R1 La frecuencia de la oscilación se determina con la realimentación positiva, y su valor es: 1 fm = 2πRC 1 Calcule los valores nominales de R3 = R4 y de C1 = C2 para que la frecuencia de oscilación esté lo más cercana posible a 50Hz. Mida los valores reales de los componentes elegidos: R= C= fm = Monte el circuito; alimente el operacional con ±5V . Visualice la señal que obtiene en la salida del operacional y dibújela en la Figura 2, indicando los valores de pico y el periodo. Figura 2: Señales del oscilador 3. Inversor Para obtener la señal seno2 usaremos el segundo operacional del integrado MC 1458N en configuración de amplificador inversor con ganancia unitaria, tal y como se indica en la Figura 3 Visualice la señal seno2 en el osciloscopio. Dibújela en la misma Figura que seno1. 4. Comparador El comparador se implementa con dos de los cuatro operacionales que contiene el integrado LM348. Monte el circuito de la Figura 4. Programe el generador de señales para que proporcione una onda triangular alterna de 1kHz y aproximadamente 0,8V de amplitud. Visualice en el canal uno del osciloscopio seno1 y en el canal dos la señal triangular del generador, tri. Compruebe que la amplitud de la triangular es ligeramente superior que la amplitud de la senoidal. Si no es ası́, aumente la amplitud de la triangular hasta que sea ligeramente 2 Figura 3: Inversor para obtener seno2 Figura 4: Comparador superior. Una vez verificado el nivel de la triangular, visualice en el osciloscopio las señales S1 y S2. Dibújelas en la Figura 6 5. Restador El restador se implementa con uno de los operacionales que queda libre en el integrado LM348. El esquema es el de la Figura 5. A la salida del restador se obtiene la señal P W M = S2 − S1 . Visualice dicha señal en el osciloscópio y dibújela en la Figura 6, debajo de S1 y S2. Conteste a las siguientes preguntas: Frecuencia de S1 = Frecuencia de S2 = Frecuencia de P W M = 6. Acoplamiento y etapa de potencia Usando dos optoaclopadores implemente un amplificador en clase D tal y como se muestra en la Figura 7. ¡NO CONECTE LAS TENSIONES DE ALI3 Figura 5: Restador: S2 − S1 = P W M MENTACIÓN +15 NI -15 HASTA CONSULTAR CON EL PROFESOR! Verifique el orden de los pines de los optoacopladores. Estos dispositivos tienen la posibilidad de utilizarse como transistores BJT utilizando el pin correspondiente a la base. Sin embargo, cuando se utilizan como optoacopladores, dicho pin debe dejarse al aire (sin conectar), ya que la corritente de base la suministra el fotodiodo interno. 4 Figura 6: Señales S1, S2 y PWM Figura 7: Acoplamiento de la señal de control con aislamiento galvánico y amplificación. 5 MC1458 MC1558 HIGH PERFORMANCE DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS ■ LOW POWER CONSUMPTION ■ LARGE INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE ■ NO LATCH-UP ■ HIGH GAIN ■ SHORT-CIRCUIT PROTECTION N DIP8 (Plastic Package) ■ NO FREQUENCY COMPENSATION REQUIRED DESCRIPTION The MC1458 is high performance monolithic dual operational amplifier intended for a wide range of analog applications: ❑ Summing amplifier D SO8 (Plastic Micropackage) ❑ Voltage follower ❑ Integrator ❑ Active filter ❑ Function generator PIN CONNECTIONS (top view) The high gain and wide range of operating voltages provide superior performance in