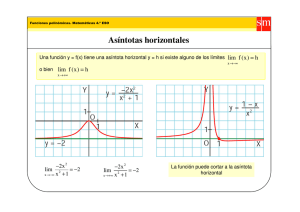
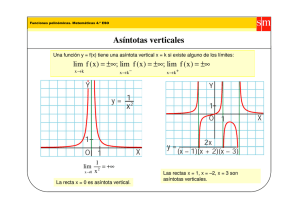
x - PublicacionesDidácticas
Anuncio

Reglas de derivación Título: Reglas de derivación. Target: Profesores de Matemáticas. Alumnos que estudian Bachillerato de Ciencias. Alumnos de primeros cursos de Grados relacionados con las Ciencias (Física, Química, Ingenierías...). Asignatura: Matemáticas. Autor: Emiliana Oliván Calzada, Licenciada en Matemáticas, Profesora de Matemáticas en Educación Secundaria. 1. CONCEPTO DE DERIVADA Y FUNCIÓN DERIVADA Definición: Sea I un intervalo de R no reducido a un punto y a I . Sea f una función de I en R. f a h f a Si el cociente: , con a h I , tiene límite real cuando h 0 , se dice que f es h derivable en a .Se denota ese límite por f a y leeremos derivada de f en a . Es decir, f a h f a . f a lim h 0 h Si f es derivable en todo a I , diremos que f es derivable en I. En este caso, la función x f x definida en I, recibe el nombre de función derivable de f, y la representaremos por f . 2. DEMOSTRACIONES DE LAS FÓRMULAS O REGLAS DE DERIVACIÓN 1.- Derivada de la función constante: f x k con k cte f x 0 f x h f x k k 0 f x lim lim 0 h 0 h 0 h h h 2.- Derivada de la función identidad: f x x f x 1 f x h f x xhx h f x lim lim 1 h 0 h 0 h h h 3.- Derivada de una constante por x: f x k x f x k f x h f x k x h k x k h f x lim lim lim k h 0 h 0 h 0 h h h 4.- Derivada de una cte por una función: yx k f x y x k f x yx h y x k f x h k f x k f x h f x lim lim h 0 h 0 h h h f x h f x k lim k f x h 0 h y x lim h 0 5.- Derivada de la suma algebraica de dos funciones: yx f x g x y x f x g x PublicacionesDidacticas.com | Nº 50 Septiembre 2014 57 de 190 f x h g x h f x g x yx h yx lim h 0 h h f x h f x g x h g x f x h f x g x h g x lim lim h 0 h 0 h h h f x h f x g x h g x lim lim f x g x h 0 h 0 h h y x lim h 0 Nota: Esto también es válido para una suma de n funciones. 6.- Derivada de un producto de funciones: a) Producto de dos funciones: y f x g x y f x g x g x f x yx h yx f x h g x h f x g x lim h 0 h 0 h h f x h g x h f x h g x f x h g x f x g x lim h 0 h f x h g x h g x g x f x h f x lim h 0 h f x h g x h g x g x f x h f x lim lim h 0 h 0 h h g x h g x f x h f x lim f x h lim lim g x lim h 0 h 0 h 0 h 0 h h f x g x g x f x y x lim Otra forma: Utilizando la derivada del logaritmo neperiano y la regla de la función compuesta: yx f x g x . Tomando logaritmos neperianos: ln f g ln f ln g . Derivando ambos lados de la igualdad: f g f g b) f g f g f g f g f g f g f g g f Producto de tres funciones: y f x g x hx y f x g x hx y f x g x hx g x f x hx hx f x g x y f x g x hx f x g x hx f x g x g x f x hx f x g x hx f x g x hx g x f x hx hx f x g x 7.