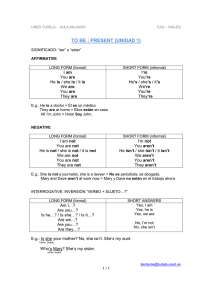
PROCESO DIRECCIÓN DE FORMACIÓN PROFESIONAL INTEGRAL FORMATO GUÍA DE APRENDIZAJE IDENTIFICACIÓN DE LA GUIA DE APRENDIZAJE Denominación del Programa de Formación: Código del Programa de Formación: Nombre del Proyecto ( si es formación Titulada): Fase del Proyecto ( si es formación Titulada): Planeación Actividad de Proyecto (si es formación Titulada: Competencia: COMPRENDER TEXTOS EN INGLÉS EN FORMA ESCRITA Y AUDITIVA Resultados de Aprendizaje Alcanzar: COMPRENDER FRASES Y VOCABULARIO HABITUAL SOBRE TEMAS DE INTERÉS PERSONAL Y TEMAS TÉCNICOS ENCONTRAR VOCABULARIO Y EXPRESIONES DE INGLÉS TÉCNICO EN ANUNCIOS, FOLLETOS, PÁGINAS WEB, ETC COMUNICARSE EN TAREAS SENCILLAS Y HABITUALES QUE REQUIEREN UN INTERCAMBIO SIMPLE Y DIRECTO DE INFORMACIÓN COTIDIANA Y TÉCNICA Duración de la Guía 24 horas. 2. PRESENTACIÓN Para iniciar el aprendizaje del idioma inglés, es necesario identificar en contexto las expresiones y estructuras gramaticales básicas para presentarse, así como aquellos elementos de uso cotidiano en el contexto escolar. Para esto, se proponen actividades que permitan afianzar el reconocimiento, apropiación y reutilización de estos conocimientos adquiridos en situaciones que pueden facilitar y garantizar competencias básicas en el idioma inglés al momento de comunicarse. En el caso particular del SENA, se cuenta con políticas enfocadas a la masificación del inglés como parte de la competencia comunicativa, no sólo de aprendices e instructores, sino también de todos los colombianos. De esta manera, a partir de un programa de formación complementaría enfocado al nivel A1- según el MCE, se espera dar inicio a un proceso que apoyará la inserción laboral y académica tanto local como global de un amplio rango de población dentro y fuera de la institución. GFPI-F-019 V03 3. FORMULACIÓN DE LAS ACTIVIDADES DE APRENDIZAJE Descripción de la(s) Actividad(es) 3.1. Actividades de reflexión inicial Lea la siguiente historia. Dentro de su formación en el SENA, Diego y Yajaira han sobresalido desde el principio. Ambos demuestran empeño, compromiso, un alto nivel de autogestión y trabajo colaborativo. Su actitud es positiva y son curiosos por naturaleza. Diego, desde su formación en el bachillerato, ha percibido el inglés más como una obligación que como una herramienta útil. Las experiencias previas con este idioma lo fueron alejando del mismo, generándole una imagen negativa y desanimándolo ante la posibilidad de aprenderlo. Yajaira, por su parte, vivió experiencias similares a las de Diego durante el bachillerato, pero las tomó como simples tropiezos en el camino del aprendizaje. Ve en el inglés a un gran aliado, una habilidad que no solo le permitirá graduarse en el SENA sino que le abrirá puertas educativas, laborales y personales. Llegado el momento de la etapa productiva, el SENA les ofrece a Diego y Yajaira la posibilidad de participar en una capacitación en San Diego, California. Durante 4 semanas podrán recibir lo más avanzado en conocimientos técnicos de su especialidad y asistir a un sinnúmero de eventos formativos y sociales que les permitirán crear lazos de amistad y trabajo con personas de todo el mundo. El principal requisito para hacer parte de este evento es saber inglés. Yajaira es aceptada y viaja a los Estados Unidos, regresando a Colombia con una nueva perspectiva del mundo y su futuro trabajo, mientras que Diego debe quedarse en Colombia, perdiéndose una gran oportunidad. 