integrator, summing amplifiers and general feedback applicatons. ORDER CODE Part Number Temperature Range MC1458 0°C, +70°C MC1458I -40°C, +105°C MC1558 -55°C, +125°C Example : MC1458N Package N D • • • • • • Output 1 1 Inverting input 1 2 - 3 + Non-inverting input 1 - 4 V CC 8 VCC+ 7 Output 2 - 6 Inverting input 2 + 5 Non-inverting input 2 N = Dual in Line Package (DIP) D = Small Outline Package (SO) - also available in Tape & Reel (DT) December 2001 1/6 MC1458-MC1558 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS Symbol VCC Parameter MC1458 MC1558 Unit Supply voltage ±22 V Vi Input Voltage ±15 V Vid Differential Input Voltage ±30 V Output Short-circuit Duration Ptot Power Dissipation Infinite D Suffix N Suffix Toper Operating Free-air Temperature Range Tstg Storage Temperature Range 2/6 MC1458I 300 500 0 to +70 -40 to +105 -65 to +150 mW -55 to +125 °C °C MC1458-MC1558 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS VCC = ±15V, Tamb = 25°C (unless otherwise specified) Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit Vio Input Offset Voltage (Rs ≤ 10kΩ) Tamb = 25°C Tmin ≤ Tamb ≤ Tmax 1 5 6 mV Iio Input Offset Current Tamb = 25°C Tmin ≤ Tamb ≤ Tmax 2 200 300 nA Iib Input Bias Current Tamb = 25°C Tmin ≤ Tamb ≤ Tmax 30 500 800 nA Avd Large Signal Voltage Gain (Vo = ±10V, RL = 2kΩ) Tamb = 25°C Tmin ≤ Tamb ≤ Tmax 50 25 200 V/mV SVR Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio (Rs ≤ 10kΩ) Tamb = 25°C Tmin ≤ Tamb ≤ Tmax 77 77 90 dB Icc Supply Current, all Amp, no load Tamb = 25°C Tmin ≤ Tamb ≤ Tmax 2.3 5 6 mA Vicm Input Common Mode Voltage Range Tamb = 25°C Tmin ≤ Tamb ≤ Tmax ±12 ±12 CMR Common Mode Rejection Ratio (Rs ≤ 10kΩ) Tamb = 25°C Tmin ≤ Tamb ≤ Tmax 70 70 90 Output Short-circuit Current Tamb = 25°C 10 20 12 10 12 10 14 13 V 0.2 0.8 V/µs Ios Output Voltage Swing Tamb = 25°C ±Vopp SR Tmin ≤ Tamb ≤ Tmax RL ≤ 10kΩ RL ≤ 2kΩ RL ≤ 10kΩ RL ≤ 2kΩ Slew Rate (VI = ±10V, RL = 2kΩ, CL = 100pF, unity Gain) dB 35 mA tr Rsie Time (VI = ±20mV, RL = 2kΩ, CL = 100pF, unity Gain) 0.3 µs KOV Overshoot (VI = 20mV, RL = 2kΩ, CL = 100pF, unity Gain) 5 % 2 MΩ RI Input Resistance Zic Common-mode Input Impedance 200 MΩ CI Input Capacitance 1.4 pF RO Output Resistance 75 Ω Full Power Bandwidth (RL = 2kΩ, VO ≥ ±10V, AVD = 1, THD ≤ 5% 14 KHz FPB 0.3 3/6 MC1458-MC1558 Symbol B Parameter Unity Gain Bandwidth (VI = 10 mV, RL = 2kΩ, CL = 100pF) GBP Gain Bandwith Product (VI = 10 mV, RL = 2kΩ, CL = 100pF f =100kHz) THD Total Harmonic Distortion (f = 1kHz, Av = 20dB, RL = 2kΩ CL = 100pF, Vo = 2Vpp) Typ. 1 0.4 1 0.02 Max. Unit MHZ MHz % 45 nV -----------Hz Phase Margin 65 Degrees Gain Margin 11 dB 120 dB en Equivalent Input Noise Voltage (f = 1kHz, Rs = 100Ω) φm Am Vo1/Vo2 Channel Separation 4/6 Min. www.fairchildsemi.com LM348/LM248 Quad Operational Amplifier Features Description • • • • • • • • • • TheLM348/LM248 is a true quad LM741. It consists of four independent, high-gain, internally compensated, low power operational amplifiers which have been designed to provide functional characteristics identical to those of the familiar LM741 operational amplifier. In addition the total supply current for all four amplifiers is comparable to the supply current of a single LM741 type OP Amp. Other features include input offset currents and input bias current which are much less