Derivades Infinit`esims (per x → 0) Fórmules de MacLaurin
Anuncio

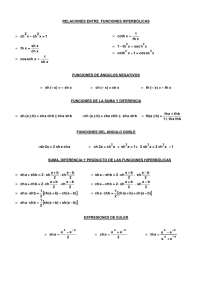
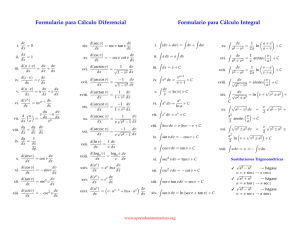
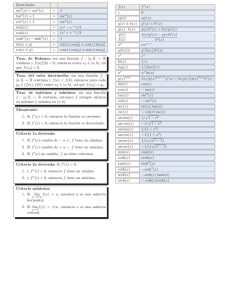
Formulari (funcions d’una variable) Infinitèsims (per x → 0) sin x = x + o(x) 1 − cos x = 1 2 x + o(x2 ) 2 log(1 + x) = x + o(x) Derivades ax − 1 = x log a + o(x) f0 f (1 + x)α − 1 = αx + o(x) xα αxα−1 (α ∈ R) tan x = x + o(x) sin x cos x sinh x = x + o(x) cos x − sin x loga x 1 x log a ax ax log a tan x cot x arcsin x arccos x arctan x arccot x π 1 (x 6= + πn, n ∈ Z) cos2 x 2 1 − 2 (x 6= πn, n ∈ Z) sin x 1 √ (−1 < x < 1) 1 − x2 1 (−1 < x < 1) −√ 1 − x2 1 1 + x2 1 − 1 + x2 sinh x cosh x cosh x sinh x cosh x − 1 = tanh x = x + o(x) Fórmules de MacLaurin ex = n X xk k=0 sin x = n X k=1 cos x = coth x 1 cosh2 x 1 − sinh2 x k! (−1)k−1 n X log(1 + x) = n X + Rn+1 (x) x2k−1 + R2n+1 (x) (2k − 1)! (−1)k k=0 tanh x 1 2 x + o(x2 ) 2 x2k + R2n+2 (x) (2k)! (−1)k−1 k=1 (1 + x)α = 1 + xk + Rn+1 (x) k n X α(α − 1) · · · (α − k + 1) k=1 k! xk + Rn+1 (x) Primitives R f 0 C 1 x+C xα xα+1 +C α+1 1 x log |x| + C ax ax +C log a sin x − cos x + C cos x sin x + C 1 cos2 x tan x + C 1 sin2 x 1 √ 1 − x2 1 1 + x2 1 √ x2 ± 1 1 1 − x2 (x 6= π + πn, n ∈ Z) 2 − cot x + C (x 6= πn, n ∈ Z) arcsin x + C (−1 < x < 1) arctan x + C √ log |x + x2 ± 1| + C 1 + x 1 2 log 1 − x + C sinh x cosh x + C cosh x sinh x + C 1 cosh2 x 1 sinh2 x f tanh x + C − coth x + C