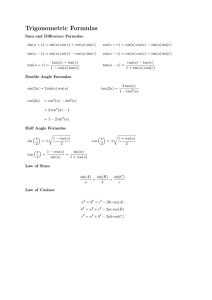
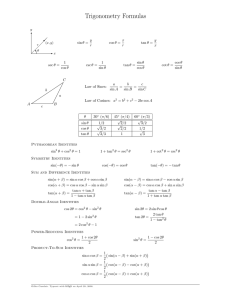
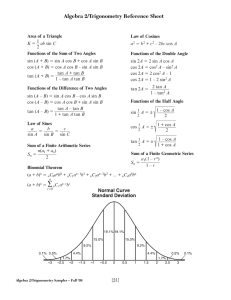
Exam 3 Formulas: Sum and Difference: tan( + ) = tan
Anuncio

Exam 3 Formulas: Sum and Difference: tan 𝑥+tan 𝑦 tan(𝑥 + 𝑦) = 1−tan 𝑥 tan 𝑦 Double Angle: 2 tan 𝑥 tan 2𝑥 = 1−tan2 𝑥 Power Reducing: 1−cos 2𝑥 tan2 𝑥 = 1+cos 2𝑥 Half Angle: 𝑥 2 1+cos 𝑥 2 𝑥 1−cos 𝑥 cos ( ) = ±√ tan 𝑥−tan 𝑦 tan(𝑥 − 𝑦) = 1+tan 𝑥 tan 𝑦 𝑥 2 1−cos 𝑥 2 sin ( ) = ±√ sin 𝑥 tan (2) = ±√1+cos 𝑥 = 1+cos 𝑥 = 1−cos 𝑥 sin 𝑥 Product to Sum: 1 sin 𝑥 cos 𝑦 = 2 [sin(𝑥 + 𝑦) + sin(𝑥 − 𝑦)] 1 sin 𝑥 sin 𝑦 = [cos(𝑥 − 𝑦) − cos(𝑥 + 𝑦)] 2 Sum to Product: 𝑥+𝑦 𝑥−𝑦 sin 𝑥 + sin 𝑦 = 2 sin ( 2 ) cos ( 2 ) 𝑥+𝑦 𝑥−𝑦 ) cos ( ) 2 2 cos 𝑥 + cos 𝑦 = 2 cos ( Law of Sines sin 𝐴 sin 𝐵 sin 𝐶 = = 𝑎 𝑏 𝑐 Law of Cosines 𝑎2 = 𝑏 2 + 𝑐 2 − 2𝑏𝑐 cos 𝐴 𝑏 2 = 𝑎2 + 𝑐 2 − 2𝑎𝑐 cos 𝐵 𝑐 2 = 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 − 2𝑎𝑏 cos 𝐶 Polar Information 𝑥 = 𝑟 cos 𝜃 𝑦 = 𝑟 sin 𝜃 Complex Numbers in Polar Form 𝑧 = 𝑟(cos 𝜃 + 𝑖 sin 𝜃) 𝑎 = 𝑟 cos 𝜃 DeMoivre’s Theorem 𝑧 𝑛 = 𝑟 𝑛 [cos(𝑛𝜃) + 𝑖 sin(𝑛𝜃)] 1 cos 𝑥 sin 𝑦 = 2 [sin(𝑥 + 𝑦) − sin(𝑥 − 𝑦)] 1 2 cos 𝑥 cos 𝑦 = [cos(𝑥 + 𝑦) + cos(𝑥 − 𝑦)] 𝑥+𝑦 𝑥−𝑦 ) sin ( 2 ) 2 𝑥+𝑦 𝑥−𝑦 −2 sin ( ) sin ( ) 2 2 sin 𝑥 − sin 𝑦 = 2 cos ( cos 𝑥 − cos 𝑦 = 𝑟2 = 𝑥2 + 𝑦2 𝑏 = 𝑟 sin 𝜃 tan 𝜃 = 𝑟 2 = 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 𝑦 𝑥 tan 𝜃 = 𝑏 𝑎