Desarrollo en serie de Taylor
Anuncio

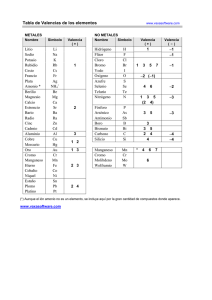
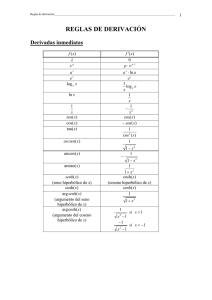
Desarrollo en serie de Taylor www.vaxasoftware.com Desarrollo en serie de Taylor para una función de una variable. El desarrollo en serie de la función f (x) en el punto a es: f ( x) = f (a ) + f ' (a )( x − a ) f ' ' (a)( x − a) 2 f n (a)( x − a) n + + ··· + + Rn 1! 2! n! Siendo Rn el resto de Lagrange: Rn = f n +1 (θ )( x − a ) n +1 , donde θ es un valor entre a y x. (n + 1) ! n ! se lee n factorial y corresponde a la multiplicación de todos los valores enteros desde n a 1: n ! = n · (n–1) · (n–2) · (n–3) · .... · 4 · 3 · 2 · 1. Ejemplo: 6 ! = 6 · 5 · 4 · 3 · 2 · 1 = 720 Cuando el punto del desarrollo es a = 0, al desarrollo se la llama también desarrollo de Maclaurin. Desarrollos en serie de algunas funciones. x2 x3 x4 + + + ··· 2! 3! 4! ex = 1 + x + ln x = ( x − 1) − ( x − 1) 2 + 2 ln(1 + x) = x − x2 x3 + − 2 3 −∞< x< ∞ ( x − 1)3 − 3 ( x − 1) 4 + 4 x4 x5 + − ··· 4 5 1 = 1 − x + x 2 − x3 + x 4 − x5 + · · · 1+ x −1 < x < 1 1 1 2 1·3 3 x − x + x − ··· 2 2·4 2·4·6 −1 < x < 1 −1 < x ≤ 1 x3 x5 x7 sen x = x − + − + ··· 3! 5! 7! −∞< x<∞ x2 x4 x6 + − + ··· 2! 4! 6! −∞< x<∞ cos x = 1 − senh x = x + x3 x5 x7 + + + ··· 3! 5! 7! −∞< x<∞ cosh x = 1 + x2 x4 x6 + + + ··· 2! 4! 6! −∞< x<∞ arcsen x = x + arccos x = −1 < x < 1 −1 < x < 1 x = x + 2 x 2 + 3x3 + 4 x 4 + 5 x5 + · · · 2 (1 − x) 1+ x = 1 + 0 < x ≤ 2 −1 < x ≤ 1 1 = 1 − 2 x + 3x 2 − 4 x3 + 5 x 4 − 6 x5 + · · · (1 + x) 2 1 = 1 + x + x 2 + x3 + x 4 + x5 + · · · 1− x ( x − 1)5 − ··· 5 1 x3 1·3 x5 1·3·5 x 7 + + + ··· 2 3 2·4 5 2·4·6 7 −1 < x < 1 ⎞ 1·3·5 x 7 1·3 x 5 1 x3 π ⎛ π − arcsen x = − ⎜⎜ x + + + + · · · ⎟⎟ 2·4·6 7 2·4 5 2 3 2 ⎝ 2 ⎠ 1 1 ⎧ π 1 ⎪− 2 − x + 3 x 3 − 5 x 5 + · · · x ≤ −1 ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ x3 x5 x7 −1 < x < 1 + − + ··· ⎪x − arctan x = ⎨ 3 5 7 ⎪ ⎪ ⎪π − 1 + 1 − 1 + ··· x ≥1 ⎪2 x 3x3 5 x5 ⎪ ⎩ www.vaxasoftware.com −1 < x < 1