- Derivada de un cociente: yx f x f x g x g x f x y x g x g x 2 PublicacionesDidacticas.com | Nº 50 Septiembre 2014 58 de 190 f x h f x f x h g x g x h f x yx h yx g x h g x g x h g x y lim lim lim h 0 h 0 h 0 h h h f x h g x f x g x f x g x g x h f x h lim h 0 g x h g x g x f x h f x f x g x h g x h lim h 0 g x h g x f x h f x f x h f x g x lim f x lim g x f x f x g x h 0 h 0 h h 2 g x g x 2 k k f x y x f x f x 2 f x f x Si el denominador es constante: yx y x k k Si el numerador es constante: y x 8.- Derivada de una potencia: f x x n f x n x n1 x h x n f x h f x lim h 0 h 0 h h n n n n n 1 n x x h x n 2 h 2 h n x n 0 1 2 n n f x lim lim h 0 h n n n h x n 1 x n 2 h h n 1 1 2 n n x n 1 n x n 1 lim 1 h 0 h 9.- Derivada de la raíz n-ésima: f x n x x 1 n f x 1 1 n n x n1 x h n x n f x h f x f x lim f x lim h 0 h 0 h h 1 1 1 1n 1 1n 1 n h n x 1n n x n x h 0 1 1 n lim h 0 h 1 1 1 1 1 1 h n x n n h n 1 1 1 1 n n x n 1 1 1 1 1 lim 1 h 0 h n nn1 n n x n 1 x 1 1 Otra forma: y f x n x y n x PublicacionesDidacticas.com | Nº 50 Septiembre 2014 59 de 190 f 1 o f x f 1 f x n x n x n f x x 1 n n n x derivando x x 1 x n n 1 n 1 n 10.- Derivada de la función logarítmica: 1 f x log a x f x log a e x n x n 1 n f x ln x f x xh log a log a x h log a x f x h f x x f x lim lim lim h 0 h 0 h 0 h h h 1 xh 1 h 1 1 lim log a lim log a 1 lim log a 1 h 0 h h 0 h x h x h 0 h h 1 x x h 1 x 1 1 1 1 lim log a 1 lim log a 1 log a e h 0 x h x h 0 x x x h h 11.- Derivada de la función seno: f x senx f x cos x sen x h senx f x h f x lim h 0 h h senx cosh cos x senh senx senx cosh 1 cos x senh lim lim h 0 h 0 h h cosh 1 cos x senh senx lim cosh 1 cos x lim senh lim senx h 0 h 0 h 0 h h h h h2 aplicando equivalenc ias senx lim 2 cos x 1 h 0 h h senx lim cos x senx 0 cos x cos x h 0 2 f x lim h 0 Otra forma: Utilizando otra fórmula trigonométrica: h h 2 cos x sen f x h f x senx h senx 2 2 f x lim lim lim h 0 h 0 h 0 h h h h h cos x sen 2 2 lim cos x h 1 cos x lim h 0 h 0 h 2 2 12.- Derivada de la función coseno: f x cos x f x senx PublicacionesDidacticas.com | Nº 50 Septiembre 2014 60 de 190 f x h f x cos x h cos x lim h 0 h h cos x cosh senx senh cos x cos x cosh 1 senx senh lim lim lim h 0 h 0 h 0 h h h 2 h2 cosh 1 senh cos x lim senx lim cos x lim 2 senx 1 h 0 h 0 h 0 h h h cos x 0 senx senx f x lim h 0 Otra forma: Utilizando otra fórmula trigonométrica: h h 2 sen x sen f x h f x cos x h cos x 2 2 f x lim lim lim h 0 h 0 h 0 h h h h h sen x sen 2 2 lim sen x h senx lim h 0 h 0 h 2 2 Otra forma: Utilizando la derivada de la función compuesta: f x cos x 1 sen 2 x f x 1 2 1 sen x 2 0 2 senx cos x 2 senx cos x senx 2 cos x 13.- Derivada de la función tangente: f x tagx senx 1 f x 1 tag 2 x 2 cos x cos x Derivando un cociente: cos x cos x senx senx cos 2 x sen 2 x 1 f x 1 tag 2 x 2 2 2 cos x cos x cos x 14.- Derivada de la función inversa: f 1 y f x 1 f x f f y 1 1 f 1 f x h f x y . lim h 0 x 0 x h y x y x 1 si x, y 0 lim lim 1 1 Ahora bien: x 0 x y x y x0 y x 1 lim 1 y x xy 1 y x Entonces: lim x 0 x x 0 y xy y lim 15.