than those of a standard LM741. Also, excellent isolation between amplifiers has been achieved by independently biasing each amplifier and using layout techniques which minimize thermal coupling. LM741 OP Amp operating characteristics Low supply current drain Class AB output stage no crossover distortion Pin compatible with the LM324/LM248 Low input offset voltage : 1mV Typ. Low input offset current : 4nA Typ. Low input bias current : 30nA Typ. Gain bandwidth (unity gain): 1.0MHz Typ. High degree of isolation between amplifiers: 120dB Overload protection for inputs and outputs 14-DIP 1 14-SOP 1 Internal Block Diagram Rev. 1.0.1 ©2001 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation LM348/LM248 Schematic Diagram (One Section Only) Absolute Maximum Ratings Parameter Supply Voltage Differential Input Voltage 2 Symbol Value Unit VCC ±18 V VI(DIFF) 36 V Input Voltage VI ±18 V Output Short Circuit Duration - Continuous - Operating Temperature LM348 LM248 TOPR 0 ~ +70 -25 ~ +85 °C Storage Temperature TSTG - 65~ +150 °C LM348/LM248 Electrical Characteristics (VCC =15V, VEE= -15V, TA=25 °C, unless otherwise specified) Parameter Symbol Input Offset Voltage VIO Input Offset Current IIO Conditions RS≤10KΩ Note 1 Note 1 LM248 Min. LM348 Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max. - 1 6.0 - 1 6.0 - - 7.5 - - 7.5 - 4 50 - 4 50 - - 125 - - 100 - 30 200 - 30 200 - - 500 - - 400 Unit mV nA nA Input Bias Current IBIAS Input Resistance RI - 0.8 2.5 - 0.8 2.5 - MΩ Supply Current (all Amplifiers) ICC - - 2.4 4.5 - 2.4 4.5 mA Large Signal Voltage Gain GV 25 160 - 25 160 - 15 - - 15 - - Channel Separation CS - 120 - - 120 - dB Common Mode Input Voltage Range VI(R) Note 1 ±12 - - ±12 - - V Small Signal Bandwidth BW GV = 1 - 1.0 - - 1.0 - MHz MPH GV = 1 - 60 - - 60 - Degree Slew Rate (Note2) SR GV = 1 - 0.5 - - 0.5 - V/µs Output Short Circuit Current ISC mA Phase Margin (Note2) Note 1 RL≥2KΩ Note 1 f = 1KHz to 20KHz - - 25 - - 25 - ±12 ±13 - ±12 ±13 - RL≥2KΩ ±10 ±12 - ±10 ±12 - RL≥10KΩ Note 1 V/mV Output Voltage Swing VO(P-P) Common Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR RS≥10KΩ Note 1 70 90 - 70 90 - dB Power Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR RS≥10KΩ Note 1 77 96 - 77 96 - dB V Note : 1. LM348: 0 ≤ TA ≤ +70 °C , LM248: -25 ≤ TA ≤ +85 °C 2. Guaranteed by design. 3 Order this document by 4N35/D SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA GlobalOptoisolator [CTR = 100% Min] The 4N35, 4N36 and 4N37 devices consist of a gallium arsenide infrared emitting diode optically coupled to a monolithic silicon phototransistor detector. *Motorola Preferred Device • Current Transfer Ratio — 100% Minimum @ Specified Conditions • Guaranteed Switching Speeds STYLE 1 PLASTIC • Meets or Exceeds all JEDEC Registered Specifications • To order devices that are tested and marked per VDE 0884 requirements, the suffix ”V” must be included at end of part number. VDE 0884 is a test option. Applications • General Purpose Switching Circuits 6 • Interfacing and coupling systems of different potentials and impedances 1 STANDARD THRU HOLE CASE 730A–04 • Regulation Feedback Circuits • Monitor & Detection Circuits • Solid State Relays SCHEMATIC MAXIMUM RATINGS (TA = 25°C unless otherwise noted) Rating Symbol Value Unit Reverse Voltage VR 6 Volts