i. summary - Biblioteca
Anuncio

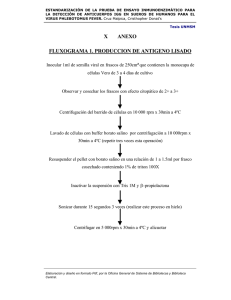
ESTANDARIZACIÓN DE LA PRUEBA DE ENSAYO INMUNOENZIMÁTICO PARA LA DETECCIÓN DE ANTICUERPOS IGG EN SUEROS DE HUMANOS PARA EL VIRUS PHLEBOTOMUS FEVER. Cruz Malpica, Cristhopher Donat's Tesis UNMSM I. SUMMARY The Phlebotomus fever virus is an arbovirus transmitted to humans by the bits of hematofagous flies with limited flight range, which belong to the genus Phlebotomus, Sergentomyia and Lutzomyia. The human infection mainly occurs among people who work and live in the jungle. An inmunoenzimatic indirect assay (ELISA) was standardized in this thesis to detect antibodies IgG against the virus in human serum. This test was applied to determine the antibody seroprevalence against this virus in people coming from Iquitos. The positive case confirmation was performed using the Plaque Reduction for Neutralization Test (PRNT). The ELISA test was performed in four stages: the antigen fixation, reaction to the serum, addition to the conjugate and reaction to the substrate. During the antigen production, the cell line Vero E-6 was used, obtaining a work dilution of 1:1500. The conjugated used is a purified antibody peroxidase labeled goat antihuman IgG, obtaining a work dilution of 1:8000. Using the ELISA test, 400 sera from Iquitos were tested, resulting with a seroprevalence of 16.25%. When confirming the results with the PRNT trial, the ELISA test showed a specificity of 83.02% and a sensitivity of 98.24%. I concluded that the ELISA test developed for the Phlebotomus fever virus is applicable to perform prevalence studies. Key words: Phlebotomus fever, ELISA, PRNT. Elaboración y diseño en formato Pdf, por la Oficina General de Sistema de Bibliotecas y Biblioteca Central. ESTANDARIZACIÓN DE LA PRUEBA DE ENSAYO INMUNOENZIMÁTICO PARA LA DETECCIÓN DE ANTICUERPOS IGG EN SUEROS DE HUMANOS PARA EL VIRUS PHLEBOTOMUS FEVER. Cruz Malpica, Cristhopher Donat's Tesis UNMSM I. RESUMEN El virus Phlebotomus fever es un arbovirus cuya transmisión al hombre ocurre por la picadura de moscas hematófagas de vuelo limitado, pertenecientes a los géneros Phlebotomus, Sergentomyia y Lutzomyia. La infección en humanos ocurre principalmente en personas que trabajan o viven en la selva. En el presente trabajo se estandarizó una prueba inmunoenzimática indirecta (ELISA) para detectar anticuerpos IgG contra el virus en sueros humanos. También se aplicó esta prueba en la determinación de la seroprevalencia de anticuerpos contra dicho virus en personas procedentes de Iquitos. La confirmación de los casos positivos se realizó mediante la Prueba de Neutralización por Reducción de Placa (PRNT). El ELISA se realizó en cuatro pasos: fijación del antígeno, reacción con el suero, adición del conjugado y reacción con el sustrato. En la producción del antígeno se utilizó la línea celular Vero E-6, siendo la dilución de trabajo 1:1500. El conjugado utilizado es un Anti IgG humano de cabra purificado y marcado con peroxidasa, siendo su dilución de trabajo 1:8 000. Se analizó con la prueba de ELISA 400 sueros procedentes de Iquitos, encontrándose una seroprevalencia de 16.25%. Al confirmar los resultados con la prueba de PRNT, el ELISA obtuvo una especificidad de 83.02% y una sensibilidad de 98.24%. ELISA desarrollado para el virus Phlebotomus fever es aplicable para realizar estudios de prevalencia. Palabras claves: Phlebotomus fever, ELISA, PRNT. Elaboración y diseño en formato Pdf, por la Oficina General de Sistema de Bibliotecas y Biblioteca Central.