Astroscopus
Anuncio
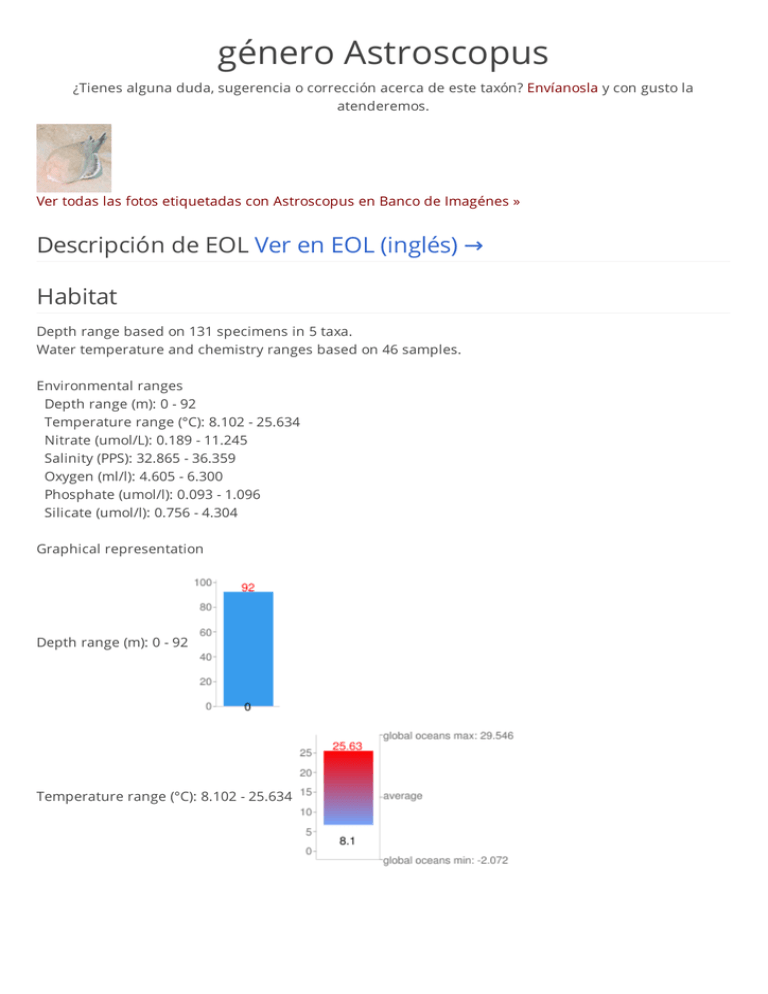
género Astroscopus ¿Tienes alguna duda, sugerencia o corrección acerca de este taxón? Envíanosla y con gusto la atenderemos. Ver todas las fotos etiquetadas con Astroscopus en Banco de Imagénes » Descripción de EOL Ver en EOL (inglés) → Habitat Depth range based on 131 specimens in 5 taxa. Water temperature and chemistry ranges based on 46 samples. Environmental ranges Depth range (m): 0 - 92 Temperature range (°C): 8.102 - 25.634 Nitrate (umol/L): 0.189 - 11.245 Salinity (PPS): 32.865 - 36.359 Oxygen (ml/l): 4.605 - 6.300 Phosphate (umol/l): 0.093 - 1.096 Silicate (umol/l): 0.756 - 4.304 Graphical representation Depth range (m): 0 - 92 Temperature range (°C): 8.102 - 25.634 Nitrate (umol/L): 0.189 - 11.245 Salinity (PPS): 32.865 - 36.359 Oxygen (ml/l): 4.605 - 6.300 Phosphate (umol/l): 0.093 - 1.096 Silicate (umol/l): 0.756 - 4.304 Note: this information has not been validated. Check this *note*. Your feedback is most welcome. Functional adaptation 1 Organ gen erates el ectri ci ty: el ectri c stargaz er The electroplax organ is a modified muscle in various marine creatures that generates high voltage, low amperage electricity by reverse polarity. Make > Generate/convert energy > Electrical energy "Six groups of fishes (skates, electric rays, electric eel, elephant fishes, electric catfishes, and one genus of stargazers) have developed electric organs used variously for communication (e.g., concerning territory or courtship), defense, and stunning prey (electric eel). The electric organ, or electroplax organ, is modified muscle in which the cells do not contract but rather reverse polarity on stimulation, producing high voltage (up to 600 V by a large electric eel down to a maximum of about 25 V in an elephant fish) but low amperage current. The electroplax organ is located in the trunk in most of the electric fishes but in the tail of skates and in an eye muscle of the stargazer. These and many other fishes also have electroreceptor organs, called ampullae of Lorenzini in elasmobranchs, to detect conspecific electrical signals, muscle contractions of hidden prey species, and potentially the electromagnetic field of Earth for navigation." (Miller 1978:4) Learn more about this functional adaptation. Statistics of barcoding coverage 2 Barcode of Life Data Systems (BOLD) Stats Specimen Records:7 Specimens with Sequences:4 Specimens with Barcodes:4 Species:2 Species With Barcodes:2 Public Records:0 Public Species:0 Public BINs:0 References 1. © The Biomimicry Institute, some rights reserved 2. © Barcode of Life Data Systems, some rights reserved











