UNIT 12: THE WITNESS
Anuncio
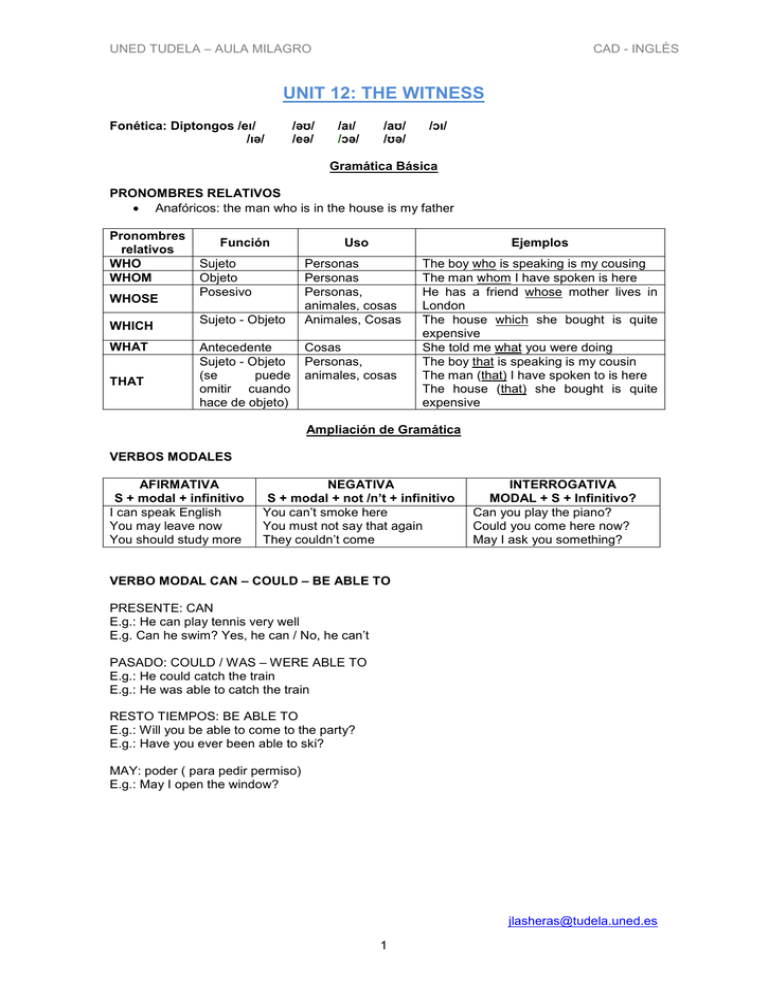
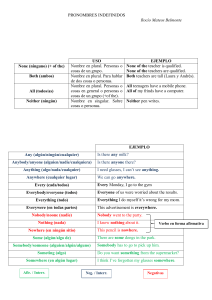
UNED TUDELA – AULA MILAGRO CAD - INGLÉS UNIT 12: THE WITNESS Fonética: Diptongos /eɪ/ /ɪə/ /əʊ/ /eə/ /aɪ/ /ɔə/ /aʊ/ /ʊə/ /ɔɪ/ Gramática Básica PRONOMBRES RELATIVOS • Anafóricos: the man who is in the house is my father Pronombres relativos WHO WHOM WHOSE WHICH WHAT THAT Función Sujeto Objeto Posesivo Sujeto - Objeto Antecedente Sujeto - Objeto (se puede omitir cuando hace de objeto) Uso Ejemplos Personas Personas Personas, animales, cosas Animales, Cosas The boy who is speaking is my cousing The man whom I have spoken is here He has a friend whose mother lives in London The house which she bought is quite expensive She told me what you were doing The boy that is speaking is my cousin The man (that) I have spoken to is here The house (that) she bought is quite expensive Cosas Personas, animales, cosas Ampliación de Gramática VERBOS MODALES AFIRMATIVA S + modal + infinitivo I can speak English You may leave now You should study more NEGATIVA S + modal + not /n’t + infinitivo You can’t smoke here You must not say that again They couldn’t come INTERROGATIVA MODAL + S + Infinitivo? Can you play the piano? Could you come here now? May I ask you something? VERBO MODAL CAN – COULD – BE ABLE TO PRESENTE: CAN E.g.: He can play tennis very well E.g. Can he swim? Yes, he can / No, he can’t PASADO: COULD / WAS – WERE ABLE TO E.g.: He could catch the train E.g.: He was able to catch the train RESTO TIEMPOS: BE ABLE TO E.g.: Will you be able to come to the party? E.g.: Have you ever been able to ski? MAY: poder ( para pedir permiso) E.g.: May I open the window? jlasheras@tudela.uned.es 1