3.1.1 Después de reflexionar sobre la lectura anterior, responde: ¿Con cuál de los personajes de esta historia te identificarías en este momento? ¿Cuál consideras que fue el principal error de Diego al enfrentarse al aprendizaje del inglés? ¿De qué manera crees que el inglés puede enriquecer tu vida y tu aprendizaje en el SENA? 3.2 Actividades de contextualización e identificación de conocimientos necesarios para el aprendizaje. En grupos de 3 aprendices, reúnete con tus compañeros y responde las siguientes preguntas. Una vez las hayan respondido, elijan a un representante, quien las compartirá con el resto del curso. En el bachillerato, ¿cuál fue el tema de inglés que más te gustó? (Números, verbo To Be, tiempo Presente Simple, Presente Perfecto, etc.). ¿Cuál fue el tema de inglés que se te dificultó más? ¿Qué habilidad del lenguaje (hablar, escuchar, leer, escribir) te parece más compleja? ¿Por qué? ¿Qué beneficios consideras que trae aprender inglés? 4. Actividades de apropiación del conocimiento (Conceptualización y Teorización). GFPI-F-019 V03 4.1. VOCABULARIO DE SALUDOS E INFORMACIÓN PERSONAL. VOCABULARY OF GREETINGS AND PERSONAL INFORMATION Hello/Hi Where are you from? Good morning Where do you live? Good afternoon Are you single/married? Good evening What do you do? How are you? Good bye What’s your name? Bye How do you spell your name? How old are you? See you tomorrow/later Good night 4.2. ARTICULOS DEFINIDO E INDEFINIDOS . DEFINITE AND INDEFINITE ARTICLES (A / AN / THE) Articulos Definido An = un, una The = el, la, los, las GFPI-F-019 V03 Indefinidos A = un, una DIFERENCIA ENTRE LOS ARTICULOS INDEFINIDOS La diferencia en uso de los artículos depende de la palabra que vaya inmediatamente después del articulo. Esto es, si la palabra empieza por una CONSONANTE, el articulo que se debe utilizar es A. Mientras que si la palabra que sigue empieza por una VOCAL, se debe utilizar AN. Ejemplos: 4.2.1 A pilot, un(a) piloto An architect, un(a) arquitecto(a) A lemon, un limón An avocado, un aguacate Esbriba los articulos A or AN delante de cada sustantivo, luego escriba la traducción correspondiente: _____ teacher _____ hairdresser _____ butcher _____ manager _____ baker _____ accountant _____ lawyer _____ architect _____ archeologist _____ journalist _____ doctor _____ engineer _____ driver _____ farmer _____ secretary _____ salesman _____ surgeon _____ office worker _____ nurse _____ receptionist 4.3 LOS NÚMEROS. THE NUMBERS GFPI-F-019 V03 Para expresar números en inglés, unimos las decenas con las unidades por medio de un guión ( - ): 26 = twenty-six 48 = forty-eight 35 thirty-five 98 = ninety-eight 53 = fifty-three 142 = one hundred forty-two 4.3.1 Escriba los siguientes números en letras: 91 34 61 36 63 75 40 54 64 18 94 38 47 84 53 93 4.4 LA HORA. THE TIME Questions What is the time? ¿Qué hora es? What time is it? ¿Qué hora es? Answers The time is…La hora es… It is…Son las… The time Para responder a la pregunta What time is it? o What is the time?, utilizamos las formas The time is o It is, seguido de la hora expresada en números. Por ejemplo: - What time is it? It is 5:34pm ( It is five thirty-four pm) Hay algunas horas que se pueden decir de varias maneras, observa la siguiente table: It is nine fifteen It is nine thirty It is nine forty It is a quater past/after nine It is half past nine It is twenty to ten GFPI-F-019 V03 09:15 09:30 09:40 4.4.1 Seleccione la respuesta correcta. Select the correct answer. 4.4.2 Empareje la columna izquiera con la columna derecho. Match the left column to the right column. 3:15 10:11 1:00 9:55 4.4.3 a. It is nine fifty- five. b. It is one o’clock. c. The time is ten eleven. d. The time is three fifteen. 4:55 a. It is five o’clock. 8:40 b. It is thirty past twelve. 5:00 c. It is five to five. 12:30 d. It is twenty to nine. Escriba la hora. Write the time. A. 1:30: It’s one thirty B. 6:25: ………………………………………………………………………. C. 10:55: ……………………………………………………………………… D. 8:15: ………………………………………………………………………. E. 4:45: ………………………………………………………………………. F. 9:37: ………………………………………………………………………. 