Forward Current — Continuous IF 60 mA LED Power Dissipation @ TA = 25°C with Negligible Power in Output Detector Derate above 25°C PD 120 mW 1.41 mW/°C 1 6 2 5 3 4 INPUT LED OUTPUT TRANSISTOR Collector–Emitter Voltage VCEO 30 Volts Emitter–Base Voltage VEBO 7 Volts Collector–Base Voltage VCBO 70 Volts Collector Current — Continuous IC 150 mA Detector Power Dissipation @ TA = 25°C with Negligible Power in Input LED Derate above 25°C PD 150 mW 1.76 mW/°C VISO 7500 Vac(pk) Total Device Power Dissipation @ TA = 25°C Derate above 25°C PD 250 2.94 mW mW/°C Ambient Operating Temperature Range(2) TA – 55 to +100 °C Tstg – 55 to +150 °C TL 260 °C PIN 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. LED ANODE LED CATHODE N.C. EMITTER COLLECTOR BASE TOTAL DEVICE Isolation Source Voltage(1) (Peak ac Voltage, 60 Hz, 1 sec Duration) Storage Temperature Range(2) Soldering Temperature (10 sec, 1/16″ from case) 1. Isolation surge voltage is an internal device dielectric breakdown rating. 1. For this test, Pins 1 and 2 are common, and Pins 4, 5 and 6 are common. 2. Refer to Quality and Reliability Section in Opto Data Book for information on test conditions. Preferred devices are Motorola recommended choices for future use and best overall value. GlobalOptoisolator is a trademark of Motorola, Inc. REV 2 Optoelectronics Device Data Motorola Motorola, Inc. 1995 1 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (TA = 25°C unless otherwise noted)(1) Symbol Min Typ(1) Max Unit VF 0.8 0.9 0.7 1.15 1.3 1.05 1.5 1.7 1.4 V Reverse Leakage Current (VR = 6 V) IR — — 10 µA Capacitance (V = 0 V, f = 1 MHz) CJ — 18 — pF Collector–Emitter Dark Current (VCE = 10 V, TA = 25°C) Collector–Emitter Dark Current (VCE = 30 V, TA = 100°C) ICEO — — 1 — 50 500 nA µA Collector–Base Dark Current (VCB = 10 V) ICBO — 0.2 100 20 — nA Collector–Emitter Breakdown Voltage (IC = 1 mA) V(BR)CEO 30 45 — V Collector–Base Breakdown Voltage (IC = 100 µA) V(BR)CBO 70 100 — V Emitter–Base Breakdown Voltage (IE = 100 µA) V(BR)EBO 7 7.8 — V DC Current Gain (IC = 2 mA, VCE = 5 V) hFE — 400 — — Collector–Emitter Capacitance (f = 1 MHz, VCE = 0) CCE — 7 — pF Collector–Base Capacitance (f = 1 MHz, VCB = 0) CCB — 19 — pF Emitter–Base Capacitance (f = 1 MHz, VEB = 0) CEB — 9 — pF IC (CTR)(2) 10 (100) 4 (40) 4 (40) 30 (300) — — — — — mA (%) VCE(sat) — 0.14 0.3 V ton — 7.5 10 µs toff — 5.7 10 tr — 3.2 — tf — 4.7 — VISO 7500 — — Vac(pk) IISO — — — — — 8 100 100 100 µA RISO 1011 — — Ω CISO — 0.2 2 pF Characteristic INPUT LED Forward Voltage (IF = 10 mA) TA = 25°C TA = –55°C TA = 100°C OUTPUT TRANSISTOR TA = 25°C TA = 100°C COUPLED Output Collector Current (IF = 10 mA, VCE = 10 V) TA = 25°C TA = –55°C TA = 100°C Collector–Emitter Saturation Voltage (IC = 0.5 mA, IF = 10 mA) Turn–On Time Turn–Off Time Rise Time (IC = 2 mA, VCC = 10 V, RL = 100 Ω)(3) Fall Time Isolation Voltage (f = 60 Hz, t = 1 sec) Isolation Current(4) (VI–O = 3550 Vpk) Isolation Current (VI–O = 2500 Vpk) Isolation Current (VI–O = 1500 Vpk) Isolation Resistance (V = 500 V)(4) Isolation Capacitance (V = 0 V, f = 1 MHz)(4) 1. 2. 3. 4. 