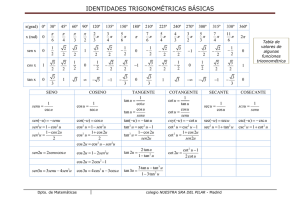
Phoenix ED [Basics of Trigonometry] 9831333221 Page 1 y = tan x y
Anuncio
![Phoenix ED [Basics of Trigonometry] 9831333221 Page 1 y = tan x y](http://s2.studylib.es/store/data/008088045_1-5ae736332d368b28c47ea0fe1ab398d4-768x994.png)
Phoenix ED y = tan x 9831333221 [Basics of Trigonometry] y = ( cos x , sin x ) Page 1 Phoenix ED [Basics of Trigonometry] θ (deg) θ (rad) sin(θ) cos(θ) tan(θ) cot(θ) sec(θ) cosec(θ) 0o 0 0 1 0 undefined 1 undefined П 12 √3 − 1 √3 + 1 √3 − 1 √3 + 1 2√2 2√2 10 + 2√5 4 √5 − 1 ඥ 10 + 2√5 15 o 18 o 22.5 o 30 o 36 o 45 o 54 o 60 o 67.5 o 72 o 75 o 9831333221 2√2 П 10 П 8 √5 − 1 4 ඨ П 6 П 5 ඨ П 4 3П 10 2П 5 5П 12 2√2 1 2 ඨ ඨ √2 + 1 2√2 10 + 2√5 4 √3 + 1 2√2 √2 + 1 2√2 √3 2 √5 + 1 4 √2 2 √3 2 ඨ ඨ 10 − 2√5 4 √5 + 1 4 П 3 3П 8 √2 − 1 2√2 √2 2 ඨ 10 − 2√5 4 1 2 ඨ √2 − 1 2√2 √3 + 1 ඥ 10 + 2√5 ඨ √2 − 1 √2 + 1 √3 3 ඥ 10 − 2√5 √3 − 1 √5 − 1 ඨ √2 + 1 √2 − 1 1 1 √5 + 1 ඥ 10 − 2√5 √3 √3 3 √2 + 1 √2 − 1 10 + 2√5 √5 − 1 √5 + 1 ඨ √2 − 1 √2 + 1 √5 − 1 ඨ 2√2 √2 + 1 2√3 3 4 √5 + 1 ඨ 2√2 √2 − 1 4 √5 − 1 ඥ 10 + 2√5 √5 − 1 2√2 √3 − 1 √3 + 1 √3 − 1 √3 − 1 ඨ 2√2 Page 2 √2 − 1 4 10 − 2√5 √2 4 √5 + 1 2√3 3 2 ඨ 2√2 2 4 10 − 2√5 ඥ 10 + 2√5 √3 + 1 ඨ √2 √5 − 1 4 √3 − 1 4 4 ඨ √5 + 1 ඥ 10 − 2√5 ඨ √3 − 1 √3 √5 + 1 ඥ 10 − 2√5 √3 + 1 ඨ ඨ 2√2 √2 + 1 4 10 + 2√5 2√2 √3 + 1 Phoenix ED 90 o 120 o 135 o 150 o 180 o 210 o 225 o 240 o 270 o 300 o 315 o 330 o 360 o 9831333221 П 2 2П 3 3П 4 5П 6 [Basics of Trigonometry] 1 √3 2 √2 2 1 2 0 П 7П 6 5П 4 − − 4П 3 − 5П 3 − 3П 2 7П 4 11П 6 2П 0 1 2 √2 2 √3 2 − − − 1 2 √2 2 √3 2 undefined −√3 -1 − -1 − − √3 2 √2 2 − 1 2 √3 3 1 1 √3 √3 3 0 0 1 -1 − √3 3 0 − √3 3 -1 1 2√3 3 √2 2√3 3 2√3 3 −√3 √3 2 − √3 1 2 1 2 −√3 −√2 √3 3 √3 2 − -1 -2 -1 undefined √2 2 √3 3 undefined 0 √2 2 − undefined 0 -1 − 0 −√2 -2 2 undefined -2 −√2 − undefined 2 √2 −√3 2√3 3 undefined 1 Page 3 2√3 3 -1 − 2√3 3 −√2 -2 undefined Phoenix ED [Basics of Trigonometry] Degree/Radian Relationship: 180° = π radians Sum and Difference Identities: Allied Angles cos(−x) = cos(x) sin(A + B) = sinA . cosB + cosA . sinB sin(−x) = −sin(x) sin(A − B) = sinA . cosB − cosA . sinB tan(−x) = −tan(x) cos(A + B) = cosA . cosB − sinA . sinB cos(90 − θ) = sin(θ) cos(A − B) = cosA . cosB + sinA . sinB sin(90 − θ) = cos(θ) tan(A + B) = tan(90 − θ) = cot(θ) cot(90 − θ) = tan(θ) sec(90 − θ) = cosec(θ) cosec(90 − θ) = sec(θ) tanA + tanB 1 − tanA . tanB tan(A - B) = tanA - tanB 1 + tanA . tanB cot(A + B) = cotA cotB - 1 cot(A - B) = cotA cotB + 1 cotA + cot B cot B - cot A Double-Angle Identities: cos(2A) Triple-Angle Identities: = cos2 A − sin2 A cos(3A) = 4cos3 A − 3cos A = 1 − 2 sin2 A sin(3A) = 3sinA - 4 sin3A = 2 tan(3A) = 3tanA –tan3A = 2 cos A – 1 2 1 − 3 tan2 A 1 − tan A 2 1 + tan A sin(2A) = 2 sinA cosA = 2 . tanA 1 + tan2 A tan(2A) = 2 . tanA 1 − tan2 A Half-Angle Identities: cos(A) Product-to-Sum Identities: 2 2 = cos (A/2) − sin (A/2) 2cosAcosB = [cos (A + B) + cos (A − B)] = 1 − 2 sin2 (A/2) 2sinA sinB = [cos (A − B) − cos (A + B)] = 2 cos2 (A/2) − 1 2sinAcosB = [sin (A + B) + sin (A − B)] sin(A) = 2 sin(A/2) . cos(A/2) 2cosAsinB = [sin (A + B) – sin (A − B)] tan(A) = 2 . tan(A/2) 1 − tan2 (A/2) Sum-to-Product Identities: sinA+sinB = 2 sin (A + B) cos(A - B) sinA−sinB = 2 cos (A + B) sin(A - B) cosA+cosB = 2 cos (A + B) cos(A - B) cosA−cosB = − 2 sin(A + B) sin(A - B) 2 2 2 2 2 9831333221 2 Important Formulae Sin (A+B) . Sin (A-B) = Sin2A – Sin2B Cos (A+B) . Cos (A-B) = Cos2A – Sin2B 2 2 Page 4