4.5 SUSTANTIVOS SINGULARES Y PLURALES. SINGULAR AND PLURAL NOUNS Un sustantivo (Noun) es el nombre de una persona o una cosa. Un sustantivo (noun) puede ser: Singular = Uno Plural = Varios GFPI-F-019 V03 Para convertir los sustantivos de singulares a plurales se deben aplicar las siguientes reglas 1. Mayoría •A la mayoría de los sustantivos agregamos -S para crear su plural •Ejemplos: car - cars, table - tables, doctor - doctors •A estos sustantivos se les agrega -ES al final 2. Terminados •Ejemplos: bus - buses, dish - dishes, box - boxes en S, SH, CH, X, Z •Se les debe quitar la F o FE, y luego agregar -ies 3. •Ejemplos: wife - wives, life - lives, thief - thieves Terminados en F o FE •Si terminan consonante + Y, se debe quitar la Y para luego agregar -ies. Si terminan en vocal + Y, se aplica la regla #1 4. •Ej: city - cities, baby - babies, day - days, boy - boys Terminados en Y •Si terminan consonante + O, se debe agregar -ES. Si terminan en vocal + O, se aplica la regla #1 5. •Ej: hero - heroes, tomato - tomatoes, zoo - zoos, video -videos Terminados en O 7. Sin cambio •Hay sustantivos que son iguales tanto en Singular como en Plural; es decir, no cambian. •Ej: sheep - sheep, deer - deer, fish - fish, series - series, species - species, moose -moose GFPI-F-019 V03 6. Irregulares •Son irregulares porque no se les puede aplicar ninguna de las reglas anteriores, se deben aprender de memoria •Ej: man - men, woman - woman, foot - feet, tooth - teeth, mouse - mice, person - people, ox -oxen, child -children 4.5.1 Escriba los plurales de los siguientes sutantivos: SINGULAR Action Body Ball Fox Dictionary Glass Class Party Elf Key Ox Day PLURAL SINGULAR Hero Church Dress Course Toy Watch Table Duty Child Mosquito Moose Foot PLURAL SINGULAR Baby Country Tomato Box City Window Monkey Dwarf House Deer Quiz Calf PLURAL 4.6 THERE IS AND THERE ARE (EXPRESSING EXISTENCE/EXPRESAR EXISTENCIA) Expresa existencia en Singular There are = HAY Expresa existencia en Plural Ej: There is a student in the classroom = Hay un estudiante en el salón Ej: There are 23 students in the classroom = Hay 23 estudiantes en el salón La forma negativa es There isn't = No hay La forma negativa es There aren't = No hay En preguntas el orden de la oración cambia: is there...? En las preguntas el orden de la oración cambia: are there...? GFPI-F-019 V03 There is = HAY 4.6.1 Encierre la opción correcta teniendo en cuenta el sustantivo resaltado, luego traduzca cada oración. Circle the best option taking into account the highlighted nouns 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. There is / are a cupboard in my bedroom. Is / are there living rooms in your house? There is / are three floors in that hotel. Is / are there a cat in the garden? Is / are there four living rooms in your house? There isn’t / aren’t four books on the desk. Is / are there a bedroom upstairs? There is / are a chair in your kitchen. There isn’t / aren’t a kitchen in my flat. Is / are there a bathroom in your house? 4.6.2. En su cuaderno describa lo que hay en su vecindario utilizando. there is, there are, there isn’t and there aren’t y vocabulario de lugares del vecindario. Example: In my neighborhood, there is a church, there are five parks, there isn’t a stadium but there are seven soccer fields… 4.7 ADJETIVOS DEMOSTRATIVOS. DEMONSTRATIVE ADJECTIVES (THIS-THAT-THESE-THOSE) SINGULAR PLURAL NEAR This These FAR That Those Se utilizan para demostrar la existencia de algo, para señalarlo. USO: Su uso depende de dos factores: GFPI-F-019 V03 1. La distancia del objeto: Cerca (Near) o Lejos (Far) 2. Si el objeto es Singular o Plural Ejemplos: This is a car = Este es un carro That is a car = Aquél es un carro _______LEJOS________ These are cars = Estos son carros Those are cars = Aquellos son carros ______LEJOS____ Cuando utilizamos los singulares: this y that. Se debe utilizar el articulo indefinido a/an y un sustantivo en singular Cuando utilizamos los plurales: these y those. NO se utiliza articulo indefinido (a, an), sino que se utilizan sustantivos en Plural 4.7.1 Escriba el plural de las siguientes oraciones. Tenga en cuenta el uso de los demostrativos, que cambian de singular a plural, y las reglas de los sustantivos para volverlos plurales. Write the plural form to the following sentences. GFPI-F-019 V03 Ej: 1. Those are dictionaries. YOU are nice HE is creative I am not patient YOU aren't selfish HE isn't lazy Am I right? Are YOU sick? Is HE friendly? SHE is pretty SHE isn't rude IT is easy IT isn't difficult Is IT hard? WE are elegant WE aren't shy Are WE funny? THEY are cheerful THEY aren't short Are THEY tall? You = Usted I = yo She = Ella He = El It = esto (animal o cosa) Is SHE confident? You = Ustedes We = Nosotros They= Ellos GFPI-F-019 V03 I am intelligent Interrogative Negative Affirmative 4.7 PRONOMBRES Y VERBO TO BE. PRONOUS AND VERB TO BE 4.7.1 Reemplace los sustantivos utilizando un pronombre sujeto (I, you, he, she, it, we, they). Replace the nouns using one of the pronouns (I, you, he, she, it, we, they) 4.7.2 Complete el texto utilizando Verbo to be. Complete the text using verb to be. Mary _______ (+) twenty-five years old. She is from Dorset. Her hair _______ (+) long and brown. She has brown eyes. She has a cat and a dog. Her pets _______ very lovely. Pat, the dog _____ (-) small, he _______ (+) very big. Mary’s cat, Fluffy______ (+) 3 years old. Mary’s mother ______ (+) Jane. She ______ (-) a teacher, she ______ (+) a nurse. She ______ (+) thirty-six years old. Her husband ______ (+) Nick. He ______ (+) thirty-eight. He ______ (-) a bus driver, he ______ (+) a mechanic. Mary has two siblings, they _____ (-) in the country now because they ______ (+) living in Miami. Her friends Richard and Amanda ______ (-) bad friends, actually they ______ (+) really good people because they always visit Mary. Richard ______ (+) tall and thin but Amanda ______ (-) as tall as Richard, she ______ (+) short and chubby. I ______ (+) Mary’s cousin Wendy, and I can tell you she ______ (+) great! I ______ (-) in the same city but anyway we ______ (+) still good friends. 4.7.3 Encuentre los errors y reescriba las oraciones utilizando verbo to be. Find the mistakes and rewrite the sentences using verb to be. ….London isn’t a country…….. ……………………………………………. ……………………………………………. ……………………………………………. ……………………………………………. ……………………………………………. ……………………………………………. ………..………………………………….. ……..…………………………………….. GFPI-F-019 V03 London aren’t a country. The United States aren’t a city. An elephant am not a small animal. English and Turkish isn’t sister languages. Mercedes aren’t a bike. Is I a student? Mrs. Stuart aren’t a poor woman. 8. Cigarettes isn’t good for people. 9. The North Pole am not hot. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. …………..……………………………….. 10. Simon are from United Kingdom. 4.7.4 Escoja la respuesta correcta. Choose the correct answer. 