2 4N35 4N36 4N37 Always design to the specified minimum/maximum electrical limits (where applicable). Current Transfer Ratio (CTR) = IC/IF x 100%. For test circuit setup and waveforms, refer to Figure 11. For this test, Pins 1 and 2 are common, and Pins 4, 5 and 6 are common. Motorola Optoelectronics Device Data GENERAL PURPOSE 6-PIN PHOTODARLINGTON OPTOCOUPLERS DESCRIPTION The 4N29, 4N30, 4N31, 4N32, 4N33 have a gallium arsenide infrared emitter optically coupled to a silicon planar photodarlington. 4N29 4N30 4N31 4N32 4N33 FEATURES • High sensitivity to low input drive current • Meets or exceeds all JEDEC Registered Specifications • VDE 0884 approval available as a test option -add option .300. (e.g., 4N29.300) SCHEMATIC ANODE 1 6 BASE APPLICATIONS • • • • • Low power logic circuits Telecommunications equipment Portable electronics Solid state relays Interfacing coupling systems of different potentials and impedances. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS CATHODE 2 5 COLLECTOR N/C 3 4 EMITTER (TA = 25°C Unless otherwise specified.) Parameter Symbol Value Units TSTG -55 to +150 °C Operating Temperature TOPR -55 to +100 °C Lead Solder Temperature TSOL 260 for 10 sec °C 250 mW 3.3 mW/°C IF 80 mA VR 3 V TOTAL DEVICE Storage Temperature Total Device Power Dissipation @ TA = 25°C Derate above 25°C EMITTER Continuous Forward Current Reverse Voltage Forward Current - Peak (300 µs, 2% Duty Cycle) PD 3.0 A 150 mW 2.0 mW/°C BVCEO 30 V Collector-Base Breakdown Voltage BVCBO 30 V Emitter-Collector Breakdown Voltage BVECO LED Power Dissipation @ TA = 25°C Derate above 25°C DETECTOR Collector-Emitter Breakdown Voltage Detector Power Dissipation @ TA = 25°C Derate above 25°C Continuous Collector Current IF(pk) PD PD IC 5 V 150 mW 2.0 mW/°C 150 mA 4/25/00 200038B GENERAL PURPOSE 6-PIN PHOTODARLINGTON OPTOCOUPLERS 4N29 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS 4N30 4N31 4N32 4N33 (TA = 25°C Unless otherwise specified.) INDIVIDUAL COMPONENT CHARACTERISTICS Parameter Test Conditions EMITTER V V (VR = 3.0 V) IR 0.001 100 µA (VF = 0 V, f = 1.0 MHz) C 150 *Collector-Base Breakdown Voltage (IC = 100 µA, IE = 0) *Emitter-Collector Breakdown Voltage (IE = 100 µA, IB = 0) DC Current Gain Unit 1.5 BVCEO *Collector-Emitter Dark Current Max 1.2 (IC = 100 µA, IB = 0) *Collector-Emitter Breakdown Voltage Typ VF *Reverse Leakage Current DETECTOR Min (IF = 10 mA) *Input Forward Voltage *Capacitance Symbol pF 30 60 BVCBO 30 100 V BVECO 5.0 8 V (VCE = 10 V, Base Open) ICEO 1 (VCE = 5.0 V, IC = 500 µA) hFE 5000 100 nA Max Units TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS DC Characteristic Test Conditions Symbol *Collector Output Current(1,2) (4N32, 4N33) Min Typ 50 (500) (4N29, 4N30) (IF = 10 mA, VCE = 10 V, IB = 0) IC (CTR) (4N31) 10 (100) mA (%) 5 (50) *Saturation Voltage(2) (4N29, 4N30, 4N32, 4N33) (4N31) (IF = 8.0 mA, IC = 2.0 mA) 1.0 VCE(sat) 1.2 V TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS AC Characteristic Turn-on Test Conditions Time(3) Turn-off Time(3) (4N32, 4N33) (IF = 200 mA, IC = 50 mA, VCC = 10 V) (Fig.7) (4N29, 4N30, 4N31) Symbol Min Typ Units 5.0 ton 100 toff Bandwidth(4,5) Max µs 40 BW 30 KHz ISOLATION CHARACTERISTICS Characteristic Test Conditions Input-Output Isolation Voltage(6) (4N29, 4N30, 4N31, 4N32, 4N33) Isolation Resistance(6) Isolation Capacitance(6) Symbol (II-O 61 µA, Vrms, t = 1 min.) *(4N32) VDC *(4N33) VDC Min Typ Max 5300 VISO Units Vac(rms) 2500 V 1500 (VI-O = 500 VDC) RISO 1011 1 (VI-O = , f = 1 MHz) CISO 0.8 pf 4/25/00 200038B