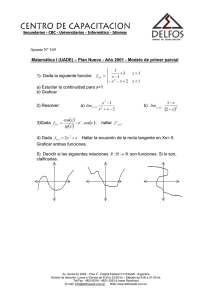
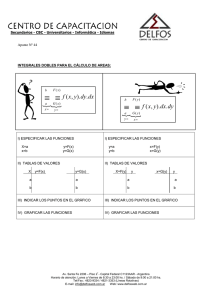
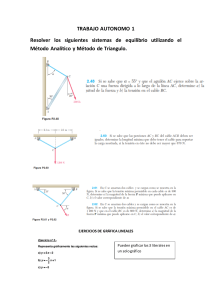
x - Cfe
Anuncio

Ejercicios sobre continuidad y cálculo de derivadas 1) Estudiar dominio, ceros, signo y continuidad de las siguientes funciones: 3x − 2 1− x 2+ x d) f : f ( x ) = ln x +1 b) f : f ( x ) = a) f : f ( x ) = g) f : f ( x ) = 2) 3) x2 − 4 e) f : f ( x ) = ln x − 3 x +1 e 1− x − h) f : f ( x ) = x e ⎧ 1 ⎪ Sea f : f ( x ) = ⎨ x − 2 ⎪⎩3 si x ≠ 2 1 x2 c) f : f ( x ) = x ln ( x + 3) f) f : f ( x ) = i) f : f ( x ) = x ln x − 3 x ln ( x ) ex estudiar continuidad y graficar. si x = 2 ⎧⎪ax 2 si x < 2 Sea f : f ( x ) = ⎨ ⎪⎩ x + 10 si x ≥ 2 Determinar a ∈ ℜ , sabiendo que f es continua ∀ x ∈ ℜ . i) ii) Graficar f para el valor de a hallado. ⎧− x 2 + ax + b ⎪ ⎪ 4) Sea f : f ( x ) = ⎨− x 2 + 4 x ⎪2 x + b ⎪⎩ Determinar a y b ∈ ℜ , para que f 5) 1+ x si x < 1 si 1 ≤ x ≤ 3 si x > 3 sea continua para todo x. Derivar las siguientes funciones: a) f : f ( x ) = x 4 + 3 x 2 − 6 x ln ( x + 3) d) f : f ( x ) = b) f : f ( x ) = 2 x 4 + 5 .(4 x + 8) c) f : f ( x ) = 2 x−3 (5 x + 1) ( ) x2 − 1 e) f : f ( x ) = ln x ( f) f : f ( x ) = ) h) f : f ( x ) = sin 5 x 2 − x + 1 ex 1 f : f ( x ) = ( x − 2 )e x + 2 g) 2x3 + x i) f : f (x ) = ( x − 2 )cos( x ) j) f : f ( x ) = tan 2 ( x )