1. Maggie and Carol …………… good friends. a) am b) are c) is d) isn’t 2. Sue ………. a science teacher. a) are not b) is d) am c) are 3. Mark Steven ………….. a student at Kennedy High School. It …….. an old school. a) am / is b) are / is c) is / am d) is / is 4. Margarita ……….. from Spain. I ………….. from Turkey. a) is / am b) are / is c) am / is d) is / are 5. You and I ……………… at the same age. a) am isn’t c) are d) is 4.8 PREPOSICIONES DE LUGAR. PREPOSITIONS OF PLACE 1. Next to 2. Between 3. Behind 4. On 5. Under 6. In front of 7. Across from 8. Above Elija las oraciones que describen la foto. Choose the sentences which describe the picture. The cat is next to the sofa. The ball is in the box. The lamp is on the table. The clock is on the wall. The lamp is on the chair. The chair is on the table. The ball is under the table. The carpet is in front the table The book is on the table. __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ _________________________ _ GFPI-F-019 V03 4.8.1 9. Near 10. Far from 11. Inside 12. Outside 13. On top of 14. On the corner of 15. Close to 4.8.2 The bank/ next to/ the post office. / is is/ The gas station/ behind/ the hotel. The museum/ in front of/ the hospital/ is The Cinema/ is/ the pharmacy. / next to the city. / The children/ in/ are ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ 4.8.3 PREPOSICIONES IN ON AT. PREPOSITIONS IN AT ON IN TIEMPO, se utiliza con: Siglos, décadas, años, meses, semanas ESPACIO, se utiliza con:Países, ciudades, vecindarios ON TIEMPO, se utiliza con: Días de la semana, El fin de semana ESPACIO, se utiliza con:Calles, Avenidas AT TIEMPO, se utiliza con: Horas ESPACIO, se utiliza con: direcciones, localización exacta GFPI-F-019 V03 Organize las oraciones que describen la imagen. Unscramble the sentences which describe the picture. 4.9 PRESENTE SIMPLE. SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE USO •El presente simple se utiliza para hablar de RUTINAS y hecho en presente. VERBOS AUXILIARES •Los auxiliares de presente simple son: •DO que se usa con: I, you, we, they •Does que se usa con: He, she, It. REGLAS GFPI-F-019 V03 •Los verbos auxiliares sólo se usan en las oraciones NEGATIVAS y en las PREGUNTAS •En las oraciones AFIRMATIVAS los verbos se deben conjugar. •En las oraciones NEGATIVAS y en PREGUNTAS los verbos NO se conjugan ESTRUCTURAS AFIRMATIVA: sujeto + verbo(conjugado) + Complemento •She studies English every day •They work in a big company •We travel to Cartagena on vacations NEGATIVA: Sujeto + Auxiliar negativo +verbo(no conjugado) + Complemento •She doesn't study English every day •They don't work in a big company •We don't travel to Cartagena on vacations PREGUNTAS SIMPLES: Auxiliar + Sujeto + Verbo(no conjugado) + Complemento + ? •Does she study English every day? •Do they work in a big company? •Do we travel to Cartagena on vacations? PREGUNTAS DE INFORMACIÓN: Wh + Auxiliar + Sujeto + Verbo(no conjugado) + Complemento + ? •What does she study every day? •Where do they work? •Where do they travel on vacations? NOTA: Las preguntas simples se responden con una Short Answer (Respuesta Corta) Las preguntas de información se responden con una oración afirmativa. SHORT ANSWERS (Respuestas Cortas) Does she study English every day? Yes, WHAT WHAT TIME WHERE WHEN WHY WHO HOW LONG HOW OFTEN she does she doesn’t GFPI-F-019 V03 Does she study English every day? No, WH QUESTIONS REGLAS DE CONJUGACIÓN DE LOS VERBOS. SPELLING RULES Estas reglas se usan cuando se cumplan dos condiciones: 1. La oración debe ser AFIRMATIVA 2. El sujeto de la oración debe ser HE, SHE, IT o cualquier nombre que los pueda reemplazar 1. Mayoría de los Verbos •Se les agrega -S al final •play - plays •work - works •speak - speaks •sing - sings •drink - drinks 2. Verbos terminados en: S, SH,CH, X, O, Z •Se les agrega -ES al final •watch - watches •Fix - fixes •buzz - buzzes •wash - washes 3. Verbos terminados en consonante + Y •Se cambia la Y por -ies •study - studies •cry - cries •try - tries EXEPCIÓN: El verbo HAVE (tener), se vuelve HAS (tener) teach ____________ start ____________ tidy _____________ mix _____________ GFPI-F-019 V03 4.9.1 Write the third person singular of the following verbs. play ____________ go ____________ wash ____________ drive ___________ carry __________ fly _______________ help ___________ kiss ___________ watch ____________ like ____________ enjoy __________ cry ____________ 4.9.2 Complete las siguientes oraciones utilizando los verbos en parenthesis en Presente Simple. Complete the sentences with the Present Simple of the verbs in brackets. 