- Derivada de la función exponencial: f x a x f x a x ln a f x e x f x e x PublicacionesDidacticas.com | Nº 50 Septiembre 2014 61 de 190 f x a x tomando log aritmos x log a a x x log a y log a a x derivando 1 a x 1 a x a x a x ln a ln a Otra forma: f x y a x . Tomando logaritmos: log a y log a a x x log a a x . Luego: x log a y xy 1 log a e . y Aplicando la expresión de la derivada de la función inversa, tenemos: y x 1 1 y y y y ln a a x ln a 1 ln e 1 x y log a e cambio de base log a e y ln a ln a 16.- Derivada de la función arco seno: f x arcsenx f x y f x arcsenx x seny xy cos y 1 sen 2 y 1 x 2 y 1 1 x2 1 1 x2 17.- Derivada de la función arco coseno: f x arccos x f x y f x arccos x x cos y x y seny 1 cos 2 y 1 x 2 y 1 x2 1 1 x2 18.- Derivada de la función arco tangente: f x arctagx f x y f x arctagx x tagy xy 1 tag 2 y 1 x 2 y 1 1 1 x2 1 1 x2 19.- Derivada de x elevado a x: f x x x f x x x 1 ln x f x x x . Tomando logaritmos a ambos lados: ln f x ln x x x ln x . Ahora derivamos en ambos lados: 1 1 1 f x 1 ln x x f x f x 1 ln x x x x ln x 1 f x x x 20.- Derivada del seno hiperbólico: f x shx f x chx f x shx e x ex 1 x 1 e x ex e e x f x e x e x 1 chx 2 2 2 2 PublicacionesDidacticas.com | Nº 50 Septiembre 2014 62 de 190 21.- Derivada del coseno hiperbólico: f x chx f x shx e x ex 1 x 1 e x ex e e x f x e x e x 1 shx 2 2 2 2 shx 22.- Derivada de la tangente hiperbólica: f x tghx f x sec h 2 x chx f x chx 2 e x e x e x ex 2 2 chx chx shx shx ch 2 x sh 2 x f x 2 2 2 ch x ch x e x e x 2 e 2x 2 e 2 x e 2 x 2 e 2 x e x 2 e x e 2 4 x 2 ex 2 2 1 x 2 sec h 2 x x ch x e e 23.- Derivada de la cotangente hiperbólica: f x ctghx chx f x cos ech 2 x shx 2 e e e x ex 2 2 shx shx chx chx sh 2 x ch 2 x f x 2 2 2 sh x sh x e x ex 2 x e 2x 2 e 2 x e 2 x 2 e 2 x e x e x 2 e 4 x ex x 2 2 2 2 1 x 2 cos ech 2 x x sh x e e 24.- Derivada de la función compuesta: y f g x Si en vez de x tenemos una función, a la que llamamos u, entonces: y x yu u , es decir f x f u u x yx h yx f g x h f g x lim h 0 h h f g x h f g x g x h g x g x h g x h y lim h 0 lim h 0 f g x h f g x g x h g x lim lim f g x g x h 0 h 0 g x h g x h 3. CONCLUSIÓN Estas demostraciones son interesantes para alumnos o alumnas de 1º Bachillerato cuando se inician en el conocimiento de la función derivada y en el cálculo de derivadas de diferentes funciones. Así, cuando los alumnos o alumnas aprenden las conocidas reglas de derivación, son capaces de comprender la procedencia de todas ellas. ● PublicacionesDidacticas.com | Nº 50 Septiembre 2014 63 de 190 Bibliografía ANTON, H. Calculus. GUZMAN, M. y otros. Matemáticas de 3º BUP y Matemáticas I de COU GAUGHAN, E. Introducción al Análisis. PublicacionesDidacticas.com | Nº 50 Septiembre 2014 64 de 190