1º DE E.S.O
Anuncio
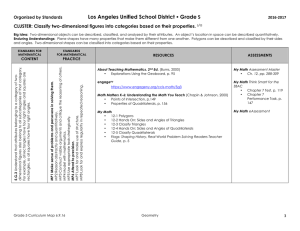
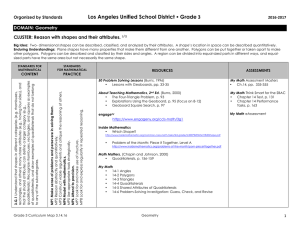
MATHS 1º DE E.S.O IES FERNANDO III CENTRO BILINGÜE MATHS UNIT 8: POLYGONS UNIT 8: POLYGONS OUTLINE 1 – POLYGONS. a. ANGLE PROPERTIES OF TRIANGLES. b. QUADRILATERALS c. REGULAR AND IRREGULAR POLYGONS d. ANGLE PROPERTIES OF POLYGONS 2 - VOCABULARY ASPECTOS LINGÜÍSTICOS PRESENT SIMPLE IMPERATIVE LOS PASADOS TO BE THERE WAS THERE WERE. VERBOS REGULARES/ IRREGULARES EN PASADO AFIRMATIVA. CONTABLES/INCONTABLES SOME/ ANY GOING TO MUST / MUSTN´T VOCABULARY POLYGONS TRIANGLES QUADRILATERALS SQUARE RHOMBUS RECTANGLE PARALLELOGRAM TRAPEZIUM PENTAGON HEXAGON OCTAGON DECAGON PHONETICS TODOS LOS SONIDOS I.E.S. FERNANDO III EL SANTO / PROYECTO BILINGÜE A.N.L.: MATHS 41 MATHS UNIT 8: POLYGONS 1.- POLYGONS. A Polygon is a 2-dimensional closed shape with straight sides. In this section, we are going to revise the properties of polygons. A. ANGLE PROPERTIES OF TRIANGLES. The following properties are true for any triangle: 1.- The angles in a triangle add up to 180º. C A B 2.- The exterior angle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles. B A I.E.S. FERNANDO III EL SANTO / PROYECTO BILINGÜE C D=A+B A.N.L.: MATHS 42 MATHS UNIT 8: POLYGONS B. QUADRILATERALS. The angles in quadrilaterals add up to 360º. There are special types of quadrilaterals: Square: The square is a regular quadrilateral. o All of its angles are equal (90º). o All of its sides are of equal length. o Opposite sides are parallel. o The diagonals bisect each other at 90º. o The diagonals are equal in length. Rhombus: o Diagonally opposite angles are equal. o All of its sides are of equal length. o Opposite sides are parallel. o It has two lines of symmetry. Rectangle: o All angles are equal. o Opposite sides are of equal length. o Opposite sides are parallel. o The diagonals are equal in length. o It has two lines of symmetry. Parallelogram: o Diagonally opposite angles are equal. o Opposite sides are of equal length. o Opposite sides are parallel. o It has no lines of symmetry. Trapezium: o One pair of opposite sides is parallel. o It has no lines of symmetry. I.E.S. FERNANDO III EL SANTO / PROYECTO BILINGÜE A.N.L.: MATHS 43 MATHS UNIT 8: POLYGONS C. REGULAR AND IRREGULAR POLYGONS The simplest polygon is a triangle ( 3 sides). Polygons can be regular or irregular. A regular polygon has sides of equal length, and all its interior angles are of equal size. Irregular polygons can have sides of any length and angles of any size. Here are the names of some common polygons: NUMBER OF SIDES NAME OF POLYGON 3 TRIANGLE 4 QUADRILATERAL 5 PENTAGON 6 HEXAGON 8 OCTAGON 10 DECAGON I.E.S. FERNANDO III EL SANTO / PROYECTO BILINGÜE SHAPE A.N.L.: MATHS 44 MATHS UNIT 8: POLYGONS D. ANGLE PROPERTIES OF POLYGONS. The formula for calculating the sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon is: Where n is the number of sides of the polygon. This formula comes from dividing the polygon up into triangles using full diagonals. We know that the interior angles of a triangle add up to 180º. For any polygon, count up how many triangles it can be split into. Then multiply the number of triangles by 180. NUMBER OF SIDES SUM OF INTERIOR ANGLES SHAPE 3 4 5 6 8 10 I.E.S. FERNANDO III EL SANTO / PROYECTO BILINGÜE A.N.L.: MATHS 45 MATHS UNIT 8: POLYGONS 2.- VOCABULARY English Pronunciation Spanish Angle /æŋgəl/ Ängulo Decagon /ˈdekagən/ Decágono Diagonals /daɪ'ægənəl/ Diagonal Hexagon /'heksəgən/ Hexágono Length /leŋθ/ Longitud Octagon /'ɒktəgən/ Octógono Parallelogram /parəleləgram/ Paralelogramo Pentagon /'pentəgən/ Pentágono Polygon /pəligən/ Polígono Quadrilateral /'kwɑ:drə'lætərəl/ Cuadrilátero Rectangle /'rektæŋgəl/ Rectángulo Rhombus /'rɒmbəs/ Rombo Sides /saɪd/ Lado Square /skweə(r)/ Cuadrado Symmetry /'sɪmətri/ Simetría Trapezium /trəpəzɪəm/ Trapecio Triangle /'traɪˌæŋgəl/ Triángulo I.E.S. FERNANDO III EL SANTO / PROYECTO BILINGÜE A.N.L.: MATHS 46