1. Peter and his friends __________ to school by bus. (go) 2. Elephants __________ leaves and grass. (eat) 3. David's father __________ in a hospital. (work) 4. The bank opens at 9.30 and __________ at 4.30. (close) 5. Tom and Jim __________ football every day after school. (play) 6. Mr. Jones is a teacher. He __________ History. (teach) 7. Our lessons __________ at 9.00 and __________ at 3.30. (start / finish) 8. My pen friend __________ in Japan. (live) 9. Mary and her brother __________ cartoons every Sunday morning. (watch) 10. John __________ his room every day. (tidy) 4.9.3 Escoja la major opción. Choose the best option. 4.9.4 Complete los espacios en blanco utilizando los verbos de la caja en presente simple. Complete the blanks with the Present Simple of the verbs in the box. GFPI-F-019 V03 Mr. Letty is a postman. He doesn't work in the post office. He always works outside in the streets. He __________ letters to all the people in the neighborhood every day. He doesn't __________ but he __________ his motorbike. At the weekend, Mr. Letty doesn't work. He __________. He __________ the countryside, so he always __________ to his country house with his wife. Mr. and Mrs. Letty __________ in the river and they __________ in the woods every weekend. READING EXERCISE Lea el siguiente texto y responda las preguntas. Read the following text and answer the questions: My name is Kate O’Hara. I live on a farm with my mother and father. I like it but I work very hard. Every morning I wake up at five o’clock and feed the horses. Then I can go back to the house. Mum makes breakfast at 5:30 and I’m not late for breakfast because I don’t like cold eggs. After breakfast I help dad for an hour. Then I have a shower and get ready for school. The school bus leaves at 8:15. I leave home at 8:00. After school I can watch TV for an hour. Then we have our dinner. We have chicken for dinner but I hate it. I eat it because mum gets angry. After dinner I do my homework. Then I go out and feed the horses. I go to bed early because I’m always very tired at the end of the day. 4.9.5 Responda las siguientes preguntas de acuerdo al texto. Answer the following questions according to the text. 1. Where does Kate live? ……………………………………………………………………………………… 2. What time does she get up every morning? ……………………………………………………………………………………… 3. Who makes breakfast every morning? ……………………………………………………………………………………… 4. Why isn’t she late for breakfast? ……………………………………………………………………………………… 5. When does she have a shower? ……………………………………………………………………………………… 6. What time does she catch the school bus? ……………………………………………………………………………………… 7. How long can she watch TV? ……………………………………………………………………………………… 8. What do they have for dinner? ……………………………………………………………………………………… 9. When does she do her homework? ……………………………………………………………………………………… 10. Why does she go to bed early? ……………………………………………………………………………………… 4.9.6 Escriba verdadero o falso a la siguiente información, de acuerdo al texto. True or False. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. She doesn’t like the farm. Kate doesn’t work very hard. Kate has a shower before 8:15. Kate’s mother doesn’t like chicken. After dinner Kate feeds the horses. _____________ ______________ ______________ ______________ ______________ 4.9.7 Cree las preguntas de acuerdo a las respuestas ya escritas. Create the questions according to the answers. GFPI-F-019 V03 1. ___________________________________________________ I sleep in the afternoon. 