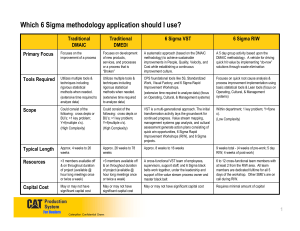
UNIVERSIDAD POLITECNICA DE ALTAMIRA MANUFACTURING PROCESSES U2H8 Student. Alejandro Solis Hernández (3151) Ing. Juan José Delgado Santos 8D PROBLEM SOLVING METHOD WHAT IS 8D AND WHAT IS IT FOR? The 8D are the eight disciplines for problem solving. It is also a tool used to deal with and solve some of the most common problems in companies. The 8D proposes eight sequential steps that we must follow to successfully solve any type of problem. WHAT ARE YOUR STEPS? D0: Prepare for the 8D process D1: Form a team of experts that covers all functions. D2: Define the problem. D3: Implement an interim containment action. D4: Identify the root cause. D5: Determine corrective actions. D6: Implement permanent corrective actions. D7: Prevent a similar problem from reappearing. D8: Recognize the efforts of the team. CONCLUSION In conclusion, this tool is very useful, since a systematized work structure is created, teamwork is carried out and a common approach is achieved. As a result, the organization's systems are improved, performance is optimized and future nonconformities and failures are prevented. SIX SIGAM APPLICATION (DFSS, DMADV, DMAIC) WHAT IS SIX SIGMA AND WHAT IS FOR IT? Six SIGMA is a process improvement methodology created in Motorola by engineer Bill Smith in the 1980s, this methodology is focused on reducing variability, reducing or eliminating defects or failures in the delivery of a product or customer service. The goal of 6 Sigma is to reach a maximum of 3.4 defects per million events or opportunities (DPMO), understanding as a defect any event in which a product or service fails to meet customer requirements. WHAT IS DFSS (DMAIC, DMADV)? First of all, DFSS stands for "Design For Six Sigma" and focuses on the idea of creating a new product or process or completely redesigning a product or process through a Six Sigma project. DFSS, DMAIC, and DMADV are acronyms and abbreviations for methodologies used in conjunction with Six Sigma process improvement. All of these methodologies help quality improvement professionals keep their projects focused on an established path to follow through to completion. Each is made up of words and phrases that represent a step in your processes and ultimately constitute the acronym or abbreviation used throughout the Six Sigma community. SIX SIGMA DFSS DMAIC DEFINE Define the problem with the product or process. DMADV DEFINE Define design objectives and processes. MEASURE Measure the current process and collect data. Measure (and identify) critical aspects for MEASURE the quality of the process / product, including risks and production capacities. ANALYZE Analyze the data to find the root causes of defects. ANALYZE Analyze to develop process designs and evaluate to select the best design for the process. DESIGN Improve the process based on data analysis and check it. (Techniques like DOE are often used in this phase). DESIGN Design the details of the process, optimize and verify the designs. VERIFY Verify the design chosen for the process with pilot tests. Implement and monitor the new process. VERIFY Control the new process and monitor defects. (SPC techniques are helpful in this phase). CONCLUSION In conclusion, the DFSS help us to have a better performance and focus of the company to be able to take the company to its maximum potential with the least of the resources, and once the focus is available on the project, we begin to define the problems. in order to find a solution. LEAN MANUFACTURING WHAT IS LEAN MANUFACTURING AND WHAT IS IT FOR? It is a process can be defined as a practice of continuous improvement. It seeks that the industries substantially improve their way of production, as well as reduce costs and eliminate everything that does not pay off in a real way. ¿WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF LEAN MANUFACTURING? • A strong reduction in overall production costs. • Improvement in the quality of production systems. • Better use and efficiency of equipment and machinery. • Cleaning of processes in production, transportation, inventories and quality control. ¿WHAT IS THE 5S METHOD? It is a management technique originating in Japan, it is enough in five very simple principles or phases, which begin with S (in Japanese) and which are the ones that give the method its name. WHICH ARE: Classification (Seiri) Order (Seiton) Cleaning (Seiso) Standardization (Seiketsu) Discipline (Shitsuke) CONCLUSION In conclusion, the 5s is the most used tool with this type of manufacturing since it is a perfect solution for lean manufacturing, because it is suitable for the optimization of many factors. since companies seek to increase their production with the minimum possible costs and this tool is very useful for companies and to have a good work organization.