Trigonometry and Pre-calculus - Division of Academic Enhancement
Anuncio

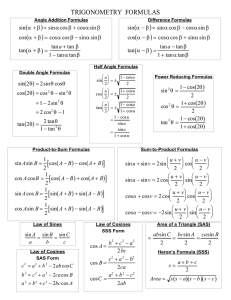
Formulas from Trigonometry opp y = hyp r adj x cosθ= = hyp r opp y sin θ tan θ= = = adj x cosθ hyp 1 csc θ= = opp sin θ hyp 1 secθ= = adj cosθ adj 1 cosθ cot θ= = = opp tan θ sin θ 2 2 sin θ+ cos θ=1 2 2 1+ tan θ= sec θ 2 2 1+ cot θ=csc θ (cos(θ), sin(θ)) sin θ= Addition Formulas sin (α+ β)=sin α cos β+ sin βcos α cos(α+ β)=cos α cosβ−sin α sin β sin ( α+β) tan α+tan β tan (α +β)= = cos( α+β) 1−tan α tan β Subtraction Formulas sin (α−β)=sin α cosβ−sin βcos α cos(α−β)=cosα cosβ+ sin α sin β sin (α−β) tan α−tan β tan (α−β)= = cos(α−β) 1+tan α tan β Half-Angle Formulas √ √ 1−cos α sin α =± 2 2 1+ cos α cos α =± 2 2 1−cosα sin α tan α = = 2 sin α 1+cosα ( ) ( ) ( ) Sine Graph Quadratic Formula 2 if a x + b x+ c=0 then −b± √b2 −4a c x= 2a −b −b vertex = ,f =(h , k ) 2a 2a ( ( )) Double Angle Formulas sin 2 α=2 sin α cosα 2 2 cos 2 α=cos α−sin α 2 = 1−2 sin α = 2 cos2 α−1 2 tan α tan 2α= 2 1− tan α 2 y= a ( x−h ) + k Cosine Graph (x +2 x , y +2 y ) 2 1 2 2 2 x − y =( x+ y)( x− y) 2 2 2 x ±2 x y+ y =( x± y) 3 3 2 2 x ± y =( x± y)( x ∓ x y+ y ) 2 Tangent Graph Circular Sector s= r θ 1 Factoring Formulas Law of Cosines 2 d = √( x1 −x 2 )2+ ( y 1− y2 )2 midpoint = sin α sin β sin γ = = a b c 2 Distance Formula Midpoint Formula Law of Sines a =b +c −2 b c cosα 2 2 2 b = a + c −2 a c cosβ 2 2 2 c =a + b −2 a b cos γ Formulas From Algebra 1 A= r 2 θ 2 Constants π=3.141592653589793238462643 e=2.718281828459045235360287 ϕ=1.618033988749894848204586 Trigonometry and Pre-Calculus Formula Sheet – University of Georgia Division of Academic Enhancement Associative Property a+ (b + c)=( a+ b)+ c a(b c)=(a b) c Commutative Property a+ b=b+ a a b=b a Distributive Property a(b+ c)=a b+ a c Exponents and Radicals x y x+ y A=l w Circle A= π r f ( x)= x P=2 l +2 w 2 C=2 π r Right Circular Cone 1 2 1 V = π r h= Abase h 3 3 2 2 S = π r √r + h 1 x √x a y=a Common Function Graphs Rectangle () a x =√ a Trapezoid 1 A= (a +b) h 2 a ∗a =a x y xy (a ) =a x x x (a b) =a b x x a a = x b b x a =a x−y ay 1 a−x = x a f ( x)= x Sphere y x 4 V = π r3 3 Line Equations y 2− y1 x 2− x 1 y=m x+ b y− y1= m( x− x1 ) S=4π r 2 2 Rectangular Box m= V =l w h S = 2 h l +2 l w+ 2 h w Right Circular Cylinder Circle Equations Center=(h, k) radius=r : 2 2 2 ( x−h) + ( y−k ) =r 2 2 y= k± √r −( x−h) Exponentials and Logarithms y y=log b x ⇔ b = x log( x y)=log ( x)+ log( y) x log =log x−log y y a log (x )=a log( x) () 2 V =π r h S = 2 π r h +2 π r 2 Circular Sector s= r θ f ( x)= x 3 1 A= r 2 θ 2 Parallelogram A= bh= absin (θ) Inverse Trigonometry Functions f ( x)=arcsin ( x) loga ( x ) a =x x log a (a )= x log(1)=0 ln (e)=1 log a (a)=1 log (x)=log 10( x) ln ( x)=log e ( x) log( x) ln ( x) log b ( x)= = log(b) ln (b) f ( x)=∣x∣ f ( x)=arccos( x) Function Modifications g( x)=a∗f (b∗x−c )+d a= vertical stretch b= horizontal squeeze c=horizontal shift d=vertical shift f ( x)= √x Formulas from Geometry Right Triangle 2 2 c =a +b 2 1 A= a b 2 f ( x)=arctan ( x) Equilateral Triangle √3 s √3 s 2 h= A= 2 4 Triangle 1 1 A= b h= a b sin (θ) 2 2 Trigonometry and Pre-Calculus Formula Sheet – University of Georgia Division of Academic Enhancement