2. ___________________________________________________ She works at a hospital. 3. ___________________________________________________ Alejandra always eats fruits for breakfast. 4. ___________________________________________________ I study languages because I want to travel abroad. 5. ___________________________________________________ I live with my parents and my three siblings. 6. ___________________________________________________ They get up at 6:00 a.m. 7. ___________________________________________________ He usually plays the piano. 8. ___________________________________________________ Juan and I live in a big city. 9. ___________________________________________________ Sergio sometimes practices German at home. 10. ___________________________________________________ Sebastian has dinner at Rodizio restaurant. Ambiente Requerido Laboratorio de Bilingüsimo Materiales Computadores Ccon acceso a internet Tablero, marcadores, borrador Tomando como referencia la planeación pedagógica y las orientaciones para elaborar guías de aprendizaje citado en la guía de desarrollo curricular 4. ACTIVIDADES DE EVALUACIÓN Tome como referencia la técnica e instrumentos de evaluación citados en la guía de Desarrollo Curricular Evidencias de Conocimiento: Desarrolla cuestionario con ejercicios de diferente tipo tales como completar, Criterios de Evaluación Elabora resúmenes cortos sobre textos sencillos, y con contenido técnico Técnicas e Instrumentos de Evaluación Técnica: Ejercicios Prácticos Instrumentos: Cuestionario GFPI-F-019 V03 Evidencias de Aprendizaje seleccionar, crear, falso o verdadero, etc.. Evidencia de desempeño: Crea y desarrolla una conversación en inglés usando saludos y preguntas y respuestas usando presente simple. Evidencia de Producto: Elabora un párrafo aplicando el tiempo presente simple y describiendo rutinas y descripciones de una tercera persona. Escribe o presenta descripciones de sí mismo, su profesión y su entorno Técnica: Conversación Instrumentos: Lista de chequeo Pronuncia adecuadamente el vocabulario y modismos básicos del idioma. Escribe o presenta descripciones de sí mismo, su profesión y su entorno. Plantea y responde preguntas sobre sí mismo Técnica: Valoración de producto Instrumento: Texto 6. GLOSARIO DE TERMINOS Role-play:To assume the attitudes, actions, and discourse of (another),especially in a makebelieve situation in an effort to understand a differing point of view or social interaction. Noun: a word that refers to a person, place, thing, event, substance, or quality. Adjective: a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Pronoun: a word that is used instead of a noun or a noun phrase. Adverb: a word that describes or gives more information about a verb, adjective, adverb, or phrase Verb: a word or phrase that describes an action, condition, or experience 7. REFERENTES BILBIOGRAFICO Web Servicio nacional de Aprendizaje SENA (2017). Bilingüismo http://www.sena.edu.co/es-co/formacion/Paginas/bilinguismo.aspx SENA. Recuperado de Nombre Autor (es) Sergio Bohórquez Tatiana López Ramírez Edgardo Contreras Sebastián Pérez Ingrid Estupiñán Cargo Instructor líder Instructora Instructor Instructor Dependenci a Fecha Centro CIES 20 de mayo de 2019 GFPI-F-019 V03 8. CONTROL DEL DOCUMENTO Jorvan Vanegas Instructora Instructor 9. CONTROL DE CAMBIOS (diligenciar únicamente si realiza ajustes a la guía) Autor (es) Miguel Galezo Cargo Instructor Dependencia Centro CIES Fecha 30 Marzo 2020 Razón del Cambio Inclusión de vocabulario, Organización de información. GFPI-F-019 V03 Nombre